Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3Q Week 3
3Q Week 3
Uploaded by
Glorylyn Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesThis lesson plan covers teaching students about the structure of the Earth and geological processes. Session 1 focuses on the Earth's layers and basic structure. Sessions 2-3 cover Earth's interior heat generation through radioactive decay and plate tectonics. Session 4 discusses magma formation through decompression melting and addition of volatiles. Hands-on activities include experiments on cooling rock and simulating magma formation. The plan aims to build students' understanding of geological hazards and energy through discussions on volcanoes, earthquakes, and geothermal power.
Original Description:
Original Title
3Q-WEEK-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis lesson plan covers teaching students about the structure of the Earth and geological processes. Session 1 focuses on the Earth's layers and basic structure. Sessions 2-3 cover Earth's interior heat generation through radioactive decay and plate tectonics. Session 4 discusses magma formation through decompression melting and addition of volatiles. Hands-on activities include experiments on cooling rock and simulating magma formation. The plan aims to build students' understanding of geological hazards and energy through discussions on volcanoes, earthquakes, and geothermal power.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pages3Q Week 3
3Q Week 3
Uploaded by
Glorylyn CruzThis lesson plan covers teaching students about the structure of the Earth and geological processes. Session 1 focuses on the Earth's layers and basic structure. Sessions 2-3 cover Earth's interior heat generation through radioactive decay and plate tectonics. Session 4 discusses magma formation through decompression melting and addition of volatiles. Hands-on activities include experiments on cooling rock and simulating magma formation. The plan aims to build students' understanding of geological hazards and energy through discussions on volcanoes, earthquakes, and geothermal power.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
School
DAILY Teacher
LESSON
Teachin
PLAN
g Week
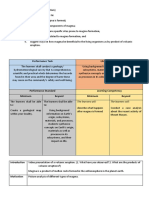
SESSIONS: SESSION 1 SESSION 2 SESSION 3 SESSION 4
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards 1. the three main categories of rocks 2. the origin and environment of formation of common minerals and rocks 3. geologic processes
that occur on the surface of the Earth such as weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation (include the role of ocean basins
in the formation of sedimentary rocks) 4. geologic processes that occur within the Earth 5. the folding and faulting of rocks 6. plate
tectonics 7. how the planet Earth evolved in the last 4.6 billion years (including the age of the Earth, major geologic time subdivisions,
and marker fossils).
B. Performance Conduct a survey to assess the possible geologic/ hydrometeorological hazards that your community may experience.
Standards
C. Learning Describe where the Earth’s internal heat comes from
Competencies/ describe how magma is formed (magmatism)
Objectives
II. CONTENT Earth's layers and the basic structure of the Earth
Definition
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide Pages
2. Learner’s Material Pages
3. Textbook Pages
4. Additional Materials from
Learning Resources
B. Other Learning
Resources
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing Start the lesson by reviewing the Begin the lesson by reviewing
concept of Earth's layers and the the basic concepts related to
basic structure of the Earth. Earth's interior structure. Discuss
Discuss what students know the layers of the Earth, focusing
about the Earth's internal heat on the mantle and core. Ask
and ask questions like: questions to gauge students'
understanding, such as:
"What is the Earth's core made
of?" "What are the layers of the
"How do you think the Earth Earth?"
generates heat?" "How do you think magma is
related to the Earth's interior?"
B. Motivation To capture students' interest, Capture students' interest with a
present a simple experiment or visual demonstration or real-
demonstration: world examples:
Conduct an experiment showing Show images or videos of
the cooling and solidification of volcanic eruptions and lava
molten material to represent the flows.
Earth's early stages. Pose questions like, "What do
you think causes volcanic
Pose questions like, "Why do you
eruptions?"
think the Earth is still warm
Share interesting facts about
inside?" famous volcanoes.
C. Learning Activities Introduction to Earth's Interior: Introduction to Magmatism:
Explain the composition of the Define magmatism as the
Earth's interior, including the process by which magma is
core, mantle, and crust. formed beneath the Earth's
Discuss the temperatures at surface.
various depths and how they Discuss the key components of
change. magma: molten rock, dissolved
gases, and mineral crystals.
Heat Generation:
Types of Magma:
Introduce the concept of Introduce the two main types of
radioactive decay and how it magma: basaltic and granitic.
contributes to heat generation Explain the differences in
within the Earth. composition, viscosity, and
Discuss the role of elements like eruption styles associated with
uranium, thorium, and potassium each type.
in releasing heat. Magma Formation:
Plate Tectonics and Heat
Transfer: Discuss the two main processes
involved in magma formation:
decompression melting and
Explain how the movement of
tectonic plates contributes to
heat transfer within the Earth.
Discuss how heat generated in addition of volatiles (water and
the Earth's interior drives gases).
processes like mantle Use diagrams or animations to
convection. illustrate these processes.
Interactive Demonstration:
Interactive Models:
Conduct a simple experiment to
Use interactive models, simulate magma formation. For
diagrams, or animations to example, demonstrate how
illustrate the processes of increasing temperature or
radioactive decay and mantle decreasing pressure can lead to
convection. melting.
Allow students to explore these
models hands-on or through
virtual platforms.
D. Applications Volcanic Hazard
Geothermal Energy Awareness:
Discussion:
Discuss the practical
applications of
Discuss the applications of
understanding
understanding Earth's internal magmatism, particularly in
heat, particularly in the assessing volcanic
context of geothermal energy. hazards.
Explore how geothermal Explore how knowledge of
energy is harnessed for magma formation helps in
electricity generation and predicting and mitigating
heating. volcanic eruptions.
Earthquake and Volcano Geothermal Energy
Study: Discussion:
Introduce the concept of
Discuss how the movement of geothermal energy and
tectonic plates and heat flow how it is related to magma
from the Earth's interior and heat from the Earth's
contribute to the occurrence interior.
of earthquakes and volcanic
activity.
Discuss how geothermal
Analyze case studies of
energy is harnessed for
earthquakes and volcanoes, electricity generation.
linking them to the Earth's
internal heat processes.
E. Generalizations Conclude the lesson with
Emphasize that the Earth's generalizations:
internal heat primarily comes
from the process of Emphasize that magma is
radioactive decay of certain formed through the
elements. processes of
Discuss how the heat decompression melting
generated drives dynamic and the addition of
volatiles.
processes like mantle
Discuss the role of
convection and plate magmatism in shaping the
tectonics. Earth's surface through
Reinforce the idea that volcanic activity.
understanding the Earth's Reinforce the idea that
internal heat is crucial for understanding magma
explaining geological formation is crucial for
phenomena and harnessing predicting volcanic
geothermal energy. eruptions and utilizing
geothermal energy.
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation who
scored below 80%
C. Did the remedial
lesson work? No. of
learners who caught
up with the lesson
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked
well? Why did these
work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials did
I use/discover which I
wish to share with
other teachers?
Prepared by: Checked and Reviewed: Noted by:
You might also like
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 7Document8 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 7Austin Capal Dela Cruz50% (2)
- LP IN EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE - EndogenicDocument4 pagesLP IN EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE - EndogenicEarl Jason RaraNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Module-9Document14 pagesEarthsci Module-9Alyssa AngelaNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 6Document6 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 6Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci Module 2Document11 pagesEarth Sci Module 2Twice GmailNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth Science I. Objectives: WWW - Bbc.co - Uk WWW - Physics.bu - EduDocument4 pagesLesson Guide in Earth Science I. Objectives: WWW - Bbc.co - Uk WWW - Physics.bu - EduallanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Earth and Life ScienceBuzz manzhjanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: What Happens To Magma After It Is Formed?Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: What Happens To Magma After It Is Formed?Buzz manzhjanaNo ratings yet
- Q1W3 - Core 4Document11 pagesQ1W3 - Core 4Mary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Shs-Earths Internal HeatDocument7 pagesShs-Earths Internal HeatFatima LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - Grade 11: What Do You Know?: Let's Travel Within!Document8 pagesEarth Science - Grade 11: What Do You Know?: Let's Travel Within!John Vincent De JesusNo ratings yet
- DLL Els Quarter 1 Week 3Document4 pagesDLL Els Quarter 1 Week 3Ryan Christopher ReynadoNo ratings yet
- QAed-SSLM EALS Q1-W3 TUBIG-EDITEDDocument6 pagesQAed-SSLM EALS Q1-W3 TUBIG-EDITEDTrash BinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan of Earthquake and Volcanoes ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan of Earthquake and Volcanoes ObjectivesBlythe RabacioNo ratings yet
- WLP-EARTH-SCIE-ELS-WEEK-8-JLADocument20 pagesWLP-EARTH-SCIE-ELS-WEEK-8-JLAjohnlowell.adalidNo ratings yet
- DLL Els Quarter 1 Week 3Document3 pagesDLL Els Quarter 1 Week 3alyssa.ballonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Chapter 10Document4 pagesAssessment Chapter 10NafisaNo ratings yet
- S11es Iid 32Document5 pagesS11es Iid 32allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Jasten Mark Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesJasten Mark Lesson PlanitsmefayealNo ratings yet
- Topic: Endogenic Processes (Magmatism) Objectives: The Students Will Be Able ToDocument3 pagesTopic: Endogenic Processes (Magmatism) Objectives: The Students Will Be Able ToJelly MarieNo ratings yet
- Els W6Document11 pagesEls W6renliejanepNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 Module 1: Describe Where The Earth's Internal Energy Comes FromDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 Module 1: Describe Where The Earth's Internal Energy Comes FromRICHARD CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Perez, Lara Maryannie STEM 12-B W4 ES L2Document6 pagesPerez, Lara Maryannie STEM 12-B W4 ES L2Lara Maryannie PerezNo ratings yet
- Module ELSDocument40 pagesModule ELSnotzi6942018890420No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science M3Document23 pagesEarth and Life Science M3Lore Isabel Mendoza PaclebNo ratings yet
- Possible Questions Reviewer ElsDocument5 pagesPossible Questions Reviewer Elspersonalizedlife6No ratings yet
- Tectonic Hazards SampleDocument14 pagesTectonic Hazards SampleALLEGRA KATTONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Endogenous Process For Lower Sixth ScienceDocument6 pagesLesson Plan On Endogenous Process For Lower Sixth Scienceeugeni madaNo ratings yet
- WLP-EARTH-SCIE-ELS-WEEK-6-JLADocument12 pagesWLP-EARTH-SCIE-ELS-WEEK-6-JLAjohnlowell.adalidNo ratings yet
- Saldivar Geothermal EnergyDocument17 pagesSaldivar Geothermal EnergyJustine Tizon SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes: Earth and Life Science Engr. Mai SasaDocument23 pagesEndogenic Processes: Earth and Life Science Engr. Mai SasaMai SasaNo ratings yet
- LP IN SCIENCE 6 (Changes in Earth Due To Volacanic Eruption)Document7 pagesLP IN SCIENCE 6 (Changes in Earth Due To Volacanic Eruption)Alvin CabanelaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: Layers of The EarthDocument4 pagesLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: Layers of The EarthJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci. Earth and LifeDocument5 pagesEarth Sci. Earth and LifeMagdalena BianesNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Document4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Arban, CG. Lesson Plan in Geothermal Energy, 11 - STEMDocument6 pagesArban, CG. Lesson Plan in Geothermal Energy, 11 - STEMCzarina Amor CabilleteNo ratings yet
- DLP Volcanic EruptionDocument14 pagesDLP Volcanic Eruptionchristianlozada000No ratings yet
- DLL-earth-and-life - 5Document4 pagesDLL-earth-and-life - 5Marilla ReybethNo ratings yet
- First Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterDocument11 pagesFirst Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterElvie CalinisanNo ratings yet
- LP in Earth Science M2Document5 pagesLP in Earth Science M2fiids.castroNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 Module 1: Describe Where The Earth's Internal Energy Comes FromDocument9 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 Module 1: Describe Where The Earth's Internal Energy Comes FromRICHARD CORTEZNo ratings yet
- EES Syllabus-OBE TemplateDocument9 pagesEES Syllabus-OBE TemplateEden ManggaNo ratings yet
- 6 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Life Science Q1 Module 6Document22 pages6 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Life Science Q1 Module 6Luigie CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document44 pagesChapter 2kd23ms057No ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Performance Standard: Learning CompetenciesDocument7 pagesLearning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Performance Standard: Learning CompetenciesSarah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Divisional Public School and Inter College Model Town, LahoreDocument4 pagesDivisional Public School and Inter College Model Town, LahoreAsra AsifNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - ElementaryDocument12 pagesLesson Plan - Elementaryannf38562No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document17 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 1NRIZA MAE CACHONo ratings yet
- Module 6 The Earth S Internal Heat PDFDocument13 pagesModule 6 The Earth S Internal Heat PDFRODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- Course/Class Name: Earth Science - Regents, Red Class Lesson Title: Continental Drift Abstract/summary of Lesson: Students Will BeDocument4 pagesCourse/Class Name: Earth Science - Regents, Red Class Lesson Title: Continental Drift Abstract/summary of Lesson: Students Will BeAda BrigoleNo ratings yet
- SCIGR9Q3 Adv PDFDocument110 pagesSCIGR9Q3 Adv PDFLeonoral BoralNo ratings yet
- Earth Science DLL Week 7Document2 pagesEarth Science DLL Week 7Maribel LescanoNo ratings yet
- Volcano LabDocument11 pagesVolcano LabjainamjainjatinNo ratings yet
- Dll-Els W3Document8 pagesDll-Els W3Genesa Buen A. PolintanNo ratings yet
- 7-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 7Document22 pages7-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 7DonabelEscotaEspaño100% (2)
- Lesson 13-Teacher's GuideDocument14 pagesLesson 13-Teacher's GuideAllyssa LimosNo ratings yet
- Mataias Contreiras - Science4 - U5 - FORM-13-18Document6 pagesMataias Contreiras - Science4 - U5 - FORM-13-18mcontrerasaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanLowel AndrewNo ratings yet
- Mountains of Fire: Exploring the Science of Volcanoes: The Science of Natural Disasters For KidsFrom EverandMountains of Fire: Exploring the Science of Volcanoes: The Science of Natural Disasters For KidsNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model For CO2 Emissions Reduction To Slow and Reverse Global WarmingDocument16 pagesMathematical Model For CO2 Emissions Reduction To Slow and Reverse Global WarmingMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- ESIMEX Catalogo 2020Document42 pagesESIMEX Catalogo 2020J Cesar CulebroNo ratings yet
- RA-05-Office SafetyDocument5 pagesRA-05-Office Safetyamritha n krishnaNo ratings yet
- 08 Vision IAS CSP21 Test 8S ENVIDocument34 pages08 Vision IAS CSP21 Test 8S ENVIpuppala mokshithaNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Atlas of The HimalayaDocument4 pagesIllustrated Atlas of The HimalayaChris HaerringerNo ratings yet
- 67) Forest Fragmentation Synergisms and The ImpoverishDocument8 pages67) Forest Fragmentation Synergisms and The ImpoverishMa O Marquez Fran QuisNo ratings yet
- 2006 - Resolution 3 With Respect To Hazardous Waste ManagementDocument36 pages2006 - Resolution 3 With Respect To Hazardous Waste ManagementAmr YehiaNo ratings yet
- Fire and Life Safety Assessment ReportDocument5 pagesFire and Life Safety Assessment ReportJune CostalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 25: Global Business Environment: Assignment Brief 1Document5 pagesUnit 25: Global Business Environment: Assignment Brief 1Do Huy Thanh (FGW HN)No ratings yet
- Mauritius Oil Spill: Warm UpDocument3 pagesMauritius Oil Spill: Warm UpBiancaNo ratings yet
- By-Products Utilization To Answer Climate Changes and Food Security: The Case of Sweet Potato (Ipomoea Batatas)Document63 pagesBy-Products Utilization To Answer Climate Changes and Food Security: The Case of Sweet Potato (Ipomoea Batatas)Lúcia FernandesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 HSE PolicyDocument1 page2.1 HSE Policybilo1984No ratings yet
- 11, EngDocument7 pages11, EngArbin HoqueNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Faculty of Social Sciences Social Sciences: Chiang Mai UniversityDocument2 pagesFaculty of Faculty of Social Sciences Social Sciences: Chiang Mai UniversityShine ToukNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352710221005623 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S2352710221005623 MainLuciana Boaventura PalharesNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakaGol D. AditNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Diplomacy Between Pakistan and AfghanistanDocument4 pagesHydro-Diplomacy Between Pakistan and AfghanistansohailsdNo ratings yet
- Peat in The Mountains of New Guinea: G.S. HopeDocument21 pagesPeat in The Mountains of New Guinea: G.S. HopeReinold HalukNo ratings yet
- Auth Recycler Dismantler 22092022Document11 pagesAuth Recycler Dismantler 22092022Navratan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- M.Plan SYLLABUS 2022-24Document54 pagesM.Plan SYLLABUS 2022-24Mili DawsonNo ratings yet
- Sikafloor 262 AS, Comp. B PDFDocument10 pagesSikafloor 262 AS, Comp. B PDFadil khanNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q2 - M3Document16 pagesScience 7 Q2 - M3Edsel BelbarNo ratings yet
- Asian CarpDocument7 pagesAsian CarpJose DanielNo ratings yet
- Waste To Energy Incineration-Basic Guide 2020Document45 pagesWaste To Energy Incineration-Basic Guide 2020SRINIVASAN TNo ratings yet
- Green Economy EssayDocument2 pagesGreen Economy EssayDilesh VeeramahNo ratings yet
- Performance, Employees, Community-Based Water and Sanitation ProgramsDocument7 pagesPerformance, Employees, Community-Based Water and Sanitation ProgramsOkta UwaNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument4 pagesResearch Proposalapi-703354548No ratings yet
- Crossrail at Canary WharfDocument8 pagesCrossrail at Canary WharfAli AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Agriculture and A Changing Environment in Northeastern India 1St Edition Sumi Krishna Editor Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Agriculture and A Changing Environment in Northeastern India 1St Edition Sumi Krishna Editor Online PDF All Chaptermarentaraaul100% (8)
- Learning From The Past - Traditional Knowledge and Sustainable DevelopmentDocument22 pagesLearning From The Past - Traditional Knowledge and Sustainable DevelopmentYusuf Hussen100% (1)