Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hardwood Cutting Instructions
Hardwood Cutting Instructions
Uploaded by
Nate ConradOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hardwood Cutting Instructions
Hardwood Cutting Instructions
Uploaded by
Nate ConradCopyright:
Available Formats
How to Propagate Plants from Dormant Hardwood Cuttings
Hardwood cuttings are even simpler to prepare than softwood or herbaceous cuttings, as we
use cuttings from dormant deciduous trees and woody plants, and this technique is very
useful for propagating fruit trees such as figs, pomegranates, mulberries and quince. Some
plums can grow well from hardwood cuttings too, while other’s don’t do so well, it depends
on the variety.
Dip the base of the cutting into rooting hormone (optional)
Treating cuttings with rooting hormone can increase the chances of stimulating root growth.
This is more critical in plants that are more difficult to root.
Simply dip the base into the rooting hormone, that’s all!
If using root hormone powder, and be sure to tap the cuttings to remove excess powder.
Prepare propagating medium and insert cutting
The cuttings can either be placed in the ground in a ‘slit trench’ outside, or they can be
placed in a container of propagating medium.
The cuttings can still lose moisture and dry out, even without leaves, so we try to place as
much of the cutting below the surface of the soil, while allowing top 3 buds at the tip to be
sitting above the soil level. Leaving 1/4 to 1/3 of the tip of the cutting above the surface
achieves this, otherwise just leave three buds unburied.
Slit Trench Method
1. Make a ‘slit trench’ by pushing a spade into soil and rocking it back and forth. In clay
soil, add some coarse sand for drainage.
2. Put cuttings in so 2/3 is below the soil, place cuttings 5cm (2”) apart and press the soil
down around them. If using multiple rows of slit trenches, place rows 30cm (12”) apart.
3. Water in the soil around the cuttings. The soil will remain damp over the winter
period. Cuttings will root and be ready to plant next autumn.
Container and Propagating Medium Method
1. Fill a container (pot) with a suitable propagating medium. Materials commonly used
as propagating medium are coarse sand, regular potting mix, coconut coir, or blends
such as a mixture of one part peat and one part Perlite (by volume), or one part peat
and one part sand (by volume).
2. Put cuttings in so 2/3 is below the soil, place cuttings 5cm (2”) apart and press the
propagating medium down around them.
3. Water in the soil around the cuttings. Keep the propagating medium slightly damp but
do not overwater as this will cause the cuttings to rot. If possible, place the container
in a cold frame of greenhouse to speed up the formation of roots. The cuttings will be
ready to transplant in spring.
You might also like
- Vocabulary Workshop Level GDocument1 pageVocabulary Workshop Level GShehab El-Menshawy33% (3)
- Tree Plantation ProjectDocument14 pagesTree Plantation ProjectANIMESH DUTTA84% (55)
- Igcse English Poetry AnthologyDocument22 pagesIgcse English Poetry AnthologyParvathy Subramanian100% (1)
- How To Cultivate and Harvest Legal Psychoactive Plants (Formatar)Document86 pagesHow To Cultivate and Harvest Legal Psychoactive Plants (Formatar)huds on100% (1)
- Biology Investigatory Project.Document12 pagesBiology Investigatory Project.Murali77% (30)
- Chapter 14 Methods of PlantingDocument21 pagesChapter 14 Methods of Plantingapi-19911503No ratings yet
- Asexual PropagationDocument121 pagesAsexual PropagationShaiannah Veylaine Recinto ApostolNo ratings yet
- Planting Woody OrnamentalsDocument8 pagesPlanting Woody OrnamentalsSharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- Gardening With Composts, Mulches, & Row Covers Gardening Guidebook For Umatilla County, OregonDocument4 pagesGardening With Composts, Mulches, & Row Covers Gardening Guidebook For Umatilla County, OregonWinter GardeningNo ratings yet
- Tree Plantation ProjectDocument11 pagesTree Plantation ProjectsethyankitaraniNo ratings yet
- Growing the Stone Fruits - With Information on Growing Cherries, Peaches and PlumsFrom EverandGrowing the Stone Fruits - With Information on Growing Cherries, Peaches and PlumsNo ratings yet
- Starting Roses From CuttingsDocument8 pagesStarting Roses From CuttingsJeffrey S DoddNo ratings yet
- Planting and Establishing Trees: Ten Steps To Proper Tree PlantingDocument9 pagesPlanting and Establishing Trees: Ten Steps To Proper Tree PlantingCHINNU_HIDAYATHNo ratings yet
- Tay BerriesDocument3 pagesTay Berriespierrecmoeller1159No ratings yet
- Spring Planting and Growing Guidelines For Plantings of American Chestnut SeedlingsDocument4 pagesSpring Planting and Growing Guidelines For Plantings of American Chestnut SeedlingsLittle BirdNo ratings yet
- How To Plant A TreeDocument6 pagesHow To Plant A TreefvhjrojvrnvorjenoojnNo ratings yet
- Planting A Home Vegetable Garden: Preparing The SeedbedDocument4 pagesPlanting A Home Vegetable Garden: Preparing The Seedbedbya316No ratings yet
- Mulching Guide Benefits of Mulch PDFDocument9 pagesMulching Guide Benefits of Mulch PDFCHP TSTPSNo ratings yet
- Planting Your Gift Tree-Potting Instructions: 17february2010Document1 pagePlanting Your Gift Tree-Potting Instructions: 17february2010Aahana LabsNo ratings yet
- WWW - Mammothwillow.Co - Uk Tel. O7586350697: Planting Season November To April - Growing GuideDocument2 pagesWWW - Mammothwillow.Co - Uk Tel. O7586350697: Planting Season November To April - Growing Guidegiles nNo ratings yet
- Marco TtingDocument4 pagesMarco TtingMark John BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Omafra Growing Blueberries For Home Gardens 23 007 en 2023 03 31Document6 pagesOmafra Growing Blueberries For Home Gardens 23 007 en 2023 03 31Fairyland Daycare WestNo ratings yet
- Fruit Trees: Planting and Care of Young Trees: PublicationDocument5 pagesFruit Trees: Planting and Care of Young Trees: PublicationGarudaOzoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 OrnamentalsDocument16 pagesModule 3 OrnamentalsDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- LAWNDocument5 pagesLAWNM CHANDRA PRABHANo ratings yet
- Development and Maintenance of Lawn UrfDocument6 pagesDevelopment and Maintenance of Lawn UrfgalaxatNo ratings yet
- Growing Chestnut Trees From Seed: Storing NutsDocument4 pagesGrowing Chestnut Trees From Seed: Storing NutsvalgurNo ratings yet
- Learn MarcottingDocument14 pagesLearn MarcottingJOVELYN Y. ALFORQUENo ratings yet
- PM819 Vegetable GardeningDocument4 pagesPM819 Vegetable Gardeningdag57No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Propagating Fruit TreesDocument47 pagesLesson 1 - Propagating Fruit TreesEspinas JadeNo ratings yet
- Resource000844 Rep884Document4 pagesResource000844 Rep884NVAzirNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Perennial Questions: SelectionDocument4 pagesFrequently Asked Perennial Questions: SelectionRoss SheNo ratings yet
- Care and Maintenance in The NurseryDocument16 pagesCare and Maintenance in The NurseryBless CamilosaNo ratings yet
- Fruit Tree Planting InstructionsDocument8 pagesFruit Tree Planting InstructionsgerardwilmotNo ratings yet
- Growing Healthy Soil - Organic GardeningDocument8 pagesGrowing Healthy Soil - Organic GardeningSchool Vegetable Gardening67% (3)
- Making A SeedboxDocument15 pagesMaking A SeedboxJob LuceroNo ratings yet
- Mthds OfVeg - Prop.cuttingslayering Technqs.Document40 pagesMthds OfVeg - Prop.cuttingslayering Technqs.Justin MillapreNo ratings yet
- Tle 6-Agri - W5Document38 pagesTle 6-Agri - W5Maria Elena LiNo ratings yet
- Ho 1Document3 pagesHo 1Llna HnNo ratings yet
- Mulching Definitions For Different CropsDocument7 pagesMulching Definitions For Different CropsnandarulsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document7 pagesLesson 11Julianne Bea Notarte100% (1)
- TerrariumDocument4 pagesTerrariumHimecka UtaNo ratings yet
- Case Ih Model Tractors Jx60 Jx70 Jx80 Jx90 Jx95 Service ManualDocument22 pagesCase Ih Model Tractors Jx60 Jx70 Jx80 Jx90 Jx95 Service Manualchristopherreilly170297rgw100% (139)
- TRANSPLANTINGDocument54 pagesTRANSPLANTINGOwell Angeles FababierNo ratings yet
- Terrarium Basics Sept 2015Document5 pagesTerrarium Basics Sept 2015Konstadinos PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- How Should Forages Be PlantedDocument10 pagesHow Should Forages Be PlantedOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Desert Rose ProductionDocument2 pagesDesert Rose ProductionBenito Neto0% (1)
- Grafting Procedure: For Sweet TamarindDocument41 pagesGrafting Procedure: For Sweet TamarindHermie LicuanNo ratings yet
- Activity Tree Planting Guide PDFDocument4 pagesActivity Tree Planting Guide PDFAnonymous xVTbc3T6No ratings yet
- FrontWalk GardenPlanDocument3 pagesFrontWalk GardenPlanSomill HwangNo ratings yet
- Land PreparationDocument86 pagesLand PreparationLove RainNo ratings yet
- Mulching: Why Mulch?Document4 pagesMulching: Why Mulch?Dell DelimanoNo ratings yet
- WLAS - TLE AFA 10 Horticulture - Q3 W 5 1Document6 pagesWLAS - TLE AFA 10 Horticulture - Q3 W 5 1wilmermelindocozo2No ratings yet
- Artificial Ways of Growing New PlantsDocument5 pagesArtificial Ways of Growing New PlantsJojit Abaya NartatesNo ratings yet
- Terrarium ConstructionDocument3 pagesTerrarium Constructionacc123440% (1)
- Cover Up With A Winter Cover CropDocument2 pagesCover Up With A Winter Cover CropsnohomishcdNo ratings yet
- Composting Yard Food Waste at HomeDocument12 pagesComposting Yard Food Waste at HomejimmiezigzagNo ratings yet
- Making A Dish GardenDocument4 pagesMaking A Dish GardenKriz YanNo ratings yet
- No Fuss Sunny GardenDocument3 pagesNo Fuss Sunny GardenNicoleta Potorac100% (1)
- Habitat Gardens - Resource Folder PrepDocument2 pagesHabitat Gardens - Resource Folder Preplaura.gomezoldNo ratings yet
- CongklakDocument2 pagesCongklakAristi Audri TrianiNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Forestry TermsDocument8 pagesGlossary of Forestry TermsJanine TugononNo ratings yet
- 113 Janoshida, Gava PosudeDocument36 pages113 Janoshida, Gava PosudeLea Vukusic100% (1)
- 7.TOMATO PPT - 0Document22 pages7.TOMATO PPT - 0Senthil MuruganNo ratings yet
- Draft Himachal Pradesh Forest (Sale of Timber) Rules, 2009.Document6 pagesDraft Himachal Pradesh Forest (Sale of Timber) Rules, 2009.dsuresh_kNo ratings yet
- To Stay Alive by Skila Brown Chapter SamplerDocument32 pagesTo Stay Alive by Skila Brown Chapter SamplerCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- Construction in HillsDocument66 pagesConstruction in HillsDivyanshu KothariNo ratings yet
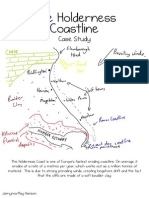
- Holderness Case StudyDocument9 pagesHolderness Case StudyJamyma-May HansonNo ratings yet
- Explaining 10 Different Types of Fasteners and Their UsesDocument16 pagesExplaining 10 Different Types of Fasteners and Their Usesrecep1No ratings yet
- Feasib FactsDocument7 pagesFeasib FactsRuby GlennNo ratings yet
- Dragonhyde Hoof Health Program BrochureDocument8 pagesDragonhyde Hoof Health Program BrochuresilkevondyckNo ratings yet
- Barrel, Pit, and Saggar Firing: Ceramics Monthly HandbookDocument22 pagesBarrel, Pit, and Saggar Firing: Ceramics Monthly HandbookferisitavNo ratings yet
- Forest Society and ColonialismDocument9 pagesForest Society and Colonialismdeborah joshiniNo ratings yet
- Law On Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesLaw On Natural ResourcesMarrielDeTorresNo ratings yet
- KONDISI VEGETASI HUTAN PINGGIRAN-Hendra PDFDocument12 pagesKONDISI VEGETASI HUTAN PINGGIRAN-Hendra PDFR. Mega MahmudiaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Cultivated Trees and Shrubs Hardy in North America, Exclusive of The Subtropical and Warmer Temperate RegionsDocument2 pagesManual of Cultivated Trees and Shrubs Hardy in North America, Exclusive of The Subtropical and Warmer Temperate RegionsWill RudyNo ratings yet
- The Woody Notes of FragranceDocument0 pagesThe Woody Notes of Fragranceosamamusa100% (1)
- Indicator Trees For Finding Morel MushroomsDocument1 pageIndicator Trees For Finding Morel MushroomsHenry Garman100% (3)
- Playground Maintenance For PlayspacesDocument83 pagesPlayground Maintenance For PlayspacesTess MichaelsNo ratings yet
- Serbian New Grape Wine VarietiesDocument4 pagesSerbian New Grape Wine Varietiesradmilo76No ratings yet
- Western Red CedarDocument11 pagesWestern Red CedarLowell SmithNo ratings yet
- A Review of Forest Policies, Institutions, and Changes in PDFDocument13 pagesA Review of Forest Policies, Institutions, and Changes in PDFpianNo ratings yet
- Hass Carmen PDFDocument23 pagesHass Carmen PDFBá Tùng PhanNo ratings yet
- 2202 - 2 Flush Door ShuttersDocument14 pages2202 - 2 Flush Door Shuttersvinay reddy100% (1)
- FormicaSamples WoodGrains.v02Document6 pagesFormicaSamples WoodGrains.v02Silvana DwijayantiNo ratings yet
- List of Forestry Universities and CollegesDocument19 pagesList of Forestry Universities and CollegesAbiyyu Muhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Minecraft Crafting Complete Recipe ListDocument12 pagesMinecraft Crafting Complete Recipe ListCamila DiasNo ratings yet