Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Task 2
Learning Task 2
Uploaded by
zyx xyzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Task 2
Learning Task 2
Uploaded by
zyx xyzCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Task 2
I. Rankine Cycle
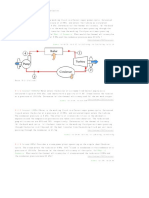
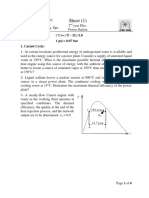
1. Consider a steam power plant operating on the simple ideal Rankine cycle. The
steam enters the turbine at 4 MPa, 400 deg. C and is condensed in the condenser at a
pressure of 100 kPa. Draw the schematic and T- s diagram of the cycle and determine
the following per unit mass of steam. (a) Turbine work, (b) Pump work, (c) Heat
added in the boiler, (d) Heat rejected in the condenser, (e) Thermal efficiency of the
cycle, (f) Heat rate, (g) Steam rate of the cycle.
2. Water is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Superheated vapor enters the
turbine at 8 MPa, 480 deg. C. The condenser pressure is 8 kPa. The net power output
of the cycle is 100 MW. Determine for the cycle (a) the rate of heat transfer to the
working fluid passing through the steam generator, in kW. (b) the thermal efficiency.
(c) the mass flow rate of condenser cooling water, in kg/h, if the cooling water enters
the condenser at 15 deg C and exits at 35 deg C with negligible pressure change.
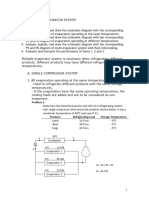
II. Improve Rankine Cycle
Identify and explain the ways with diagram on how to increase the efficiency of a
Rankine cycle.
You might also like
- 1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFDocument1 page1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFsuby100% (1)
- ET II Assignment 2 - ModifiedDocument3 pagesET II Assignment 2 - ModifiedbaliamajhiNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 1Document2 pagesProblems Set 1suby0% (1)
- Water Is The Working Fluid in An Ideal Rankine CycleDocument1 pageWater Is The Working Fluid in An Ideal Rankine CycleMochammad Gama AdriansyahNo ratings yet
- Assign#4 Vapor CycleDocument3 pagesAssign#4 Vapor Cyclemihreteab ghebregzabherNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - 151906 - Conventional Power EngineeringDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - 151906 - Conventional Power EngineeringSai BalaNo ratings yet
- Aços Carbono Construção CivilDocument5 pagesAços Carbono Construção CivilIrvin WilliamNo ratings yet
- Taller EficienciasDocument2 pagesTaller EficienciasJohan Maldonado100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Important QuestionsMaha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- ME267 Assignment01Document1 pageME267 Assignment01InsaneNo ratings yet
- ATD RAnkin Assignment-2011Document3 pagesATD RAnkin Assignment-2011Yuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Reheat Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesSheet (2) Reheat Rankine CycleHamadaMohassabNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Ciclo RankineDocument1 pageEjercicios Ciclo RankinecarlosNo ratings yet
- SHEET (6) Simple Rankine CycleDocument1 pageSHEET (6) Simple Rankine CycleAhmedTahaNo ratings yet
- Consider A Steam Power Plant Operating On The Ideal Rankine CycleDocument1 pageConsider A Steam Power Plant Operating On The Ideal Rankine CyclegandhiramNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Vapor Power CyclesDocument2 pagesSheet 2 Vapor Power CyclesAhmed Mahmoud AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- Tugas Turbin Uap: of Problem 2 Above Is Modified To Include ReheatDocument2 pagesTugas Turbin Uap: of Problem 2 Above Is Modified To Include ReheatRudy ArthaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engg Assignment-1Document2 pagesPower Plant Engg Assignment-1keyredin selmanNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle: Ideal CyclesDocument13 pagesRankine Cycle: Ideal CyclesTylerNo ratings yet
- 20130511233558467Document3 pages20130511233558467ahmadskhanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Termo IDocument1 pageTugas Termo IAditia Syamputra TanjungNo ratings yet
- Problemario MFCDocument31 pagesProblemario MFCPonce MrlnNo ratings yet
- Problemario MFCDocument80 pagesProblemario MFCBassaldua AlfreedNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle ProblemDocument2 pagesRankine Cycle ProblemJohn Paul RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ch04b 1st Law OS-EXAMPLESDocument9 pagesCh04b 1st Law OS-EXAMPLESTSEGAAB NIGUSSENo ratings yet
- Thermo I Set of Questions 2022Document6 pagesThermo I Set of Questions 2022Paa Kwesi ArhinfulNo ratings yet
- Assig1-Due On Feb 1,2018Document3 pagesAssig1-Due On Feb 1,2018Graeme KendallNo ratings yet
- Thermo of MechDocument2 pagesThermo of MecheyobNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument3 pagesTutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesShariff Mohamad Fairuz0% (1)
- Rankine CycleDocument3 pagesRankine Cyclefor gameunliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 02 2014Document11 pagesTutorial Sheet 02 2014checkmeout803No ratings yet
- Questions Topic-Vapour Power Cycle Subject-Applied ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesQuestions Topic-Vapour Power Cycle Subject-Applied ThermodynamicsXerox WorldNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TermodinamikaDocument24 pagesContoh Soal TermodinamikaDea FarhaniNo ratings yet
- ME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFDocument5 pagesME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFVikasKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- 8.1prob Sheet Vapor Power CyclesDocument3 pages8.1prob Sheet Vapor Power CyclesAnonymous mXicTi8hB100% (1)
- Kmem 2216 - Al2Document1 pageKmem 2216 - Al2Daniel WongNo ratings yet
- End Prob. CengelDocument5 pagesEnd Prob. CengelErvz MissionNo ratings yet
- PPE AssignmentDocument3 pagesPPE AssignmentAshish Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Net Power Output of The Cycle Is 110 MW. DetermineDocument3 pagesNet Power Output of The Cycle Is 110 MW. DetermineDhias VidathyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Problems and Solutions, Chapter-9Document20 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - Problems and Solutions, Chapter-9ZelNo ratings yet
- 01-Sheet 01Document9 pages01-Sheet 01samir mohamedNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1Anagha ChimankarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Gas Power CyclesDocument26 pagesModule 5 Gas Power CyclesJatskinesisNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- (Ɪ) Choose The Correct AnswerDocument3 pages(Ɪ) Choose The Correct AnswerHamadaMohassabNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document3 pagesModule 1സാരംഗ്എസ്കുമാർNo ratings yet
- A Simple Rankine Cycle Uses Water As The Working Fluid. The Boiler Operates at 6000 KpaDocument2 pagesA Simple Rankine Cycle Uses Water As The Working Fluid. The Boiler Operates at 6000 KpaLizethVegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter RankineDocument32 pagesChapter RankineZack ZukhairiNo ratings yet
- ATD RAnkin Assignment-2011Document3 pagesATD RAnkin Assignment-2011Mradul Yadav0% (2)
- Lectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PDocument2 pagesLectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PPritam PaulNo ratings yet
- Ch04b 1st Law Os-ExamplesDocument23 pagesCh04b 1st Law Os-ExamplesBereketNo ratings yet
- Sheet 8 (Cha (7,8) )Document2 pagesSheet 8 (Cha (7,8) )chemicalengineering321No ratings yet
- Problems Carnot and RankineDocument12 pagesProblems Carnot and RankineHassan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions: (A) The Exit Velocity, in M/sDocument2 pagesTwo Mark Questions: (A) The Exit Velocity, in M/sRajvir Preet GillNo ratings yet
- Problem-Set 2Document20 pagesProblem-Set 2ERROLL ZANDRE NACAYA ANOBARNo ratings yet
- Steam Cycles TutorialsDocument1 pageSteam Cycles TutorialsSakhile Nhlakanipho ZithaNo ratings yet
- Wor ShopDocument4 pagesWor ShopDavid Santiago Ayala RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MEE 302 - Tutorial 2-1Document2 pagesMEE 302 - Tutorial 2-1anthonysakachiva1No ratings yet
- Sheet No.1 (Carnot-Rankine)Document6 pagesSheet No.1 (Carnot-Rankine)Farah SayedNo ratings yet
- Non Con PlantsDocument19 pagesNon Con Plantszyx xyzNo ratings yet
- 3ma M3 AssignDocument12 pages3ma M3 Assignzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- 2023 Nov Algebra 4Document2 pages2023 Nov Algebra 4zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- MODULE III Sub Cooling and SuperheatingDocument11 pagesMODULE III Sub Cooling and Superheatingzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument14 pagesGas Turbinezyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Fuels CombustionDocument15 pagesFuels Combustionzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Fluid Mech Fluid Mach IceDocument4 pagesProblem Set Fluid Mech Fluid Mach Icezyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2 (Module 2 Lesson 5)Document14 pagesThermo 2 (Module 2 Lesson 5)zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- MODULE VI. Multiple Evap SystemDocument19 pagesMODULE VI. Multiple Evap Systemzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- MODULE I Basic Concepts DefinitionsDocument3 pagesMODULE I Basic Concepts Definitionszyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Phed 104 - Lesson 1 & 2Document10 pagesPhed 104 - Lesson 1 & 2zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- C - Fluid Mechanics - PP - TestDocument2 pagesC - Fluid Mechanics - PP - Testzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- ME Boards 1 Problem Set 04Document6 pagesME Boards 1 Problem Set 04zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Ensc 102 Module-VDocument22 pagesEnsc 102 Module-Vzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 3Document1 pageLearning Activity 3zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Activity No.5 - MEES 102Document1 pageActivity No.5 - MEES 102zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4,5 &6Document12 pagesLesson 4,5 &6zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument18 pagesGeometryzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- C - Fluid Mechanics - SeDocument2 pagesC - Fluid Mechanics - Sezyx xyzNo ratings yet
- ME Boards 1 Problem Set 02Document6 pagesME Boards 1 Problem Set 02zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Fluids Last QuizDocument4 pagesFluids Last Quizzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 5Document1 pageLearning Activity 5zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Integral Cal Activity 1Document1 pageIntegral Cal Activity 1zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Activity 4-1Document1 pageActivity 4-1zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- PreliminariesDocument4 pagesPreliminarieszyx xyzNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 LaboratoryDocument3 pagesMODULE 2 Laboratoryzyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document16 pagesLesson 3zyx xyzNo ratings yet