Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxonomy Sheet 2
Taxonomy Sheet 2
Uploaded by
lettresaccelerer.0eCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ed 4 PHARMACOGNOSY PDFDocument52 pagesEd 4 PHARMACOGNOSY PDFShubham Sabale PatilNo ratings yet
- 10-Kingdom PlantaeDocument67 pages10-Kingdom Plantaemilky waysssNo ratings yet
- Plants ReviewDocument2 pagesPlants ReviewAngi ShenNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Animalia ChuchunessDocument61 pagesKingdom Plantae Animalia Chuchuness639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- Topic 8eDocument18 pagesTopic 8eFa QistinaNo ratings yet
- Plant Evolution: Chapter 22 & 23 Pearson Bio 2012Document53 pagesPlant Evolution: Chapter 22 & 23 Pearson Bio 2012Soulfused 12No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesPlant Kingdom _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Plants&FungiDocument7 pagesPlants&FungiYsabella PolanaNo ratings yet
- Plants FUngi Noted PDFDocument30 pagesPlants FUngi Noted PDFXiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarDocument14 pagesChapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Gymnosperms AngiospermsDocument36 pages1.6 Gymnosperms AngiospermsaixyaehNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms: Evolution of The Seed: ReductionDocument28 pagesGymnosperms: Evolution of The Seed: ReductionКристина ГанищенкоNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Plants - (Students)Document41 pagesUnit 5 - Plants - (Students)ajtorresbritoNo ratings yet
- C 3588945 U283241 s1241689Document23 pagesC 3588945 U283241 s1241689jha.crexa11No ratings yet
- Plant EvolutionDocument50 pagesPlant EvolutionjoyfrangonzagaNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument16 pagesKingdom PlantaeKristianaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes PharmacognosyDocument52 pagesShort Notes PharmacognosyVinay sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1696 FdoDocument6 pages1696 FdoNhlanhla HlátzNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction - Vascular and Non Vascular PlantsDocument26 pagesPlant Reproduction - Vascular and Non Vascular PlantsRachel Jasmine AblanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Characteristics of Major Plant Groups: Answer "Yes" or "No" If Any Group Has The CharacteristicDocument4 pagesSummary of Characteristics of Major Plant Groups: Answer "Yes" or "No" If Any Group Has The CharacteristicBianca PatelNo ratings yet
- GymnospermsDocument48 pagesGymnospermsjane kangNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratoryDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDat HoangNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: AP BiologyDocument19 pagesKingdom Plantae: AP Biology임민수No ratings yet
- Pteridophytes PDFDocument80 pagesPteridophytes PDFJBNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom M PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanNo ratings yet
- Botany Part I Plant OverviewDocument31 pagesBotany Part I Plant Overviewjandy danzalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1Document21 pagesUnit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1PEPE CISERNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Lecture 2 - Reproduction in Flowering Plant PDFDocument36 pagesWeek 6 Lecture 2 - Reproduction in Flowering Plant PDFAndy PikiNo ratings yet
- Core CH 19 BiodiversityDocument8 pagesCore CH 19 Biodiversitystudy.stkgNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Biology Systems in Plants 3Document6 pagesBiology Systems in Plants 3Alyana Grace GuquibNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomArnavNo ratings yet
- The Seed Plants II. Angiosperms: Major Reference: Plant Systematics by Michael Simpson Various UrlsDocument65 pagesThe Seed Plants II. Angiosperms: Major Reference: Plant Systematics by Michael Simpson Various UrlsJBNo ratings yet
- Pollination and Fertilization (18 Files Merged)Document87 pagesPollination and Fertilization (18 Files Merged)salmanazli24No ratings yet
- Bryophytes Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesBryophytes Kingdom PlantaeAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- 11 BryophytesDocument8 pages11 BryophytesAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytes Ferns PDFDocument8 pagesPteridophytes Ferns PDFTamura SangmaNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytes Ferns PDFDocument8 pagesPteridophytes Ferns PDFTamura SangmaNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Nonvascular PDFDocument55 pagesVascular and Nonvascular PDFMiedy Corazon TabangNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- Keys and Classification of The Six KingdomsDocument1 pageKeys and Classification of The Six KingdomsYe' Thi HaNo ratings yet
- MRQ LWCT Note 14Document95 pagesMRQ LWCT Note 14Faris AdityaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Essential QuestionsDocument8 pagesKingdom Plantae: Essential QuestionsKrish D.No ratings yet
- 12.5. Classification of Plants and AnimalsDocument22 pages12.5. Classification of Plants and Animalsjameschileshe55No ratings yet
- Phylum LycophytaDocument1 pagePhylum LycophytaSha EspirituNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant Reproductionamethyst grande100% (1)
- Gametophyte or ProthallusDocument31 pagesGametophyte or Prothallusjha.crexa11No ratings yet
- Fern and Fern Allies 1Document3 pagesFern and Fern Allies 1Paolo TenorioNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 1Document31 pagesPlant Diversity 1anmbeltran31No ratings yet
- 11.5 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom PlantaeDocument34 pages11.5 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom PlantaeMuhammad HusniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1BRYAN TING ZHONG CHENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Biology LessonDocument33 pagesBiology LessonJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Genipa Americana: Rubiaceae LDocument5 pagesGenipa Americana: Rubiaceae LvitazzoNo ratings yet
- English Garden: Landscape ArchitectureDocument31 pagesEnglish Garden: Landscape ArchitectureVernika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- New Tree Training Systems For Custard AppleDocument63 pagesNew Tree Training Systems For Custard AppleBerns ReyesNo ratings yet
- Identification and Morphological Characterization of Pathogens Infecting Melia Dubia in Tamil NaduDocument8 pagesIdentification and Morphological Characterization of Pathogens Infecting Melia Dubia in Tamil NaduSp SarathyNo ratings yet
- Genetic Analysis and Marker Assisted Breeding For DroughtDocument14 pagesGenetic Analysis and Marker Assisted Breeding For DroughtSagini KevinNo ratings yet
- Lab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)Document28 pagesLab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)marcNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy PHD ThesisDocument5 pagesPlant Taxonomy PHD Thesisafcmtzlda100% (2)
- Optimisation of Growth Yield and Quality of Strawberry Cultivars Through Organic Farming M. H. A. RashidDocument9 pagesOptimisation of Growth Yield and Quality of Strawberry Cultivars Through Organic Farming M. H. A. RashidLekhonVlogsNo ratings yet
- Camas WorksheetDocument5 pagesCamas Worksheetapi-510366840No ratings yet
- WeedingDocument38 pagesWeedingVerna Joy EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Cotton An IntroductionDocument6 pagesCotton An IntroductionMukarram Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- The World's Flora and FaunaDocument8 pagesThe World's Flora and Faunakleberviteri120No ratings yet
- Common Orchard TreesDocument11 pagesCommon Orchard TreesChloe Sofia ManaloNo ratings yet
- Types of Cropping SystemsDocument31 pagesTypes of Cropping SystemsRahulNo ratings yet
- 2021 Lee, G.E. & S.R. Gradstein. Guide To The Genera of Liverworts and Hornworts of MalaysiaDocument236 pages2021 Lee, G.E. & S.R. Gradstein. Guide To The Genera of Liverworts and Hornworts of MalaysiaLee Gaik EeNo ratings yet
- Micropropagation A General Method For Commercial BDocument36 pagesMicropropagation A General Method For Commercial BMartin DofNo ratings yet
- Bach Biodynamic Calendar 2014Document35 pagesBach Biodynamic Calendar 2014Tomsondeal100% (1)
- Course Notes - Bryophyte Training Day For RangersDocument13 pagesCourse Notes - Bryophyte Training Day For RangersMartin HindNo ratings yet
- The Tulip. A Symbol of Two Nations PDFDocument83 pagesThe Tulip. A Symbol of Two Nations PDFefevianNo ratings yet
- Plant List On Lot 99 Hickey Street, Iluka NSWDocument5 pagesPlant List On Lot 99 Hickey Street, Iluka NSWclarencegirlNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Vegetable LessonDocument5 pagesFruits and Vegetable LessonRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- Fact File On RainforestsDocument4 pagesFact File On Rainforestsmarzia malhotra100% (1)
- Effect of Concentration Mutagen Sodium Azide (Nan) On Germination and Rice Seed Performance of Upland Rice Varieties Jambek Rotan Generation of M-1Document6 pagesEffect of Concentration Mutagen Sodium Azide (Nan) On Germination and Rice Seed Performance of Upland Rice Varieties Jambek Rotan Generation of M-1Dewi HutaurukNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-1Document4 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-1haadiya aliNo ratings yet
- 17UBOP02 EnglishDocument22 pages17UBOP02 EnglishRaja ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Pramod VermaDocument4 pagesPramod VermaRahul AnandNo ratings yet
- Effect of Seed Drying On Germination Behaviour in CitrusDocument6 pagesEffect of Seed Drying On Germination Behaviour in CitrusPhuwanai PalakachenNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Fill in The BlanksDocument2 pagesAgriculture Fill in The BlanksDaksh bhallaNo ratings yet
- Kit Klehm Finally Have The Garden That You Have Been Dreaming ofDocument3 pagesKit Klehm Finally Have The Garden That You Have Been Dreaming ofkit klehmNo ratings yet
- Adopting Quinoa in Southeastern Idaho - Crop ProtectionDocument6 pagesAdopting Quinoa in Southeastern Idaho - Crop ProtectionCatherine TangNo ratings yet
Taxonomy Sheet 2
Taxonomy Sheet 2
Uploaded by
lettresaccelerer.0eOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxonomy Sheet 2
Taxonomy Sheet 2
Uploaded by
lettresaccelerer.0eCopyright:
Available Formats
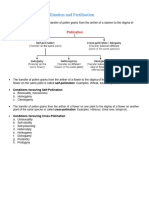
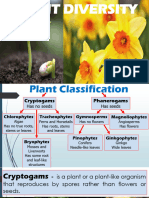
PLANT
CLASSIFICATION
CLADE NAME KEY PHYLA EXAMPLES GENERAL TRAITS KEYWORDS
Gametophyte dominates life cycles
Reduced sporophyte is dependent
on gametophyte for survival
Flagellated sperm
Bryophytes Hornworts, Mosses, Sporophyte consists of seta, foot and Rhizoids anchor gametophytes,
Bryophyta sporangia
(Nonvascular) Liverworts no roots
Majority have no vascular tissue
Majority have minimal vertical
growth
Most exist in moist habitats
Flagellated sperm
Most exist in moist habitats
Most are heterosporous
Independent gametophyte and Roots: structural support and
Club Moss, Quillworts, sporophyte life cycles water absorption
Vascular Plants Lycophyta,
Fern, Horsetail Formed the first forests during the Lignin: helps support vascular
(Seedless) Pterophyta Carboniferous period (ferns) tissue
Vascular tissue (xylem and phloem); Leaves: improved photosynthesis
water and nutrient transport makes
survival in more arid environments
possible
Unprotected seeds
Majority do not have flagellated Pollen: improved fertilization
Fir, Spruce, Aspen, sperm efficiency
Gymnosperms All are heterosporous
Red Wood, Pine, Conifers Seeds: improved dispersal and
Pollen often carried by wind durability
Ovules
Vascular Plants
(With Seeds)
Protected seeds exist in fruit
(ovaries)
Flowering Plants,
Most abundant type of plant
Angiosperms Magnoliophyta
Non-flagellated sperm
Flowers and fruits
Exhibit double fertilization (some
gymnosperms do too)
You might also like
- Ed 4 PHARMACOGNOSY PDFDocument52 pagesEd 4 PHARMACOGNOSY PDFShubham Sabale PatilNo ratings yet
- 10-Kingdom PlantaeDocument67 pages10-Kingdom Plantaemilky waysssNo ratings yet
- Plants ReviewDocument2 pagesPlants ReviewAngi ShenNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Animalia ChuchunessDocument61 pagesKingdom Plantae Animalia Chuchuness639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- Topic 8eDocument18 pagesTopic 8eFa QistinaNo ratings yet
- Plant Evolution: Chapter 22 & 23 Pearson Bio 2012Document53 pagesPlant Evolution: Chapter 22 & 23 Pearson Bio 2012Soulfused 12No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesPlant Kingdom _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Plants&FungiDocument7 pagesPlants&FungiYsabella PolanaNo ratings yet
- Plants FUngi Noted PDFDocument30 pagesPlants FUngi Noted PDFXiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarDocument14 pagesChapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Gymnosperms AngiospermsDocument36 pages1.6 Gymnosperms AngiospermsaixyaehNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms: Evolution of The Seed: ReductionDocument28 pagesGymnosperms: Evolution of The Seed: ReductionКристина ГанищенкоNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Plants - (Students)Document41 pagesUnit 5 - Plants - (Students)ajtorresbritoNo ratings yet
- C 3588945 U283241 s1241689Document23 pagesC 3588945 U283241 s1241689jha.crexa11No ratings yet
- Plant EvolutionDocument50 pagesPlant EvolutionjoyfrangonzagaNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument16 pagesKingdom PlantaeKristianaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes PharmacognosyDocument52 pagesShort Notes PharmacognosyVinay sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1696 FdoDocument6 pages1696 FdoNhlanhla HlátzNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction - Vascular and Non Vascular PlantsDocument26 pagesPlant Reproduction - Vascular and Non Vascular PlantsRachel Jasmine AblanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Characteristics of Major Plant Groups: Answer "Yes" or "No" If Any Group Has The CharacteristicDocument4 pagesSummary of Characteristics of Major Plant Groups: Answer "Yes" or "No" If Any Group Has The CharacteristicBianca PatelNo ratings yet
- GymnospermsDocument48 pagesGymnospermsjane kangNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratoryDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDat HoangNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: AP BiologyDocument19 pagesKingdom Plantae: AP Biology임민수No ratings yet
- Pteridophytes PDFDocument80 pagesPteridophytes PDFJBNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom M PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanNo ratings yet
- Botany Part I Plant OverviewDocument31 pagesBotany Part I Plant Overviewjandy danzalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1Document21 pagesUnit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1PEPE CISERNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Lecture 2 - Reproduction in Flowering Plant PDFDocument36 pagesWeek 6 Lecture 2 - Reproduction in Flowering Plant PDFAndy PikiNo ratings yet
- Core CH 19 BiodiversityDocument8 pagesCore CH 19 Biodiversitystudy.stkgNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Biology Systems in Plants 3Document6 pagesBiology Systems in Plants 3Alyana Grace GuquibNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant KingdomArnavNo ratings yet
- The Seed Plants II. Angiosperms: Major Reference: Plant Systematics by Michael Simpson Various UrlsDocument65 pagesThe Seed Plants II. Angiosperms: Major Reference: Plant Systematics by Michael Simpson Various UrlsJBNo ratings yet
- Pollination and Fertilization (18 Files Merged)Document87 pagesPollination and Fertilization (18 Files Merged)salmanazli24No ratings yet
- Bryophytes Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesBryophytes Kingdom PlantaeAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- 11 BryophytesDocument8 pages11 BryophytesAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytes Ferns PDFDocument8 pagesPteridophytes Ferns PDFTamura SangmaNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytes Ferns PDFDocument8 pagesPteridophytes Ferns PDFTamura SangmaNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Nonvascular PDFDocument55 pagesVascular and Nonvascular PDFMiedy Corazon TabangNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- Keys and Classification of The Six KingdomsDocument1 pageKeys and Classification of The Six KingdomsYe' Thi HaNo ratings yet
- MRQ LWCT Note 14Document95 pagesMRQ LWCT Note 14Faris AdityaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Essential QuestionsDocument8 pagesKingdom Plantae: Essential QuestionsKrish D.No ratings yet
- 12.5. Classification of Plants and AnimalsDocument22 pages12.5. Classification of Plants and Animalsjameschileshe55No ratings yet
- Phylum LycophytaDocument1 pagePhylum LycophytaSha EspirituNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant Reproductionamethyst grande100% (1)
- Gametophyte or ProthallusDocument31 pagesGametophyte or Prothallusjha.crexa11No ratings yet
- Fern and Fern Allies 1Document3 pagesFern and Fern Allies 1Paolo TenorioNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 1Document31 pagesPlant Diversity 1anmbeltran31No ratings yet
- 11.5 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom PlantaeDocument34 pages11.5 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom PlantaeMuhammad HusniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1BRYAN TING ZHONG CHENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Biology LessonDocument33 pagesBiology LessonJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Genipa Americana: Rubiaceae LDocument5 pagesGenipa Americana: Rubiaceae LvitazzoNo ratings yet
- English Garden: Landscape ArchitectureDocument31 pagesEnglish Garden: Landscape ArchitectureVernika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- New Tree Training Systems For Custard AppleDocument63 pagesNew Tree Training Systems For Custard AppleBerns ReyesNo ratings yet
- Identification and Morphological Characterization of Pathogens Infecting Melia Dubia in Tamil NaduDocument8 pagesIdentification and Morphological Characterization of Pathogens Infecting Melia Dubia in Tamil NaduSp SarathyNo ratings yet
- Genetic Analysis and Marker Assisted Breeding For DroughtDocument14 pagesGenetic Analysis and Marker Assisted Breeding For DroughtSagini KevinNo ratings yet
- Lab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)Document28 pagesLab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)marcNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy PHD ThesisDocument5 pagesPlant Taxonomy PHD Thesisafcmtzlda100% (2)
- Optimisation of Growth Yield and Quality of Strawberry Cultivars Through Organic Farming M. H. A. RashidDocument9 pagesOptimisation of Growth Yield and Quality of Strawberry Cultivars Through Organic Farming M. H. A. RashidLekhonVlogsNo ratings yet
- Camas WorksheetDocument5 pagesCamas Worksheetapi-510366840No ratings yet
- WeedingDocument38 pagesWeedingVerna Joy EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Cotton An IntroductionDocument6 pagesCotton An IntroductionMukarram Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- The World's Flora and FaunaDocument8 pagesThe World's Flora and Faunakleberviteri120No ratings yet
- Common Orchard TreesDocument11 pagesCommon Orchard TreesChloe Sofia ManaloNo ratings yet
- Types of Cropping SystemsDocument31 pagesTypes of Cropping SystemsRahulNo ratings yet
- 2021 Lee, G.E. & S.R. Gradstein. Guide To The Genera of Liverworts and Hornworts of MalaysiaDocument236 pages2021 Lee, G.E. & S.R. Gradstein. Guide To The Genera of Liverworts and Hornworts of MalaysiaLee Gaik EeNo ratings yet
- Micropropagation A General Method For Commercial BDocument36 pagesMicropropagation A General Method For Commercial BMartin DofNo ratings yet
- Bach Biodynamic Calendar 2014Document35 pagesBach Biodynamic Calendar 2014Tomsondeal100% (1)
- Course Notes - Bryophyte Training Day For RangersDocument13 pagesCourse Notes - Bryophyte Training Day For RangersMartin HindNo ratings yet
- The Tulip. A Symbol of Two Nations PDFDocument83 pagesThe Tulip. A Symbol of Two Nations PDFefevianNo ratings yet
- Plant List On Lot 99 Hickey Street, Iluka NSWDocument5 pagesPlant List On Lot 99 Hickey Street, Iluka NSWclarencegirlNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Vegetable LessonDocument5 pagesFruits and Vegetable LessonRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- Fact File On RainforestsDocument4 pagesFact File On Rainforestsmarzia malhotra100% (1)
- Effect of Concentration Mutagen Sodium Azide (Nan) On Germination and Rice Seed Performance of Upland Rice Varieties Jambek Rotan Generation of M-1Document6 pagesEffect of Concentration Mutagen Sodium Azide (Nan) On Germination and Rice Seed Performance of Upland Rice Varieties Jambek Rotan Generation of M-1Dewi HutaurukNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-1Document4 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-1haadiya aliNo ratings yet
- 17UBOP02 EnglishDocument22 pages17UBOP02 EnglishRaja ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Pramod VermaDocument4 pagesPramod VermaRahul AnandNo ratings yet
- Effect of Seed Drying On Germination Behaviour in CitrusDocument6 pagesEffect of Seed Drying On Germination Behaviour in CitrusPhuwanai PalakachenNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Fill in The BlanksDocument2 pagesAgriculture Fill in The BlanksDaksh bhallaNo ratings yet
- Kit Klehm Finally Have The Garden That You Have Been Dreaming ofDocument3 pagesKit Klehm Finally Have The Garden That You Have Been Dreaming ofkit klehmNo ratings yet
- Adopting Quinoa in Southeastern Idaho - Crop ProtectionDocument6 pagesAdopting Quinoa in Southeastern Idaho - Crop ProtectionCatherine TangNo ratings yet