Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsRegulation of Heart Rate (Autosaved)
Regulation of Heart Rate (Autosaved)
Uploaded by
GAYANHNA gUNARATThe document discusses factors that affect heart rate, including gender, autonomic activity, age, hormones, activity level, temperature, and emotional status. It explains that heart rate is regulated by the sinoatrial node, which acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart and determines heart rate. When damaged, the atrioventricular node can take over this role, though it has a slower intrinsic rate. Heart rate directly impacts cardiac output, with higher rates increasing output and lower rates decreasing it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Blank Lab Work ReportsDocument8 pagesBlank Lab Work ReportsPamTremble100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan-AscitesDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan-AscitesKayki Louise75% (4)
- Responses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To AssessmentDocument254 pagesResponses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To Assessmentlouradel100% (1)
- Physiology of The HeartDocument34 pagesPhysiology of The Heartalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Physio AssigmentDocument16 pagesBlood Pressure Physio AssigmentNoorNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument23 pagesBlood PressuresureshNo ratings yet
- Cardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10Document33 pagesCardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10bakuNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood PressureDocument4 pagesPhysiology of Blood PressureNoorNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in CVSDocument63 pagesDrugs Acting in CVSMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Domingo, Precious Mae TDocument56 pagesDomingo, Precious Mae Tbevzie datuNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure PhysiologyDocument15 pagesBlood Pressure PhysiologyNoorNo ratings yet
- CV RegulatnDocument28 pagesCV RegulatnShahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovasular SystemPhai KoemhienNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Control: Marinette Rumusud-Jambaro, MD Diplomate in Internal MedicineDocument48 pagesCardiovascular Control: Marinette Rumusud-Jambaro, MD Diplomate in Internal MedicineVerlette Roselle Aguisanda LizardoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Response To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCirculatory Response To ExerciseFarhad GulNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiology Sist - KV@DR - ZainiDocument46 pagesAnatomi Fisiology Sist - KV@DR - ZainiDikdik Iskandar DwiyantoNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Transport System in MammalsDocument41 pages8.1 Transport System in MammalsTheresa IzaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Regulatory MechanismDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Regulatory Mechanismhia natasyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Dr. Roger Joseph Ii R. JecinoDocument17 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Dr. Roger Joseph Ii R. JecinoFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Peer TutorialDocument11 pagesPeer Tutorialmashe1No ratings yet
- No VideoDocument47 pagesNo VideoTimothy John BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac OutputDocument79 pagesCardiac OutputBrian Adoka OmdangNo ratings yet
- Regulation of ECF VolumeDocument49 pagesRegulation of ECF VolumeGeorge LusanaNo ratings yet
- Heart RateDocument30 pagesHeart Ratefzfz5210No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument65 pagesHypertensionImtiyazNo ratings yet
- NCM 103-Cardio Anatomy & PhysioDocument56 pagesNCM 103-Cardio Anatomy & Physiolouradel100% (1)
- Anatomy NotesDocument86 pagesAnatomy NoteskNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology - 2Document33 pagesCardiovascular Physiology - 2Luiz Jorge MendonçaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesJonalynCollodChewacheoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typescut irnandaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typesghisma ocvintiaNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument4 pagesHeartArvin TaylorNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output, BP and Heart RateDocument13 pagesCardiac Output, BP and Heart RatenidhiNo ratings yet
- LC 5 Circulatory Responses To ExerciseDocument66 pagesLC 5 Circulatory Responses To ExercisealsafaparamedicsNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument57 pagesBlood PressureMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument58 pagesCardiovascular Systemabromley100% (2)
- 05 Cardiovascular System PhysiologyDocument34 pages05 Cardiovascular System PhysiologyKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument6 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyatefmaboodNo ratings yet
- Cvs 5 New 24Document4 pagesCvs 5 New 24Kim Sa-buNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: (Pulse & Blood Pressure)Document47 pagesVital Signs: (Pulse & Blood Pressure)nessa100% (1)
- Vital Signs Lecture PDFDocument47 pagesVital Signs Lecture PDFArchana SahuNo ratings yet
- PHS 213 Wk11 Cardiac output-BPDocument33 pagesPHS 213 Wk11 Cardiac output-BPPRINCE ADEWUMI JONATHANNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation HandoutDocument10 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation Handoutsac50900100% (2)
- Biochemistry of The Heart and Blood Vessels 2021 3 4Document44 pagesBiochemistry of The Heart and Blood Vessels 2021 3 4jakukNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia & TachycardiaDocument14 pagesBradycardia & TachycardiaHendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 4EDocument41 pagesChapter 05 4Elikhovandy10No ratings yet
- Cardio AssessmentDocument104 pagesCardio Assessmentlowell.cerezo.ihsNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle of The Heart PPT 3Document18 pagesCardiac Cycle of The Heart PPT 3pshantanu123No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Heart: Dr. George PearceDocument26 pagesPhysiology of The Heart: Dr. George PearceぴよんNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The HeartDocument38 pagesPhysiology of The HeartPanasheNo ratings yet
- Control of Heart RateDocument2 pagesControl of Heart RateelendriaNo ratings yet
- Baroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemDocument5 pagesBaroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemS GNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Pressure RegulationDocument21 pagesArterial Blood Pressure Regulationnaresh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Normal Heart Rhythm: Mutiara Budi AzharDocument27 pagesNormal Heart Rhythm: Mutiara Budi AzharAditya Fresno Dwi WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument27 pagesBlood Pressureanupam manu100% (1)
- Cardiac Out PutDocument31 pagesCardiac Out PutAyurveda Pg100% (1)
- Cardiac OutputDocument31 pagesCardiac OutputDylan BhuriNo ratings yet
- 10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument140 pages10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - HeartDocument22 pagesCardiovascular System - HeartZyrick Laurence Eslao TimmangoNo ratings yet
- Nervous Regulation of The Circulation and Rapid Control of Arterial PressureDocument2 pagesNervous Regulation of The Circulation and Rapid Control of Arterial Pressuremcwnotes100% (2)
- WK 1& 2 LectureDocument149 pagesWK 1& 2 LectureElma SekikorolevuNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Incentives SO - P05Document1 pageIncentives SO - P05GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Market Return Note Format 2024 - NewDocument1 pageMarket Return Note Format 2024 - NewGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Subsidy FormatDocument1 pageVehicle Subsidy FormatGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Credit Application (New 1) - 14.12.2023Document1 pageCredit Application (New 1) - 14.12.2023GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Secondary Trade Load Scheme - P05-2024 (Retails)Document1 pageSecondary Trade Load Scheme - P05-2024 (Retails)GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- SO Itinerary - P05 - 2024Document1 pageSO Itinerary - P05 - 2024GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 6-1 CivicDocument4 pages6-1 CivicGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Engsi 1079Document4 pagesEngsi 1079GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 6 Civics-2Document7 pages6 Civics-2GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 1HC GR 06 English 1st Term Exam Paper EDocument4 pages1HC GR 06 English 1st Term Exam Paper EGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 6-1 GeographyDocument5 pages6-1 GeographyGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 2023 - SP Handout 02Document15 pages2023 - SP Handout 02GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Nil AnthaDocument1 pageNil AnthaGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Sajini CV NewDocument1 pageSajini CV NewGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- SM - Math - G10 - T3 - I, II PP Ans - 2018Document17 pagesSM - Math - G10 - T3 - I, II PP Ans - 2018GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Nqoao O Uh - I: Wjidk JDR Míëkh 2022Document9 pagesNqoao O Uh - I: Wjidk JDR Míëkh 2022GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Application Sinhala 1 HettiarachchiDocument6 pagesApplication Sinhala 1 HettiarachchiGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Workshop Officer Training RegistrationDocument1 pageWorkshop Officer Training RegistrationGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Spastic Effects of Footbaths in Post-Stroke Patients: A Proof-Of-Principle StudyDocument10 pagesAnti-Spastic Effects of Footbaths in Post-Stroke Patients: A Proof-Of-Principle StudyMuhamad Ibnu HasanNo ratings yet
- Types of MaskDocument40 pagesTypes of MaskADZRIN JUSALINo ratings yet
- Acupuncture (Acup) : 2017-18 CalendarDocument4 pagesAcupuncture (Acup) : 2017-18 CalendarElanghovan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Stop Think Before You ThrowDocument1 pageStop Think Before You ThrowNaresh ChilkuriNo ratings yet
- Hayden Et Al-2021-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument553 pagesHayden Et Al-2021-Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviewsprofessor do valeNo ratings yet
- Era University College of Nursing Lucknow: Submitted To-: Submitted byDocument7 pagesEra University College of Nursing Lucknow: Submitted To-: Submitted byAru Verma100% (1)
- Gavin, Nicole - Final Thesis - RedactedDocument245 pagesGavin, Nicole - Final Thesis - RedactedKarlo MedeirosNo ratings yet
- F.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. AryabiantaraDocument35 pagesF.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. Aryabiantaraarnawaiputu60No ratings yet
- Study On Probiotics and Their PreparationDocument9 pagesStudy On Probiotics and Their PreparationShrishti Singh100% (3)
- Initial Medical Evaluation Form For JO1 ApplicantsDocument1 pageInitial Medical Evaluation Form For JO1 ApplicantsBilly Joe BaradiNo ratings yet
- What Is Vitamin D and Why Is It ImportantDocument7 pagesWhat Is Vitamin D and Why Is It Importanthealthnfobd info100% (1)
- NLE Review PycheDocument7 pagesNLE Review PycheChin ChanNo ratings yet
- Prescription - Writing PartDocument38 pagesPrescription - Writing PartJnanesh PuniNo ratings yet
- A Newborn With Simmering Bleeding After CircumcisionDocument5 pagesA Newborn With Simmering Bleeding After Circumcisionmustafa akmanNo ratings yet
- How To Treat Covid-19 - IppocrateOrgDocument7 pagesHow To Treat Covid-19 - IppocrateOrgMassimo RiserboNo ratings yet
- Asthma Bronchiale: Dr. Ramelan Navy Hospital SurabayaDocument53 pagesAsthma Bronchiale: Dr. Ramelan Navy Hospital SurabayaCornelia CindyNo ratings yet
- Stroke SimulationDocument6 pagesStroke SimulationShirsho ShreyanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Regarding Breastfeeding - A Cross-Sectional Survey Among Postpartum Mothers in A North Indian StateDocument8 pagesKnowledge Regarding Breastfeeding - A Cross-Sectional Survey Among Postpartum Mothers in A North Indian StateIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- GP MCQ 8Document4 pagesGP MCQ 8Marta MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Vaksinasi Dewasa Sby 14Document51 pagesVaksinasi Dewasa Sby 14Ku Ha KuNo ratings yet
- Latest Research in HomeopathyDocument76 pagesLatest Research in Homeopathywww nambisons com100% (3)
- PracCourt Doctor's AffidavitDocument2 pagesPracCourt Doctor's AffidavitmarkbulloNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Cardiomyopat HYDocument43 pagesSeminar ON: Cardiomyopat HYmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- 2 Wilkes1989Document9 pages2 Wilkes1989LAURA MARCELA BARRENECHE CALLENo ratings yet
- Critikon CUFFS Catalog US - REVDocument16 pagesCritikon CUFFS Catalog US - REVJuan Moya BlasNo ratings yet
- Local AnestheticsDocument44 pagesLocal Anestheticsblack pink in ur area 21No ratings yet
- Appendix ADocument7 pagesAppendix ANoavilNo ratings yet
Regulation of Heart Rate (Autosaved)
Regulation of Heart Rate (Autosaved)
Uploaded by
GAYANHNA gUNARAT0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesThe document discusses factors that affect heart rate, including gender, autonomic activity, age, hormones, activity level, temperature, and emotional status. It explains that heart rate is regulated by the sinoatrial node, which acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart and determines heart rate. When damaged, the atrioventricular node can take over this role, though it has a slower intrinsic rate. Heart rate directly impacts cardiac output, with higher rates increasing output and lower rates decreasing it.
Original Description:
Original Title
Regulation of heart rate [Autosaved]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses factors that affect heart rate, including gender, autonomic activity, age, hormones, activity level, temperature, and emotional status. It explains that heart rate is regulated by the sinoatrial node, which acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart and determines heart rate. When damaged, the atrioventricular node can take over this role, though it has a slower intrinsic rate. Heart rate directly impacts cardiac output, with higher rates increasing output and lower rates decreasing it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesRegulation of Heart Rate (Autosaved)
Regulation of Heart Rate (Autosaved)
Uploaded by
GAYANHNA gUNARATThe document discusses factors that affect heart rate, including gender, autonomic activity, age, hormones, activity level, temperature, and emotional status. It explains that heart rate is regulated by the sinoatrial node, which acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart and determines heart rate. When damaged, the atrioventricular node can take over this role, though it has a slower intrinsic rate. Heart rate directly impacts cardiac output, with higher rates increasing output and lower rates decreasing it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Regulation of heart rate
Regulation of heart rate
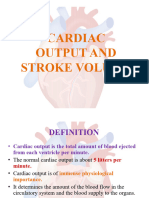
• Heart rate is the major determinant of cardiac output.
• If Heart rate rises cardiac output increases
• When the heart rate falls cardiac output falls.
• Heart rate = Pulse rate
• With Each beat blood is pumped out of the heart
Affected factors on heart rate
1.Gender- Heart rate is passed than women than
men
2 Autonomic activity- heartbeat is a balance
between sympathetic and parasympathetic
activity
3 Age- In babies and small children the heart
rate is more rapid than in older children and
adults.
2 Circulating hormones-
Adrenaline and No adrenalin secreted by the adrenal medulla
increase the heart rate
Thyroxine increases the HT rate
Hypoxia and elevating the CO2 stimulate the heart rate
Electrolytes imbalance – Hyperkalemia leads to Bradycardia means a
slow heart rate
Antagonists such as Atenolol used in Hypertension can also cause
tachycardia
5.Activity and exercise- Active muscles increase the heart rate
6. Temperature- Heart rate rises and falls with body temperature
7. The baroreceptor reflex-
2 Emotional status- during anxiety Heart rate is increased
• Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptors that allows for relaying
information derived from blood pressure within the autonomic
nervous system. Information is then passed in rapid sequence to alter
the total peripheral resistance and cardiac output, maintaining blood
pressure within a preset, normalized range. There are two types of
baroreceptors: high-pressure arterial baroreceptors and low-pressure
volume receptors, which are both stimulated by stretching of the
vessel wall. Arterial baroreceptors are located within the carotid
sinuses and the aortic arch. Low-pressure volume receptors, or
cardiopulmonary receptors, are located within the atria, ventricles,
and pulmonary vasculature.
Regulation of heart rate
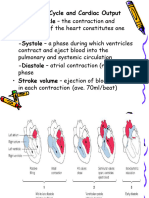
• Contraction of the heart is regulated by special cardiac cells.
• The sinoatrial node (S.A node) and Atrio Ventricular node (A.V node)
are composed of special cardiac cells.
• Those S.A Node and A.V Node regions known as
“Pacemaker” regions of the heart
• S.A Node region is responsible for determining the heart rate.
• When the S.A node region is damaged The region of the A.V node can
take over.
• The A.V node has a slower spontaneous rate of depolarization than
the S.A node
• Heart rate= Pulse rate
• With each beat blood is pumped out of the heart
➢ pacemaker cells spontaneously depolarize without stimulus
➢Depolarization generates electrical currents which
neighboring cells lasting them to contract
( Depolarizing the heart involves the sequential, orderly flow
of electrical current through the heart muscle, converting
each cell )
You might also like
- Blank Lab Work ReportsDocument8 pagesBlank Lab Work ReportsPamTremble100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan-AscitesDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan-AscitesKayki Louise75% (4)
- Responses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To AssessmentDocument254 pagesResponses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To Assessmentlouradel100% (1)
- Physiology of The HeartDocument34 pagesPhysiology of The Heartalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Physio AssigmentDocument16 pagesBlood Pressure Physio AssigmentNoorNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument23 pagesBlood PressuresureshNo ratings yet
- Cardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10Document33 pagesCardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10bakuNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood PressureDocument4 pagesPhysiology of Blood PressureNoorNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in CVSDocument63 pagesDrugs Acting in CVSMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Domingo, Precious Mae TDocument56 pagesDomingo, Precious Mae Tbevzie datuNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure PhysiologyDocument15 pagesBlood Pressure PhysiologyNoorNo ratings yet
- CV RegulatnDocument28 pagesCV RegulatnShahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovasular SystemPhai KoemhienNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Control: Marinette Rumusud-Jambaro, MD Diplomate in Internal MedicineDocument48 pagesCardiovascular Control: Marinette Rumusud-Jambaro, MD Diplomate in Internal MedicineVerlette Roselle Aguisanda LizardoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Response To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCirculatory Response To ExerciseFarhad GulNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiology Sist - KV@DR - ZainiDocument46 pagesAnatomi Fisiology Sist - KV@DR - ZainiDikdik Iskandar DwiyantoNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Transport System in MammalsDocument41 pages8.1 Transport System in MammalsTheresa IzaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Regulatory MechanismDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Regulatory Mechanismhia natasyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Dr. Roger Joseph Ii R. JecinoDocument17 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Dr. Roger Joseph Ii R. JecinoFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Peer TutorialDocument11 pagesPeer Tutorialmashe1No ratings yet
- No VideoDocument47 pagesNo VideoTimothy John BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac OutputDocument79 pagesCardiac OutputBrian Adoka OmdangNo ratings yet
- Regulation of ECF VolumeDocument49 pagesRegulation of ECF VolumeGeorge LusanaNo ratings yet
- Heart RateDocument30 pagesHeart Ratefzfz5210No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument65 pagesHypertensionImtiyazNo ratings yet
- NCM 103-Cardio Anatomy & PhysioDocument56 pagesNCM 103-Cardio Anatomy & Physiolouradel100% (1)
- Anatomy NotesDocument86 pagesAnatomy NoteskNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology - 2Document33 pagesCardiovascular Physiology - 2Luiz Jorge MendonçaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesJonalynCollodChewacheoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typescut irnandaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typesghisma ocvintiaNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument4 pagesHeartArvin TaylorNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output, BP and Heart RateDocument13 pagesCardiac Output, BP and Heart RatenidhiNo ratings yet
- LC 5 Circulatory Responses To ExerciseDocument66 pagesLC 5 Circulatory Responses To ExercisealsafaparamedicsNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument57 pagesBlood PressureMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument58 pagesCardiovascular Systemabromley100% (2)
- 05 Cardiovascular System PhysiologyDocument34 pages05 Cardiovascular System PhysiologyKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument6 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyatefmaboodNo ratings yet
- Cvs 5 New 24Document4 pagesCvs 5 New 24Kim Sa-buNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: (Pulse & Blood Pressure)Document47 pagesVital Signs: (Pulse & Blood Pressure)nessa100% (1)
- Vital Signs Lecture PDFDocument47 pagesVital Signs Lecture PDFArchana SahuNo ratings yet
- PHS 213 Wk11 Cardiac output-BPDocument33 pagesPHS 213 Wk11 Cardiac output-BPPRINCE ADEWUMI JONATHANNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation HandoutDocument10 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation Handoutsac50900100% (2)
- Biochemistry of The Heart and Blood Vessels 2021 3 4Document44 pagesBiochemistry of The Heart and Blood Vessels 2021 3 4jakukNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia & TachycardiaDocument14 pagesBradycardia & TachycardiaHendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 4EDocument41 pagesChapter 05 4Elikhovandy10No ratings yet
- Cardio AssessmentDocument104 pagesCardio Assessmentlowell.cerezo.ihsNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle of The Heart PPT 3Document18 pagesCardiac Cycle of The Heart PPT 3pshantanu123No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Heart: Dr. George PearceDocument26 pagesPhysiology of The Heart: Dr. George PearceぴよんNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The HeartDocument38 pagesPhysiology of The HeartPanasheNo ratings yet
- Control of Heart RateDocument2 pagesControl of Heart RateelendriaNo ratings yet
- Baroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemDocument5 pagesBaroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemS GNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Pressure RegulationDocument21 pagesArterial Blood Pressure Regulationnaresh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Normal Heart Rhythm: Mutiara Budi AzharDocument27 pagesNormal Heart Rhythm: Mutiara Budi AzharAditya Fresno Dwi WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument27 pagesBlood Pressureanupam manu100% (1)
- Cardiac Out PutDocument31 pagesCardiac Out PutAyurveda Pg100% (1)
- Cardiac OutputDocument31 pagesCardiac OutputDylan BhuriNo ratings yet
- 10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument140 pages10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - HeartDocument22 pagesCardiovascular System - HeartZyrick Laurence Eslao TimmangoNo ratings yet
- Nervous Regulation of The Circulation and Rapid Control of Arterial PressureDocument2 pagesNervous Regulation of The Circulation and Rapid Control of Arterial Pressuremcwnotes100% (2)
- WK 1& 2 LectureDocument149 pagesWK 1& 2 LectureElma SekikorolevuNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Incentives SO - P05Document1 pageIncentives SO - P05GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Market Return Note Format 2024 - NewDocument1 pageMarket Return Note Format 2024 - NewGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Subsidy FormatDocument1 pageVehicle Subsidy FormatGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Credit Application (New 1) - 14.12.2023Document1 pageCredit Application (New 1) - 14.12.2023GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Secondary Trade Load Scheme - P05-2024 (Retails)Document1 pageSecondary Trade Load Scheme - P05-2024 (Retails)GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- SO Itinerary - P05 - 2024Document1 pageSO Itinerary - P05 - 2024GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 6-1 CivicDocument4 pages6-1 CivicGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Engsi 1079Document4 pagesEngsi 1079GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 6 Civics-2Document7 pages6 Civics-2GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 1HC GR 06 English 1st Term Exam Paper EDocument4 pages1HC GR 06 English 1st Term Exam Paper EGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 6-1 GeographyDocument5 pages6-1 GeographyGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- 2023 - SP Handout 02Document15 pages2023 - SP Handout 02GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Nil AnthaDocument1 pageNil AnthaGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Sajini CV NewDocument1 pageSajini CV NewGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- SM - Math - G10 - T3 - I, II PP Ans - 2018Document17 pagesSM - Math - G10 - T3 - I, II PP Ans - 2018GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Nqoao O Uh - I: Wjidk JDR Míëkh 2022Document9 pagesNqoao O Uh - I: Wjidk JDR Míëkh 2022GAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Application Sinhala 1 HettiarachchiDocument6 pagesApplication Sinhala 1 HettiarachchiGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- Workshop Officer Training RegistrationDocument1 pageWorkshop Officer Training RegistrationGAYANHNA gUNARATNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Spastic Effects of Footbaths in Post-Stroke Patients: A Proof-Of-Principle StudyDocument10 pagesAnti-Spastic Effects of Footbaths in Post-Stroke Patients: A Proof-Of-Principle StudyMuhamad Ibnu HasanNo ratings yet
- Types of MaskDocument40 pagesTypes of MaskADZRIN JUSALINo ratings yet
- Acupuncture (Acup) : 2017-18 CalendarDocument4 pagesAcupuncture (Acup) : 2017-18 CalendarElanghovan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Stop Think Before You ThrowDocument1 pageStop Think Before You ThrowNaresh ChilkuriNo ratings yet
- Hayden Et Al-2021-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument553 pagesHayden Et Al-2021-Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviewsprofessor do valeNo ratings yet
- Era University College of Nursing Lucknow: Submitted To-: Submitted byDocument7 pagesEra University College of Nursing Lucknow: Submitted To-: Submitted byAru Verma100% (1)
- Gavin, Nicole - Final Thesis - RedactedDocument245 pagesGavin, Nicole - Final Thesis - RedactedKarlo MedeirosNo ratings yet
- F.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. AryabiantaraDocument35 pagesF.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. Aryabiantaraarnawaiputu60No ratings yet
- Study On Probiotics and Their PreparationDocument9 pagesStudy On Probiotics and Their PreparationShrishti Singh100% (3)
- Initial Medical Evaluation Form For JO1 ApplicantsDocument1 pageInitial Medical Evaluation Form For JO1 ApplicantsBilly Joe BaradiNo ratings yet
- What Is Vitamin D and Why Is It ImportantDocument7 pagesWhat Is Vitamin D and Why Is It Importanthealthnfobd info100% (1)
- NLE Review PycheDocument7 pagesNLE Review PycheChin ChanNo ratings yet
- Prescription - Writing PartDocument38 pagesPrescription - Writing PartJnanesh PuniNo ratings yet
- A Newborn With Simmering Bleeding After CircumcisionDocument5 pagesA Newborn With Simmering Bleeding After Circumcisionmustafa akmanNo ratings yet
- How To Treat Covid-19 - IppocrateOrgDocument7 pagesHow To Treat Covid-19 - IppocrateOrgMassimo RiserboNo ratings yet
- Asthma Bronchiale: Dr. Ramelan Navy Hospital SurabayaDocument53 pagesAsthma Bronchiale: Dr. Ramelan Navy Hospital SurabayaCornelia CindyNo ratings yet
- Stroke SimulationDocument6 pagesStroke SimulationShirsho ShreyanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Regarding Breastfeeding - A Cross-Sectional Survey Among Postpartum Mothers in A North Indian StateDocument8 pagesKnowledge Regarding Breastfeeding - A Cross-Sectional Survey Among Postpartum Mothers in A North Indian StateIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- GP MCQ 8Document4 pagesGP MCQ 8Marta MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Vaksinasi Dewasa Sby 14Document51 pagesVaksinasi Dewasa Sby 14Ku Ha KuNo ratings yet
- Latest Research in HomeopathyDocument76 pagesLatest Research in Homeopathywww nambisons com100% (3)
- PracCourt Doctor's AffidavitDocument2 pagesPracCourt Doctor's AffidavitmarkbulloNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Cardiomyopat HYDocument43 pagesSeminar ON: Cardiomyopat HYmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- 2 Wilkes1989Document9 pages2 Wilkes1989LAURA MARCELA BARRENECHE CALLENo ratings yet
- Critikon CUFFS Catalog US - REVDocument16 pagesCritikon CUFFS Catalog US - REVJuan Moya BlasNo ratings yet
- Local AnestheticsDocument44 pagesLocal Anestheticsblack pink in ur area 21No ratings yet
- Appendix ADocument7 pagesAppendix ANoavilNo ratings yet