Professional Documents
Culture Documents
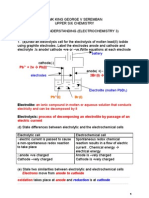
Ex Cell Notation
Ex Cell Notation
Uploaded by
veemueOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ex Cell Notation
Ex Cell Notation
Uploaded by
veemueCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell notation and potential
Problems
For the following problems, if the concentration is not indicated, assume the system to be in standard state.
c = 1 mol/L, p = 101.3 kPa, T = 25 °C.
1. For each of the following cell notation, write the corresponding balanced redox equation. Also, calculate
the cell potential (E) assuming standard conditions. From the potential, tell if whether the reaction is
spontaneous or not.
a) Mn(s) | Mn2+(aq) , HCl(aq) | H2(g) | Pt
b) Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq), H2SO4(aq) || Cd2+, H2SO4(aq) | Cd
c) Pt(s) | H2(g) | H+(aq) , Сl− | AgCl(s) | Ag (s)
2. From each of the following redox reactions, write a suitable cell notation.
a) Volta: Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) (hydrogen is produced on a copper electrode)
b) Daniell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) (Cu2+ reacts with Zn therefore: 2 half-cells)
c) Nicholson / Carlisle: H2O(l) H2(g)+ O2(g) (water electrolysis with NaCl(aq) on Pt electrodes)
d) Grove cell: Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) + 2HNO3(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 2NO2(g)
(NO2(g) is produced on Pt(s) in HNO3)
3. Consider the Beketov series: (+) Ca, Al, Mn, Cr, Zn, Cd, Fe, Pb, [H 2], Cu, Ag, Au (−)
Use this series to predict whether or not each of the following reaction is spontaneous.
a) Zn2+ + Pb4+ Zn + Pb2+
b) Al 3+
+ Cu +
Al + Cu2+
c) Cr + Cd2+ Cr2+ + Cd
d) H2 + Ag +
2H+ + Ag
4. Sketch a complete electrochemical cell based on the following cell notation
a) Cd(s) | Cd2+(aq, c = 0.15 M) || Ag+(aq, c = 0.20 M) | Ag(s)
b) Zn°(s) | Zn(NO3)2(aq), HCl(aq) | AgCl(s) | Ag°(s)
5. Write the cell notation corresponding to the following electrochemical cells.
a) Lithium battery for pacemaker b) Nickel-cadmium battery
Answers:
1. a) Mn(s) Mn2+(aq) + 2e– E° = 1.18 V
2H (aq) + 2e
+ –
H2(g) E° = 0.00 V
2H (aq) + Mn(s)
+
Mn (aq) + H2(g)
2+
E° = 1.18 V spontaneous
b) Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e– E° = -0.340 V
Cd (aq) + 2e
2+ –
Cd(s) E° = -0.403 V
Cu(s) + Cd (aq)
2+
Cu (aq) + Cd(s)
2+
E° = -0.743 V not spontaneous
c) H2(g) 2H+(aq) + 2e– E° = 0.00 V
2AgCl(s) + 2e –
2Ag(s) + 2Cl (aq)
–
E° = 0.2223 V
2AgCl(s) + H2(g) 2Ag(s) + 2Cl (aq) + 2H (aq) E° =
– +
0.2223 V spontaneous
2. a) Zn | Zn2+(aq, c = 1 mol/L) H+(aq, c = 1 mol/L) | H2(g) | Pt
b) Zn | ZnSO4(aq, c = 1 mol/L) || CuSO4(aq, c = 1 mol/L) | Cu
c) Pt | O2(g, p = 1 atm) | H2O(l), NaCl(aq, c = 1 mol/L) | H2(g, p = 1 atm) | Pt
d) Zn | ZnSO4(aq, c = 1 mol/L) || HNO3(aq, c = 1 mol/L) | NO2(g, p = 1 atm) | Pt
3. a) not-spontaneous b) not-spontaneous c) spontaneous d) spontaneous
4.
a) b)
5. a) Li(s) | LiI(s) | I2(s) | Ti(s)
b) Cd(s) | CdO(s) | KOH(aq. sat) | NiOOH(s) | NiOH2(s) | Ni(s)
You might also like
- Electrochemical Cells Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesElectrochemical Cells Worksheet AnswersNurul Hana Omar100% (2)
- Ammonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestDocument2 pagesAmmonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestSantosh Kumar Sahu100% (1)
- A Comparative Analysis On The Effectiveness of Star FruitDocument19 pagesA Comparative Analysis On The Effectiveness of Star FruitMaria Danica de Villa67% (3)
- Electrochemistry: (See Page 3 For Formulas and An Answer Key) P R A C T I C E T E S TDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry: (See Page 3 For Formulas and An Answer Key) P R A C T I C E T E S TBiniyam haileNo ratings yet
- Extract 10 PagesDocument10 pagesExtract 10 PageskuoklukeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 Electrochem 1Document5 pagesAssignment 6 Electrochem 1Kester Yuree L. GimongalaNo ratings yet
- CHEM2310 Electrochemistry Tutorial Solutions - Typed - Nov 2013Document4 pagesCHEM2310 Electrochemistry Tutorial Solutions - Typed - Nov 2013ClaytonMitchellJr.No ratings yet
- A2 Extension1 Electrochemistry and RedoxDocument10 pagesA2 Extension1 Electrochemistry and RedoxDavid MathewsNo ratings yet
- Soal ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesSoal ElectrochemistryHerlinda OktaNo ratings yet
- DebateDocument3 pagesDebatebbangeles1No ratings yet
- MCQ - Test 3 With - KeyDocument6 pagesMCQ - Test 3 With - KeyShubham Baxla (CSEAIML23310662409:30)No ratings yet
- Elec ChemDocument5 pagesElec ChemArrianne Jaye MataNo ratings yet
- P19 Answers Albert KweyeteDocument6 pagesP19 Answers Albert KweyetedenisNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Problem Set Answer KeyDocument3 pagesModule 7 Problem Set Answer KeyPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- CHEM1070A: Principles of Modern Chemistry: Tutorial 9 ElectochemsitryDocument7 pagesCHEM1070A: Principles of Modern Chemistry: Tutorial 9 ElectochemsitrymirandatwongNo ratings yet
- Exam 4-SolutionsDocument6 pagesExam 4-SolutionsUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips 2 Write The Chemical Formulas of The Products and Balance The Following Spontaneous ReactionsDocument40 pagesSilo - Tips 2 Write The Chemical Formulas of The Products and Balance The Following Spontaneous ReactionsAkash BhoiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Level 2 Worked SolutionsDocument11 pagesTutorial 9 - Level 2 Worked SolutionsBloodCypherNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Understanding - AnswersDocument11 pagesElectrochem Understanding - AnswersSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Standard Electrode Potentials in Aqueous Solution at 25°C: TablesDocument2 pagesStandard Electrode Potentials in Aqueous Solution at 25°C: TablesLouie G NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrochemistry ElectrochemistryDocument29 pagesElectrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrochemistryسليمان القباقليNo ratings yet
- EPOTPPDocument28 pagesEPOTPPapi-3706290100% (2)
- EpotppsDocument31 pagesEpotppsHelpful HandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Electrochemistrymeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- HTTPWWW - occc.edukmbaileyChem1115TutorialsNet Ionic Eqns Answers - HTMDocument1 pageHTTPWWW - occc.edukmbaileyChem1115TutorialsNet Ionic Eqns Answers - HTMVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2122 Course Revision Questions Chemistry Level M T2 MSDocument127 pages2122 Course Revision Questions Chemistry Level M T2 MSDana JrabNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 30AP Electrochemistry Workbook: Net Ionic EquationsDocument27 pagesChemistry 30AP Electrochemistry Workbook: Net Ionic EquationsDayanul AlamNo ratings yet
- Test Bank - Ch.19-New PDFDocument2 pagesTest Bank - Ch.19-New PDFBinit KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 BANKDocument16 pagesChapter 18 BANKMeowCat123456789No ratings yet
- Standard Electrode Potential SeriesDocument1 pageStandard Electrode Potential SeriesWONG KEE PING MoeNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions Jee ModuleDocument49 pagesLiquid Solutions Jee ModuleAfsheen TahiraNo ratings yet
- Reduction-Oxidation Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesReduction-Oxidation Reactions and Electrochemistrykaushi123No ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesReview QuestionsMarikNo ratings yet
- AP Electro Chem 1515 Ex AnsDocument40 pagesAP Electro Chem 1515 Ex AnsYj TehNo ratings yet
- Net Ionic EditedDocument8 pagesNet Ionic EditedMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ElectrokeychangDocument3 pagesElectrokeychangshee34461No ratings yet
- Chapter9 AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter9 AnswersedytfuyNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 Exercise 3 - Spontaneous ReactionsDocument1 pageTopic 13 Exercise 3 - Spontaneous ReactionsdenisNo ratings yet
- BATTERYDocument19 pagesBATTERYRaja PRNo ratings yet
- AJ98172 Tutorial Topic 9Document2 pagesAJ98172 Tutorial Topic 9WilfredNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Electrochemistry: Decreases PH of Solution (D) Electrolysis of CusoDocument28 pagesSubject: Chemistry Electrochemistry: Decreases PH of Solution (D) Electrolysis of CusoQwertyNo ratings yet
- Past Year Question: ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesPast Year Question: ElectrochemistryLuk HKNo ratings yet
- CHM143 Answer For Tutorial 6Document5 pagesCHM143 Answer For Tutorial 62023502121No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 DmsDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 DmsCik ApaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Document9 pagesWorksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Dagim YenenehNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument13 pagesElectrochemical Cellsshivendra tiwariNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Chemistry 30 WorksheetsDocument49 pagesElectrochemistry: Chemistry 30 Worksheetsdan anna stylesNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 Datasheet May 2020Document4 pagesCHEM1 Datasheet May 2020Miku HatsuneNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry Review WorksheetqqchiuNo ratings yet
- NIE - and - Particulate - Drawings - Worksheet - Answers at End - 2017-1Document8 pagesNIE - and - Particulate - Drawings - Worksheet - Answers at End - 2017-1Jane Ivanova100% (1)
- C 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017Document16 pagesC 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerDocument7 pagesTopic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerCheng Xun LeeNo ratings yet
- 10 ElectrochemistryDocument77 pages10 ElectrochemistrySyamil Adzman100% (1)
- Electrochemistry MCQ SendDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry MCQ SendRajendra ChikkamathNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios QuímicaDocument3 pagesEjercicios QuímicaAndreaForteRuizNo ratings yet
- 02 ElectrochemistryDocument6 pages02 ElectrochemistryGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry CPPDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry CPPSukanya PaulNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrochemistry Solved ProblemsDocument17 pagesBasic Electrochemistry Solved ProblemsAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Prob SetDocument2 pagesElectrochem Prob SetOri SeinNo ratings yet
- E, Will The Reactions Be Spontaneous Not ?: Cell oDocument2 pagesE, Will The Reactions Be Spontaneous Not ?: Cell oWi LernNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- RIL 4Q FY18 Analyst Presentation 27apr18 PDFDocument110 pagesRIL 4Q FY18 Analyst Presentation 27apr18 PDFneethuNo ratings yet
- Du Dub PDFDocument55 pagesDu Dub PDFSURESH100% (1)
- Chemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitDocument4 pagesChemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitNur E Alam NuruNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Seals - MICRO SEALSDocument26 pagesMechanical Seals - MICRO SEALSMICRO SEALSNo ratings yet
- EN# EN Name SAE UNS DIN Carbon SteelsDocument4 pagesEN# EN Name SAE UNS DIN Carbon Steels'viki ArtNo ratings yet
- Process Hazard Analysis DM Plant - 25.01.18Document51 pagesProcess Hazard Analysis DM Plant - 25.01.18Debabrata TantubaiNo ratings yet
- Ion-Exchange Membranes: Preparative Methods For Electrodialysis and Fuel Cell ApplicationsDocument23 pagesIon-Exchange Membranes: Preparative Methods For Electrodialysis and Fuel Cell ApplicationsJose Antonio Siñani VilteNo ratings yet
- 15A51101 Engineering ChemistryDocument1 page15A51101 Engineering ChemistryJayakanthNo ratings yet
- Questionpaper Unit2WCH02 October2018 IAL Edexcel ChemistryDocument24 pagesQuestionpaper Unit2WCH02 October2018 IAL Edexcel ChemistrySadman SlenderNo ratings yet
- Itec 2018-Akc-IrDocument63 pagesItec 2018-Akc-IrJohn F ServilleNo ratings yet
- Incropera Appendix - 2011Document32 pagesIncropera Appendix - 2011Gracylla RoseNo ratings yet
- Dulux Spalling DocumentDocument3 pagesDulux Spalling Documentashish100% (1)
- Periodic Classification of Elements: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements: Multiple Choice QuestionsAryanNo ratings yet
- Asl 6 217Document27 pagesAsl 6 217SaliniNo ratings yet
- GCColumnsDocument4 pagesGCColumnsasel ppNo ratings yet
- Stirred Ultrafiltration Cells: User GuideDocument32 pagesStirred Ultrafiltration Cells: User Guidesofiane ladegNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters and Natural Oils Under Neat ConditionsDocument5 pagesHomogeneous Hydrogenation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters and Natural Oils Under Neat ConditionsEnrique GallegosNo ratings yet
- Pigments For Plastics Product Selection GuideDocument21 pagesPigments For Plastics Product Selection GuideAndrew IMCDNo ratings yet
- Free Energies of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Reagents and Their ApplicationsDocument49 pagesFree Energies of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Reagents and Their ApplicationsZongxin JinNo ratings yet
- Us2438259 PDFDocument3 pagesUs2438259 PDFDakota EllisonNo ratings yet
- Global Downstream Outlook To 2035Document16 pagesGlobal Downstream Outlook To 2035psnshreemaxNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Hydrotreating Process: Presented byDocument16 pagesPresentation On Hydrotreating Process: Presented bySantoso WijayaNo ratings yet
- STAININGDocument38 pagesSTAININGCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Notes in BiologyDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates: Notes in BiologyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- The Common Ion Effect ExamplesDocument4 pagesThe Common Ion Effect ExamplesresultbhardwajNo ratings yet
- Characterizing The Materials Composition and Recovery Potential From WasteDocument23 pagesCharacterizing The Materials Composition and Recovery Potential From WasteYahaira Barrueto JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Voest Alpine-WireDocument2 pagesVoest Alpine-WireAnonymous wUv02fNo ratings yet
- Mti Connect 2023 Issue 2 - SpreadsDocument21 pagesMti Connect 2023 Issue 2 - SpreadsMandeep SinghNo ratings yet