Professional Documents
Culture Documents
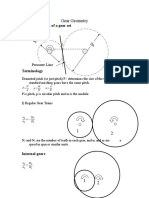
Motion Transmission Ex
Motion Transmission Ex
Uploaded by
MuntoiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motion Transmission Ex
Motion Transmission Ex
Uploaded by
MuntoiaCopyright:
Available Formats
A.Y.
2020/21 Applied Mechanics motion transmission
29
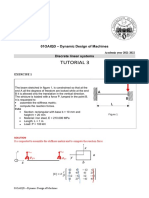
The shown reducer transmits the motion from the motor to
the user, the spur gears have all the same module. Motor
shaft is connected to gear 1. Gear 1 and gear 4 are coaxial.
Determine:
- angular velocity 4
- output torque C4 (on shaft 4)
- reaction forces R on supports A and B of the chassis.
Data:
z1 = z3 = 17; z2 = 52;
C1 = 10 Nm;
n1 = 3000 giri/min;
b = 80 cm.
[4 = 33.57 rad/s; C4 = 93.56 Nm; RA = RB = 104.5 N]
30
Motor M drives the lifting of mass m by means of reducer
R and drum T. Efficiency of the reducer is and the gears
have all the same module.
Data:
m = 100 kg; dT = 200 mm (drum diameter);
z1 = 18; z2 = 36, z3 = 20 (teeth numbers of gears 1, 2, 3);
= 0.95 (reducer efficiency);
Determine:
1. teeth numbers of gear 4;
2. transmission ratio of the reducer
With the hypothesis of constant lifting velocity V
determine:
3. motor torque
4. reaction torque from the ground to the reducer
carter
31
Body 1, having mass M is lifted with constant velocity V,
by means of the ideal rope 2 wrapped around drum 6. Rope
4 is wrapped around two pulleys: one is the driven pulley 3
fixed to the drum 6, the other is the driving pulley 5.
Data:
M = 100 kg; = 30°; V = 0.5 m/s;
f =0.3 (dynamic friction coefficient body 1- inclined plan)
R6
= 0.2 m (radius of drum 6);
R3
=0.3 m (radius of pulley 3 ),
R5
=0.1 m (radius of driving pulley 5).
Determine friction force T, tension T1 and T2 on of the rope,
torque Cm on the driving pulley 5, transmission ratio i,
power Pm necessary for the lifting of body 1.
You might also like
- Dom Assignment 1Document2 pagesDom Assignment 1Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Key QP21568 DynamicsofMachineryDocument11 pagesKey QP21568 DynamicsofMachineryVaidyanathan RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Programming Exercise 3: 3D Controller and Trajectory GenerationDocument10 pagesProgramming Exercise 3: 3D Controller and Trajectory GenerationhemanthkandulaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in VibrationDocument57 pagesSolved Problems in VibrationRasikaPereraNo ratings yet
- Adaptive State Controller For Inverted Pendulum: Nenad Muškinja, Boris TovornikDocument6 pagesAdaptive State Controller For Inverted Pendulum: Nenad Muškinja, Boris TovornikNeagu AdrianNo ratings yet
- Balancing of Reciprocating Masses 1Document43 pagesBalancing of Reciprocating Masses 1Anshul BediNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and BrakesDocument17 pagesPower Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and Brakesrip111176No ratings yet
- ThaDocument4 pagesThaJoses AlornyoNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Practical ActivityDocument4 pagesFlywheel Practical ActivityAnonymous FGryb4rEgNNo ratings yet
- Epicyclic Gear Train Write UpDocument8 pagesEpicyclic Gear Train Write UpkulkajinkyaNo ratings yet
- DOM TutorialsDocument11 pagesDOM TutorialsNishankzattNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Balancing of Reciprocating MassesDocument43 pagesUnit 5 Balancing of Reciprocating MassesNAVEENNo ratings yet
- рисунки PDFDocument18 pagesрисунки PDFLeo KutsNo ratings yet
- HW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationDocument8 pagesHW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- A Slider-Crank Experiment To Determine The Action of Static ForcesDocument10 pagesA Slider-Crank Experiment To Determine The Action of Static ForcesRazali Yusoff100% (1)
- Design of Machinery Jntua Previous PapersDocument20 pagesDesign of Machinery Jntua Previous PapersHimadhar SaduNo ratings yet
- Mock 14513 1625259162064Document28 pagesMock 14513 1625259162064Jatin prasad TandanNo ratings yet
- Vibration Paper3Document32 pagesVibration Paper3Debabrata PaulNo ratings yet
- Assignment Questions Dom Me 5004Document5 pagesAssignment Questions Dom Me 5004sharmasweeta927No ratings yet
- 9A03502 Dynamics of MachineryDocument4 pages9A03502 Dynamics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ME3001 Problem Set - 1 3-8-2013Document2 pagesME3001 Problem Set - 1 3-8-2013Athul JohnNo ratings yet
- Tut 3 - BalancingDocument3 pagesTut 3 - Balancinglittleprince889No ratings yet
- Dynamics ManualDocument30 pagesDynamics ManualRiyaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Mekanik MesinDocument8 pagesTest 1 Mekanik MesinApek Suasana0% (1)
- Machine Design IIDocument11 pagesMachine Design IIExequiel MedinaNo ratings yet
- DOM QP ScribdDocument5 pagesDOM QP ScribdvsanthanamNo ratings yet
- ME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRDocument1 pageME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery QuestionsDocument11 pagesDynamics of Machinery Questionslogeshboy0070% (1)
- ME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRDocument1 pageME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- MIN 301 Dynamics of Machines ExperimentsDocument12 pagesMIN 301 Dynamics of Machines ExperimentsSaifullah AhmadNo ratings yet
- ME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRDocument1 pageME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines - 1 PDFDocument8 pagesMechanics of Machines - 1 PDFtetirichie100% (1)
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- ME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRDocument1 pageME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Apr May 2019Document6 pagesApr May 2019VenkadeshNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machine 2 NotesDocument117 pagesMechanics of Machine 2 NotesChris MuturiNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Balancing of RECIPROCATING MASSESDocument43 pagesUnit 5 Balancing of RECIPROCATING MASSESswetha shree chavan mNo ratings yet
- Balancing - Rotating MassesDocument25 pagesBalancing - Rotating MassesEngineering DesignNo ratings yet
- ME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDocument4 pagesME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsMukul Chandra0% (1)
- Ch09 SSM 070904Document26 pagesCh09 SSM 070904VinhTranNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machineryrajamutyala4uNo ratings yet
- Balancing OF Reciprocating Masses: Slider Crank MechanismDocument43 pagesBalancing OF Reciprocating Masses: Slider Crank MechanismHiiNo ratings yet
- Calculation Salim 1Document9 pagesCalculation Salim 1Abdullahi AwwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document13 pagesUnit 3pbpawarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Force AnalysisDocument5 pagesDynamic Force AnalysisKarthik CruiseNo ratings yet
- ME3001 A3 Balancing of Reciprocating MassesDocument2 pagesME3001 A3 Balancing of Reciprocating MassesAkshay KakaniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- FlywheelsDocument33 pagesFlywheelsKaranSinghNo ratings yet
- Vibrations Solutions - PartialDocument15 pagesVibrations Solutions - Partialayariseifallah100% (1)
- Problems On FlywheelDocument16 pagesProblems On FlywheelkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Dom MCQ Bank 2Document4 pagesDom MCQ Bank 219006 Sahel GamitNo ratings yet
- Fig. 1 Schematic of Exhaust Valve Table 1.: P.I. (30 Points) An Emergency Valve (Fig. 1) Is Pressed AgainstDocument1 pageFig. 1 Schematic of Exhaust Valve Table 1.: P.I. (30 Points) An Emergency Valve (Fig. 1) Is Pressed Againstsandi123inNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Shashank SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRDocument1 pageME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRDocument1 pageME 501 Full Marks: 30 Time: 1 HRPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Estructuras DosDocument11 pagesEstructuras DosMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Cortante Utb 2020Document12 pagesCortante Utb 2020MuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics With FrictionDocument2 pagesDynamics With FrictionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics2 SlidesDocument17 pagesKinematics2 SlidesMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Notes Motion TransmissionDocument12 pagesNotes Motion TransmissionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Effective BreadthDocument9 pagesEffective BreadthMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Buckling Utb 2020Document12 pagesBuckling Utb 2020MuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial FEM - SolutionDocument18 pagesTutorial FEM - SolutionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - DDM MechatronicsDocument22 pagesTutorial 1 - DDM MechatronicsMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Rotors - SolutionDocument25 pagesTutorial Rotors - SolutionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Spanos ARMA Algorithms For Ocean Wave ModelingDocument10 pagesSpanos ARMA Algorithms For Ocean Wave ModelingMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Spanos A Direct Determination of ARMA Algorithms For The Simulation Fo Stationary Random ProcessesDocument14 pagesSpanos A Direct Determination of ARMA Algorithms For The Simulation Fo Stationary Random ProcessesMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Lin Methods of Stochastic Structural DynamicsDocument28 pagesLin Methods of Stochastic Structural DynamicsMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 5 - WhiteDocument40 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 5 - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Quentin Estimation and Prediction of Wave Inpit and System States Based On Local Hydropressure and Machinery ResponseDocument78 pagesQuentin Estimation and Prediction of Wave Inpit and System States Based On Local Hydropressure and Machinery ResponseMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- DDM - Mechatronics - Project 1Document3 pagesDDM - Mechatronics - Project 1MuntoiaNo ratings yet
- SimulationofDeep WaterWavesBasedonDocument5 pagesSimulationofDeep WaterWavesBasedonMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 4 WhiteDocument61 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 4 WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteDocument49 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 1aDocument36 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 1aMuntoiaNo ratings yet