Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Basic Principle Behind Most Engines
The Basic Principle Behind Most Engines
Uploaded by
prashanthOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Basic Principle Behind Most Engines
The Basic Principle Behind Most Engines
Uploaded by
prashanthCopyright:
Available Formats
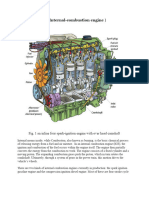
The basic principle behind most engines is the conversion of energy from one form
to another. In the case of internal combustion engines, which are the most common
type of engine used in cars and trucks, chemical energy stored in fuel is converted
into mechanical energy that can be used to power the vehicle.
Here's a breakdown of the basic engine operation:
Intake: The engine begins by drawing in air, which is mixed with fuel (gasoline or
diesel) in a precise ratio. This air-fuel mixture is then drawn into the cylinders.
Compression: Once the air-fuel mixture is inside the cylinder, the piston moves
up, compressing the mixture. This compression increases the pressure and temperature of
the mixture, making it more volatile.
Combustion: At the top of the compression stroke, a spark plug ignites the compressed air-
fuel mixture, causing it to burn rapidly. This combustion creates a hot, high-pressure gas that
expands rapidly.
Power: The expanding gas pushes the piston down, creating a force that is transferred
through a connecting rod to the crankshaft. The rotation of the crankshaft is what ultimately
powers the wheels of the vehicle.
Exhaust: After the power stroke is complete, the piston moves back up, pushing the exhaust
gases out of the cylinder through the exhaust valve. This process is repeated for each
cylinder in the engine, creating a continuous cycle of power.
You might also like
- Two and Three Wheeler NotesDocument49 pagesTwo and Three Wheeler NotesAbishek AbhNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Petrol EngineDocument9 pages4 Stroke Petrol EngineZahid MughalNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engines VsDocument4 pagesDiesel Engines VsSiraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Wroking EngineDocument1 pageWroking EngineSteven AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Foro Adiciona YanacDocument6 pagesForo Adiciona Yanacdaniel yanacNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: Chapter Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: Chapter Learning ObjectivesRahul KhatriNo ratings yet
- 1.FSAE Turbocharger Design and ImplementationDocument27 pages1.FSAE Turbocharger Design and ImplementationJoy NagNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument142 pagesLecturesMuhammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine1virkDocument3 pagesPetrol Engine1virkapi-3703711No ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Enginespramodkb_cusatNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument27 pagesIc EngineSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- Gasoline EngineDocument6 pagesGasoline EngineJonan TutaanNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Engines Section BDocument45 pagesReciprocating Engines Section BJuly TadeNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument46 pagesInternal Combustion EngineJoseph Rebanal AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document13 pagesLect 2khalid mustafaNo ratings yet
- Assign#1 Thermo Lab. 2019p-ME-18Document8 pagesAssign#1 Thermo Lab. 2019p-ME-18Abdul Rasheed GhaziNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06: To Investigate The Operation 4 Stroke Diesel Engine For Power GenerationDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 06: To Investigate The Operation 4 Stroke Diesel Engine For Power GenerationAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Essential For Engine OperationDocument13 pagesEssential For Engine OperationVõ Thanh LiêmNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine For Power Generation: Dates Back To 1939Document6 pagesGas Turbine For Power Generation: Dates Back To 1939Wakwkaka JssjaaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Chapter 5Document32 pagesScience Form 5 Chapter 5Shamini Segari GunasakaranNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke EngineDocument9 pagesFour Stroke Enginepawarsikander100% (3)
- Motori e Biofuel ENGDocument3 pagesMotori e Biofuel ENGIrene FranchinNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument8 pagesIC EnginesNo MINo ratings yet
- 2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesDocument27 pages2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesAHMADNo ratings yet
- Lec 02Document16 pagesLec 02cattykaif1No ratings yet
- Technical DefinitionDocument3 pagesTechnical Definitionapi-356313044No ratings yet
- Heat Engine DesignDocument25 pagesHeat Engine DesignEamonn McStravickNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: Course No: M02-052 Credit: 2 PDHDocument24 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: Course No: M02-052 Credit: 2 PDHdoxoNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesFour Stroke Enginemnoorulain80No ratings yet
- Relation of Gas Law in A Cars Engine: By: Khaled AldhaheriDocument9 pagesRelation of Gas Law in A Cars Engine: By: Khaled AldhaheriSara AlhamesNo ratings yet
- Asi Unit 3Document21 pagesAsi Unit 3Raja RamNo ratings yet
- To: Mr. Tan Xiao Long, Technical Manager From: NG Hon Meng, Cadet Engineer Re: The Working of A Four-Stroke Engine Date: April, 8 2012Document1 pageTo: Mr. Tan Xiao Long, Technical Manager From: NG Hon Meng, Cadet Engineer Re: The Working of A Four-Stroke Engine Date: April, 8 2012Ng Hon MengNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument14 pages1 PDFinsanNo ratings yet
- Petrol and Diesel EngineDocument7 pagesPetrol and Diesel Enginegangstarvegas919No ratings yet
- Four Stroke Cycle EnginesDocument1 pageFour Stroke Cycle EnginesIrshad AfridiNo ratings yet
- Petrol EnginesoDocument7 pagesPetrol Enginesoapi-3731257No ratings yet
- ICE (Internal Combustion Engine)Document22 pagesICE (Internal Combustion Engine)johnlloydsantossssNo ratings yet
- Meec Prelim CompilationDocument16 pagesMeec Prelim CompilationBen Aldrian IbañezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internal Combustion Engines.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics ME 1052Document7 pagesIntroduction To Internal Combustion Engines.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics ME 1052Supun AmarasingheNo ratings yet
- Me 56Document9 pagesMe 56RhizhailNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine (Nehru Garden, JalandharDocument7 pagesPetrol Engine (Nehru Garden, Jalandharapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Applied Physics WORDDocument19 pagesApplied Physics WORDMojtaba AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: 1-Four-Stroke IC EngineDocument21 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: 1-Four-Stroke IC EngineZahid HussainNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine ExplainedDocument6 pagesInternal Combustion Engine ExplainedBogdan VarlanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine: Rotary Engine Energy Combustion Compressor ChamberDocument11 pagesGas Turbine: Rotary Engine Energy Combustion Compressor ChamberRauf DogarNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Petrol Engine: What Is An Engine?Document4 pagesFour Stroke Petrol Engine: What Is An Engine?UsamaNo ratings yet
- Four-Stroke Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesFour-Stroke Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSam B. SucalitNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Chapter 5Document32 pagesScience Form 5 Chapter 5Yarminee GunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ElevatorsDocument4 pagesHydraulic ElevatorsAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- ENGINEDocument7 pagesENGINEayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Communication Lab 4-Stroke Petrol Engine: Hemanth Kumar R 07ME034Document6 pagesCommunication Lab 4-Stroke Petrol Engine: Hemanth Kumar R 07ME034Hemu723No ratings yet
- Study of Components, Systems & Working of Diesel Engine ModelDocument11 pagesStudy of Components, Systems & Working of Diesel Engine ModelFaisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- How A Car Engine WorksDocument2 pagesHow A Car Engine Worksanthony muthuiNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Diesel EngineDocument4 pagesFour Stroke Diesel EngineSwati SutarNo ratings yet
- Artifact 4 Parts Small Engines PowerpointDocument56 pagesArtifact 4 Parts Small Engines Powerpointapi-240922530No ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsFrom EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Learn to Drive: Everything New Drivers Need to KnowFrom EverandLearn to Drive: Everything New Drivers Need to KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)