Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus CUET PG Economics 2024
Syllabus CUET PG Economics 2024
Uploaded by
komalkushwaha12110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesThis document outlines the syllabus for an economics course covering microeconomics, macroeconomics, money and inflation, consumption and investment functions, open economy models, economic growth, statistical and mathematical methods, and the Indian economy. Key topics in microeconomics include consumer theory, production theory, and price determination under different market structures. Macroeconomics covers national income accounting, aggregate demand and supply, and classical and Keynesian theories. The syllabus also addresses monetary policy, consumption and investment functions, open economy models, economic growth models, statistical analysis, mathematical methods, and an overview of the colonial Indian economy.
Original Description:
Cuet Pg Ma(Eco) Syllabus
Original Title
Syllabus CUET PG Economics 2024_fc2979b6-7aae-46d3-a882-75732a4835fb
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the syllabus for an economics course covering microeconomics, macroeconomics, money and inflation, consumption and investment functions, open economy models, economic growth, statistical and mathematical methods, and the Indian economy. Key topics in microeconomics include consumer theory, production theory, and price determination under different market structures. Macroeconomics covers national income accounting, aggregate demand and supply, and classical and Keynesian theories. The syllabus also addresses monetary policy, consumption and investment functions, open economy models, economic growth models, statistical analysis, mathematical methods, and an overview of the colonial Indian economy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesSyllabus CUET PG Economics 2024
Syllabus CUET PG Economics 2024
Uploaded by
komalkushwaha1211This document outlines the syllabus for an economics course covering microeconomics, macroeconomics, money and inflation, consumption and investment functions, open economy models, economic growth, statistical and mathematical methods, and the Indian economy. Key topics in microeconomics include consumer theory, production theory, and price determination under different market structures. Macroeconomics covers national income accounting, aggregate demand and supply, and classical and Keynesian theories. The syllabus also addresses monetary policy, consumption and investment functions, open economy models, economic growth models, statistical analysis, mathematical methods, and an overview of the colonial Indian economy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
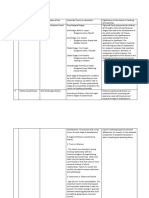
Syllabus for Economics (PGQP44)
Micro Economics:
Consumer Theory or Behaviour: Demand, Utility, Indifference Curve, Revealed Preference
Theory, Consumer Surplus
Production Theory: Production Function, Law of Variable Proportions, Returns to Scale,
Cost Function, types and concepts
Price and Output determination in Market: Perfect and Imperfect Competition
(Monopoly, Price Discrimination, Monopolistic, Duopoly and Oligopoly models) General
Equilibrium, Efficiency and Welfare: Equilibrium and efficiency under pure exchange and
production; overall efficiency and welfare economics, externality
Macro Economics:
National Income Accounting
Income and Output Determination: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply, Effective
Demand Principle, Classical and Keynesian Theory
Money and Inflation:
Demand and Supply of Money, Money Multiplier and High Powered Money, Credit
Creation, Role of Reserve Bank of India and Commercial Banks, Quantitative Theories of
Money, Philip’s Curve
Monetary and Fiscal Policy of India and its role.
Consumption and Investment Function:
Permanent, Relative and Life Cycle Hypothesis, determinants of business fixed
investment; residential investment and inventory investment, Multiplier and Accelerator
Open Economy Models: Mundell and Fleming Model (IS, LM and BP curve) , Balance of
Payments, exchange rate determination, Purchasing Power Parity
Economic Growth: Harrod-Domar Model, Solow Model
Statistical Methods in Economics:
Mean, Mode, Median, Dispersion, Skewness, Quartile Deviation, Average Deviation,
Standard Deviation
Correlation
Simple Regression Model Probability Distribution Sampling
Mathematical Methods in Economics:
Sets and Vector
Functions of one and several real variable Single and Multi variable optimization
Integration of functions
Difference equations
Determinants Matrix
Linear Programming Probability
Differential Equations
Indian Economy:
Overview of colonial economy:
Macro Trends: National Income; population; occupational structure.
Agriculture: Agrarian structure and land relations; agricultural markets and institutions –
credit, commerce and technology; trends in performance and productivity; famines.
Railways and Industry: Railways; the de-industrialisation debate; evolution of
entrepreneurial and industrial structure; nature of industrialisation in the interwar
period; constraints to industrial breakthrough; labour relations.
Economy and State in the Imperial Context
The imperial priorities and the Indian economy; drain of wealth; international trade,
capital
Flows and the colonial economy – changes and continuities; government and fiscal policy.
New Economic Policy:
Public Economics: Public and Private Goods, Externalities, Budget, Deficits, Public Debt,
Fiscal Federalism in India,
Taxation: its economic effects; dead weight loss and distortion, efficiency and equity
considerations, tax incidence, optimal taxation.
International Trade Theories: Adam Smith, Ricardo, Heckscher-Ohlin model and New
Trade Theories
You might also like
- Economics Waec PDFDocument6 pagesEconomics Waec PDFAndrew Tandoh75% (4)
- CUET SyllabusDocument2 pagesCUET SyllabusSravani ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- PGQP56Document2 pagesPGQP56ShubhamJainNo ratings yet
- Coqp10 EconomicsDocument3 pagesCoqp10 EconomicsDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Ecoholics: UGC NET Economics SyllabusDocument15 pagesEcoholics: UGC NET Economics SyllabusFaisal QureshiNo ratings yet
- Economics Coqp10Document3 pagesEconomics Coqp10Yasoda KumariNo ratings yet
- Eco-201 3rd SemeDocument5 pagesEco-201 3rd SemeAtiq ur Rehman QamarNo ratings yet
- IIT JAM Economics SyllabusDocument4 pagesIIT JAM Economics SyllabusAtharvNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument2 pagesEconomicskhajuriaonlineNo ratings yet
- BachelorsDocument74 pagesBachelorsiamsrz07No ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics and MicroeconomicsDocument4 pagesBasic Mathematics and Microeconomicsbilal12941No ratings yet
- Sri Dev Suman Uttarakhand Vishwavidylay, Badshahithaul (Tehri GarhwalDocument9 pagesSri Dev Suman Uttarakhand Vishwavidylay, Badshahithaul (Tehri GarhwalShrey RawatNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Entrance Examination For MA Progamme in Economics-2012Document2 pagesSyllabus For Entrance Examination For MA Progamme in Economics-2012Mahboob HassanNo ratings yet
- Nvs PGT SyllabusDocument2 pagesNvs PGT SyllabusSneha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Slec502 MeDocument3 pagesSlec502 MeIshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- GROUP-10 Statistic and EconomicsDocument3 pagesGROUP-10 Statistic and Economicsmeghaagarg986No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Syllabus 2Document3 pagesMacroeconomics Syllabus 2chhetribharat08No ratings yet
- Ba Eco (Hons.) LuDocument30 pagesBa Eco (Hons.) LuNeha ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Course Information 2013-14 EC1002 Introduction To EconomicsDocument2 pagesCourse Information 2013-14 EC1002 Introduction To EconomicsAngel LillyNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTARY ECONOMICS - 4 Credit Paper: Topic No. of HrsDocument1 pageELEMENTARY ECONOMICS - 4 Credit Paper: Topic No. of HrsDeepti PiplaniNo ratings yet
- Indian Economic Service-Standard and Syllabi: General EnglishDocument6 pagesIndian Economic Service-Standard and Syllabi: General EnglishAman UtpalNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICSDocument6 pagesECONOMICSmudassar bajwaNo ratings yet
- 02 CisDocument2 pages02 CisMuhammad_Khan_6193No ratings yet
- OUCET Economics Syllabus & Exam PatternDocument1 pageOUCET Economics Syllabus & Exam PatternpavaniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Bachelor of Arts (Economics) Batch 2019 OnwardDocument8 pagesSyllabus: Bachelor of Arts (Economics) Batch 2019 OnwardShivani 5019No ratings yet
- Wassce / Waec Economics Syllabus: PreambleDocument7 pagesWassce / Waec Economics Syllabus: PreambleMichael Asante NsiahNo ratings yet
- Pà Áðlpà Gádå G À Áå Àpàgà Cºàðvá Àjãpéë (Pé - Émï)Document8 pagesPà Áðlpà Gádå G À Áå Àpàgà Cºàðvá Àjãpéë (Pé - Émï)naveenNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICSDocument6 pagesECONOMICSsalifu mansarayNo ratings yet
- Documents 08 ECONOMICSDocument2 pagesDocuments 08 ECONOMICSSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Hs 230 Economic Theory: An Introduction (3 0 0 6)Document1 pageHs 230 Economic Theory: An Introduction (3 0 0 6)Sofia JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Waec Syllabus For Economics PDFDocument6 pagesWaec Syllabus For Economics PDFXanderian XavierNo ratings yet
- Em MM 2020 2021Document11 pagesEm MM 2020 2021Deo Dua Nao HetNo ratings yet
- 06 EconomicsDocument6 pages06 EconomicsdrisyanandaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Economics: B. Sc. (Hons) AgricultureDocument30 pagesAgricultural Economics: B. Sc. (Hons) AgricultureMane omprakash50% (2)
- MicrowaveDocument1 pageMicrowavebinatacr438No ratings yet
- Ba EconomicsDocument3 pagesBa EconomicsandostyNo ratings yet
- 2 - Econ - Advanced Economic Theory (Eng)Document1 page2 - Econ - Advanced Economic Theory (Eng)David JackNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For P.G. Entrance in Economics (2020) University of Kashmir, Srinagar (Based On UG Syllabus Operational For Semester System Under CBCS)Document3 pagesSyllabus For P.G. Entrance in Economics (2020) University of Kashmir, Srinagar (Based On UG Syllabus Operational For Semester System Under CBCS)Mirza MuneebNo ratings yet
- SYLLBUSDocument2 pagesSYLLBUSshiv_2506No ratings yet
- Economics Preliminary SyllabusDocument3 pagesEconomics Preliminary Syllabusசுப.தமிழினியன்100% (2)
- MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesMacroeconomicsPramod Pyara ShresthaNo ratings yet
- MA EconomicsDocument2 pagesMA Economicsishika mannaNo ratings yet
- 116 EconomicsDocument2 pages116 EconomicsSuresh mandadiNo ratings yet
- Principles of MacroeconomicsDocument1 pagePrinciples of MacroeconomicsNaziyaa PirzadaNo ratings yet
- Econ 101Document3 pagesEcon 101wuwjpubgNo ratings yet
- Cpa Economics Revision Q&aDocument270 pagesCpa Economics Revision Q&aMercyNo ratings yet
- IIT JAM Economics SyllabusDocument4 pagesIIT JAM Economics Syllabuskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Economics EnglishSET 2019Document3 pagesEconomics EnglishSET 2019Md IstiakNo ratings yet
- Course Information 2013-14 EC1002 Introduction To EconomicsDocument2 pagesCourse Information 2013-14 EC1002 Introduction To Economics27031993No ratings yet
- MA-Economics GC FSDocument42 pagesMA-Economics GC FSTipu SultanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Micro Economics: FOR B.A., LL.B. (HONS.)Document5 pagesSyllabus of Micro Economics: FOR B.A., LL.B. (HONS.)Dakshita DubeyNo ratings yet
- Economics 1Document6 pagesEconomics 1ChiemerieokwuchiNo ratings yet
- Annexure-172. B.com. Programme Ge CoursesDocument4 pagesAnnexure-172. B.com. Programme Ge CoursesANANT AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- 9 EconomicsDocument25 pages9 EconomicsMalsawmkima Maski-aNo ratings yet
- SYBMS SEM III Managerial Economics-IIDocument1 pageSYBMS SEM III Managerial Economics-IISunny Kesarwani0% (1)
- EFM College NotesDocument178 pagesEFM College Notesrahul100% (1)
- ECONOMICSDocument6 pagesECONOMICStamarauebikoloNo ratings yet
- PGT EconomicsDocument3 pagesPGT EconomicsAshish KiroNo ratings yet
- Economics in Micro and Macro Consistency: Challenging Old Biases with New InsightsFrom EverandEconomics in Micro and Macro Consistency: Challenging Old Biases with New InsightsNo ratings yet
- Stresses in SoilDocument37 pagesStresses in SoilRadhaAnanthalekshmiNo ratings yet
- Aplicación Manual DiasysDocument63 pagesAplicación Manual DiasysbetsabevegaaNo ratings yet
- Post-to-Pre Conversion Ufone COPS/CS/SOP/460/12.0: FranchiseDocument5 pagesPost-to-Pre Conversion Ufone COPS/CS/SOP/460/12.0: FranchiseHaseeb ShahidNo ratings yet
- Lignocellulosic Biorefinery: Integrated-Bioethanol and Chemicals Production in Pilot Plant Bioethanol G2Document1 pageLignocellulosic Biorefinery: Integrated-Bioethanol and Chemicals Production in Pilot Plant Bioethanol G2Moery MrtNo ratings yet
- National Security PolicyDocument10 pagesNational Security PolicySagar SantwaniNo ratings yet
- The Nicoll Highway Collapse PDF FreeDocument140 pagesThe Nicoll Highway Collapse PDF FreeJohn WongNo ratings yet
- 2019 Recitation Chap 2 PDFDocument21 pages2019 Recitation Chap 2 PDFGull100% (1)
- Receptionists Competency Standard Booklet Printed PDFDocument19 pagesReceptionists Competency Standard Booklet Printed PDFMicula OanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Recognizing and Using Nouns CompressedDocument16 pagesLesson 1 Recognizing and Using Nouns CompressedJian DeluanaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Plumbing System MACRO 15sep20Document20 pagesWEEK 4 Plumbing System MACRO 15sep20qweqweNo ratings yet
- Catalog GIPPS (March 2023) - EnglishDocument16 pagesCatalog GIPPS (March 2023) - EnglishgbcomsrlNo ratings yet
- QA-QC Inspection Request FormDocument1 pageQA-QC Inspection Request FormShaikh Ubaid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- GenII Main Rotor Sikorsky S76 Pushrod 1.00Document23 pagesGenII Main Rotor Sikorsky S76 Pushrod 1.00agripinaluzmilaaNo ratings yet
- Hiponatremia Acute ApendicitisDocument13 pagesHiponatremia Acute ApendicitisDeliciousNo ratings yet
- PNP PDFDocument41 pagesPNP PDFGulshirin AvediyevaNo ratings yet
- Rock Sheds-Japanese Design Presentation PDFDocument59 pagesRock Sheds-Japanese Design Presentation PDFagugNo ratings yet
- Passive Suppression of Nonlinear Panel Flutter Using Piezoelectric Materials With Resonant CircuitDocument12 pagesPassive Suppression of Nonlinear Panel Flutter Using Piezoelectric Materials With Resonant CircuitYonghui XUNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development - Ichien SomelhigDocument12 pagesTheories of Development - Ichien SomelhigIchien SomelhigNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing-A Tool To Aid Decision MakingDocument54 pagesActivity Based Costing-A Tool To Aid Decision MakingSederiku KabaruzaNo ratings yet
- Emaco Nanocrete R3 - PDS - ASEAN - 241110Document3 pagesEmaco Nanocrete R3 - PDS - ASEAN - 241110Andri AjaNo ratings yet
- SSE 107 Macroeconomics SG 4Document10 pagesSSE 107 Macroeconomics SG 4Aila Erika EgrosNo ratings yet
- Absurdity Incongruity and LaughterDocument24 pagesAbsurdity Incongruity and LaughterMHardt1No ratings yet
- Corporate PPT Template 20Document10 pagesCorporate PPT Template 20Mustafa RahmanNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Case Study: RADULKO Transport: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksDocument30 pagesTroubleshooting Case Study: RADULKO Transport: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksAustin SpillerNo ratings yet
- Dual Tone Multi Frequency SignalingDocument4 pagesDual Tone Multi Frequency Signalingmrana_56No ratings yet
- Topsolid NCSIMUL Interface enDocument2 pagesTopsolid NCSIMUL Interface ennnn765No ratings yet
- High Resolution Video Endoscopy System: Sonoscape Medical CorpDocument4 pagesHigh Resolution Video Endoscopy System: Sonoscape Medical CorpTaha OpedNo ratings yet
- 18300038, Assignment 1, Bus 411Document5 pages18300038, Assignment 1, Bus 411Md RifatNo ratings yet
- Standards and Competency of 5 Years Old ChildrenDocument14 pagesStandards and Competency of 5 Years Old ChildrenFrancis kevin Parre�oNo ratings yet
- The Sargent & Wallace Policy Ineffectiveness Proposition, Lucas CritiqueDocument8 pagesThe Sargent & Wallace Policy Ineffectiveness Proposition, Lucas CritiquehishamsaukNo ratings yet