Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.3. Structure and Bonding of Carbon
2.3. Structure and Bonding of Carbon
Uploaded by
atemisgoddesofhunt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
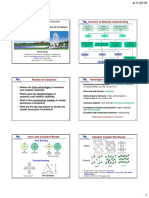
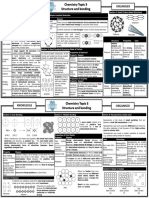
7 views1 pageCarbon forms four types of structures: diamond, graphite, fullerenes, and nanotubes. Diamond has a giant covalent structure with each carbon atom bonded to four others in a rigid tetrahedral arrangement. Graphite has layers of hexagonal rings that slide over each other, giving it a soft, slippery texture and the ability to conduct electricity between layers. Fullerenes and nanotubes are hollow structures composed entirely of carbon that can be used in electronics, composites, and drug delivery.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCarbon forms four types of structures: diamond, graphite, fullerenes, and nanotubes. Diamond has a giant covalent structure with each carbon atom bonded to four others in a rigid tetrahedral arrangement. Graphite has layers of hexagonal rings that slide over each other, giving it a soft, slippery texture and the ability to conduct electricity between layers. Fullerenes and nanotubes are hollow structures composed entirely of carbon that can be used in electronics, composites, and drug delivery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page2.3. Structure and Bonding of Carbon
2.3. Structure and Bonding of Carbon
Uploaded by
atemisgoddesofhuntCarbon forms four types of structures: diamond, graphite, fullerenes, and nanotubes. Diamond has a giant covalent structure with each carbon atom bonded to four others in a rigid tetrahedral arrangement. Graphite has layers of hexagonal rings that slide over each other, giving it a soft, slippery texture and the ability to conduct electricity between layers. Fullerenes and nanotubes are hollow structures composed entirely of carbon that can be used in electronics, composites, and drug delivery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
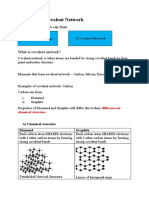
4 covalent bonds per Conducts electricity
Strong covalent Soft and
bonds carbon atom slippery
Delocalised electron
Rigid structure Layers slide
per carbon atom
over each other
Very high
melting point Very hard
Giant covalent 3 covalent bonds No covalent bonds
structure per carbon atom between layers
Properties
Layers of
Graphite hexagonal rings
Does not conduct
electricity
Diamond
High melting point Strong
covalent bonds
No charged
particles
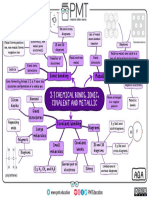
2.3 STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF CARBON
Used to make Graphene
composites Sheet of
Buckminsterfullerene Hollow
Hollow
Fullerenes carbon atoms
shapes Very strong
sphere One layer
Carbon atoms arranged of graphite Conducts
in hexagonal rings
Nanotubes electricity due
Can also form Uses to delocalised
rings of 5 or 7 electrons
carbon atoms Deliver drugs High length to
Good diameter ratio
into the body Very light
catalysts Electronics and
composites
AQA
https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
https://bit.ly/pmt-edu https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
You might also like
- Solid State Class 12th NotesDocument32 pagesSolid State Class 12th NotesSumit Patil100% (8)
- AlloyDocument11 pagesAlloyadibiab05No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Bonding NotesDocument13 pagesTopic 4 Bonding NotesThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Carbon NanomaterialDocument4 pagesCarbon NanomaterialAshish Dev (B21MT009)No ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument2 pagesAllotropes of Carbonethanli29728No ratings yet
- MINDMAP - Covalent BondingDocument1 pageMINDMAP - Covalent BondingalanchenyinNo ratings yet
- Giant Molecule StructureDocument5 pagesGiant Molecule StructureNAURAH AISYAH NAWAWI ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids SummaryDocument2 pagesBonding in Solids SummaryarachnidkatNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent MoleculesDocument34 pagesGiant Covalent MoleculesaqutiaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemistryFatma SharifNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Bonding Structure and The Properties of MatterDocument8 pagesTopic 2 - Bonding Structure and The Properties of MatterSrusti RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17-Chapter 12 - Ceramics and Polymer (I) PDFDocument10 pagesLecture 17-Chapter 12 - Ceramics and Polymer (I) PDFtaylor CNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1Document1 pageTopic 2.1duneraoreedNo ratings yet
- Graphene and Fullerenes - Shalom Education HandsDocument3 pagesGraphene and Fullerenes - Shalom Education HandsstaphilokaiNo ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- solid state corrected note pdfDocument32 pagessolid state corrected note pdfadityaaher2006No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5s1062579No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument131 pagesChemical BondingAnant VashishtNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'sDocument54 pages12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'srohan rajNo ratings yet
- 3 2 4-MacromoleculesDocument10 pages3 2 4-Macromoleculesareeb9187No ratings yet
- Chap 16Document20 pagesChap 16AmandaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding GCSE Review and 10QsDocument5 pagesCovalent Bonding GCSE Review and 10QsPuja DhawanNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument1 pageAllotropes of CarbonarabellaokNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument10 pagesUntitled NotebookRohith reddyNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Giant Covalent StructuresDocument2 pages9.3 Giant Covalent StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
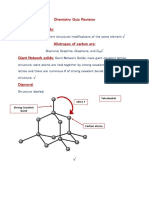
- Chemistry QuizDocument3 pagesChemistry QuizKarim AL-TijaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Zoe 171121Document2 pagesChemistry Zoe 171121NavNo ratings yet
- AQA Combined Science Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesAQA Combined Science Structure and Bondingali.a.226No ratings yet
- Bonding Intermolecular Forces Series - Covalent Bonding MindmapDocument1 pageBonding Intermolecular Forces Series - Covalent Bonding MindmapmonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- cc7b.3 StrengthenDocument1 pagecc7b.3 StrengthenFaiar Rob Year 9No ratings yet
- 1.PPT - Chapter 1 Semiconductor TheoryDocument12 pages1.PPT - Chapter 1 Semiconductor TheoryHaftamu HilufNo ratings yet
- MS Worksheet 9Document2 pagesMS Worksheet 9alvaressaschaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 2: Date: 24/09/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedDocument2 pagesChemistry Test 2: Date: 24/09/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- 2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of SubstancesDocument1 page2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of SubstancesatemisgoddesofhuntNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument1 pageAllotropes of Carboninnukhan.sweetNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Ionic BondingDocument2 pages6.1 Ionic Bondingroyrozman90510% (1)
- Lead Batteries For Utility Energy StorageDocument1 pageLead Batteries For Utility Energy StorageANDREA MORENO ROSASNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument2 pagesAllotropes of Carbonversha29No ratings yet
- Revisions About Chapter 3Document21 pagesRevisions About Chapter 3杨国涓faithNo ratings yet
- 50 Polimeros NanocompuestosDocument35 pages50 Polimeros NanocompuestosMONICA XIMENA ERAS VARGASNo ratings yet
- Discovering Covalent NetworkDocument3 pagesDiscovering Covalent NetworkOng Yun YiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anita S. Ethiraj Associate ProfessorDocument12 pagesDr. Anita S. Ethiraj Associate ProfessorGovarthananNo ratings yet
- Solid LatticesDocument9 pagesSolid LatticesWamia RahmanNo ratings yet
- State of Matter Part 2Document24 pagesState of Matter Part 2cognitastradingNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument1 pageAllotropes of Carboninnukhan.sweetNo ratings yet
- SCINOTESDocument2 pagesSCINOTESMark Beduya CuffeeNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structure-4Document4 pagesGiant Covalent Structure-4Ahmet SezginNo ratings yet
- Summary MEC681 Notes For Final Exam - 2slides - HandoutsDocument26 pagesSummary MEC681 Notes For Final Exam - 2slides - HandoutsRed NevlysNo ratings yet
- Types of SubstanceDocument7 pagesTypes of SubstanceTreshan StaynNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument17 pagesMetallic Bondingaudrey.sengeNo ratings yet
- Notes Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 4 1Document5 pagesNotes Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 4 1Beverly Caroline Jre100% (8)
- Chemical Bonding SummaryDocument1 pageChemical Bonding Summarychong56No ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry Revision PDFjoud amjadNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds CH4Document14 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds CH4SuryaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds - Shobhit NirwanDocument17 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- ChemDocument4 pagesChemBrian Lim Fong Chee (Amkss)No ratings yet
- Physics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic MediumFrom EverandPhysics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic MediumRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Topical Advanced Level PhysicsDocument13 pagesTopical Advanced Level PhysicsAde Boy Rogba0% (1)
- Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Lattice DynamicsDocument73 pagesLecture Notes Chapter 1 Lattice Dynamicsd460023100% (1)
- 00-023-0677 Nov 30, 2018 12:45 PM (Cristian-Radiometria)Document2 pages00-023-0677 Nov 30, 2018 12:45 PM (Cristian-Radiometria)Ing. Física 2015No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 (Subjective) Carrier TransportDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 (Subjective) Carrier TransportAniket SinghNo ratings yet
- SWCNT ScapsDocument10 pagesSWCNT ScapsMd Arif Ul Islam-KowshikNo ratings yet
- 3.6. Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (Mesfets)Document5 pages3.6. Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (Mesfets)Chirag JainNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2: BJT Characteristics: Operation of Transistor in Active ModeDocument3 pagesExperiment No 2: BJT Characteristics: Operation of Transistor in Active ModeGREATJUSTGREATNo ratings yet
- MCQ For Module2Document3 pagesMCQ For Module2Ijaz Talib100% (1)
- Topics in Applied Physics Volume 56Document367 pagesTopics in Applied Physics Volume 56Ernesto FrancoNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 Intermolecular ForcesDocument14 pagesLesson2 Intermolecular ForcesJenny Rose Butac Ocden100% (1)
- Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Class 12 Important QuestionsDocument32 pagesImportant Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Class 12 Important QuestionsTharun VasuNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument116 pagesDevicesresearch4maniNo ratings yet
- RetrieveDocument7 pagesRetrieveSoul KingNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Exercise 5 - Structure and Bonding Summary 1Document2 pagesTopic 3 Exercise 5 - Structure and Bonding Summary 1jcdiekcNo ratings yet
- Materials Science & EngineeringDocument5 pagesMaterials Science & EngineeringSathya MoorthyNo ratings yet
- 19CH1002-Module 1 Chemical Bonding - Part ADocument10 pages19CH1002-Module 1 Chemical Bonding - Part AAbel Thampy JohnNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument38 pagesChemical Bondingsmileworker utkarshsinghNo ratings yet
- CY121 SyllabusDocument2 pagesCY121 SyllabusSAURABH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Study of The Frequency Dependence of TheDocument4 pagesStudy of The Frequency Dependence of Thevilla rabehNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in Physical ScienceMELTON MERZANo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2211379723001274 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2211379723001274 MainArunNo ratings yet
- Structural Relations First-Row Transition Metals T.: Pla-Nck Ins-Titut Heisenbergstrasse GermanyDocument12 pagesStructural Relations First-Row Transition Metals T.: Pla-Nck Ins-Titut Heisenbergstrasse GermanyCarlitos TapiaNo ratings yet
- 2014 - The Simulated Vibrational Spectra of HfO2Document11 pages2014 - The Simulated Vibrational Spectra of HfO2VB ReneNo ratings yet
- Gupta - Gupta Civil Complete SolutionDocument5,933 pagesGupta - Gupta Civil Complete SolutionSabahat MehboobNo ratings yet
- The Hückel Approximation: H C C H H C C H H C CHDocument10 pagesThe Hückel Approximation: H C C H H C C H H C CHazuldraconNo ratings yet
- Energy BandsDocument9 pagesEnergy BandsSheikh SaifNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Band Theory of Solids NotesDocument28 pagesUnit I - Band Theory of Solids Notesmirae kangNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Photoactive Phases For Perovskite PhotovoltaicsDocument18 pagesStabilization of Photoactive Phases For Perovskite PhotovoltaicsLIU BOWENNo ratings yet
- 2 Surface Additives VTWDocument109 pages2 Surface Additives VTWcyclo DreamNo ratings yet