Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsBiochem Reviewer
Biochem Reviewer
Uploaded by
realistic0830The document discusses biochemical topics including:
- Fructose is found in grapes and lactose is composed of glucose and galactose.
- Glycogen, proteins, fatty acids, and nucleic acids play various structural and functional roles in cells and organisms.
- Cellular respiration involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to oxidize glucose and produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.
- Aerobic respiration generates more ATP than anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid and alcohol fermentations are anaerobic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Metabolism Exam Questions2Document4 pagesMetabolism Exam Questions2Hussein Al SaediNo ratings yet
- Rr322302 Analytical Techniques in BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesRr322302 Analytical Techniques in Biotechnologygeddam06108825No ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument27 pagesCell RespirationJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument3 pagesBioenergeticslai weng hongNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationCJ100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 21 RespiDocument48 pagesBio Lesson 21 RespiChlzy ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationDocument4 pagesHsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- Bio I - CHP 7 Workfile UploadDocument2 pagesBio I - CHP 7 Workfile Uploadcynthia lottNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Is AnDocument4 pagesGlycolysis Is AnKarla RubinNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsjanakiramannadesanNo ratings yet
- 2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoDocument6 pages2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoLucas BuSheaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-MetabolismDocument103 pagesUnit 8-Metabolismnumberr515No ratings yet
- PhyicsDocument4 pagesPhyicsRider 006No ratings yet
- An Overview of Glycolysis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Glycolysis and Cellular Respirationabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Introduction To Cellular RespirationDocument14 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To Cellular Respirationbabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 6Document35 pagesBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument18 pagesAnaerobic Respiration and FermentationSean Nixter BallestraNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1w7Document9 pagesScience 9 q1w7seanfelix07102009No ratings yet
- Joenni Hans (2301884362) Basic Food Biochemistry: MetabolismDocument6 pagesJoenni Hans (2301884362) Basic Food Biochemistry: Metabolismjoenni hansNo ratings yet
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- 228 Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument43 pages228 Carbohydrate MetabolismAmanullahNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument19 pagesCarbohydratesNaina YadavvNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesCellular RespirationInday 123No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Metabolism Summary Ch25Document8 pagesMetabolism Summary Ch25Victor EkutaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Chemical EnergyDocument43 pagesHow Cells Release Chemical EnergyDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of FoodDocument13 pagesBiological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of Foodsagar sagu100% (1)
- Ellular Espiration: Big PictureDocument3 pagesEllular Espiration: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Microbio Metabolism LectureDocument32 pagesMicrobio Metabolism LecturesweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- 8 3Document22 pages8 3lianneNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويDocument9 pagesCellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويIraqiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument16 pagesCitric Acid CycleStarNo ratings yet
- FATTY ACID OXIDATION (Beta-Oxidation) ...Document9 pagesFATTY ACID OXIDATION (Beta-Oxidation) ...atifzeaNo ratings yet
- Fermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02Document14 pagesFermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02skNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismDocument8 pagesPHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismsydneykatelynnNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio Reviewer 2nd QuarterauroraroderosNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDocument60 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaFerybkiAyubNo ratings yet
- Fermentation and RespirationDocument45 pagesFermentation and RespirationNedhal Mahmoud KaleefahNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument8 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismJessicaOktavianusNo ratings yet
- CellRespi 2Document21 pagesCellRespi 2Nudiya SappalNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument37 pagesCellular Respirationamarali11420222No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationDocument10 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationIan Gabriel MayoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anabolic Metabolism Lipid MetabolismDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Anabolic Metabolism Lipid MetabolismAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesDifference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleKuresh RabidNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022Document59 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 2022Catherine SilokaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument25 pagesCellular RespirationLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument14 pages4 - Metabolism of CarbohydratesmooshadabNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument19 pagesGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 9Document11 pagesGeneral Biology 9aleenloli95No ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science-ConstellationDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Science-Constellationrealistic0830No ratings yet
- Grade 9science LP ClimatechangeDocument1 pageGrade 9science LP Climatechangerealistic0830No ratings yet
- Grade 9science LPDocument1 pageGrade 9science LPrealistic0830No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument2 pagesCHEMISTRYrealistic0830No ratings yet
- SPED MELCsDocument7 pagesSPED MELCsrealistic0830No ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Protein SynthesisDocument27 pagesGenetic Control of Protein SynthesisDICKSONNo ratings yet
- MBS-FTA Card Sample Collection InstructionDocument2 pagesMBS-FTA Card Sample Collection InstructionGandi SogandiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of E.coli PathogenicityDocument13 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of E.coli PathogenicityJonatan SBNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument74 pagesDNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisNabilah Rizky Khairunnisa100% (1)
- Wa0028Document3 pagesWa0028Mohit MishraNo ratings yet
- 90 MCQ Cell BiologyDocument92 pages90 MCQ Cell BiologyAnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Supercoiling of DNA: 1. TopologyDocument29 pagesSupercoiling of DNA: 1. TopologybiolimNo ratings yet
- List of Candidates For Appointment As Assistant Professor On Ad-Hoc Basis For Biomedical Sciences (Supplementary Panel) (General Category)Document18 pagesList of Candidates For Appointment As Assistant Professor On Ad-Hoc Basis For Biomedical Sciences (Supplementary Panel) (General Category)asanyogNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Morfologi, Biokimia, Dan Molekuler Isolat Khamir Ik-2 Hasil Isolasi Dari Jus Buah Sirsak (Annona Muricata L.)Document8 pagesKarakteristik Morfologi, Biokimia, Dan Molekuler Isolat Khamir Ik-2 Hasil Isolasi Dari Jus Buah Sirsak (Annona Muricata L.)Rauzah SaniraNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Memory Consolidation: The Role of RNA-binding Proteins With Prion-Like DomainsDocument19 pagesLong-Term Memory Consolidation: The Role of RNA-binding Proteins With Prion-Like DomainsfaizNo ratings yet
- AyadDocument12 pagesAyadKinaNo ratings yet
- MetabolismeDocument33 pagesMetabolismeNiza LailaNo ratings yet
- Vessel CompatibilityDocument2 pagesVessel CompatibilitydnajenNo ratings yet
- A Sublime Technique To Solve DNA Repair ModelDocument6 pagesA Sublime Technique To Solve DNA Repair Modelmohit.aryaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1 Mod6 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration v3Document45 pagesScience 9 q1 Mod6 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration v3Keith Kevin Dave DandanNo ratings yet
- Biology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellDocument8 pagesBiology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellmIZZshaNaNo ratings yet
- Immun-Blot® PVDF Membrane For Protein Blotting Instruction ManualDocument9 pagesImmun-Blot® PVDF Membrane For Protein Blotting Instruction ManualdnajenNo ratings yet
- Genome Wide Association Studies and Genomic Selection - Promises and PremisesDocument16 pagesGenome Wide Association Studies and Genomic Selection - Promises and Premisessalman672003No ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunoassaysDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Immunoassaysvidhi100% (1)
- DNA Mutation RatesDocument37 pagesDNA Mutation RatesSean Pitman, MDNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetAshley JohnsNo ratings yet
- MTPC 140: Molecular Biology and DiagnosticsDocument17 pagesMTPC 140: Molecular Biology and DiagnosticsValdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDocument12 pagesTransfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDiana Gabriela NinaNo ratings yet
- CH 17 KEYDocument5 pagesCH 17 KEYJohnathan BeversNo ratings yet
- Chemie Ingenieur Technik - 2022 - Palm - Development and Characterization of SpyCatcher Glycosyltransferase Fusion ProteinsDocument1 pageChemie Ingenieur Technik - 2022 - Palm - Development and Characterization of SpyCatcher Glycosyltransferase Fusion ProteinsZ MaNo ratings yet
- G22 Serapion-Module 9 EnzymesDocument3 pagesG22 Serapion-Module 9 Enzymestherese angelieNo ratings yet
- Ich GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIch GuidelinesVijay RavindranathNo ratings yet
- ABO Grouping BB LabDocument5 pagesABO Grouping BB LabBless MarieNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Sentiment Analyze Craft and Structure Page 344. Read Pages 338-340 HW: Read Pages 341-342Document12 pagesDeclaration of Sentiment Analyze Craft and Structure Page 344. Read Pages 338-340 HW: Read Pages 341-342يزن جانسيزNo ratings yet
Biochem Reviewer
Biochem Reviewer
Uploaded by
realistic08300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe document discusses biochemical topics including:
- Fructose is found in grapes and lactose is composed of glucose and galactose.
- Glycogen, proteins, fatty acids, and nucleic acids play various structural and functional roles in cells and organisms.
- Cellular respiration involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to oxidize glucose and produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.
- Aerobic respiration generates more ATP than anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid and alcohol fermentations are anaerobic processes.
Original Description:
Review
Original Title
BIOCHEM-REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses biochemical topics including:
- Fructose is found in grapes and lactose is composed of glucose and galactose.
- Glycogen, proteins, fatty acids, and nucleic acids play various structural and functional roles in cells and organisms.
- Cellular respiration involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to oxidize glucose and produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.
- Aerobic respiration generates more ATP than anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid and alcohol fermentations are anaerobic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesBiochem Reviewer
Biochem Reviewer
Uploaded by
realistic0830The document discusses biochemical topics including:
- Fructose is found in grapes and lactose is composed of glucose and galactose.
- Glycogen, proteins, fatty acids, and nucleic acids play various structural and functional roles in cells and organisms.
- Cellular respiration involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to oxidize glucose and produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.
- Aerobic respiration generates more ATP than anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid and alcohol fermentations are anaerobic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
BIOCHEM
The simple sugar that we can found from grapes is fructose.
C12H22O11 is a disaccharide.
The molecule of glucose has same number of hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms.
Lactose is composed of glucose and galactose.
Most mammals are unable to metabolize cellulose and lactose.
Glycogen is a highly-branched polysaccharide found in animals.
Transport proteins serve as a channel across biological membranes that allow their substrate to pass.
Defensive proteins help in producing antibodies to help your immune system from foreign bodies.
Contractile proteins mediate sliding and shrinking fibers of a cell’s cytoskeleton.
Enzyme is a protein that serve as a chemical catalyst that changes the rate of chemical reaction.
Structural protein is responsible for functions ranging from cell shape and movement.
Palmitoleic acid is a common constituent of glycerides of human adipose tissue and generally found in liver.
Omega-6 is a fatty acid which is colorless liquid at room temperature.
Oleic acid is found in animal and vegetable sources like insects such as bees and ants.
Trans fat is fat that do not promote good health and is toxic for the body. Also present in junk food.
Omega-3 is a family of unsaturated fatty acids that benefits the health to prevent cancerous and lifetime diseases.
Triglyceride functions as a long-term energy storage that contain three (3) fatty acids attached to each glycerol molecule,
fat and oil.
Types of nucleic acids: DNA, RNA, double-helix molecule
DNA: A-T, C-G / RNA: A-U, C-G
Untrue about nucleic acid: DNA is single-stranded in some viruses.
Photosynthesis and respiration both occur in plants.
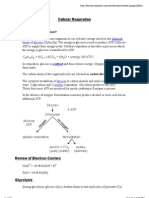
Two (2) ATP molecules are used in the initial steps and four are produced in the latter stages, for a net gain of two (2)
ATP molecules.
Pyruvate is a 3-carbon molecule and is one of the final products of glycolysis.
ATP Math -2+4=2
Glycolysis produces ATP, pyruvate, and NADH by oxidizing glucose.
The breakdown of sugar takes place in Cytoplasm.
Pyruvate is transformed into Acetyl CoA and CO2 in preparatory phase.
Acetyl CoA is responsible in breaking down pyruvate.
Cellular Respiration is the “charging station”.
Cellular Respiration do not turn NADH and NAD+, instead, it produces 2 net ATP, converts ADP to ATP and produces 38
ATP up to ETC.
When a plant produces 4 pyruvates after the process of glycolysis. It will have 4 Acetyl CoA and 4 CO2 after the prep
stage.
Mitochondria is the organelle where Kreb’s cycle and the beginning of prep step occur.
Aerobic respiration is the continuing process to produce more energy.
There is more energy in aerobic (38) compare to anaerobic (2).
Aerobic Respiration is essential for alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation.
NADH and FADH2 are the products of Kreb’s Cycle essential for oxidative phosphorylation.
Single molecule of glucose generates 2 molecules of Acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA is formed from pyruvate by oxidative decarboxylation reaction.
During the Kreb’s cycle, Isocitrate, Succinate are formed, not lactate.
Mitochondrial matrix is the organelle responsible in conducting the process of Kreb’s cycle.
Acetyl CoA is the carbon compound that enters the Krebs cycle and serve as an indicator to start the process.
In converting succinate to fumerate, FADH2 is produced.
In converting ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA, CO2 and NADH are produced.
Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetate = Citrate
Oxidation is the loss of electrons caused by oxidizing agents.
Electron Transport System is present in inter-membrane space.
ATP synthesis by ATP synthase is driven by the movement of protons.
Oxidative Phosphorylation results in the formation of ATP+H2O.
PO4 is added to ADP to produce ATP at the end of ETC.
O2+4E-+4H+ = 2 H2O in ETC.
ETC has nothing to do with FAD.
Oxygen molecule is absent during alcohol fermentation.
Ethanol and CO2 are products of alcohol fermentation.
Butter making is not a common use of yeast for alcohol fermentation.
Ethanol is produces when pyruvate undergoes decarboxylation.
Muscle cells sometimes turn to lactic acid fermentation when they do not receive enough oxygen during strenuous
exercise.
You might also like
- Metabolism Exam Questions2Document4 pagesMetabolism Exam Questions2Hussein Al SaediNo ratings yet
- Rr322302 Analytical Techniques in BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesRr322302 Analytical Techniques in Biotechnologygeddam06108825No ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument27 pagesCell RespirationJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument3 pagesBioenergeticslai weng hongNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationCJ100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 21 RespiDocument48 pagesBio Lesson 21 RespiChlzy ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationDocument4 pagesHsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- Bio I - CHP 7 Workfile UploadDocument2 pagesBio I - CHP 7 Workfile Uploadcynthia lottNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Is AnDocument4 pagesGlycolysis Is AnKarla RubinNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsjanakiramannadesanNo ratings yet
- 2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoDocument6 pages2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoLucas BuSheaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-MetabolismDocument103 pagesUnit 8-Metabolismnumberr515No ratings yet
- PhyicsDocument4 pagesPhyicsRider 006No ratings yet
- An Overview of Glycolysis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Glycolysis and Cellular Respirationabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Introduction To Cellular RespirationDocument14 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To Cellular Respirationbabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 6Document35 pagesBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument18 pagesAnaerobic Respiration and FermentationSean Nixter BallestraNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1w7Document9 pagesScience 9 q1w7seanfelix07102009No ratings yet
- Joenni Hans (2301884362) Basic Food Biochemistry: MetabolismDocument6 pagesJoenni Hans (2301884362) Basic Food Biochemistry: Metabolismjoenni hansNo ratings yet
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- 228 Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument43 pages228 Carbohydrate MetabolismAmanullahNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument19 pagesCarbohydratesNaina YadavvNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesCellular RespirationInday 123No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Metabolism Summary Ch25Document8 pagesMetabolism Summary Ch25Victor EkutaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Chemical EnergyDocument43 pagesHow Cells Release Chemical EnergyDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of FoodDocument13 pagesBiological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of Foodsagar sagu100% (1)
- Ellular Espiration: Big PictureDocument3 pagesEllular Espiration: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Microbio Metabolism LectureDocument32 pagesMicrobio Metabolism LecturesweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- 8 3Document22 pages8 3lianneNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويDocument9 pagesCellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويIraqiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument16 pagesCitric Acid CycleStarNo ratings yet
- FATTY ACID OXIDATION (Beta-Oxidation) ...Document9 pagesFATTY ACID OXIDATION (Beta-Oxidation) ...atifzeaNo ratings yet
- Fermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02Document14 pagesFermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02skNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismDocument8 pagesPHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismsydneykatelynnNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio Reviewer 2nd QuarterauroraroderosNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDocument60 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaFerybkiAyubNo ratings yet
- Fermentation and RespirationDocument45 pagesFermentation and RespirationNedhal Mahmoud KaleefahNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument8 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismJessicaOktavianusNo ratings yet
- CellRespi 2Document21 pagesCellRespi 2Nudiya SappalNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument37 pagesCellular Respirationamarali11420222No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationDocument10 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationIan Gabriel MayoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anabolic Metabolism Lipid MetabolismDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Anabolic Metabolism Lipid MetabolismAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesDifference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleKuresh RabidNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022Document59 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 2022Catherine SilokaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument25 pagesCellular RespirationLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument14 pages4 - Metabolism of CarbohydratesmooshadabNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument19 pagesGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 9Document11 pagesGeneral Biology 9aleenloli95No ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science-ConstellationDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Science-Constellationrealistic0830No ratings yet
- Grade 9science LP ClimatechangeDocument1 pageGrade 9science LP Climatechangerealistic0830No ratings yet
- Grade 9science LPDocument1 pageGrade 9science LPrealistic0830No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument2 pagesCHEMISTRYrealistic0830No ratings yet
- SPED MELCsDocument7 pagesSPED MELCsrealistic0830No ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Protein SynthesisDocument27 pagesGenetic Control of Protein SynthesisDICKSONNo ratings yet
- MBS-FTA Card Sample Collection InstructionDocument2 pagesMBS-FTA Card Sample Collection InstructionGandi SogandiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of E.coli PathogenicityDocument13 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of E.coli PathogenicityJonatan SBNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument74 pagesDNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisNabilah Rizky Khairunnisa100% (1)
- Wa0028Document3 pagesWa0028Mohit MishraNo ratings yet
- 90 MCQ Cell BiologyDocument92 pages90 MCQ Cell BiologyAnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Supercoiling of DNA: 1. TopologyDocument29 pagesSupercoiling of DNA: 1. TopologybiolimNo ratings yet
- List of Candidates For Appointment As Assistant Professor On Ad-Hoc Basis For Biomedical Sciences (Supplementary Panel) (General Category)Document18 pagesList of Candidates For Appointment As Assistant Professor On Ad-Hoc Basis For Biomedical Sciences (Supplementary Panel) (General Category)asanyogNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Morfologi, Biokimia, Dan Molekuler Isolat Khamir Ik-2 Hasil Isolasi Dari Jus Buah Sirsak (Annona Muricata L.)Document8 pagesKarakteristik Morfologi, Biokimia, Dan Molekuler Isolat Khamir Ik-2 Hasil Isolasi Dari Jus Buah Sirsak (Annona Muricata L.)Rauzah SaniraNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Memory Consolidation: The Role of RNA-binding Proteins With Prion-Like DomainsDocument19 pagesLong-Term Memory Consolidation: The Role of RNA-binding Proteins With Prion-Like DomainsfaizNo ratings yet
- AyadDocument12 pagesAyadKinaNo ratings yet
- MetabolismeDocument33 pagesMetabolismeNiza LailaNo ratings yet
- Vessel CompatibilityDocument2 pagesVessel CompatibilitydnajenNo ratings yet
- A Sublime Technique To Solve DNA Repair ModelDocument6 pagesA Sublime Technique To Solve DNA Repair Modelmohit.aryaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1 Mod6 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration v3Document45 pagesScience 9 q1 Mod6 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration v3Keith Kevin Dave DandanNo ratings yet
- Biology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellDocument8 pagesBiology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellmIZZshaNaNo ratings yet
- Immun-Blot® PVDF Membrane For Protein Blotting Instruction ManualDocument9 pagesImmun-Blot® PVDF Membrane For Protein Blotting Instruction ManualdnajenNo ratings yet
- Genome Wide Association Studies and Genomic Selection - Promises and PremisesDocument16 pagesGenome Wide Association Studies and Genomic Selection - Promises and Premisessalman672003No ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunoassaysDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Immunoassaysvidhi100% (1)
- DNA Mutation RatesDocument37 pagesDNA Mutation RatesSean Pitman, MDNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetAshley JohnsNo ratings yet
- MTPC 140: Molecular Biology and DiagnosticsDocument17 pagesMTPC 140: Molecular Biology and DiagnosticsValdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDocument12 pagesTransfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDiana Gabriela NinaNo ratings yet
- CH 17 KEYDocument5 pagesCH 17 KEYJohnathan BeversNo ratings yet
- Chemie Ingenieur Technik - 2022 - Palm - Development and Characterization of SpyCatcher Glycosyltransferase Fusion ProteinsDocument1 pageChemie Ingenieur Technik - 2022 - Palm - Development and Characterization of SpyCatcher Glycosyltransferase Fusion ProteinsZ MaNo ratings yet
- G22 Serapion-Module 9 EnzymesDocument3 pagesG22 Serapion-Module 9 Enzymestherese angelieNo ratings yet
- Ich GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIch GuidelinesVijay RavindranathNo ratings yet
- ABO Grouping BB LabDocument5 pagesABO Grouping BB LabBless MarieNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Sentiment Analyze Craft and Structure Page 344. Read Pages 338-340 HW: Read Pages 341-342Document12 pagesDeclaration of Sentiment Analyze Craft and Structure Page 344. Read Pages 338-340 HW: Read Pages 341-342يزن جانسيزNo ratings yet