Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 viewsInfectious Document
Infectious Document
Uploaded by
Mohan SrinivasThis document summarizes and compares information about several bacterial diseases: typhoid fever, Q-fever, brucellosis, typhus, yersiniosis, and listeriosis. It outlines the etiology, source of infection, transmission, incubation period, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention for each disease. The diseases are caused by different bacteria and affect humans and animals through various modes of transmission, including direct contact, food/water contamination, and vectors. Symptoms vary but often include fever, weakness and gastrointestinal or respiratory issues. Diagnosis involves tests like culture, ELISA and PCR. Treatment generally involves antibiotics like doxycycline and prevention focuses on sanitation and food safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Prognosis and Discharge PlanDocument6 pagesPrognosis and Discharge Planjanelee2824No ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Dwi YuliaDocument10 pagesDaftar Pustaka Dwi YuliaGaluh AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- All Therapy 200 RATOS 2010Document284 pagesAll Therapy 200 RATOS 2010Bhargavi SunkiNo ratings yet
- Pleomorphic Adenoma AmeloblastomaDocument65 pagesPleomorphic Adenoma AmeloblastomaWilliam Tan CebrianNo ratings yet
- Topics For CA. (Yu)Document6 pagesTopics For CA. (Yu)Charlotte CorderoNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases RuminantDocument34 pagesViral Diseases RuminantNorwood Everett DaduloNo ratings yet
- Capsu Foot and Mouth Disease FMDDocument18 pagesCapsu Foot and Mouth Disease FMDmaun04No ratings yet
- Mindmaps of Human Health and Diseases - 10215057 - 2022 - 09 - 26 - 12 - 20Document4 pagesMindmaps of Human Health and Diseases - 10215057 - 2022 - 09 - 26 - 12 - 20trishasingh8970No ratings yet
- Final Coaching VMCB - VPHDocument73 pagesFinal Coaching VMCB - VPHKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis and CestodesDocument4 pagesTuberculosis and CestodesRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Cattle Diseases and ParasitesDocument6 pagesCattle Diseases and ParasitesNorman Rodriguez LlorandoNo ratings yet
- Mosby Chap. 18.2,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26Document567 pagesMosby Chap. 18.2,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26rizaNo ratings yet
- Both Young and Old RBC Young RBC Young RBC Old RBC: Rizal ST., Albay Dist., Legazpi CityDocument3 pagesBoth Young and Old RBC Young RBC Young RBC Old RBC: Rizal ST., Albay Dist., Legazpi CityAbegail ListancoNo ratings yet
- Common DiseaseDocument7 pagesCommon Diseaseqmr4hq8t5pNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis FDocument1 pageLeptospirosis FKeto PrehranaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous DiseasesDocument5 pagesMiscellaneous DiseasesengrdavedespabiladerasNo ratings yet
- Community in Tables AllTalabaDocument14 pagesCommunity in Tables AllTalabaAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Tropical Fevers Table Case 2 by Rahaf AlzoubiDocument1 pageTropical Fevers Table Case 2 by Rahaf AlzoubiR. nounNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Insectborne DiseaseDocument5 pagesInsectborne DiseaseengrdavedespabiladerasNo ratings yet
- 1.12. Transmisi Virus Dan Bakteri Dari BinatangDocument43 pages1.12. Transmisi Virus Dan Bakteri Dari BinatangsyiqaNo ratings yet
- Paramyxo PPRDocument14 pagesParamyxo PPRstraihan234No ratings yet
- 8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)Document55 pages8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)ssatechies62No ratings yet
- ParvoviridaeDocument22 pagesParvoviridaeSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- DIPTHERIADocument1 pageDIPTHERIAGrace StephanieNo ratings yet
- ArbovirusesDocument4 pagesArbovirusesማላያላም ማላያላምNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalDocument21 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalPatricia CabisonNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides GEO Dist: HabitatDocument3 pagesIntestinal Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides GEO Dist: HabitatMegat Muhammad Syarif HamdaniNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerElla Mae SadiuaNo ratings yet
- High Prevalence and Diversity of Zoonotic and Other Intestinal Parasites in Dogs From Eastern SpainDocument8 pagesHigh Prevalence and Diversity of Zoonotic and Other Intestinal Parasites in Dogs From Eastern SpainKuyinNo ratings yet
- MedicineDocument82 pagesMedicineDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NRSGDocument63 pagesCommunicable Disease NRSGValeryn QuimanNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806No ratings yet
- Para Lec TransesDocument5 pagesPara Lec Transeslewistulio004No ratings yet
- Final - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsDocument5 pagesFinal - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsVijay JadhavNo ratings yet
- CYRUSSDocument13 pagesCYRUSSRienna Marie HentoloroNo ratings yet
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Farm Animal DiseasesDocument15 pagesGrade 8 Farm Animal DiseasesbelleNo ratings yet
- Cestodes SummaryDocument6 pagesCestodes SummaryabigailNo ratings yet
- Notes - Sporozoa PDFDocument15 pagesNotes - Sporozoa PDFJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- CDN2Document68 pagesCDN2Hanna BaddiriNo ratings yet
- Mt639 Unit 1 For Quiz Doc YoloDocument7 pagesMt639 Unit 1 For Quiz Doc YoloJorelle NogoyNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 Variole MamifereDocument25 pagesCurs 3 Variole MamifereAlejandro XandirNo ratings yet
- Para LabDocument22 pagesPara LabClaudine DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesDocument4 pagesReviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesGeriel QuidesNo ratings yet
- ANCYLOSTOMATIDAEDocument6 pagesANCYLOSTOMATIDAEPhobos DeimosNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases TableKavya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Strangles: Distemper, Infectious Adenitis Strept ThroatDocument21 pagesStrangles: Distemper, Infectious Adenitis Strept ThroatMuhammad Hamza AlviNo ratings yet
- ParamyxoviridaeDocument54 pagesParamyxoviridaeA UllahNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic DiseasesDocument64 pagesZoonotic Diseasesselulekontshangase31No ratings yet
- Up To Date: Mode of Action of The Main Anti-Parasitic DrugsDocument13 pagesUp To Date: Mode of Action of The Main Anti-Parasitic DrugsPeter MjeeNo ratings yet
- Agata Infectious DiseasesDocument34 pagesAgata Infectious DiseasesMartaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease NotesDocument19 pagesInfectious Disease Notesshwetlana rampureNo ratings yet
- Large Ruminant DiseasesDocument96 pagesLarge Ruminant DiseasesJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- Pathologic and NonDocument11 pagesPathologic and NonAisha DoreenNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument10 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMarisol DizonNo ratings yet
- 9 - Additional Notes For NematodesDocument1 page9 - Additional Notes For NematodesRich NyleNo ratings yet
- Cestodes Worksheet No. 1Document5 pagesCestodes Worksheet No. 1Denika AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesHealth and Diseasereet.patidar18No ratings yet
- DNA VIRUSES-handout PDFDocument11 pagesDNA VIRUSES-handout PDFROTHESSA MARY CARINGALNo ratings yet
- Zoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKDocument64 pagesZoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKakun internetNo ratings yet
- Xii Zoology Human Health and Diseases Jinush HssliveDocument4 pagesXii Zoology Human Health and Diseases Jinush HssliveADWAITH LALUNo ratings yet
- V9N5P239Document4 pagesV9N5P239Phạm Hồng SáuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)Document4 pagesNursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)jay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- CDDocument6 pagesCDMei JoyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Jaundice in The Hospitalized Patient PDFDocument16 pagesAssessment of Jaundice in The Hospitalized Patient PDFlaura canoNo ratings yet
- Liver TransplantDocument16 pagesLiver TransplantNephrology On-DemandNo ratings yet
- Hertspo2015 ProgramDocument16 pagesHertspo2015 ProgramΟδυσσεας ΚοψιδαςNo ratings yet
- VirologyLearnTable 2017-Sketchy PDFDocument4 pagesVirologyLearnTable 2017-Sketchy PDFdfgbdfgNo ratings yet
- HC2017 - New Drugs Approved by Health Canada in 2017Document2 pagesHC2017 - New Drugs Approved by Health Canada in 2017BhushanNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion: DR Vishwabharathi TDocument28 pagesBlood Transfusion: DR Vishwabharathi TSuma0% (1)
- Coc 2022 Reviewed Q & ADocument74 pagesCoc 2022 Reviewed Q & ASneeze LouderNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin Key ConceptDocument7 pagesHepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin Key ConceptMai Hoàng Dương QuangNo ratings yet
- 03 NCP 1 Viral HepatitisDocument17 pages03 NCP 1 Viral Hepatitisamit100% (2)
- Asymptomatic TransaminitisDocument2 pagesAsymptomatic TransaminitisrieseNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2213429Document11 pagesNejmoa 2213429Niramol WeerasunthornNo ratings yet
- 30 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Common Unit Conversions - Commonly Measured Laboratory Values - Abbreviations - IndexDocument28 pages30 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Common Unit Conversions - Commonly Measured Laboratory Values - Abbreviations - IndexRazrin RazakNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics PG Exam PapersDocument39 pagesPediatrics PG Exam Paperscooldude_secbad1712100% (1)
- Viral Misconceptions by Jeff Green TranscriptionDocument13 pagesViral Misconceptions by Jeff Green TranscriptionGlista100% (1)
- Michael Fraser BookletDocument5 pagesMichael Fraser BookletRushika PurohitNo ratings yet
- Kle University: Jawaharlal Nehru Medical CollegeDocument16 pagesKle University: Jawaharlal Nehru Medical Collegesujan maharjanNo ratings yet
- Who Expert Committee On Biological Standardization: Fifty-Fifth ReportDocument146 pagesWho Expert Committee On Biological Standardization: Fifty-Fifth ReportEsteban FiumaraNo ratings yet
- DHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtDocument49 pagesDHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtNatasha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Immunization - Dr. SarahDocument14 pagesImmunization - Dr. Sarahf6bk6xnppyNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument30 pagesLiverNisini ImanyaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination of Healthcare WorkersDocument16 pagesVaccination of Healthcare WorkersBenjamin RuotiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Pregnant Women Towards Hepatitis B InfectionDocument11 pagesAssessment of The Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Pregnant Women Towards Hepatitis B InfectionbamcobgyneNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Hbsag With Decrease in Viral Load With Herbal Formulation, Hd-03/Es: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesReduction of Hbsag With Decrease in Viral Load With Herbal Formulation, Hd-03/Es: A Case Studynaveen palNo ratings yet
- Pemberian Obat Pada Kelainan Fungsi HeparDocument21 pagesPemberian Obat Pada Kelainan Fungsi Heparari rujatiNo ratings yet
Infectious Document
Infectious Document
Uploaded by
Mohan Srinivas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views8 pagesThis document summarizes and compares information about several bacterial diseases: typhoid fever, Q-fever, brucellosis, typhus, yersiniosis, and listeriosis. It outlines the etiology, source of infection, transmission, incubation period, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention for each disease. The diseases are caused by different bacteria and affect humans and animals through various modes of transmission, including direct contact, food/water contamination, and vectors. Symptoms vary but often include fever, weakness and gastrointestinal or respiratory issues. Diagnosis involves tests like culture, ELISA and PCR. Treatment generally involves antibiotics like doxycycline and prevention focuses on sanitation and food safety.
Original Description:
Ddx of infectious agents
Original Title
Infectious document
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes and compares information about several bacterial diseases: typhoid fever, Q-fever, brucellosis, typhus, yersiniosis, and listeriosis. It outlines the etiology, source of infection, transmission, incubation period, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention for each disease. The diseases are caused by different bacteria and affect humans and animals through various modes of transmission, including direct contact, food/water contamination, and vectors. Symptoms vary but often include fever, weakness and gastrointestinal or respiratory issues. Diagnosis involves tests like culture, ELISA and PCR. Treatment generally involves antibiotics like doxycycline and prevention focuses on sanitation and food safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views8 pagesInfectious Document
Infectious Document
Uploaded by
Mohan SrinivasThis document summarizes and compares information about several bacterial diseases: typhoid fever, Q-fever, brucellosis, typhus, yersiniosis, and listeriosis. It outlines the etiology, source of infection, transmission, incubation period, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention for each disease. The diseases are caused by different bacteria and affect humans and animals through various modes of transmission, including direct contact, food/water contamination, and vectors. Symptoms vary but often include fever, weakness and gastrointestinal or respiratory issues. Diagnosis involves tests like culture, ELISA and PCR. Treatment generally involves antibiotics like doxycycline and prevention focuses on sanitation and food safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
TITLE TYPHOID FEVER Q-FEVER BRUCELLOSIS
ETIOL Salmonella enterica Coxiella burnetti Brucella is
OGY serotype typhi and zooontdisease
salmonella enterica
serotype paratyphi
SOUR -Person to person -Cattle,sheeps and goats -In ruminants (brucella
CE OF contact -Raw milk melitensis),In cattle
INFEC -Contaminated food (brucella
TION and water abortus),brucells in pigs
(brucella suis),brucella
canis for dogs
TRANS Fecal-oral -Direct infection -Sick animals,meat,milk
MISSI -vector transmission
ON
INCUB 5-30 days (most -Acute=2-6 weeks -From 2-4 weeks
ATION commonly 7-14 days) -Chronic=months to years
PERIO
D
SYMP -Week 1 =rise in -Acute=Flu-like -Acute/subacute=
TOMS temperature,bradyca symptoms(fever,chills,malaise,myalgia,hea Fever,chiills,sweating(
rdia,headache,consti dache,photopphobia,rhinitis,laryngitis,phar more at
pation or diarrhea yngitis),Atypical pneumonia,hepatitis night),osteoartciular,po
-Week 2=Persistent -Chronic=low-grade fever,night lyarthroneuromyalgia,li
fever,Rose-coloured sweats,weight loss,sweeling,Endocarditis mitation of movements
spots,typhoid of affected
tongue(greyish- joints,weaknesss
yellow -Chronic=
tongue),yellow-green Sufebrile
diarrhea temperature,weakness,
-Week limitation of
3=hepatosplenomeg movements,neurobruc
aly,git bleeding ellosis
DIAG Anemia,leukopenia -Serology -elisa
NOSIS or -PCR -pcr
leukocytosis,eosinop -Liver test -wright reaction
enia,lymphocytosis,a -Isolation of culture of
bnormal liver brucella
function test,bllod
cultures,
TREAT -Fluroquinoloes -Acute -First line=Doxycycline
MENT (ciprofloxacin) First=Doxycycline and rifampin
-Azithromycin Second=azithromycin
-Severe =third- -Chronic=Doxycycline and
generation hydroxychloroquine
cephalosporins(ceftri
axone)
PREV Food,vaccines Avoid unpasteurized milk products Be careful with animals
TITLE TYPHUS YERSINOSIS LISTERIOS
IS
ETIOLOGY -Endemic typhus:-ricketsia typhi (8-16 days) -yersinia entercolitica It is caused
-Epidemic typhus is caused by:-ricketsia -yersinia by listeria
prowazekii pseudotuberculosis monocytoge
-Scrub typhus is caused by orientia nes
tsutsugamush (7-10)days
SOURCE Rats and cats Dogs,pigs,rodents,milk,un -Animals
OF dercooked (domestic
INFECTION and wild),
birds, fish,
insects and
ticks
TRANSMIS Through vector Food-bourne inhalation of
SION -contaminated waters dust
-animals contaminate
d with the
pathogen,
intrauterine
transmission
of the
pathogen
through the
placenta or
by contact of
the newborn
INCUBATIO Endemic typhi (8-16) days 1-14 days on average 3-7 The
N PERIOD -Scrub typhus (7-10) days days incubation
period
usually lasts
one to two
weeks, but
can vary
from a few
days up to
90 days
SYMPTOM Fever,headache,malaise,bradycardia,noescha - Abdominal pain, nausea, - increase in
S r,maculopapular rash on trunks vomiting, general body
weakness, decreased temperature
ability to work, muscle ,
pain, fever, chills, headache,
diarrhea, joint pain, rash general
on the palms and soles weakness,
lack of
appetite,
pain in
bones,
muscles,
tendons,
joints, etc
DIAGNOSIS Positive weil-felix test,immunoflorescence -Cbc -cbc
-urine analysis -elisa
-elisa -pcr
-bacteriological culture -
-pcr
TREATMEN Doxycycline / chloramphenicol -Trimethoprim-
T sulfamethazole -First
-Fluroquinoles line=ampicilli
(ciprofloxacin) n
-Second-
line=azithro
mycin
PREVENTIO vaccinations -It is necessary to beware It is
N of eating raw or necessary to
undercooked dairy and beware of
meat products, as well as eating raw
unwashed and rotting or
vegetables, and keep raw undercooke
meat separate from ready- d dairy and
to-eat culinary products. meat
Remember that Listeria is products, as
able to multiply at well as
temperatures from 1 to 45 unwashed
*C and rotting
vegetables,
and keep
raw meat
separate
from ready-
to-eat
culinary
products.
Remember
that Listeria
is able to
multiply at
temperature
s from 1 to
45 * C.-
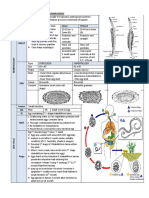
TITLE LEPTOSPIROSIS TOXOPLASMOSIS LEISHMANIASIS
ETIOLOGY Leptospra interrogans Toxoplasma gondii Leishmania donovani
SOURCE OF Soil,food,water,urine of Animals,unpasteurized Animals like
INFECTION animals milk,blood transfusion dogs,rodents,humans
TRANSMISSIO Contact with animals -Oral ingestion -Vector=sandflies
N -cat feces -Reservoir=mammals
-raw meat
-Transplacental transmission
INCUBATION 2-30 days 5 days to 3 weeks -Cutaneous can vary
-Visceral 2-6 months
SYMPTOMS -Mild=high -Mainly asymptomatic -Cutaneous=reddish
fever,headache,conjuctival -Symptomatic=bilateral macules with central
effusion,photophobia cervical ulceration
-Severe=fever,hepatitis,aki adenopathy,encephalitis,vis -Mucosal (mucosal
ual imapirment bleeding,nasal
blocakage)
DIAGNOSIS -urine and blood samples -Serology(igM,igG) -
-serological -PCR Microscopy=macrophag
tests(igM,microscopic -Ct/mri es having amastigotes
agglutination test) -Pcr
-pcr -Culture
-cbc
Kidney function test
-liver function test
TREATMENT - Pyrimethamine and Amphotericin b
Mild=doxycycline,azithromyc sulfadiazine and leucovorin
in
-Severe=3 gen
cephalosporins
PREVENTION Vaccination,pest control Avoid contact with Cover your skin,apply
garden ,avoid untreated insect repellent mosepel
water
TITLE SALMONELLOSIS SHIGELLOSIS CHOLERA
ETIOLOGY -salmonella enteric serotype -Bacillary Vibrio cholera
enteritidis dysentery=Shigella
-salmonella enterica serotype dysentriae
typhimurium
-salmonella enteric serotype
heidelberg
SOURCE OF -Poultry,raw eggs,milk,turtles,snakes Food and water Undercooked
INFECTION seafood
TRANSMISSION -food-bourne -fecal-oral route -fecal-oral
-reptiles -sexual contact
INCUBATION 0-3 days 0-2 0-2 days
PERIOD
SYMPTOMS -Fever which resolves in 2 -Last till 7 days -Low grade
days,myalgia,headache,chills,vomiting, -high fever fever,vomiting,rice-
abdominal pain,bloody diarrhea -tenesmus and water stools
bloody diarrhea
DIAGNOSIS -Stool analysis -Stool analysis -Stool culture
-Fluid analysis -pcr -dipstick
TREATMENT -Supportive treatment (bland -Supportive -Symptomatic
diet,oral-rehydration therapy) treatment treatment (fluids for
-AB for 7-10 days -ab therapy dehydration and
Ciprofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin or hypovolemia
trimethoprim/sulfamethaxazole azithromycin -doxyxycyline or
azithromycin
PREVENTION No vaccines available Personal hygiene Use proper water
TITLE BOTULINUM TOXINS CRYTOSPORID ENTEROVIRUSES
IOSIS
ETIOLOGY CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM Crytosporidium Norovirus,rotavirus,adenovirus(adenivir
-c.hominis idae,adenoviridae)
-c.parvum
-c.meleagridis
SOURCES Honey,juice,sand,food,can -Contaminated -vomiting
OF ned foods water
INFECTIO
N
TRANSMIS Food-bourne,wound -contact with Norvirus=fecal-oral route
SION animals and
already sick
person
INCUBATI -food-bourne (12-36) 5-7 days Norvirus=0-2 days
ON -infant (days to 4 weeks) Rotavirus=1-3 days
PERIOD -wound (10 days) Adenovirus =4-5 days
SYMPTOM - -chronic watery -fever,malaise,abdominal
S dysarhthria,diplopia,dysph diarrhea,nausea,a pain,vomiting,watery diarrhea mild to
agia,dyspnea bdominal pain severe dehydration
-adeno=febrile
pharyngitis,gastroenteritis,myocarditis,
conjunctivitis
DIAGNOSI -stool -stool analysis -elisa
S -serum -pcr
-vomit
TREATME -Horse derived botulism -symtomatic=oral -Supportive treatment(fluid,electrolyte)
NT antitoxins and antimotility -iv fluid resuscitation
-Removing toxins through agrnts
medication from bowel -antiparasitic
(nitazoxanide)
PREVENTI Boil food,iv drug avoid Personal hygene vaccines
ON
TITLE AMEBIC DYSENTRY HEPATITS A HEPATITS B
ETIOLOGY Entamoeba histolytica Hepatotropic hepatitis a virus Hepatitis b virus
SOURCE OF Sexual contact, water, sometimes The source of infection is a
INFECTION contact,contaminated alimentary person
food and waterand
endemic regions
travelling
TRANSMISSIO Fecal-oral fecal-oral parenteral, sexual, from
N mother to baby.
SYMPTOMS Loose stools with -Prodomal= -Prodomal=
mucous and bright red . Flu-like variant (fever, 1. Arthralgic variant (joint
blood,tenesmus,weigh catarrhal syndrome) pain) • 2. Dyspeptic variant
t lossabdominal pain • 2. Dyspeptic variant (nausea, vomiting,
(nausea, vomiting, decreased decreased or lack of
or lack of appetite, appetite, sometimes – loose
sometimes – loose stools) • 3.
-peak(icteric phase) Asthenovegetative variant
The feature of viral hepatitis (weakness, dizziness, sleep
A is that the patient's disturbance) • 4. Mixed
condition improves (this is variant
important!!!!): nausea is less, -Peak(icteric phase)
vomiting stops, the Jaundice appears,
temperature normalizes. • sometimes pronounced •
But • Jaundice appears • Darkening of urine • Aholic
Darkening of urine • Aholic stool • Hepatomegaly,
stool • Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly • Symptoms
sometimes splenomegaly of hepatic intoxication
(pronounced weakness,
adynamia, dizziness, lack of
appetite, nausea, vomiting,
irritability, poor sleep at
night, drowsiness during the
day) • In severe cases –
hemorrhagic syndrome
(nasal, gingival bleeding,
hemorrhages at injection
sites etc
INCUBATION 1-4 weeks 14 – 50 days 60-120 days
PERIOD
DIAGNOSIS -Stool analysis -elisa(igM) -biochemical (increased
-elisa -pcr(hepatitis a virus rna) alt,ast)
-pcr -biochemical (increased -
-colonoscopy alt,ast) cbc=leucopenia,lymphocyte
- s
cbc=leucopenia,lymphocytosi - biochemical (increased
s alt,ast)
-Elisa (hbsAG and hbeAG
=positive)
-pcr (hepatitis b virus dna
found)
TREATMENT -Symtomatic Diet No. 5, bed rest • Copious - Diet No. 5, bed rest •
=metronidazole then drinking • Detoxification Copious drinking •
luminal agents therapy (intravenous Detoxification therapy
(paramomycin) infusions - glucose solution, (intravenous infusions -
saline solution) glucose solution, saline
solution
PREVENTION Food and water Vaccination • Hygiene Vaccination • Anti-epidemic
hygiene measures measures
TITLE HEPATITIS C HEPATITIS D HEPATITIS E
ETIOLOGY Hepatituc c virus Hepatitis d Hepatitis e
SOURCE OF INFECTION The source of infection Broken skin,blood -Humans and animals
is a person products contact -water and food
TRANSMISSION - parenteral, sexual Sexual.parenteral.perinatal Fecal-oral
INCUBATION PERIOD 2 weeks to 6 months -Coinfection=1-6 months 2-8 weeks
-Superinfection=2-8 weeks
SYMPTOMS Its symptoms are -Similar to acute hbv Similar to hepatitis a
similar as hepatitis b infection
DIAGNOSIS -Elisa(anti-hcv igM -elisa -Self-remiting
=positive),antihcv igG -pcr Labs are same as
positive hepatitis a
-Pcr (detection of -ELISA
hepatitis c virus rna) -pcr
TREATMENT Antiviral Pegylated interferon alpha Supportive care
agents=sofosbuvir and
velpatasvir
PRECAUTIONS Educate and screening Lifestyle modification No vaccines available
keeping hygiene in mind
You might also like
- Prognosis and Discharge PlanDocument6 pagesPrognosis and Discharge Planjanelee2824No ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Dwi YuliaDocument10 pagesDaftar Pustaka Dwi YuliaGaluh AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- All Therapy 200 RATOS 2010Document284 pagesAll Therapy 200 RATOS 2010Bhargavi SunkiNo ratings yet
- Pleomorphic Adenoma AmeloblastomaDocument65 pagesPleomorphic Adenoma AmeloblastomaWilliam Tan CebrianNo ratings yet
- Topics For CA. (Yu)Document6 pagesTopics For CA. (Yu)Charlotte CorderoNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases RuminantDocument34 pagesViral Diseases RuminantNorwood Everett DaduloNo ratings yet
- Capsu Foot and Mouth Disease FMDDocument18 pagesCapsu Foot and Mouth Disease FMDmaun04No ratings yet
- Mindmaps of Human Health and Diseases - 10215057 - 2022 - 09 - 26 - 12 - 20Document4 pagesMindmaps of Human Health and Diseases - 10215057 - 2022 - 09 - 26 - 12 - 20trishasingh8970No ratings yet
- Final Coaching VMCB - VPHDocument73 pagesFinal Coaching VMCB - VPHKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis and CestodesDocument4 pagesTuberculosis and CestodesRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Cattle Diseases and ParasitesDocument6 pagesCattle Diseases and ParasitesNorman Rodriguez LlorandoNo ratings yet
- Mosby Chap. 18.2,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26Document567 pagesMosby Chap. 18.2,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26rizaNo ratings yet
- Both Young and Old RBC Young RBC Young RBC Old RBC: Rizal ST., Albay Dist., Legazpi CityDocument3 pagesBoth Young and Old RBC Young RBC Young RBC Old RBC: Rizal ST., Albay Dist., Legazpi CityAbegail ListancoNo ratings yet
- Common DiseaseDocument7 pagesCommon Diseaseqmr4hq8t5pNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis FDocument1 pageLeptospirosis FKeto PrehranaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous DiseasesDocument5 pagesMiscellaneous DiseasesengrdavedespabiladerasNo ratings yet
- Community in Tables AllTalabaDocument14 pagesCommunity in Tables AllTalabaAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Tropical Fevers Table Case 2 by Rahaf AlzoubiDocument1 pageTropical Fevers Table Case 2 by Rahaf AlzoubiR. nounNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Insectborne DiseaseDocument5 pagesInsectborne DiseaseengrdavedespabiladerasNo ratings yet
- 1.12. Transmisi Virus Dan Bakteri Dari BinatangDocument43 pages1.12. Transmisi Virus Dan Bakteri Dari BinatangsyiqaNo ratings yet
- Paramyxo PPRDocument14 pagesParamyxo PPRstraihan234No ratings yet
- 8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)Document55 pages8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)ssatechies62No ratings yet
- ParvoviridaeDocument22 pagesParvoviridaeSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- DIPTHERIADocument1 pageDIPTHERIAGrace StephanieNo ratings yet
- ArbovirusesDocument4 pagesArbovirusesማላያላም ማላያላምNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalDocument21 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalPatricia CabisonNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides GEO Dist: HabitatDocument3 pagesIntestinal Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides GEO Dist: HabitatMegat Muhammad Syarif HamdaniNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerElla Mae SadiuaNo ratings yet
- High Prevalence and Diversity of Zoonotic and Other Intestinal Parasites in Dogs From Eastern SpainDocument8 pagesHigh Prevalence and Diversity of Zoonotic and Other Intestinal Parasites in Dogs From Eastern SpainKuyinNo ratings yet
- MedicineDocument82 pagesMedicineDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NRSGDocument63 pagesCommunicable Disease NRSGValeryn QuimanNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806No ratings yet
- Para Lec TransesDocument5 pagesPara Lec Transeslewistulio004No ratings yet
- Final - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsDocument5 pagesFinal - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsVijay JadhavNo ratings yet
- CYRUSSDocument13 pagesCYRUSSRienna Marie HentoloroNo ratings yet
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Farm Animal DiseasesDocument15 pagesGrade 8 Farm Animal DiseasesbelleNo ratings yet
- Cestodes SummaryDocument6 pagesCestodes SummaryabigailNo ratings yet
- Notes - Sporozoa PDFDocument15 pagesNotes - Sporozoa PDFJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- CDN2Document68 pagesCDN2Hanna BaddiriNo ratings yet
- Mt639 Unit 1 For Quiz Doc YoloDocument7 pagesMt639 Unit 1 For Quiz Doc YoloJorelle NogoyNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 Variole MamifereDocument25 pagesCurs 3 Variole MamifereAlejandro XandirNo ratings yet
- Para LabDocument22 pagesPara LabClaudine DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesDocument4 pagesReviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesGeriel QuidesNo ratings yet
- ANCYLOSTOMATIDAEDocument6 pagesANCYLOSTOMATIDAEPhobos DeimosNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases TableKavya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Strangles: Distemper, Infectious Adenitis Strept ThroatDocument21 pagesStrangles: Distemper, Infectious Adenitis Strept ThroatMuhammad Hamza AlviNo ratings yet
- ParamyxoviridaeDocument54 pagesParamyxoviridaeA UllahNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic DiseasesDocument64 pagesZoonotic Diseasesselulekontshangase31No ratings yet
- Up To Date: Mode of Action of The Main Anti-Parasitic DrugsDocument13 pagesUp To Date: Mode of Action of The Main Anti-Parasitic DrugsPeter MjeeNo ratings yet
- Agata Infectious DiseasesDocument34 pagesAgata Infectious DiseasesMartaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease NotesDocument19 pagesInfectious Disease Notesshwetlana rampureNo ratings yet
- Large Ruminant DiseasesDocument96 pagesLarge Ruminant DiseasesJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- Pathologic and NonDocument11 pagesPathologic and NonAisha DoreenNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument10 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMarisol DizonNo ratings yet
- 9 - Additional Notes For NematodesDocument1 page9 - Additional Notes For NematodesRich NyleNo ratings yet
- Cestodes Worksheet No. 1Document5 pagesCestodes Worksheet No. 1Denika AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesHealth and Diseasereet.patidar18No ratings yet
- DNA VIRUSES-handout PDFDocument11 pagesDNA VIRUSES-handout PDFROTHESSA MARY CARINGALNo ratings yet
- Zoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKDocument64 pagesZoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKakun internetNo ratings yet
- Xii Zoology Human Health and Diseases Jinush HssliveDocument4 pagesXii Zoology Human Health and Diseases Jinush HssliveADWAITH LALUNo ratings yet
- V9N5P239Document4 pagesV9N5P239Phạm Hồng SáuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)Document4 pagesNursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)jay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- CDDocument6 pagesCDMei JoyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Jaundice in The Hospitalized Patient PDFDocument16 pagesAssessment of Jaundice in The Hospitalized Patient PDFlaura canoNo ratings yet
- Liver TransplantDocument16 pagesLiver TransplantNephrology On-DemandNo ratings yet
- Hertspo2015 ProgramDocument16 pagesHertspo2015 ProgramΟδυσσεας ΚοψιδαςNo ratings yet
- VirologyLearnTable 2017-Sketchy PDFDocument4 pagesVirologyLearnTable 2017-Sketchy PDFdfgbdfgNo ratings yet
- HC2017 - New Drugs Approved by Health Canada in 2017Document2 pagesHC2017 - New Drugs Approved by Health Canada in 2017BhushanNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion: DR Vishwabharathi TDocument28 pagesBlood Transfusion: DR Vishwabharathi TSuma0% (1)
- Coc 2022 Reviewed Q & ADocument74 pagesCoc 2022 Reviewed Q & ASneeze LouderNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin Key ConceptDocument7 pagesHepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin Key ConceptMai Hoàng Dương QuangNo ratings yet
- 03 NCP 1 Viral HepatitisDocument17 pages03 NCP 1 Viral Hepatitisamit100% (2)
- Asymptomatic TransaminitisDocument2 pagesAsymptomatic TransaminitisrieseNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2213429Document11 pagesNejmoa 2213429Niramol WeerasunthornNo ratings yet
- 30 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Common Unit Conversions - Commonly Measured Laboratory Values - Abbreviations - IndexDocument28 pages30 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Common Unit Conversions - Commonly Measured Laboratory Values - Abbreviations - IndexRazrin RazakNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics PG Exam PapersDocument39 pagesPediatrics PG Exam Paperscooldude_secbad1712100% (1)
- Viral Misconceptions by Jeff Green TranscriptionDocument13 pagesViral Misconceptions by Jeff Green TranscriptionGlista100% (1)
- Michael Fraser BookletDocument5 pagesMichael Fraser BookletRushika PurohitNo ratings yet
- Kle University: Jawaharlal Nehru Medical CollegeDocument16 pagesKle University: Jawaharlal Nehru Medical Collegesujan maharjanNo ratings yet
- Who Expert Committee On Biological Standardization: Fifty-Fifth ReportDocument146 pagesWho Expert Committee On Biological Standardization: Fifty-Fifth ReportEsteban FiumaraNo ratings yet
- DHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtDocument49 pagesDHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtNatasha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Immunization - Dr. SarahDocument14 pagesImmunization - Dr. Sarahf6bk6xnppyNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument30 pagesLiverNisini ImanyaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination of Healthcare WorkersDocument16 pagesVaccination of Healthcare WorkersBenjamin RuotiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Pregnant Women Towards Hepatitis B InfectionDocument11 pagesAssessment of The Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Pregnant Women Towards Hepatitis B InfectionbamcobgyneNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Hbsag With Decrease in Viral Load With Herbal Formulation, Hd-03/Es: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesReduction of Hbsag With Decrease in Viral Load With Herbal Formulation, Hd-03/Es: A Case Studynaveen palNo ratings yet
- Pemberian Obat Pada Kelainan Fungsi HeparDocument21 pagesPemberian Obat Pada Kelainan Fungsi Heparari rujatiNo ratings yet