Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L7 A. Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
L7 A. Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
Uploaded by
jowlyughnOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L7 A. Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
L7 A. Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
Uploaded by
jowlyughnCopyright:
Available Formats
General Biology 1
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
BLOCK NAMES GROUP #
LABORATORY SCHEDULE DATE
Laboratory Activity 7- A
Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
INTRODUCTION
Paper chromatography is a process that uses special filter paper to separate and identify the different
substances in a mixture. Chromatography means “to write with color”. The substances in the mixture dissolve in
the alcohol and move up the paper. The heavier substances move up the paper more slowly. The lighter
substances move up the paper more quickly. So, heavy and light substances get separated from one another on the
paper. Plants contain chlorophyll, a green pigment, as well as carotenoid, a pigment that ranges in color from red
to orange to yellow.
MATERIALS
• 2 different types of leaves ruler
• graduated cylinder scissors
• Filter paper/ chromatography paper strip pencil/ colored pencils
• Ethanol / Isopropyl alcohol penny
PROCEDURES
1. Draw a line in pencil across the paper 1.5 cm from the bottom.
2. Starting at the line, taper the bottom of the paper with scissors.
3. Your chromatogram should resemble the picture shown below (Figure 1).
4. Place leaf over the line on the filter strip.
5. Using a penny, rub the leaf to transfer pigment onto the line.
6. Move the leaf and repeat several times until a dark green line of leaf pigment is visible on the pencil line.
7. Place the filter strip into the graduated cylinder with 10 ml of ethanol/ isopropyl alcohol.
(DO NOT INHALE THE SOLVENT).
8. Fold the top of the paper over the edge of the graduated cylinder. Be sure the paper doesn’t sink further
into the solvent. The green line should not be in the solvent.
9. Wait for fifteen minutes, or until the pigments fully separate. There should be different colors of pigment
visible on the strip.
10. Remove the filter strip and let it dry.
11. Sketch your pigment bands.
Place leaf over pencil line and rub
Figure 1.
Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
DATA AND OBSERVATIONS
Type of Leaf Color of Pigment Name of Pigment
Identifying the pigments: Use the information below to identify which pigments are in your leaf.
Chlorophyll a- bright green yellow
Chlorophyll b- dull blue green or khaki
Carotene- orange or yellow
Xanthophyll- pale yellow
Results:
Filter Paper Use colored pencils or crayons to draw your
observations
Before paper chromatography
After paper chromatography
QUESTIONS FOR RESEARCH
1. Does your data support this statement: “Chlorophyll is the most abundant and important photosynthetic plant
pigment”? Explain.
2. Why is paper chromatography an appropriate technique to use to determine if different pigments are present in
leaf?
Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
3. Why do most leaves contain one or more than one type of pigment? What is the purpose of pigments?
4. Explain the technique of paper chromatography.
5. Based on what you have learned, explain why leaves tend to change color in the fall.
6. Leaves in New England change color in the fall. However, leaves in Florida do not change color in the fall.
Why is this so? (Hint: Think of the difference between the two locations that might act as a trigger for leaves to
change color in the fall).
REFERENCES:
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
Paper Chromatography of Leaf Pigments
You might also like
- (Download PDF) General Organic and Biological Chemistry Structures of Life Karen C Timberlake Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) General Organic and Biological Chemistry Structures of Life Karen C Timberlake Online Ebook All Chapter PDFralph.wolfe712100% (13)
- Chapter 16-Acids and BasesDocument33 pagesChapter 16-Acids and BasesGörkem DamdereNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPaper Chromatography Lab ReportGeraldineMay50% (2)
- Ap Bio Lab Report 4Document4 pagesAp Bio Lab Report 4api-392960219No ratings yet
- Problem Materials: Photosynthesis, You Might Remember, Is The Process in Which Plants Convert LightDocument2 pagesProblem Materials: Photosynthesis, You Might Remember, Is The Process in Which Plants Convert LightHazel SalañoNo ratings yet
- Chromatography of Chlorophyll Lab Pre-APDocument1 pageChromatography of Chlorophyll Lab Pre-APkegalinaNo ratings yet
- Chromotography Lab 2018Document2 pagesChromotography Lab 2018AndrewNo ratings yet
- Chromatography LabDocument2 pagesChromatography LabXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Chromatography LabDocument2 pagesChromatography LabAniqah SaifuladliNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument15 pagesChromatographyManogna Sai PadiNo ratings yet
- Leaf ChromatographyDocument2 pagesLeaf ChromatographyKamaldeep MaanNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography - Chloroplast PigmentsDocument3 pagesPaper Chromatography - Chloroplast PigmentsTsering ChorolNo ratings yet
- Corrected Photosynthesis LabDocument4 pagesCorrected Photosynthesis LabAbby Shay GayleNo ratings yet
- LeafchromatographyDocument3 pagesLeafchromatographyHanisjasymah HamidonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Separating Leave Pigments Through Paper Chromatography - SLCCDocument6 pagesAP Biology - Separating Leave Pigments Through Paper Chromatography - SLCCShengLeungCheungCasadoNo ratings yet
- Ink ChromatographyDocument5 pagesInk ChromatographyClain ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Chromatography+of+Spinach 08Document4 pagesChromatography+of+Spinach 082858keshvi8bNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment in Extraction of Plant PigmentsDocument4 pagesLab Experiment in Extraction of Plant Pigmentsaiah bitolinamisaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Chromotography.Document10 pagesLeaf Chromotography.Mostafa KharbouchNo ratings yet
- LAB Chlorophyl ChromatographyDocument3 pagesLAB Chlorophyl ChromatographyVirly vcNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5 - Paper Chromatography of Plant PigmentsDocument13 pagesLab Report 5 - Paper Chromatography of Plant PigmentsCornnelya SaiminNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography For Photosynthetic PigmentsDocument2 pagesPaper Chromatography For Photosynthetic PigmentsJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Pigment Analysis Via Paper ChromatographyDocument5 pagesExercise 4 Pigment Analysis Via Paper ChromatographyToby TrollyNo ratings yet
- Chromatographyofspinachleaf Chem1004Document6 pagesChromatographyofspinachleaf Chem1004palsuhani45No ratings yet
- Colourspread WriteupDocument2 pagesColourspread WriteupJay WalleNo ratings yet
- Pigment Chromatography 3BGU February 2022Document16 pagesPigment Chromatography 3BGU February 2022johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment PigmentsDocument3 pagesLaboratory Experiment PigmentscharonskieyamyamNo ratings yet
- Chromatography of Photosynthetic PigmentsDocument3 pagesChromatography of Photosynthetic PigmentsJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Chromatography LabDocument3 pagesChromatography LabOuissal HichourNo ratings yet
- Chroma Notes 2Document8 pagesChroma Notes 2Marielle GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Plant PhysiologyDocument10 pagesLab 6 Plant Physiologyapi-384292787No ratings yet
- Lab Reort - Chromatography of Plant PigmentsDocument3 pagesLab Reort - Chromatography of Plant Pigmentsapi-257546392No ratings yet
- Concept of Leaf ChromatographyDocument2 pagesConcept of Leaf ChromatographyvnnrbkahNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Lab PreAPDocument4 pagesChromatography Lab PreAPDeltric WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project2Document14 pagesChemistry Project2Arsha preethaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document6 pagesLab Report 3api-392377025No ratings yet
- Untitleddocument 1Document7 pagesUntitleddocument 1api-317223049No ratings yet
- Leaves and Pigments PDFDocument16 pagesLeaves and Pigments PDFnurul annisa lubisNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography ExperimentDocument5 pagesPaper Chromatography ExperimentbagaipogwynethNo ratings yet
- Measure 2 CM From The Bottom of The Paper Strip andDocument3 pagesMeasure 2 CM From The Bottom of The Paper Strip andprsenterpriseNo ratings yet
- Lab # 4 Planning and DesigningDocument2 pagesLab # 4 Planning and Designingshadow100% (3)
- Paper Chromatography ExperimentDocument5 pagesPaper Chromatography Experimentsiguro hwahahahNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument3 pagesPaper Chromatographymod002botNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 06Document3 pagesChromatography 06Gaurav GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chromatography LabDocument3 pagesChromatography Labashleygaboy86No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument19 pagesBiologyBODDU HARSHITHANo ratings yet
- Plant Pigment ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPlant Pigment ChromatographyflfyNo ratings yet
- Paper ChematographyDocument4 pagesPaper ChematographyCS.LEENo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Lab ActivityDocument4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS Lab ActivityMaybelynNo ratings yet
- Terminology 3. Experiment Page 4-11: What Color Is That Drink Mix?Document19 pagesTerminology 3. Experiment Page 4-11: What Color Is That Drink Mix?SigalitChanaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography For EXPERI-MENTALDocument16 pagesChromatography For EXPERI-MENTALjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Photo 2 Co CHROMDocument5 pagesPhoto 2 Co CHROMsmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Plant Pigment ChromatographyDocument2 pagesPlant Pigment ChromatographyjwalantkbhattNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson Plan JannDocument2 pagesChemistry Lesson Plan Jannjules blancoNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 THDocument8 pagesBiology 12 THshankarNo ratings yet
- Anela Pahilanga - Perf Task No 2.1 Paper Chromatography - Answer SheetDocument3 pagesAnela Pahilanga - Perf Task No 2.1 Paper Chromatography - Answer SheetJohn Daniel AntolinNo ratings yet
- Anela Pahilanga - Perf Task No 2.1 Paper Chromatography - Answer SheetDocument3 pagesAnela Pahilanga - Perf Task No 2.1 Paper Chromatography - Answer SheetJohn Daniel AntolinNo ratings yet
- In Chemical AnalysisDocument5 pagesIn Chemical AnalysisVarad GhugeNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument1 pagePaper ChromatographyCarlaAbelarNo ratings yet
- sbl1023 Lab 6 Plant PhysiologyDocument7 pagessbl1023 Lab 6 Plant Physiologyapi-385146128No ratings yet
- [2020년 기출] 대원외국어고등학교 (서울 광진구) 1학년 2학기 기말 영어 능률(양현권)Document13 pages[2020년 기출] 대원외국어고등학교 (서울 광진구) 1학년 2학기 기말 영어 능률(양현권)yeniyenykNo ratings yet
- Spaceandmore HORECA KatalógusDocument619 pagesSpaceandmore HORECA KatalógusMolnár KataNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Ch-1 NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry - Ch-1 NoteskomalNo ratings yet
- Protein Models 3Document16 pagesProtein Models 3dkisNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Benzoic AcidDocument2 pagesSynthesis of Benzoic AcidVarun JogiNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1 Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument8 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1 Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingBrady100% (1)
- Example of Parts of A Research PlanDocument4 pagesExample of Parts of A Research PlanMa. Kathleen Monjardin100% (1)
- Prima Coffee Advanced Brewing CourseDocument11 pagesPrima Coffee Advanced Brewing Courseavila83_14No ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Drill and InstructionDocument12 pagesFire Fighting Drill and InstructionAsif HussainNo ratings yet
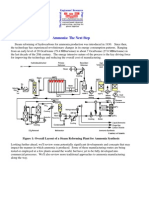
- Ammonia The Next StepDocument11 pagesAmmonia The Next StepmuralleroNo ratings yet
- 2019 FY10 EBasic Science Detailed SolutionsDocument32 pages2019 FY10 EBasic Science Detailed SolutionsManavi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Prelim: History of Forensic Chemistry and ToxicologyDocument106 pagesPrelim: History of Forensic Chemistry and ToxicologyShaina Pauline GayaniloNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Supercritical FluidsDocument8 pagesThe Journal of Supercritical FluidsJeni NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Process Scale-Up, 3rd Edition: Drug Development and Industrial PharmacyDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical Process Scale-Up, 3rd Edition: Drug Development and Industrial PharmacyrajuvadlakondaNo ratings yet
- Cell Chemistry QuestionsDocument2 pagesCell Chemistry QuestionskevinNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes And: HaloarenesDocument24 pagesHaloalkanes And: HaloarenesWild SageNo ratings yet
- Paint Procedure CP-01Document3 pagesPaint Procedure CP-01Gonzalo PerezNo ratings yet
- 2017 Winter Model Answer PaperDocument17 pages2017 Winter Model Answer PaperAkash ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Flammable Gas and VapoursDocument1 pageFlammable Gas and Vapoursanais trifanNo ratings yet
- Los Pesticidas: Clasificación, Necesidad de Un Manejo Integrado y Alternativas para Reducir Su Consumo Indebido: Una RevisiónDocument23 pagesLos Pesticidas: Clasificación, Necesidad de Un Manejo Integrado y Alternativas para Reducir Su Consumo Indebido: Una RevisiónCielo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Basic of PigmentsDocument20 pagesBasic of PigmentsMae Ann DerechoNo ratings yet
- Astm B224 16Document3 pagesAstm B224 16reza acbariNo ratings yet
- 2022 Question PaperDocument15 pages2022 Question PaperlafaNo ratings yet
- ESAS ReviewerDocument79 pagesESAS ReviewerPink LaoNo ratings yet
- OXTERIL® 350 BATH Food Grade - Technical Documentation - Rev - 2016 - 02Document19 pagesOXTERIL® 350 BATH Food Grade - Technical Documentation - Rev - 2016 - 02Wahid Agung Laksono100% (2)
- Group 1 Introduction To Environmental EngineeringDocument27 pagesGroup 1 Introduction To Environmental EngineeringMarc CabardoNo ratings yet
- Enzim-Enzim Dalam Biologi Molekuler - 2022Document21 pagesEnzim-Enzim Dalam Biologi Molekuler - 2022303 - Azrial AzharNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument4 pagesDifference Between Sterilization and Disinfectiontaz_taz3No ratings yet





























































![[2020년 기출] 대원외국어고등학교 (서울 광진구) 1학년 2학기 기말 영어 능률(양현권)](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/742834203/149x198/1ef1dabe16/1718621313?v=1)