Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wave
Wave
Uploaded by
naazarianaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wave
Wave
Uploaded by
naazarianaCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No.B.
s
Aim: To determine the cocfficient of viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring the terminal velocity of
givenspherical body.
a Apparatus used: One meter tall graduated glass-cylinder with stand, lead shots of different sizes, stop watch
and glycerine.
Theory/Formula used: The
coefficient of viscosity of aliquid is given by
2
(p-o)r'g
where
= Terminal velocity of
= Radius of the spherical body
Density of
spherical body
the material of the body
o= Density of the liquid
g =
Procedure:
Acceleration due to gravity
1. First of all place the glass cylinder on
the stand and clamp it.
2 Now fill the glass
glycerine.
cylinder by
Rubber
q Now take a lead shot and
measure
its diameter with the help of screw
Cork
gauge, in two mutually perpendicular
directions as shown in Fig. B-5.2.
4, Drop the first ball no. A,, gently in
Gummed
the liquid. After dropping through a
few centimeters, the ball falls with Paper
uniformn terminal velocity.
5. Start the stop-watch when the ball
gains terminal velocity and note its
position.
6. Stop the stop-watch just when the Glycerine
ball reaches lowest Ball
convenient
division and note its position. Bearings
7. Repeat the step 3 to 6 with other lead
shots.
Fig.B-5.1 Fig. B-5.2
8. Note the temperature of the glycerine with the help of
thermometer.
Observations:
AS Temperature of glycerine, e= . . c
(i) Density of glycerig G= 26...gm/cm3
(iii) Density of(leac) shots, p = .:.5..gm/cm
(tv Pitch of the screw gauge, Cm
Total no. of division of circular scale, N=
(vùr Least count of screw gauge =
P Cm
N .Cm
Practical Manual in Physics--XI 69
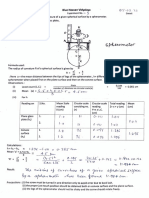
(vi) Table for Radius of Lead shots:
Reading of Serew Gauge
S.No.
Along ah. long cd MeanDlameter Mean radins
(cm")
of Lead Total
C.S.R. Toál Reading d d, - d, d
cm
Ball M.S.R. C.S.R. Reading M.S.R.
y (cm) A, - x t y (em)
x (em) y (cm) x (cm)
y cm (em),
A,
T,=......
A,
T,..........
A,
A,
T.=.....
(vii) Table for Terminal Velocity:
Time taken balle to Terminal Velocity
S. No. of Distance
Lead Ball fallen s (cm) ,cm/sec.
Mean, t= 2
A
A
50tm
A,
A, ...........
A,
Calculations: Plot a graph between terminal velocity (v) and
square of the radius (), by taking r along X-axis and v along Scale :
Y-axis. The graph comes to be a straight line. Y4
X-axis:1 cm = cm?
Y-axis:1 cm = cm²
BC
Slope =
CA
2
-V.
=
**.*poise
Actual value of coefficient of viscosity, n' = ......p.oise
Calculate value of coefficient of viscosity, n =.....p.oise
P (em')
n'-n
oage error = X100 =
Result: n' Fig.B-5.3
() The observed value of coefficient of viscosity n for glycerine
(ii) Percentage error =...... =..........poise
70 Practical Manual in Physics -XI
precautions:
the lead sheots
1 The size of should be smal1.
lead
2 The shots should bedropped gently.
3. The liquid (medium) should be homogeneous.
The liquid should be highly viscous.
c The temperature should be noted.
Source of Error:
1 The liquid may not has uniform density.
The balls may not be perfectly spherical.
You might also like
- Coefficient of Viscosity ,ϰ: ApparatusDocument2 pagesCoefficient of Viscosity ,ϰ: ApparatusSonal WanigasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalsDocument86 pagesPhysics PracticalsGvns Reddy100% (1)
- Technical Guide On Wood& Biomass Pellets ProductionDocument20 pagesTechnical Guide On Wood& Biomass Pellets ProductionLeal Cindy100% (1)
- Physics EXPERIMENTs Term2Document6 pagesPhysics EXPERIMENTs Term2cutuNo ratings yet
- Dynamic MethodDocument4 pagesDynamic MethodMohammad Sahedul MarufNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PhysicsDocument3 pagesExperiment 5 PhysicsKartikNo ratings yet
- Physics Expt 0 - Vernier and Screw GaugeDocument7 pagesPhysics Expt 0 - Vernier and Screw GaugeDebayan MaitiNo ratings yet
- Viscosity 1 PDFDocument6 pagesViscosity 1 PDFAjay Kumar GantiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 21-Oct-2022Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 21-Oct-2022vihaja pathakNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document5 pagesLab 4Tawsif ahmedNo ratings yet
- area and volume f3 2Document13 pagesarea and volume f3 2卓嬋娟No ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum TotalDocument5 pagesThe Simple Pendulum TotalMEXI EVYNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Kinematics ViscosityDocument12 pagesMeasurement of Kinematics ViscosityAngel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3Shubhra Nil DeyNo ratings yet
- EEE - MPE - IPE Lab ManualDocument44 pagesEEE - MPE - IPE Lab Manualfisherman.psychNo ratings yet
- Young's Modulus by Bending of BeamsDocument3 pagesYoung's Modulus by Bending of BeamsAwny Habib100% (1)
- 2022 Exp 4 Compound PendulumDocument2 pages2022 Exp 4 Compound PendulumSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Youngs Modulus 2016Document4 pagesYoungs Modulus 2016Darshan BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Grade 11Document4 pagesExperiment 7 Grade 11Varnit MehraNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument1 pageSimple PendulumASNNo ratings yet
- 2.rigidity ModulusDocument4 pages2.rigidity Modulusmanas100% (1)
- Phy Lab ManualDocument25 pagesPhy Lab ManualSriharshith BalaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ExperimentsDocument25 pagesClass 11 ExperimentsSoham Nag100% (1)
- Expt No 1 Stokes LawDocument3 pagesExpt No 1 Stokes Lawriderrider170No ratings yet
- Determine G by Using Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesDetermine G by Using Simple PendulumMohammad Sahedul MarufNo ratings yet
- X Icse Physics Practicals 2023-2024Document30 pagesX Icse Physics Practicals 2023-2024bhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument4 pagesSolution of TrianglesSiti Najikhah Mohd Isa100% (1)
- PendulumDocument4 pagesPendulumAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 TrigonometryDocument23 pagesChapter 11 TrigonometryHameed KhanNo ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument2 pagesPython BasicsNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Vernier CalliperDocument23 pagesVernier CalliperminecrafygameNo ratings yet
- Sem PRACTICALSDocument14 pagesSem PRACTICALSghanshyam3647.be20No ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 11th 2021-22Document5 pagesEXPERIMENT 11th 2021-22Dolly ParmarNo ratings yet
- Percobaan ViskositasDocument3 pagesPercobaan ViskositasSonia TinambunanNo ratings yet
- Materials RequiredDocument5 pagesMaterials Requiredzeeshan ahmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Physics Lab Manual PDFDocument64 pagesBasic Physics Lab Manual PDFAnkit Singh ChouhanNo ratings yet
- FLYWHEELDocument5 pagesFLYWHEELsarthak MongaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Ballistic PendulumDocument6 pagesLab 5 Ballistic PendulumJaimukeshNo ratings yet
- Bar PendulumDocument4 pagesBar Pendulumvidhiichauhan7No ratings yet
- Screw Guage1Document4 pagesScrew Guage1Shamla PKNo ratings yet
- XIIPhys. HW 2Document1 pageXIIPhys. HW 2Sahil LakhyaniNo ratings yet
- Practical Hand Book 2 2022Document10 pagesPractical Hand Book 2 2022rugaikwad1736No ratings yet
- Final Lab Report For Phy 112 and 110Document28 pagesFinal Lab Report For Phy 112 and 110fireballhunter646No ratings yet
- Trigonometric R Atios & Identities: JEE-MathematicsDocument15 pagesTrigonometric R Atios & Identities: JEE-MathematicsAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Determine The Density & VolumeDocument4 pagesDetermine The Density & Volumeimniloybhattacharjee15No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes Ex 13 7Document11 pagesNcert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes Ex 13 7Pritesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Math P2 1 2022 MarDocument7 pagesMath P2 1 2022 MaryingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Sector and Segment of A Circle - Worksheets PackDocument5 pagesSector and Segment of A Circle - Worksheets PackRAMNo ratings yet
- XIIth Manual 2010Document22 pagesXIIth Manual 2010kiranpatel0100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectParnika Chandala67% (3)
- Mixed Geometry Questions (Angle Facts, Area of A Triangle, Pythagoras' Theorem, Trigonometry, Sine Rule and Cosine Rule, Similarity) 1Document11 pagesMixed Geometry Questions (Angle Facts, Area of A Triangle, Pythagoras' Theorem, Trigonometry, Sine Rule and Cosine Rule, Similarity) 1JonOstiguyNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Simple PendulumDocument2 pagesExp 5 Simple PendulumPriti UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 1 PUC Manual-17Document22 pages1 PUC Manual-17shyla100% (1)
- Screw GaugeDocument6 pagesScrew GaugeSubhajit Das X-E-10No ratings yet
- Compound Angle Workbook 1684260269770Document12 pagesCompound Angle Workbook 1684260269770shlokshukla280300No ratings yet
- Newtons Ring Experiment1Document4 pagesNewtons Ring Experiment1Mahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulumpiyushdua01No ratings yet
- Determine The Viscosity of Water by Poiseuille S Method: Viscosity Is Defined As The Resistance To FlowDocument21 pagesDetermine The Viscosity of Water by Poiseuille S Method: Viscosity Is Defined As The Resistance To FlowDeepraj Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-14 Maintenance BookDocument57 pagesUnit-14 Maintenance Bookrama_subbuNo ratings yet
- Danish Progressive RockDocument26 pagesDanish Progressive RockrpilNo ratings yet
- Luci Hulme Research AnalysisDocument16 pagesLuci Hulme Research Analysisapi-358990183No ratings yet
- Ghirri - Redutores - Classificação - Um-Vs-Rev.20.06.06-Eng3Document35 pagesGhirri - Redutores - Classificação - Um-Vs-Rev.20.06.06-Eng3Jeferson DantasNo ratings yet
- Y8 History 2020Document44 pagesY8 History 2020mahaNo ratings yet
- LOC Taxed Under ITADocument3 pagesLOC Taxed Under ITARizhatul AizatNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design Part I: Road Alignment - Principles & Factors Controlling Road AlignmentDocument10 pagesGeometric Design Part I: Road Alignment - Principles & Factors Controlling Road Alignmentsydney augustNo ratings yet
- Gear Windage: A Review: Carol N. EastwickDocument6 pagesGear Windage: A Review: Carol N. EastwickR Prabhu SekarNo ratings yet
- DrupalDocument344 pagesDrupalMike Nall100% (4)
- Kalaignar Centenary LibraryDocument3 pagesKalaignar Centenary Librarygkavin616No ratings yet
- 8 SWOT Analysis Tools For Small Businesses: 1. SmartsheetDocument3 pages8 SWOT Analysis Tools For Small Businesses: 1. SmartsheetSantu BiswaaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Public and Private InsuranceDocument21 pagesComparative Study Between Public and Private InsuranceNadeemNo ratings yet
- DownloadLecture 10 - Entropy, Clausius InequalityDocument4 pagesDownloadLecture 10 - Entropy, Clausius Inequalityeuglena6No ratings yet
- Cuzco GuideDocument11 pagesCuzco GuideGuillermo Huyhua QuispeNo ratings yet
- A List of Run Commands For Windows 7: Windows Logo Key + RDocument2 pagesA List of Run Commands For Windows 7: Windows Logo Key + RDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On CustomerDocument13 pagesA Project Report On CustomerDrishti BhushanNo ratings yet
- SeptemberDocument119 pagesSeptemberThami KNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm and Lung Ultrasound To Predict Weaning Outcome: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument11 pagesDiaphragm and Lung Ultrasound To Predict Weaning Outcome: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisPablo IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Shared Information ModelDocument16 pagesShared Information Modelrohitchawandke100% (1)
- Problem Set - AlgebraDocument2 pagesProblem Set - AlgebraGela EcalNo ratings yet
- ICF-Ankle Trimalleolar FractureDocument18 pagesICF-Ankle Trimalleolar FracturedvenumohanNo ratings yet
- Bismillah - I Am A Muslim Nasheed Lyrics (Aasiah)Document1 pageBismillah - I Am A Muslim Nasheed Lyrics (Aasiah)begum121100% (1)
- Fenomenele Postvulcanice Utóvulkáni Mûködések Post Volcanic PhenomenaDocument1 pageFenomenele Postvulcanice Utóvulkáni Mûködések Post Volcanic PhenomenaCosmin FlorinNo ratings yet
- J. P7327 - Apdx A (SCH Daywork Rate) (28 Mar 2012)Document4 pagesJ. P7327 - Apdx A (SCH Daywork Rate) (28 Mar 2012)MRSA Engineering ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Theory of Metal Cutting Q&A For StudentDocument8 pages2.1 Theory of Metal Cutting Q&A For Studentnikhilbatham0% (1)
- 13IPST068 Fabian PerezDocument7 pages13IPST068 Fabian Perezquisi123No ratings yet
- CL3600-2023-Lecture 4-Cell Growth KineticsDocument62 pagesCL3600-2023-Lecture 4-Cell Growth KineticsJodie BakerNo ratings yet
- QuadriplegiaDocument11 pagesQuadriplegiaDr. Vinod GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Object-Oriented Database ModelDocument9 pagesChapter 5 - Object-Oriented Database Modelyoseffisseha12No ratings yet