Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patterns
Patterns
Uploaded by
Aaron TrevorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patterns
Patterns
Uploaded by
Aaron TrevorCopyright:
Available Formats
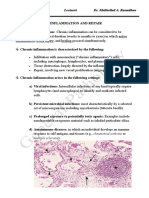
1) Segregated glandular inflammation: This morphologic pattern of inflammation is characterized by
inflammation limited to the glands. It typically involves the infiltration of inflammatory cells, such as
neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells, in and around the glands. The inflammation may result in
glandular destruction and dysfunction.
2) Periglandular inflammation: In this pattern, inflammation surrounds the glands without direct
involvement of the glandular tissue. The inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes and plasma cells, are
concentrated in the periglandular area. This type of inflammation can be seen in various organs, such as
the liver, pancreas, and salivary glands.
3) Diffuse stromal inflammation: Diffuse stromal inflammation refers to inflammation involving the
connective tissue or stroma of an organ or tissue. The inflammatory cells infiltrate the stroma, which is
the supportive tissue surrounding the functional components of an organ. This pattern can be observed
in various organs and is often associated with chronic inflammation.
4) Isolated stromal lymphoid nodules: This morphologic pattern of inflammation is characterized by the
formation of discrete lymphoid nodules within the stroma of an organ or tissue. These nodules consist of
aggregations of lymphocytes and plasma cells. Isolated stromal lymphoid nodules are commonly
observed in chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and chronic gastritis.
5) Acute necrotizing inflammation: Acute necrotizing inflammation is characterized by the presence of
tissue necrosis, along with an intense inflammatory response. The affected tissue undergoes cellular
death, resulting in tissue destruction and the release of inflammatory mediators. This pattern is often
seen in severe infections, such as gangrenous appendicitis or necrotizing pneumonia.
6) Focal granulomatous inflammation: Focal granulomatous inflammation refers to the formation of
granulomas, which are organized collections of immune cells, including macrophages, lymphocytes, and
multinucleated giant cells. Granulomas are typically found in response to chronic infections or certain
immune-mediated conditions. They can be seen in various organs, such as the lungs, liver, and lymph
nodes.
You might also like
- Chapter 33 Guyton and HallDocument4 pagesChapter 33 Guyton and Hallg_komolafeNo ratings yet
- Definition: Prolonged Inflammatory Process (Weeks or Months) Where AnDocument7 pagesDefinition: Prolonged Inflammatory Process (Weeks or Months) Where Anعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflammationDocument29 pagesChronic Inflammationsunday danielNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument10 pagesAcute InflammationLydia Angel HartonoNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflamDocument35 pagesChronic InflamAnam ShahidNo ratings yet
- Granuloma Is Defined As A Circumscribed, Tiny Lesion, About 1 MM in Diameter, Composed PredominantlyDocument6 pagesGranuloma Is Defined As A Circumscribed, Tiny Lesion, About 1 MM in Diameter, Composed PredominantlyIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Types of Inflammation-1Document9 pagesInflammation and Types of Inflammation-1Shalabh JoharyNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument8 pagesInflammationHarjot RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Inflammasi - 2: Nunuk Purwanti Biomedika Kedokteran GigiDocument41 pagesInflammasi - 2: Nunuk Purwanti Biomedika Kedokteran GigiMonica Abigail Wohing AtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inflammation, Tissue Repair & FeverDocument8 pagesChapter 6 - Inflammation, Tissue Repair & FeverChrista CastorNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory CellsDocument5 pagesInflammatory CellsFahad KhanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation NotesDocument12 pagesInflammation NotesavidadarkestevillearnNo ratings yet
- Inflammation 30.08.2022Document39 pagesInflammation 30.08.2022Abdur RaquibNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio;Ogy of Inflammation تم حفظه تلقائياDocument59 pagesPathophysio;Ogy of Inflammation تم حفظه تلقائياbebba habdouNo ratings yet
- Inflammation Is Part of The Complex Biological Response of Vascular Tissues To Harmful StimuliDocument2 pagesInflammation Is Part of The Complex Biological Response of Vascular Tissues To Harmful StimuliGabitza GabiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Chronic InflammationDocument34 pagesModule 4 Chronic InflammationAllan SigangaNo ratings yet
- Patho 4Document9 pagesPatho 4ambiliNo ratings yet
- Inflamation 2Document6 pagesInflamation 2Khadija YousafNo ratings yet
- The Agents Causing Inflammation May BeDocument3 pagesThe Agents Causing Inflammation May BemidoNo ratings yet
- Inflammation - Oral Maxillofacial Pathology - IUPDocument36 pagesInflammation - Oral Maxillofacial Pathology - IUPExnon RdXNo ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammation 2021 - MMSDocument91 pagesChronic Inflammation 2021 - MMSAbhigna PenthalaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation: Bocharova TetianaDocument79 pagesInflammation: Bocharova Tetianaсветлый поповNo ratings yet
- ChronicDocument19 pagesChronicMubasharNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Inflammatory MediatorsDocument28 pagesInflammation and Inflammatory Mediatorsla.instagramawaNo ratings yet
- 4 Chronic Inflammation IDocument38 pages4 Chronic Inflammation IAlex XanderNo ratings yet
- Inflammation 3Document44 pagesInflammation 3mikiyaskayleNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument17 pagesInflammationNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflammationDocument46 pagesChronic Inflammationفاطمه علي رسولNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Inflammation: Yacob Alemu (MD) May 2021Document89 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammation: Yacob Alemu (MD) May 2021Tazeb AyeleNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document24 pagesLec 1Ab AbNo ratings yet
- Overview of InflammationDocument6 pagesOverview of InflammationNauzaina IjazNo ratings yet
- Pathology For Dentistry Lect 6Document5 pagesPathology For Dentistry Lect 6Mohamad AladdinNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflammationDocument13 pagesChronic Inflammationmouid0.2003No ratings yet
- Exp - No 6 Chronic InflammationDocument13 pagesExp - No 6 Chronic InflammationNatasha BalochNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document65 pagesSession 2kasper mkNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflammationDocument18 pagesChronic InflammationRabeez HaiderNo ratings yet
- CH17Document22 pagesCH17JoshMatthewsNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous InflammationDocument96 pagesGranulomatous InflammationIvonne Trujillo TorbiscoNo ratings yet
- 3.acute InflammationDocument38 pages3.acute Inflammationyaqeenallawi23No ratings yet
- Blood Physiology LAb2Document8 pagesBlood Physiology LAb2DOROTA NIEOCZYMNo ratings yet
- Innate ImmunityDocument32 pagesInnate ImmunityYik sNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument12 pagesAcute InflammationEslam NassarNo ratings yet
- Basic PathologyDocument71 pagesBasic Pathologycocopandanenak100% (1)
- Physiology Summary Chapter 33Document5 pagesPhysiology Summary Chapter 33gail018100% (1)
- Short Notes InflammationDocument3 pagesShort Notes InflammationDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation LRDocument12 pagesInflammation LRMahnoor MansoorNo ratings yet
- Immunity - Ag-Ab ReactionDocument120 pagesImmunity - Ag-Ab Reactionnuaa11140No ratings yet
- Chronic InflammationDocument26 pagesChronic Inflammationbhatti106100% (4)
- Chronic Inflammation BPTDocument26 pagesChronic Inflammation BPTbpt2No ratings yet
- 04.inflammation 4-ChronicInflammationDocument34 pages04.inflammation 4-ChronicInflammationShameena KnNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chroic Inflammlation1Document36 pages2 - Chroic Inflammlation1aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Immunity 2Document4 pagesImmunity 2Mkhize KhabazelaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1Document8 pagesUnit 4.1Bloody MarieNo ratings yet
- Inflammation ContiDocument2 pagesInflammation ContiKiranNo ratings yet
- Session 10 Chronic InflammationDocument40 pagesSession 10 Chronic InflammationGodfrey GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammation and Granulomatous InfectionsDocument81 pagesChronic Inflammation and Granulomatous Infectionshouse.of.ssekamwaNo ratings yet
- InflammationsDocument68 pagesInflammationsAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument60 pagesInflammationОлексій ПрилуцькийNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument36 pagesInflammationBuchNo ratings yet