Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Riveted Joints
Riveted Joints
Uploaded by
sanyam KanungaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Riveted Joints
Riveted Joints
Uploaded by
sanyam KanungaCopyright:
Available Formats
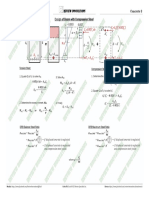
Riveted Joints Riveted joints: Types of joints, Modes of failure, Strength and efficiency of riveted joints, Pitch of the
he rivets,
Design stresses, Structural joints of lap and butt type.
2. Design a double riveted butt joint to join two plates of thickness 12 mm. 3. Design a triple riveted butt joint to join two plates of thickness 10 mm. The pitch Riveted joints: Types of joints, Modes of failure, Strength and efficiency of riveted joints, Pitch of the rivets,
Two cover plates are of equal width and are having chain type riveting. of the rivets in the extreme rows, which are in single shear is twice the pitch of Design stresses, Structural joints of lap and butt type.
𝜎! = 140 𝑀𝑃𝑎, 𝜎" = 90 𝑀𝑃𝑎, 𝜏 = 56 𝑀𝑃𝑎 rivets in the inner rows which are in double shear. The design stresses of the
materials of the main plate and rivets are as follows:
For plate material in tension, 𝜎t=120 MPa, for rivet material in compression, 𝜎c = 2. Design a double riveted butt joint to join two plates of thickness 12 mm. 3. Design a triple riveted butt joint to join two plates of thickness 10 mm. The pitch
160 MPa and for rivet material in shear, 𝜏 = 80 MPa Two cover plates are of equal width and are having chain type riveting. of the rivets in the extreme rows, which are in single shear is twice the pitch of
𝜎! = 140 𝑀𝑃𝑎, 𝜎" = 90 𝑀𝑃𝑎, 𝜏 = 56 𝑀𝑃𝑎 rivets in the inner rows which are in double shear. The design stresses of the
materials of the main plate and rivets are as follows:
For plate material in tension, 𝜎t=120 MPa, for rivet material in compression, 𝜎c =
160 MPa and for rivet material in shear, 𝜏 = 80 MPa
*Note
You might also like
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Khuthi Munarini-A2Document1 pageKhuthi Munarini-A2anzaniNo ratings yet
- Acuv Stage 5-PlansDocument1 pageAcuv Stage 5-PlansMonde Tidimalo Lunathi MbaluNo ratings yet
- Ramothibe T - Stage 4-Acuv300Document2 pagesRamothibe T - Stage 4-Acuv300Monde Tidimalo Lunathi MbaluNo ratings yet
- 2104-20 Manhole DetailsDocument1 page2104-20 Manhole DetailsJULIEN GEORGES NGUELE BALLANo ratings yet
- Alice Ncube-1Document1 pageAlice Ncube-1electristar4No ratings yet
- Castillejos WELL DataDocument3 pagesCastillejos WELL DataJohn Christopher BaquingNo ratings yet
- Benja PlanDocument1 pageBenja Planmasumba patrickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Dislocations in Crystals: Young's ModulusDocument67 pagesChapter 3: Dislocations in Crystals: Young's Modulusjohn parkerNo ratings yet
- Staircase Design: Number of Stairs: N KV/ HDocument3 pagesStaircase Design: Number of Stairs: N KV/ HSara AwadNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 3 MonoDocument2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 3 MonoDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Muloho A3 Page SizeDocument1 pageMuloho A3 Page SizeanzaniNo ratings yet
- Strength of Adhesive Joints - Lectures 18+19Document11 pagesStrength of Adhesive Joints - Lectures 18+19Roger FeltmanNo ratings yet
- Endmill Vol16 e PDFDocument388 pagesEndmill Vol16 e PDFdaniel ortiz fuentesNo ratings yet
- Drawing 3.Document1 pageDrawing 3.tiyaniNo ratings yet
- Concrete 3 May 2021Document4 pagesConcrete 3 May 2021Lucifer MorningstarNo ratings yet
- R O A D SITE PLAN Scale 1: 500Document1 pageR O A D SITE PLAN Scale 1: 500Mercyline MaworereNo ratings yet
- Working Drawings ExampleDocument1 pageWorking Drawings ExampleRufaro TonhomaNo ratings yet
- A Louver Detail B Accent Wall Groove Front Elevation: Drawn By: Project Title: Owner: LocationDocument1 pageA Louver Detail B Accent Wall Groove Front Elevation: Drawn By: Project Title: Owner: LocationBrylle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CFSB3 - Permanent Restraint - Bracing of Chords & Web MembersDocument2 pagesCFSB3 - Permanent Restraint - Bracing of Chords & Web MembersTodd HenryNo ratings yet
- Eduardo Penteado Engenharia SSP: Notas GeraisDocument1 pageEduardo Penteado Engenharia SSP: Notas GeraisAllison LimaNo ratings yet
- Expansion Joint کاتالوگ و اطلاعات فنی محصولاتDocument76 pagesExpansion Joint کاتالوگ و اطلاعات فنی محصولاتmehran asadiNo ratings yet
- Chauke Deon A1 PageDocument1 pageChauke Deon A1 PageanzaniNo ratings yet
- Dia. 13mm CWSP: R.C Wall/Block Wall Dia. 50mm Vent PipeDocument1 pageDia. 13mm CWSP: R.C Wall/Block Wall Dia. 50mm Vent PipeAmadi HenryNo ratings yet
- KENT Year 2 Sustainable-Housing A3Document1 pageKENT Year 2 Sustainable-Housing A3Ralph KentNo ratings yet
- Pin ConnectionDocument10 pagesPin ConnectionngocnnNo ratings yet
- Novagate: A Minimalistic Antenna With Great PerformanceDocument2 pagesNovagate: A Minimalistic Antenna With Great PerformanceLavric CristianNo ratings yet
- Notes: Roof: Concrete Roof Tiles On TrussesDocument1 pageNotes: Roof: Concrete Roof Tiles On TrussesanzaniNo ratings yet
- UPTŽ (G.15.11) - Nacrt Armature Kampade CC G.002 - K2Document1 pageUPTŽ (G.15.11) - Nacrt Armature Kampade CC G.002 - K2Kenan BegagicNo ratings yet
- Backup of DRW 24Document1 pageBackup of DRW 24thomas wesleyNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2.Document1 pageDrawing 2.tiyaniNo ratings yet
- C/C of Bearing: South East Central RailwayDocument1 pageC/C of Bearing: South East Central RailwayRavpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- BOQ & Specification SS 316 Tanks - TekzoneDocument18 pagesBOQ & Specification SS 316 Tanks - TekzoneMonty KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Drawing - BasementDocument1 pageDrawing - BasementCanny EngineerNo ratings yet
- 1255 - Sheet - S-1B - Basement 2 Top Reinforcement-Layout1Document1 page1255 - Sheet - S-1B - Basement 2 Top Reinforcement-Layout1tedi sopguiNo ratings yet
- Nakron - Stud - K16SD - Conectores NelsonDocument40 pagesNakron - Stud - K16SD - Conectores NelsonRui ConceiçãoNo ratings yet
- Building Service DrawingDocument3 pagesBuilding Service DrawingRUBANGAKENE MARVIN ANYWARNo ratings yet
- Punctuation Buzz: How To AssembleDocument7 pagesPunctuation Buzz: How To AssemblejamesNo ratings yet
- Plates No. 4-9: S R T U V WDocument1 pagePlates No. 4-9: S R T U V WToni Garrote FerreroNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CDocument2 pagesJurnal CMARRUNG JAYA COMPUTERNo ratings yet
- Kiguli STR 1Document1 pageKiguli STR 1Seremba SolomonNo ratings yet
- Construction Details - Seating Element: Section Aa' Section BB'Document1 pageConstruction Details - Seating Element: Section Aa' Section BB'Vaishnavi MhatreNo ratings yet
- STR DEX CON WIS CAR: Saving ThrowsDocument2 pagesSTR DEX CON WIS CAR: Saving Throwssemola72No ratings yet
- FW SstdeDocument1 pageFW SstdeJan Michael VecillesNo ratings yet
- 2006 Trenier RW CustomDocument7 pages2006 Trenier RW CustomBetoguitar777No ratings yet
- 01 JumboplanDocument1 page01 Jumboplanarantxa16No ratings yet
- Punctuation Buzz: How To AssembleDocument7 pagesPunctuation Buzz: How To AssemblejamesNo ratings yet
- Torque-Tension Reference GuideDocument1 pageTorque-Tension Reference GuideJacob Sánchez67% (3)
- Lecture 8: Voltage Regulation: ECE 5984: Power Distribution System AnalysisDocument34 pagesLecture 8: Voltage Regulation: ECE 5984: Power Distribution System Analysisante mitarNo ratings yet
- Mc616ste 20Document2 pagesMc616ste 20ahmed ktebahNo ratings yet
- Fpa101249 BR (D) 001-003Document3 pagesFpa101249 BR (D) 001-003chriscundyNo ratings yet
- SeparatorsDocument6 pagesSeparatorsKADİR durmaz100% (1)
- 500 Series Flow ChartsDocument4 pages500 Series Flow Chartsoscar garciaNo ratings yet
- George 3BHKDocument1 pageGeorge 3BHKTWIJUKYE HUZAIFANo ratings yet
- Copy of Head-Loss-calcaulation 4-6-2024Document3 pagesCopy of Head-Loss-calcaulation 4-6-2024mostafaelgarhy343No ratings yet
- Motor StartingDocument1 pageMotor StartingMoazam AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 SlidesDocument15 pagesLecture 11 SlidesDanishNo ratings yet
- Li.05-DR-2500 Typical Landscape DetailsDocument1 pageLi.05-DR-2500 Typical Landscape Detailsstupido3337No ratings yet
- Cable Trench and Road Banka Combine PDFDocument3 pagesCable Trench and Road Banka Combine PDFManas MondalNo ratings yet
- Curved BeamsDocument1 pageCurved Beamssanyam KanungaNo ratings yet
- Welded JointsDocument1 pageWelded Jointssanyam KanungaNo ratings yet
- L13, L14 ElectromagnetismDocument22 pagesL13, L14 Electromagnetismsanyam KanungaNo ratings yet
- L16 Complex Number and Representation of ACDocument14 pagesL16 Complex Number and Representation of ACsanyam KanungaNo ratings yet
- Sam Report 12Document18 pagesSam Report 12Sabab ZamanNo ratings yet
- Английский язык 2Document9 pagesАнглийский язык 2Mariam ChubabriaNo ratings yet
- (SB0A012) Smith Meter® Integrated Biofuels Blending SkidsDocument8 pages(SB0A012) Smith Meter® Integrated Biofuels Blending SkidsRoberto Carlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- (Guy - Exton) - Brexit and Game Theory A Single-Case AnalysisDocument9 pages(Guy - Exton) - Brexit and Game Theory A Single-Case AnalysisAmairani IbáñezNo ratings yet
- 368 Truth Table Abbreviated Cheat SheetDocument2 pages368 Truth Table Abbreviated Cheat SheetLauren PickNo ratings yet
- TIP35/35A/35B/35C: Silicon NPN Power TransistorsDocument4 pagesTIP35/35A/35B/35C: Silicon NPN Power TransistorsJose David Perez ParadaNo ratings yet
- The Genesis Project PDFDocument19 pagesThe Genesis Project PDFvikas kansalNo ratings yet
- 8 y 9 Sem MATERIAL de ESTUDIO INGLES V Unit V Do You Know Where It Is Unit VI Since WhenDocument12 pages8 y 9 Sem MATERIAL de ESTUDIO INGLES V Unit V Do You Know Where It Is Unit VI Since WhenJoseph MartinezNo ratings yet
- Salleh2021 Article TheEmergenceOfVeryLargeContainDocument21 pagesSalleh2021 Article TheEmergenceOfVeryLargeContainSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Engineering, 2005, 339 Pages, Mike Martin, Roland Schinzinger, 0072831154, 9780072831153, Mcgraw-Hill Education, 2005Document17 pagesEthics in Engineering, 2005, 339 Pages, Mike Martin, Roland Schinzinger, 0072831154, 9780072831153, Mcgraw-Hill Education, 2005Zakir HossenNo ratings yet
- PNR Metro Commuter PDFDocument5 pagesPNR Metro Commuter PDFABCDNo ratings yet
- Samsung 2600mah ICR18650-26ADocument16 pagesSamsung 2600mah ICR18650-26AStreet_skNo ratings yet
- A Is For Alienation ArticleDocument4 pagesA Is For Alienation ArticleFamily Court-CorruptionNo ratings yet
- Indotech Power Transformers BrochureDocument2 pagesIndotech Power Transformers BrochurenmanjNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Viscosity As A Function of No Avg Molecular Weight (Mark-Houwink)Document1 pageIntrinsic Viscosity As A Function of No Avg Molecular Weight (Mark-Houwink)ankur2061No ratings yet
- JJRM PPT Marxism PSM1Document20 pagesJJRM PPT Marxism PSM1Jeff Rey ColumnaNo ratings yet
- Gen4 Product Manual V3.0Document118 pagesGen4 Product Manual V3.0velmusNo ratings yet
- PM Handbook - Business Club, IIT BHUDocument54 pagesPM Handbook - Business Club, IIT BHUYOGESH GUTTA 5-Yr IDD Material Sci. & Tech.No ratings yet
- Mod 11.9Document55 pagesMod 11.9trcabhijeet123No ratings yet
- Intelligent Urbanism: Convivial Living in Smart Cities: Stephanie Santoso Andreas KuehnDocument5 pagesIntelligent Urbanism: Convivial Living in Smart Cities: Stephanie Santoso Andreas KuehnAdrian VodițăNo ratings yet
- India-France Joint StatementDocument8 pagesIndia-France Joint StatementDinkar AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten: ForecastingDocument49 pagesChapter Ten: ForecastingK59 Tran Gia KhanhNo ratings yet
- CO 126 F FRESDENLEN 410358301910485666 Candy 126 F Optima Wash SystemDocument41 pagesCO 126 F FRESDENLEN 410358301910485666 Candy 126 F Optima Wash SystemSweetOfSerbiaNo ratings yet
- Puchasing and ProcurementDocument15 pagesPuchasing and ProcurementShruti DhawanNo ratings yet
- Sol Gel ThesisDocument5 pagesSol Gel Thesiskriscundiffevansville100% (2)
- QM.J2 Doc Ref MatrixDocument2 pagesQM.J2 Doc Ref MatrixProsenjit DasNo ratings yet
- Report Workshop Gas WeldingDocument6 pagesReport Workshop Gas WeldingDzulkhairie DK0% (1)
- Suitcase X-Treme 12Vs: Ce and Non-Ce ModelsDocument44 pagesSuitcase X-Treme 12Vs: Ce and Non-Ce ModelsBaskoro PMCKNo ratings yet
- Mispa I2 User ManualDocument43 pagesMispa I2 User ManualJosef GrapesNo ratings yet
- GEHC Service Manual CASE RevA v6!6!2009Document364 pagesGEHC Service Manual CASE RevA v6!6!2009Karljames MoninNo ratings yet