Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Financeshort2016
Math Financeshort2016
Uploaded by
Nora Petruța0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThis document discusses the history and development of risk management in finance. It covers 3 key areas:
1) Physics - Einstein's work on Brownian motion in 1905 laid the foundations for understanding random processes. This was applied to financial markets.
2) Economics - Theoretical economists studied risk hedging contracts in the 1950s-60s. Black and Scholes published an influential pricing formula in 1973.
3) Trading - Trading now encompasses complex derivative contracts. There is high demand for people trained in financial mathematics to help manage risk.
Original Description:
Original Title
math-financeshort2016
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the history and development of risk management in finance. It covers 3 key areas:
1) Physics - Einstein's work on Brownian motion in 1905 laid the foundations for understanding random processes. This was applied to financial markets.
2) Economics - Theoretical economists studied risk hedging contracts in the 1950s-60s. Black and Scholes published an influential pricing formula in 1973.
3) Trading - Trading now encompasses complex derivative contracts. There is high demand for people trained in financial mathematics to help manage risk.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMath Financeshort2016
Math Financeshort2016
Uploaded by
Nora PetruțaThis document discusses the history and development of risk management in finance. It covers 3 key areas:
1) Physics - Einstein's work on Brownian motion in 1905 laid the foundations for understanding random processes. This was applied to financial markets.
2) Economics - Theoretical economists studied risk hedging contracts in the 1950s-60s. Black and Scholes published an influential pricing formula in 1973.
3) Trading - Trading now encompasses complex derivative contracts. There is high demand for people trained in financial mathematics to help manage risk.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
www.warwick.ac.
uk/go/statistics
A Brief History of Risk Risk and Reward
With uncertainty comes both risk and the potential for profit.
Nobel Prizes Consider the following game:
Banks and other financial a coin is tossed and you gain one pound if heads The “suitable assumptions” do not often apply
Major theoretical advances have transformed
is showing and nothing otherwise. What would in reality. However, variations of this famous
institutions have to look after this type of trading.
it be fair to pay to enter this game? If heads and formula are still used today in many financial
(and ideally profit from) money Physics: tails are equally likely then you might expect situations.
in risky environments. They In 1905, Einstein’s miraculous year, he to make about fifty pence each time you play
published five revolutionary papers. One of (averaged over a large number of games). This
somehow have to manage the suggests that paying more than fifty pence
these developed the mathematical model of
risk: something which has never Brownian motion; a model for the motion of per game would be extravagant whilst paying What’s it about?
been more apparent to experts or individual molecules. In 1921 he received the less would seem to be a good deal. A price of
Nobel prize for his contributions to physics. fifty pence, the so-called expected payoff, seems Sophisticated tools are needed to capture
to the general public; it is certain the influence and interaction of time and
Many famous mathematicians have worked about right.
that specialists in the mathematics on this model developing a rich and powerful uncertainty. One key area is probability
of risk will be highly in demand theory of random motion which can be applied Generalising this idea to real world situations theory. Topics such as martingales
to the price of financial instruments as easily as can be a first step towards dealing with (things which on average neither
for years to come. Financial
to the positions of molecules. uncertainty, but it can be far from easy! increased nor decrease), Brownian
mathematics provides the tools Consider a stock instead of a coin. The value of motion (a process which characterises
required to manage risk effectively. Economics: the stock ST at a future time, T, is unknown : it’s pure diffusion) and stochastic calculus
Theoretical economists in the 50’s and 60’s a random quantity. In a “European call option” (the mathematical framework used
studied the contracts that were being used to you pay an amount Vo to have the option to buy to produce the Black-Scholes formula)
hedge risk. In 1973, Black and Scholes published one unit of the stock at time T for an amount
were once studied exclusively by
From Farming to Futures a powerful formula for pricing these contracts K. If it turns out that ST>K then you will be able
postgraduates but have now found their
using Einstein’s Brownian Motion to model to gain a profit of ST -K; otherwise you won’t
Risk has been present since the dawn the underlying random phenomena. Scholes way into the undergraduate syllabus of
exercise the option. The overall gain at time T will
of human civilisation. In the first days of received the Nobel prize in 1997. many universities worldwide – including
be the positive part of ST -K.
agriculture it became apparent that in Warwick.
some years crops fail whilst in others there
may be a glut. Farmers found that both
Trading in Risk What is the fair price Vo for this option? The
There has been an explosion of demand in
answer is not as obvious as you might think
extremes worked against them: in times It’s now commonplace for trading to having considered the coin problem. In the the Finance Industry for suitably-trained
of famine they had nothing to sell and in encompass complex derivative contracts based coin problem the profit was immediate; in the graduates ranging from those with a
times of excess the value of their crops fell on share prices, currencies, interest rates or stock market problem it is not and we have to specialist Master’s degree in Financial
to almost nothing. Both merchants and debt. Recently credit derivatives (especially consider the profit we could make by investing Mathematics to those with a PhD in
farmers found it to be to their advantage “insurance” against defaults) have been of K elsewhere. Black and Scholes produced a the mathematical sciences. This makes
to draw up contracts which provided interest to the general public and much marvellous answer to this problem in 1973. for a dynamic, challenging and exciting
both sides with a measure of security by discussed by the mainstream media. The trade environment in which to work. Finance
fixing a price for grain prior to its harvest. in such contracts has reached trillions of dollars Under suitable assumptions, they showed has also developed rapidly as an academic
With the passage of time, this idea of worldwide and financial institutions must, that the fair price in this setting is discipline and there are consequently
trading in “futures” has widened: from as we have all seen, manage their exposure So Φ(d)-KerT Φ(d- σ√T) where σ measures the many opportunities for mathematicians
grain to metals, coffee, sugar and even to all types of risk (and often the best way to rate at which the stock price varies randomly,Φ seeking a career in academia.
concentrated orange juice. Indeed, much eliminate risk is to make it worthwhile for is the cumulative distribution function for
more abstract “financial instruments” have another party to acquire it): they need highly the standard normal random variable,
been derived from the same basic ideas. skilled individuals who know how to use the r is the compound interest rate and
theory in the right way. dσ√T=In(So/K)+(r+ σ2 /2)T
MORSE ⎢3
You might also like
- BWR-04 Winding ThermometerDocument17 pagesBWR-04 Winding ThermometerJorge Alexander Román Morales100% (2)
- NIssan Patrol Series 1 Engine Electrical SystemDocument228 pagesNIssan Patrol Series 1 Engine Electrical SystemKofeto88% (8)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Mark Joshi 1: T&T Note: Check Word Spacing Before PressDocument7 pagesMark Joshi 1: T&T Note: Check Word Spacing Before PressoscarNo ratings yet
- On - The - Statistical - Differences - Between Binary Forecasts and Real World Payoffs PDFDocument11 pagesOn - The - Statistical - Differences - Between Binary Forecasts and Real World Payoffs PDFRavi TejNo ratings yet
- Circle in A Circle - The EconomistDocument3 pagesCircle in A Circle - The EconomistYassine aouinaNo ratings yet
- Bloomberg Markets 2020-06&07 PDFDocument84 pagesBloomberg Markets 2020-06&07 PDFJairon Merchán HazNo ratings yet
- Complexity Investing: Brinton Johns and Brad SlingerlendDocument46 pagesComplexity Investing: Brinton Johns and Brad SlingerlendRajat MittalNo ratings yet
- 1015 Didier Sornette PDFDocument95 pages1015 Didier Sornette PDFani_meherNo ratings yet
- Be Careful What You Model - 2005Document3 pagesBe Careful What You Model - 2005JoarisoNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document139 pagesUntitled 2divya chawlaNo ratings yet
- Financial BubblesDocument52 pagesFinancial BubblesFrancisco Antonio Álvarez CanoNo ratings yet
- MostdangerousequationDocument9 pagesMostdangerousequationanuragsingh19524No ratings yet
- Economics Needs A Scientific Revolution: EssayDocument1 pageEconomics Needs A Scientific Revolution: EssayMichelle HoNo ratings yet
- The Mathematical Equation That Caused The Banks To Crash - Science - The ObserverDocument4 pagesThe Mathematical Equation That Caused The Banks To Crash - Science - The ObserverlenovojiNo ratings yet
- 685 686OpinionFarmer2Document3 pages685 686OpinionFarmer2kumar.x.pankajNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Forecasting: Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Yaneer Bar-Yam, Pasquale CirilloDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Forecasting: Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Yaneer Bar-Yam, Pasquale CirilloStewart HendersonNo ratings yet
- Economics of Bubbles and Busts SC AmDocument8 pagesEconomics of Bubbles and Busts SC AmSkyler ChenNo ratings yet
- Doob - The Development of Rigor in Mathematical Probability (1900-1950)Document12 pagesDoob - The Development of Rigor in Mathematical Probability (1900-1950)Harry KrishnaNo ratings yet
- FDI and Political Risk Mini Case 6jYVszDT1oDocument7 pagesFDI and Political Risk Mini Case 6jYVszDT1oNikitha NithyanandhamNo ratings yet
- George A. Akerlof: The American Economic Review, Vol. 92, No. 3. (Jun., 2002), Pp. 411-433Document54 pagesGeorge A. Akerlof: The American Economic Review, Vol. 92, No. 3. (Jun., 2002), Pp. 411-433SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Chari Boru's File:-Suchitra Document From Today December 26Document24 pagesChari Boru's File:-Suchitra Document From Today December 26MUSSE YATENENo ratings yet
- Brand New Line of Credit No Photo (2004)Document2 pagesBrand New Line of Credit No Photo (2004)parkparadigmNo ratings yet
- Review of Secret Life of Real EstateDocument7 pagesReview of Secret Life of Real EstateAkbar ShakoorNo ratings yet
- DR RickardsreactionfinalDocument9 pagesDR RickardsreactionfinalDavid BriggsNo ratings yet
- Extreme Value Theory Can Save Your NeckDocument5 pagesExtreme Value Theory Can Save Your NeckAnastasia ZhuravliovaNo ratings yet
- Strategy at The Edge of ChaosDocument10 pagesStrategy at The Edge of Chaossaurabh_mathur171626100% (5)
- Taleb 2009Document16 pagesTaleb 2009roznica100% (1)
- Inevitability: by Charles PlattDocument4 pagesInevitability: by Charles PlattadvancedatheistNo ratings yet
- Espen Gaarder Haug: Space-Time FinanceDocument14 pagesEspen Gaarder Haug: Space-Time Financedeenutz93No ratings yet
- Fooled by RandomnessDocument9 pagesFooled by RandomnessNikunj Patel100% (3)
- Forum Winter 2020Document12 pagesForum Winter 2020Yixuan XiaNo ratings yet
- Stalking The Black SwanDocument7 pagesStalking The Black SwansonuaeroNo ratings yet
- Perpetual E-Motion: Steorn, The Economist & "Irrational Exuberance"Document12 pagesPerpetual E-Motion: Steorn, The Economist & "Irrational Exuberance"Cris VillarNo ratings yet
- Black Swan - Naylor - Wongchoti - ChenDocument34 pagesBlack Swan - Naylor - Wongchoti - Chenfreebanker777741No ratings yet
- Birthdays and Investment Risk: Confessions of An InvestorDocument10 pagesBirthdays and Investment Risk: Confessions of An InvestorSwati BahetiNo ratings yet
- I. Volatility Operates On A Sliding Scale Depending On The Size of The Antifragile System. IIDocument3 pagesI. Volatility Operates On A Sliding Scale Depending On The Size of The Antifragile System. IIDeepti MhatreNo ratings yet
- Classical and Keynesian MacroeconomicsDocument8 pagesClassical and Keynesian MacroeconomicsarigatonituNo ratings yet
- Tirole Economia Del Bien Comun Cap 2Document15 pagesTirole Economia Del Bien Comun Cap 2angyNo ratings yet
- On Single Point Forecasts For Fat-Tailed VariablesDocument10 pagesOn Single Point Forecasts For Fat-Tailed VariableslerhlerhNo ratings yet
- A Guide For The Perplexed Quant: EatureDocument5 pagesA Guide For The Perplexed Quant: Eaturezahedahmed5379No ratings yet
- Engle 2004Document18 pagesEngle 2004Martin EncinaNo ratings yet
- Gril AftDocument7 pagesGril Aftkid frostNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 3 From Risk Free Returns To Return Free RiskDocument16 pages2015 - 3 From Risk Free Returns To Return Free RiskSerigne Modou NDIAYENo ratings yet
- 14 358 149822091462 64 PDFDocument3 pages14 358 149822091462 64 PDFcrystal evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Should Economists Adopt Methods From PhysicsDocument3 pagesShould Economists Adopt Methods From PhysicsTraderCat SolarisNo ratings yet
- 36 2021 Lipton Review The Man Who Solved The Market How Jim Simons Launched The Quant RevolutionDocument5 pages36 2021 Lipton Review The Man Who Solved The Market How Jim Simons Launched The Quant RevolutionRodrigo RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Lutec and Zero PointDocument8 pagesLutec and Zero PointRed Bluelight100% (1)
- 1 Bounded Rationality - AumannDocument13 pages1 Bounded Rationality - Aumannqed16No ratings yet
- Marketplace of PerceptionsDocument11 pagesMarketplace of PerceptionsmohdsahilaliNo ratings yet
- Harvard MagazineDocument11 pagesHarvard MagazineVoytek100% (1)
- Preparing For The Next 'Black Swan'Document5 pagesPreparing For The Next 'Black Swan'Edward Chai Ming HuaNo ratings yet
- Riezgo e Innovación El Mapa de Los Animales No EsperadosDocument8 pagesRiezgo e Innovación El Mapa de Los Animales No EsperadosMara ProvenzanoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory of InvestmentDocument73 pagesQuantum Theory of Investmentnaveenhs18No ratings yet
- Summary of Trillion Dollar BetDocument2 pagesSummary of Trillion Dollar BetMuhammad Wasil Khalil Pathan100% (1)
- From Rationality To Hyperrality Paradigm Poker SSRN-id1392793Document14 pagesFrom Rationality To Hyperrality Paradigm Poker SSRN-id1392793Carina FernándezNo ratings yet
- Child REHDocument14 pagesChild REHSonia BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Error of SolvencyDocument4 pagesError of SolvencyRatiu SilviuNo ratings yet
- 1 Sornette 2Document90 pages1 Sornette 2Indir JaganjacNo ratings yet
- Fact-Free LearningDocument14 pagesFact-Free LearningscribbbyNo ratings yet
- Agorachronotistics Speculations On Mark PDFDocument23 pagesAgorachronotistics Speculations On Mark PDFGoha OulaiNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Wall Street: A Brief History of Predicting the UnpredictableFrom EverandThe Physics of Wall Street: A Brief History of Predicting the UnpredictableRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Strength 5 May 2021Document2 pagesStrength 5 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- Water-Cooled Screw Chiller: Nominal Cooling Capacity: 335 1392kWDocument12 pagesWater-Cooled Screw Chiller: Nominal Cooling Capacity: 335 1392kWمحمد مرسيNo ratings yet
- b097 Banhart2007.pdfertrtDocument11 pagesb097 Banhart2007.pdfertrtGarvit GoelNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Implement of Hybrid ANN PandO Based MPPT Controller To Enhance Efficiency of Photovoltaic SystemDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Implement of Hybrid ANN PandO Based MPPT Controller To Enhance Efficiency of Photovoltaic SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Dual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcDocument4 pagesDual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcRoberto SNo ratings yet
- 1 Hnov 2022 AnsDocument28 pages1 Hnov 2022 AnsbluewholemilkNo ratings yet
- Automatic Waste SegregationDocument6 pagesAutomatic Waste SegregationDeepak ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
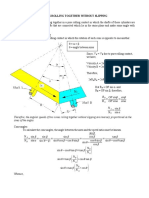
- Cones Rolling Together Without Slipping: R R OP sinα sinα N NDocument2 pagesCones Rolling Together Without Slipping: R R OP sinα sinα N NAllaine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Design Steps As Per NBC For Structrual Analysis of Residential BuildingDocument3 pagesDesign Steps As Per NBC For Structrual Analysis of Residential BuildingKhem Thapa0% (1)
- CDP 115 EnglishDocument2 pagesCDP 115 EnglishPuguh Tri HandoyoNo ratings yet
- Safety Observation Report (SOR)Document4 pagesSafety Observation Report (SOR)yassin ABERHOUCHNo ratings yet
- EMT 3253 Solid Structural Mechanics IDocument4 pagesEMT 3253 Solid Structural Mechanics IezraNo ratings yet
- Unit ExamDocument10 pagesUnit Examapi-296429098No ratings yet
- Introduction To Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery 2Nd Edition Cho W S To Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery 2Nd Edition Cho W S To Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFbenito.bennett742100% (11)
- Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Nickel: Standard Specification ForDocument3 pagesPressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Nickel: Standard Specification ForSofiaJabadanEspulgarNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Low Noise Pseudomorphic HEMT in A Surface Mount Plastic PackageDocument15 pagesData Sheet: Low Noise Pseudomorphic HEMT in A Surface Mount Plastic PackageÍtalo CésarNo ratings yet
- LatinDocument3 pagesLatinpdrharigmailcomNo ratings yet
- What Is A Demagnetization Curve?: More Than Just Your SupplierDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Demagnetization Curve?: More Than Just Your Suppliersurabhi0706No ratings yet
- Grundfos - CR 10 5 A FJ A E HQQEDocument11 pagesGrundfos - CR 10 5 A FJ A E HQQErosneyNo ratings yet
- BS EN 736-3 Valves Terminology - Definition TermsDocument12 pagesBS EN 736-3 Valves Terminology - Definition TermsLuis Daniel ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Materials Chemistry and PhysicsDocument16 pagesMaterials Chemistry and PhysicsRiandy PutraNo ratings yet
- Hagedorn-Brown Correlation: Multi-Phase Flow in PipesDocument48 pagesHagedorn-Brown Correlation: Multi-Phase Flow in PipesFarah Taha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument17 pagesFinalg ambrishNo ratings yet
- 2018 Book IntroductoryQuantumMechanicsDocument641 pages2018 Book IntroductoryQuantumMechanicsAlfangNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Non-Polar Covalent Bond (Formed by Equal Sharing of Electrons) and (3) Metallic Bond IsDocument7 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Non-Polar Covalent Bond (Formed by Equal Sharing of Electrons) and (3) Metallic Bond IsSharon May JavierNo ratings yet
- Polymer Technologies TDS CatalogDocument249 pagesPolymer Technologies TDS CatalogAminur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Horiz. DC Motor PDFDocument178 pagesHoriz. DC Motor PDFPedro RiveraNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Shell and Coil Heat Exchanger by Using Different Mass Flow Rate For Hot and Cold FluidDocument19 pagesCFD Analysis of Shell and Coil Heat Exchanger by Using Different Mass Flow Rate For Hot and Cold FluidIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet