Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsHVDC Transmission Basic Circuit
HVDC Transmission Basic Circuit
Uploaded by
DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWThe document describes the major components of a high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system. It discusses the key components of a converter station including converter units made of thyristor valves arranged in a 12-pulse configuration, converter transformers, filters for alternating current and direct current, and reactive power sources. It also mentions other components like smoothing reactors and direct current switchgear that are part of a converter station.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Romualdi 1964Document16 pagesRomualdi 1964Isabela LauferNo ratings yet
- MTC-2 - Service STRCDocument1 pageMTC-2 - Service STRCHema NandhNo ratings yet
- HVDC ReportDocument43 pagesHVDC ReportD Sreenivas KarthikNo ratings yet
- HVDC Unit IIDocument20 pagesHVDC Unit IISaduMunisekharNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationmeraatNo ratings yet
- HVDC PPTDocument34 pagesHVDC PPTBattinapati Shiva100% (1)
- WINSEM2023-24 BEEE406L TH VL2023240502855 2024-03-12 Reference-Material-IDocument14 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BEEE406L TH VL2023240502855 2024-03-12 Reference-Material-IRahul ganthNo ratings yet
- Commutation in HVDCDocument8 pagesCommutation in HVDCUsama ZafarNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Part 2Document41 pagesHVDC Transmission Part 2srinimeha@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- HVDC Lecture 2Document18 pagesHVDC Lecture 2MuHammad AbuNaga0% (1)
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission SystemDocument45 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission SystemPramod DadmalNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document78 pagesFinal 1Steve JantzenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HVDC TransmissionDocument25 pagesChapter 5 HVDC TransmissionTalha Khanzada100% (1)
- HVDC 1Document73 pagesHVDC 1Adani PowerNo ratings yet
- 3 Level InverterDocument63 pages3 Level InverterThirumal ValavanNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationRajmohan100% (1)
- Industrial Visit Report MeghaDocument21 pagesIndustrial Visit Report MeghaMegha SaranNo ratings yet
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 246Document1 pageSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 246mydearteacherNo ratings yet
- HVDC TransmissionDocument26 pagesHVDC TransmissionAditya TiwariNo ratings yet
- p185 PDFDocument24 pagesp185 PDFதமிழன்No ratings yet
- Ijset 2014 201Document7 pagesIjset 2014 201Innovative Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase RectificationDocument30 pages3 Phase RectificationKobby Brine100% (1)
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument25 pagesEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Power InverterDocument11 pagesPower Inverterriz2010No ratings yet
- Component of HVDC Transmission NetworkDocument5 pagesComponent of HVDC Transmission NetworkIqbalilah RamdaniNo ratings yet
- HVDC HandoutDocument40 pagesHVDC Handouts.suresh k.swaminathanNo ratings yet
- Early Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofDocument4 pagesEarly Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofPoonam bhavsarNo ratings yet
- HVDC CourseworkDocument4 pagesHVDC CourseworkNawshin DastagirNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument5 pagesRectifierpreethiNo ratings yet
- Power Inverter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesPower Inverter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSubbaReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 - Harmonics & FiltersDocument10 pagesUnit-5 - Harmonics & Filtersravikumar_ranganNo ratings yet
- Converters and Rectifiers (NEW)Document29 pagesConverters and Rectifiers (NEW)I AM NOT CHINESENo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission SystemDocument2 pagesHVDC Transmission SystemmahmudurbidNo ratings yet
- HVDCDocument32 pagesHVDCSamsung TabletNo ratings yet
- HVDCDocument21 pagesHVDCsubhankarprusty5259No ratings yet
- HVDC and FACTS - PPT PDFDocument19 pagesHVDC and FACTS - PPT PDFManu KasturiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- HVDC Terminal StationDocument28 pagesHVDC Terminal Stationmaka27No ratings yet
- RectifierDocument11 pagesRectifierasislakhaNo ratings yet
- HVDC TransmissionDocument22 pagesHVDC TransmissionheemadaveNo ratings yet
- Study of AC and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and-WPS OfficeBeena PalNo ratings yet
- Derive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitDocument9 pagesDerive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitS DispiserNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power System Analysis - Unit-2Document84 pagesAdvanced Power System Analysis - Unit-2Aryesh Vasudevan NamboodiriNo ratings yet
- DC - AC ConvertorsDocument3 pagesDC - AC Convertorskarthick LNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- Power InverterDocument10 pagesPower Inverterdakshina656087100% (1)
- Rectifier - 1 Half-Wave Rectification - 2 Full-Wave Rectification - Peak Loss - The Full-Wave Bridge - RectifierDocument9 pagesRectifier - 1 Half-Wave Rectification - 2 Full-Wave Rectification - Peak Loss - The Full-Wave Bridge - Rectifierysn_usmaniNo ratings yet
- Equipement Required For HVDC SystemsDocument3 pagesEquipement Required For HVDC Systemsmehta_aakash100No ratings yet
- HVDCDocument80 pagesHVDCJayarajan Jayarajan C NNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionDocument77 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionVijay SaiNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)Document9 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)oeric2kNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument40 pagesDocumentationRajani Kancharla100% (1)
- Major Components of The HVDC Converter Station (Single Line Diagram Explained)Document12 pagesMajor Components of The HVDC Converter Station (Single Line Diagram Explained)Iyung RuslanNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission System: Lectured by Dr. Dong ChenDocument9 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission System: Lectured by Dr. Dong ChenSalem HassaniNo ratings yet
- HVDC 8Document124 pagesHVDC 8Bvijaya krishnaNo ratings yet
- HVDC1Document62 pagesHVDC1n anushaNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConvertorDocument6 pagesDC DC ConvertorFlorin CristiNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument13 pagesReflectionCharlie KingNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsFrom EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNo ratings yet
- II B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016Document2 pagesII B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- I -1 +1 Ic βI I I I or Ico I: II B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016Document2 pagesI -1 +1 Ic βI I I I or Ico I: II B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- S V Engineering College For Women: Eee - ADocument2 pagesS V Engineering College For Women: Eee - ADEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Vemu HVDC NotesDocument125 pagesVemu HVDC NotesDEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Dti Unit 1Document17 pagesDti Unit 1DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Eadsm Unit-IDocument23 pagesEadsm Unit-IDEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Prob. Sheet Basic ConceptsDocument3 pagesProb. Sheet Basic ConceptsAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Welding Rod SpecDocument1 pageWelding Rod SpecMuhammad Hasbi AsidiqiNo ratings yet
- In Mould DuctileDocument6 pagesIn Mould Ductilejose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Chi-Cong Vu, Olivier Plé, Jérôme Weiss, David AmitranoDocument21 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Chi-Cong Vu, Olivier Plé, Jérôme Weiss, David Amitranochristian ricaldi100% (1)
- 4.0 States of MatterDocument13 pages4.0 States of MatterTafadzwa MachongweNo ratings yet
- Film and Dropwise CondensationDocument14 pagesFilm and Dropwise CondensationakpNo ratings yet
- Poster Presentation - BiomimicryDocument1 pagePoster Presentation - BiomimicrySantosh VemulaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Passive Harmonic Filter Using Simulation ToolDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Passive Harmonic Filter Using Simulation TooljigsaiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Frank ColumbusDocument194 pagesReinforced Concrete Frank ColumbusKamilly100% (3)
- Solution Thermodynamics Properties: Engineer Zubair HashmiDocument10 pagesSolution Thermodynamics Properties: Engineer Zubair HashmiMohammadAslamNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument7 pagesCoulomb's LawUnconscious MindNo ratings yet
- ETH Diss 12675Document139 pagesETH Diss 12675nschneebergerNo ratings yet
- MSE 222 Materials Science LabDocument12 pagesMSE 222 Materials Science LabRewanNo ratings yet
- 22 - Ashrafizadeh2017 - Erosive and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Polyurethane LinersDocument24 pages22 - Ashrafizadeh2017 - Erosive and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Polyurethane LinersYargo DuranNo ratings yet
- Crystalloche Istry of V-P-O Phases and Applxcation To CatalysisDocument28 pagesCrystalloche Istry of V-P-O Phases and Applxcation To CatalysisNoel ErkelenzNo ratings yet
- Nickel Titanium Alloys / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument182 pagesNickel Titanium Alloys / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- 5 - Efficient Dielectric Function For FDTD Simulation of The Optical Properties of Silver and Gold NanoparticlesDocument4 pages5 - Efficient Dielectric Function For FDTD Simulation of The Optical Properties of Silver and Gold NanoparticlesMarcio Antônio CostaNo ratings yet
- Swami Vivekananda University M.tech MD Syllabus SEM 1Document7 pagesSwami Vivekananda University M.tech MD Syllabus SEM 1syampnaiduNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit EP BESTDocument12 pagesDC Circuit EP BESThenryNo ratings yet
- L7-9 Transmission Characteristics of Optical FibersDocument75 pagesL7-9 Transmission Characteristics of Optical FibersSami Ullah100% (1)
- Design of One-Way Slab SystemDocument12 pagesDesign of One-Way Slab SystemibrahimNo ratings yet
- Vortex DynamicsDocument15 pagesVortex DynamicsAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- 0625 Thermal Processes - P2 - QPDocument8 pages0625 Thermal Processes - P2 - QPapdrenlNo ratings yet
- 010e Chap-01Document14 pages010e Chap-01Mohamed RabeaNo ratings yet
- 2015 n3 August Industrial Electronics Question Paper PDFDocument9 pages2015 n3 August Industrial Electronics Question Paper PDFNkanyiso ZondiNo ratings yet
- Black Silicon Carbide Grains For Coated Abrasive Applications - SIKA® ABR P Product InformationDocument1 pageBlack Silicon Carbide Grains For Coated Abrasive Applications - SIKA® ABR P Product InformationKhansa LathifahNo ratings yet
- 12.1 PPTDocument14 pages12.1 PPTKingProNo ratings yet
HVDC Transmission Basic Circuit
HVDC Transmission Basic Circuit
Uploaded by
DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEW0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThe document describes the major components of a high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system. It discusses the key components of a converter station including converter units made of thyristor valves arranged in a 12-pulse configuration, converter transformers, filters for alternating current and direct current, and reactive power sources. It also mentions other components like smoothing reactors and direct current switchgear that are part of a converter station.
Original Description:
Original Title
HVDC Transmission basic circuit
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the major components of a high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system. It discusses the key components of a converter station including converter units made of thyristor valves arranged in a 12-pulse configuration, converter transformers, filters for alternating current and direct current, and reactive power sources. It also mentions other components like smoothing reactors and direct current switchgear that are part of a converter station.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesHVDC Transmission Basic Circuit
HVDC Transmission Basic Circuit
Uploaded by
DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWThe document describes the major components of a high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system. It discusses the key components of a converter station including converter units made of thyristor valves arranged in a 12-pulse configuration, converter transformers, filters for alternating current and direct current, and reactive power sources. It also mentions other components like smoothing reactors and direct current switchgear that are part of a converter station.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
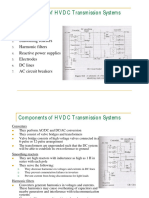
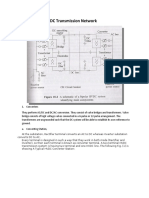
1.4 Description of DC transmission system
The major components of a HVDC transmission system are converter stations
where conversions from AC to DC (Rectifier station) and from DC to AC (Inverter
station) are performed. A point to point transmission requires two converter stations. The
role of rectifier and inverter stations can be reversed (resulting in power reversals) by
suitable converter control. A typical converter station with two 12 pulse converter units
per pole is shown in figure below. The block diagram of converter station is given above.
Figure 1.4.1 Schematic diagram of a typical HVDC converter station
[Source: “HVDC Power Transmission Systems” by K.P.Padiyar, page-11]
Converter Unit:
This usually consists of two three phase converter bridges connected in series to form a
12 pulse converter unit as shown in above figure. The total number of valves in such a
unit is twelve.
EE8017 HIGH VOLTAGE DC TRANSMISSION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Figure 1.4.2 12-pulse converter station
[Source: “HVDC Power Transmission Systems” by K.P.Padiyar, page-12]
The valves can be packaged as single valve, double valve or quadrivalve
arrangements. Each valve is used to switch in segment of an AC voltage waveform. The
converter is fed by converter transformers connected in star/star and star/delta
arrangements.
The valves are cooled by air, oil, water of freon. Liquid cooling using deionized
water is more efficient and results in the reduction of station losses. The design of valves
is based on the modular concept where each module contains a limited number of series
connected thyristor levels.
Valve firing signals are generated in the converter control at ground potential and
are transmitted to each thyristor in the valve through a fiber optic light guide system.
The valves are protected using snubber circuits, protective firing and gapless surge
arrestors.
Converter Transformer:
The converter transformer has three different configurations-
(i) three phase, two winding,
(ii) single phase, three winding and
(iii) single phase, two winding
The valve side windings are connected in parallel with neutral grounded. The
leakage reactance of the transformer is chosen to limit the short circuit currents
through any valves.
EE8017 HIGH VOLTAGE DC TRANSMISSION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
The converter transformers are designed to withstand DC voltage stresses and
increased eddy current losses due to harmonic currents. One problem that can arise is
due to the DC magnetization of the core due to unsymmetrical firing of valves.
Filters:
There are three types of filters used which are
1. AC Filters:
These are passive circuits used to provide how impedance, shunt paths for
AC harmonic currents. Both tuned and damped filter arrangements are used.
2. DC Filters:
These are similar to AC filters and are used for the filtering of DC
harmonics.
3. High Frequency (RF/PLC) Filters:
These are connected between the converter transformer and the station AC
bus to suppress any high frequency currents. Sometimes such filters are provided on high-
voltage DC bus connected between the DC filter and DC line and also on the neutral side.
Reactive power source:
Converter stations require reactive power supply that is dependent on the active
power loading. But part of the reactive power requirement is provided by AC filters. In
addition, shunt capacitors, synchronous condensors and static VAR systems are used
depending on the speed of control desired.
Smoothing Reactor:
A sufficiently large series reactor is used on DC side to smooth DC current and
also for protection. The reactor is designed as a linear reactor and is connected on the line
side, neutral side or at intermediate location.
DC Switchgear:
It is modified AC equipment used to interrupt small DC currents. DC breakers or
Metallic Return Transfer Breakers (MRTB) are used, if required for interruption of rated
load currents.
In addition to the DC switchgear, AC switchgear and associated equipment for
protection and measurement are also part of the converter station.
EE8017 HIGH VOLTAGE DC TRANSMISSION
You might also like
- Romualdi 1964Document16 pagesRomualdi 1964Isabela LauferNo ratings yet
- MTC-2 - Service STRCDocument1 pageMTC-2 - Service STRCHema NandhNo ratings yet
- HVDC ReportDocument43 pagesHVDC ReportD Sreenivas KarthikNo ratings yet
- HVDC Unit IIDocument20 pagesHVDC Unit IISaduMunisekharNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationmeraatNo ratings yet
- HVDC PPTDocument34 pagesHVDC PPTBattinapati Shiva100% (1)
- WINSEM2023-24 BEEE406L TH VL2023240502855 2024-03-12 Reference-Material-IDocument14 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BEEE406L TH VL2023240502855 2024-03-12 Reference-Material-IRahul ganthNo ratings yet
- Commutation in HVDCDocument8 pagesCommutation in HVDCUsama ZafarNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Part 2Document41 pagesHVDC Transmission Part 2srinimeha@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- HVDC Lecture 2Document18 pagesHVDC Lecture 2MuHammad AbuNaga0% (1)
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission SystemDocument45 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission SystemPramod DadmalNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document78 pagesFinal 1Steve JantzenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HVDC TransmissionDocument25 pagesChapter 5 HVDC TransmissionTalha Khanzada100% (1)
- HVDC 1Document73 pagesHVDC 1Adani PowerNo ratings yet
- 3 Level InverterDocument63 pages3 Level InverterThirumal ValavanNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationRajmohan100% (1)
- Industrial Visit Report MeghaDocument21 pagesIndustrial Visit Report MeghaMegha SaranNo ratings yet
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 246Document1 pageSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 246mydearteacherNo ratings yet
- HVDC TransmissionDocument26 pagesHVDC TransmissionAditya TiwariNo ratings yet
- p185 PDFDocument24 pagesp185 PDFதமிழன்No ratings yet
- Ijset 2014 201Document7 pagesIjset 2014 201Innovative Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase RectificationDocument30 pages3 Phase RectificationKobby Brine100% (1)
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument25 pagesEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Power InverterDocument11 pagesPower Inverterriz2010No ratings yet
- Component of HVDC Transmission NetworkDocument5 pagesComponent of HVDC Transmission NetworkIqbalilah RamdaniNo ratings yet
- HVDC HandoutDocument40 pagesHVDC Handouts.suresh k.swaminathanNo ratings yet
- Early Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofDocument4 pagesEarly Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofPoonam bhavsarNo ratings yet
- HVDC CourseworkDocument4 pagesHVDC CourseworkNawshin DastagirNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument5 pagesRectifierpreethiNo ratings yet
- Power Inverter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesPower Inverter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSubbaReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 - Harmonics & FiltersDocument10 pagesUnit-5 - Harmonics & Filtersravikumar_ranganNo ratings yet
- Converters and Rectifiers (NEW)Document29 pagesConverters and Rectifiers (NEW)I AM NOT CHINESENo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission SystemDocument2 pagesHVDC Transmission SystemmahmudurbidNo ratings yet
- HVDCDocument32 pagesHVDCSamsung TabletNo ratings yet
- HVDCDocument21 pagesHVDCsubhankarprusty5259No ratings yet
- HVDC and FACTS - PPT PDFDocument19 pagesHVDC and FACTS - PPT PDFManu KasturiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- HVDC Terminal StationDocument28 pagesHVDC Terminal Stationmaka27No ratings yet
- RectifierDocument11 pagesRectifierasislakhaNo ratings yet
- HVDC TransmissionDocument22 pagesHVDC TransmissionheemadaveNo ratings yet
- Study of AC and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and-WPS OfficeBeena PalNo ratings yet
- Derive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitDocument9 pagesDerive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitS DispiserNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power System Analysis - Unit-2Document84 pagesAdvanced Power System Analysis - Unit-2Aryesh Vasudevan NamboodiriNo ratings yet
- DC - AC ConvertorsDocument3 pagesDC - AC Convertorskarthick LNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- Power InverterDocument10 pagesPower Inverterdakshina656087100% (1)
- Rectifier - 1 Half-Wave Rectification - 2 Full-Wave Rectification - Peak Loss - The Full-Wave Bridge - RectifierDocument9 pagesRectifier - 1 Half-Wave Rectification - 2 Full-Wave Rectification - Peak Loss - The Full-Wave Bridge - Rectifierysn_usmaniNo ratings yet
- Equipement Required For HVDC SystemsDocument3 pagesEquipement Required For HVDC Systemsmehta_aakash100No ratings yet
- HVDCDocument80 pagesHVDCJayarajan Jayarajan C NNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionDocument77 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionVijay SaiNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)Document9 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)oeric2kNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument40 pagesDocumentationRajani Kancharla100% (1)
- Major Components of The HVDC Converter Station (Single Line Diagram Explained)Document12 pagesMajor Components of The HVDC Converter Station (Single Line Diagram Explained)Iyung RuslanNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission System: Lectured by Dr. Dong ChenDocument9 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission System: Lectured by Dr. Dong ChenSalem HassaniNo ratings yet
- HVDC 8Document124 pagesHVDC 8Bvijaya krishnaNo ratings yet
- HVDC1Document62 pagesHVDC1n anushaNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConvertorDocument6 pagesDC DC ConvertorFlorin CristiNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument13 pagesReflectionCharlie KingNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsFrom EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNo ratings yet
- II B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016Document2 pagesII B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- I -1 +1 Ic βI I I I or Ico I: II B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016Document2 pagesI -1 +1 Ic βI I I I or Ico I: II B.Tech I Semester II Midterm (Objective) Examinations November-2016DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- S V Engineering College For Women: Eee - ADocument2 pagesS V Engineering College For Women: Eee - ADEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Vemu HVDC NotesDocument125 pagesVemu HVDC NotesDEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Dti Unit 1Document17 pagesDti Unit 1DEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Eadsm Unit-IDocument23 pagesEadsm Unit-IDEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- Prob. Sheet Basic ConceptsDocument3 pagesProb. Sheet Basic ConceptsAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Welding Rod SpecDocument1 pageWelding Rod SpecMuhammad Hasbi AsidiqiNo ratings yet
- In Mould DuctileDocument6 pagesIn Mould Ductilejose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Chi-Cong Vu, Olivier Plé, Jérôme Weiss, David AmitranoDocument21 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Chi-Cong Vu, Olivier Plé, Jérôme Weiss, David Amitranochristian ricaldi100% (1)
- 4.0 States of MatterDocument13 pages4.0 States of MatterTafadzwa MachongweNo ratings yet
- Film and Dropwise CondensationDocument14 pagesFilm and Dropwise CondensationakpNo ratings yet
- Poster Presentation - BiomimicryDocument1 pagePoster Presentation - BiomimicrySantosh VemulaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Passive Harmonic Filter Using Simulation ToolDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Passive Harmonic Filter Using Simulation TooljigsaiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Frank ColumbusDocument194 pagesReinforced Concrete Frank ColumbusKamilly100% (3)
- Solution Thermodynamics Properties: Engineer Zubair HashmiDocument10 pagesSolution Thermodynamics Properties: Engineer Zubair HashmiMohammadAslamNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument7 pagesCoulomb's LawUnconscious MindNo ratings yet
- ETH Diss 12675Document139 pagesETH Diss 12675nschneebergerNo ratings yet
- MSE 222 Materials Science LabDocument12 pagesMSE 222 Materials Science LabRewanNo ratings yet
- 22 - Ashrafizadeh2017 - Erosive and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Polyurethane LinersDocument24 pages22 - Ashrafizadeh2017 - Erosive and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Polyurethane LinersYargo DuranNo ratings yet
- Crystalloche Istry of V-P-O Phases and Applxcation To CatalysisDocument28 pagesCrystalloche Istry of V-P-O Phases and Applxcation To CatalysisNoel ErkelenzNo ratings yet
- Nickel Titanium Alloys / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument182 pagesNickel Titanium Alloys / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- 5 - Efficient Dielectric Function For FDTD Simulation of The Optical Properties of Silver and Gold NanoparticlesDocument4 pages5 - Efficient Dielectric Function For FDTD Simulation of The Optical Properties of Silver and Gold NanoparticlesMarcio Antônio CostaNo ratings yet
- Swami Vivekananda University M.tech MD Syllabus SEM 1Document7 pagesSwami Vivekananda University M.tech MD Syllabus SEM 1syampnaiduNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit EP BESTDocument12 pagesDC Circuit EP BESThenryNo ratings yet
- L7-9 Transmission Characteristics of Optical FibersDocument75 pagesL7-9 Transmission Characteristics of Optical FibersSami Ullah100% (1)
- Design of One-Way Slab SystemDocument12 pagesDesign of One-Way Slab SystemibrahimNo ratings yet
- Vortex DynamicsDocument15 pagesVortex DynamicsAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- 0625 Thermal Processes - P2 - QPDocument8 pages0625 Thermal Processes - P2 - QPapdrenlNo ratings yet
- 010e Chap-01Document14 pages010e Chap-01Mohamed RabeaNo ratings yet
- 2015 n3 August Industrial Electronics Question Paper PDFDocument9 pages2015 n3 August Industrial Electronics Question Paper PDFNkanyiso ZondiNo ratings yet
- Black Silicon Carbide Grains For Coated Abrasive Applications - SIKA® ABR P Product InformationDocument1 pageBlack Silicon Carbide Grains For Coated Abrasive Applications - SIKA® ABR P Product InformationKhansa LathifahNo ratings yet
- 12.1 PPTDocument14 pages12.1 PPTKingProNo ratings yet