Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seance TD1 Haigh Exercise
Seance TD1 Haigh Exercise
Uploaded by
mohamed ouaidCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Workout Plan No 3981212179Document32 pagesWorkout Plan No 3981212179Kiana RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kelistrikan KapalDocument14 pagesSistem Kelistrikan KapalJohann Sjbt94% (17)
- 03 Speakout Reading Listening Extra Pre Intermediate With KeyDocument14 pages03 Speakout Reading Listening Extra Pre Intermediate With Keywai phyo67% (3)
- HW 9Document2 pagesHW 9azizieh5701No ratings yet
- Blogilates Meal PlanDocument6 pagesBlogilates Meal PlanSiennaNo ratings yet
- Yoga HandoutDocument2 pagesYoga Handoutapi-587969236No ratings yet
- Fatigue Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesFatigue Practice ProblemsBoyzz ChinNo ratings yet
- Precast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350Document55 pagesPrecast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350civixxNo ratings yet
- Mech6036 40Document20 pagesMech6036 40Vikas Keshari100% (1)
- TD MRDocument4 pagesTD MRahmed ghassoulNo ratings yet
- Sahyd c23 EngDocument7 pagesSahyd c23 EngDragos NackaNo ratings yet
- Wave Equation Analysis of Driven Piles: Lecture #14Document8 pagesWave Equation Analysis of Driven Piles: Lecture #14Eric Juana PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - FluctatingLoadDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 - FluctatingLoadSanthosh AmaraNo ratings yet
- Design Standards and SpecsDocument9 pagesDesign Standards and SpecsDenise Ann CuencaNo ratings yet
- Technical Report 2 - FatigueDocument3 pagesTechnical Report 2 - FatigueBhartendu TavriNo ratings yet
- MDoT Sample Exam PaperDocument22 pagesMDoT Sample Exam PapersamdelcalNo ratings yet
- Et 11Document2 pagesEt 11Thiet PhamNo ratings yet
- Ram HBMDocument12 pagesRam HBMkkkoooNo ratings yet
- Part (A) : Ship Stability : Ports and Maritime Organization Seafarer's Examination and Certification DirectorateDocument1 pagePart (A) : Ship Stability : Ports and Maritime Organization Seafarer's Examination and Certification DirectorateJim JimiNo ratings yet
- Machine Lab CombineDocument38 pagesMachine Lab Combinelakha ramNo ratings yet
- Naval Architecture18Document6 pagesNaval Architecture18Thiet PhamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-3 For Industrial Electronics SCRDocument2 pagesAssignment 2-3 For Industrial Electronics SCRPranjal GaurNo ratings yet
- Module-2b Fatigue Strength (Bhaskar)Document35 pagesModule-2b Fatigue Strength (Bhaskar)AckshayaNo ratings yet
- Design 09b 2Document4 pagesDesign 09b 2Jim BennyNo ratings yet
- ENG782S2Document8 pagesENG782S2Emperor RocaNo ratings yet
- FEMtutorial Bits30026Document47 pagesFEMtutorial Bits300262023ht30176No ratings yet
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1aa8846No ratings yet
- Material 7Document18 pagesMaterial 7Giannis ZarogiannisNo ratings yet
- Dam I33Document47 pagesDam I33Trung ConNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IiDocument3 pagesAssignment - IichritNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Maintain Load Test Using Anchor Reaction SystemDocument17 pagesMethod Statement For Maintain Load Test Using Anchor Reaction Systemchin thye limNo ratings yet
- Engi4258 Assignments Set1 SolutionsDocument29 pagesEngi4258 Assignments Set1 SolutionscristinacintiaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution MachineDocument2 pagesNumerical Solution Machinenimesh patelNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets (Pre-Stressed) PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Sets (Pre-Stressed) PDFleanne DespaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Desgn For Fatigue Strength - MD - IDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 - Desgn For Fatigue Strength - MD - ISR SuryaNo ratings yet
- FM 1 PDFDocument2 pagesFM 1 PDFVijeesh VijayalayamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1-Design For Static and Fatigue StrengthDocument5 pagesTutorial - 1-Design For Static and Fatigue StrengthSouradeepBhattacharya50% (2)
- Answer: 250Mm, 0.74mpa, 2.75M: Reinforced Concrete - Lecture03 - August2019Document5 pagesAnswer: 250Mm, 0.74mpa, 2.75M: Reinforced Concrete - Lecture03 - August2019hazelNo ratings yet
- 18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Document22 pages18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Thirumal K SNo ratings yet
- Overview:: RemarksDocument5 pagesOverview:: RemarksThinh ViproNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Fluctuating LoadDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Fluctuating Loadabhishek chaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Conductor-Sizing IECDocument2 pagesConductor-Sizing IECnb nbNo ratings yet
- Prolemario 2Document4 pagesProlemario 2Emiliano LozanoNo ratings yet
- 1.02 Ramesh PinjaniDocument16 pages1.02 Ramesh PinjanimchkppNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Combined LoadingDocument51 pagesChapter 8 - Combined Loadingfaiz fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Structural CalculationDocument20 pagesStructural CalculationOmr'GzmnNo ratings yet
- Ahts ProjectDocument39 pagesAhts ProjectSurya Chala PraveenNo ratings yet
- 5.a ME8539 - Question PaperDocument3 pages5.a ME8539 - Question PapersowthaminiNo ratings yet
- 1A - OCC and Load Characteristics of A Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDocument4 pages1A - OCC and Load Characteristics of A Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorAkash MNo ratings yet
- r5310305 Design of Machine Members IDocument1 pager5310305 Design of Machine Members IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- RCD Lecture 4 PDF 2Document19 pagesRCD Lecture 4 PDF 2Paul Zaivan RoldanNo ratings yet
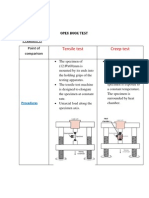
- Open Book Test AnwsersDocument5 pagesOpen Book Test Anwsersإبراهيم مرجاويNo ratings yet
- Railway BridgeDocument21 pagesRailway BridgeAzzahra BilqisNo ratings yet
- 2019物理習題第9回Document6 pages2019物理習題第9回廖亮鈞No ratings yet
- Rr310204-Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageRr310204-Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument22 pagesExercisessiakeehoNo ratings yet
- Pe SS Final Ex 2010Document4 pagesPe SS Final Ex 2010Saif UddinNo ratings yet
- GTP 145 KV CBDocument3 pagesGTP 145 KV CBVipul HavaleNo ratings yet
- Is 6938Document13 pagesIs 6938Dhanashri Patil100% (1)
- Question PapersDocument89 pagesQuestion PapersDreamer ChavanNo ratings yet
- Job 8Document3 pagesJob 8M Usama TabassumNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationFrom EverandShape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination in MAPEH 2019 2020Document5 pages2nd Quarter Examination in MAPEH 2019 2020MinaYaguelValenzuela100% (1)
- Preseason Resistance Training For FootballDocument4 pagesPreseason Resistance Training For FootballSeyfullah DumazNo ratings yet
- Datta WorkOut Upper Lower 2Document27 pagesDatta WorkOut Upper Lower 2designfordummyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Daily Activities: Pair Work. Take Turns. Now Talk About Your Busiest Day of The WeekDocument5 pagesUnit 7 Daily Activities: Pair Work. Take Turns. Now Talk About Your Busiest Day of The WeekWindi MeliyanaNo ratings yet
- Boo OoksDocument3 pagesBoo Ookssiaogila0% (1)
- DBD Week 1 Day 1 - LegsDocument5 pagesDBD Week 1 Day 1 - LegsSaw Min ThuNo ratings yet
- English For Starters 8 - SBDocument100 pagesEnglish For Starters 8 - SBRenz Louie LedseyNo ratings yet
- Pe10 q1 Mod1 Lifestyleandweightmanagement v5Document30 pagesPe10 q1 Mod1 Lifestyleandweightmanagement v5regiegetalla7No ratings yet
- Lower Back Pains ExercisesDocument13 pagesLower Back Pains ExercisesArlhona Juana RagoNo ratings yet
- 31 Hardcore Work Out Finishers FinalDocument24 pages31 Hardcore Work Out Finishers FinalMaxim Borodin90% (10)
- Olymp20159 10dashanrDocument5 pagesOlymp20159 10dashanrHratsin PoghosyanNo ratings yet
- The Tight Tan Slacks of Dezso BanDocument7 pagesThe Tight Tan Slacks of Dezso BanCD KHUTIYALENo ratings yet
- Long WireDocument4 pagesLong Wirelu1agpNo ratings yet
- MUHS BPTH I Year Amended 180609Document22 pagesMUHS BPTH I Year Amended 180609Kumar G PalaniNo ratings yet
- Can Cannot ExerciseDocument4 pagesCan Cannot ExerciseRezky TarihoranNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Q2 M1 PDFDocument40 pagesMapeh 10 Q2 M1 PDFzenqdumbasfNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Look and write: Bài Tập Cơ BảnDocument8 pagesExercise 1: Look and write: Bài Tập Cơ BảnKhánh Linh NghiêmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Visakh A SNo ratings yet
- Part I - Content Update: in The BeginningDocument11 pagesPart I - Content Update: in The BeginningEarshad Shinichi IIINo ratings yet
- Speed Dating TDocument5 pagesSpeed Dating TЛілія ТютінаNo ratings yet
- New-Module-2-PEH 12-Outdoor Reacreational ActivitiesDocument9 pagesNew-Module-2-PEH 12-Outdoor Reacreational ActivitiesJohnlloyd MontierroNo ratings yet
- Mco 6100.14Document9 pagesMco 6100.14guimonteirotereNo ratings yet
- Summary Pathfit 1Document3 pagesSummary Pathfit 1Cham ZapataNo ratings yet
- Health Is Wealth: Basic ProfileDocument18 pagesHealth Is Wealth: Basic ProfilekristhelynNo ratings yet
- Sanatate KineticaDocument14 pagesSanatate KineticacrinaconstantNo ratings yet
- 2021 Rincon, PHYSICAL THERAPY TREATMENT IN A PARA-POWERLIFTING AND PARA-SWIMMING ATHLETE WITH ACHONDROPLASIA. CASE REPORTDocument10 pages2021 Rincon, PHYSICAL THERAPY TREATMENT IN A PARA-POWERLIFTING AND PARA-SWIMMING ATHLETE WITH ACHONDROPLASIA. CASE REPORTdanielalejandrorin04No ratings yet
Seance TD1 Haigh Exercise
Seance TD1 Haigh Exercise
Uploaded by
mohamed ouaidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Seance TD1 Haigh Exercise
Seance TD1 Haigh Exercise
Uploaded by
mohamed ouaidCopyright:
Available Formats
Master 2 de Mécanique
Master 2 STRAINS
FATIGUE OF MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
Exercises to manipulate the Haigh diagram and damage accumulation
Exercise 1: Lifetime of a connecting rod of naval engine
The life of a 50 mm diameter boat engine connecting rod
made of steel (σD=145MPa; Re=490MPa and
Rm=680MPa) is to be determined for several operating
conditions.
Its surface condition reveals a roughness of 5 m.
A reliability index of 90% is sought.
The solicitation is uniaxial of traction-compression type,
with a frequency of 1 Hz.
1. Operation 1 : the connecting rod is subjected to a
dynamic stress at the most stressed point : σm=120MPa
and σa=65MPa
a. Draw the Haigh diagram
b. Calculate the safety coefficient using the
Goodman approximation corrected to Rm-σD/2
(see Engineering Techniques).
2. Operation 2 : the mode of use includes a part of journeys where it is overloaded (during 1% of the
time), with in normal load the solicitation previously described and during the overloads a dynamic
solicitation such as at the most stressed point: σm=180MPa et σa=100MPa
a. Adapting the previous Haigh plot, determine the corresponding endurance limit for the overload
loading
b. Deduce the number of cycles to fatigue initiation corresponding to
c. Considering a very fast crack propagation, i.e. an immediate rupture after the initiation, deduce
the life of the engine
3. Operation 3 : on this ship, loaded like the previous one but sailing on a more difficult sea route, we
note a variable load, described by the following block, at the most stressed point:
σmi (MPa) σai (MPa) ni (number of cycles)
120 65 200 000
180 100 2 000
240 130 400
a. As in operation 2, by adapting the previous Haigh plot, determine the corresponding endurance
limit for the overload loading σm=240MPa et σa=130MPa.
b. Determine the ratios ni/Ni
c. Assuming a linear damage accumulation (Miner's approximation) such that damage is reached
for ni/Ni=1, determine the engine lifetime.
d. Comment on the validity of this reasoning based on elastic loading and an endurance fatigue
mode with Miner damage accumulation.
Exercise 2 : Fatigue resistance of a crankshaft
A steel crankshaft with the following characteristics σD=650MPa et Rm=1200MPa is submitted to a
variable loading. A numerical analysis by finite elements (see figure) gives at the most stressed point,
by the engine cycles, the stress distribution indicated in the table below.
1. Check its unlimited fatigue life and the corresponding safety coefficient using the Haigh diagram.
2. Comment on the result and the proposed verification method.
You might also like
- Workout Plan No 3981212179Document32 pagesWorkout Plan No 3981212179Kiana RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kelistrikan KapalDocument14 pagesSistem Kelistrikan KapalJohann Sjbt94% (17)
- 03 Speakout Reading Listening Extra Pre Intermediate With KeyDocument14 pages03 Speakout Reading Listening Extra Pre Intermediate With Keywai phyo67% (3)
- HW 9Document2 pagesHW 9azizieh5701No ratings yet
- Blogilates Meal PlanDocument6 pagesBlogilates Meal PlanSiennaNo ratings yet
- Yoga HandoutDocument2 pagesYoga Handoutapi-587969236No ratings yet
- Fatigue Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesFatigue Practice ProblemsBoyzz ChinNo ratings yet
- Precast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350Document55 pagesPrecast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350civixxNo ratings yet
- Mech6036 40Document20 pagesMech6036 40Vikas Keshari100% (1)
- TD MRDocument4 pagesTD MRahmed ghassoulNo ratings yet
- Sahyd c23 EngDocument7 pagesSahyd c23 EngDragos NackaNo ratings yet
- Wave Equation Analysis of Driven Piles: Lecture #14Document8 pagesWave Equation Analysis of Driven Piles: Lecture #14Eric Juana PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - FluctatingLoadDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 - FluctatingLoadSanthosh AmaraNo ratings yet
- Design Standards and SpecsDocument9 pagesDesign Standards and SpecsDenise Ann CuencaNo ratings yet
- Technical Report 2 - FatigueDocument3 pagesTechnical Report 2 - FatigueBhartendu TavriNo ratings yet
- MDoT Sample Exam PaperDocument22 pagesMDoT Sample Exam PapersamdelcalNo ratings yet
- Et 11Document2 pagesEt 11Thiet PhamNo ratings yet
- Ram HBMDocument12 pagesRam HBMkkkoooNo ratings yet
- Part (A) : Ship Stability : Ports and Maritime Organization Seafarer's Examination and Certification DirectorateDocument1 pagePart (A) : Ship Stability : Ports and Maritime Organization Seafarer's Examination and Certification DirectorateJim JimiNo ratings yet
- Machine Lab CombineDocument38 pagesMachine Lab Combinelakha ramNo ratings yet
- Naval Architecture18Document6 pagesNaval Architecture18Thiet PhamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-3 For Industrial Electronics SCRDocument2 pagesAssignment 2-3 For Industrial Electronics SCRPranjal GaurNo ratings yet
- Module-2b Fatigue Strength (Bhaskar)Document35 pagesModule-2b Fatigue Strength (Bhaskar)AckshayaNo ratings yet
- Design 09b 2Document4 pagesDesign 09b 2Jim BennyNo ratings yet
- ENG782S2Document8 pagesENG782S2Emperor RocaNo ratings yet
- FEMtutorial Bits30026Document47 pagesFEMtutorial Bits300262023ht30176No ratings yet
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1aa8846No ratings yet
- Material 7Document18 pagesMaterial 7Giannis ZarogiannisNo ratings yet
- Dam I33Document47 pagesDam I33Trung ConNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IiDocument3 pagesAssignment - IichritNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Maintain Load Test Using Anchor Reaction SystemDocument17 pagesMethod Statement For Maintain Load Test Using Anchor Reaction Systemchin thye limNo ratings yet
- Engi4258 Assignments Set1 SolutionsDocument29 pagesEngi4258 Assignments Set1 SolutionscristinacintiaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution MachineDocument2 pagesNumerical Solution Machinenimesh patelNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets (Pre-Stressed) PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Sets (Pre-Stressed) PDFleanne DespaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Desgn For Fatigue Strength - MD - IDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 - Desgn For Fatigue Strength - MD - ISR SuryaNo ratings yet
- FM 1 PDFDocument2 pagesFM 1 PDFVijeesh VijayalayamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1-Design For Static and Fatigue StrengthDocument5 pagesTutorial - 1-Design For Static and Fatigue StrengthSouradeepBhattacharya50% (2)
- Answer: 250Mm, 0.74mpa, 2.75M: Reinforced Concrete - Lecture03 - August2019Document5 pagesAnswer: 250Mm, 0.74mpa, 2.75M: Reinforced Concrete - Lecture03 - August2019hazelNo ratings yet
- 18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Document22 pages18me52 Dme 1 Febarch 2022Thirumal K SNo ratings yet
- Overview:: RemarksDocument5 pagesOverview:: RemarksThinh ViproNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Fluctuating LoadDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Fluctuating Loadabhishek chaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Conductor-Sizing IECDocument2 pagesConductor-Sizing IECnb nbNo ratings yet
- Prolemario 2Document4 pagesProlemario 2Emiliano LozanoNo ratings yet
- 1.02 Ramesh PinjaniDocument16 pages1.02 Ramesh PinjanimchkppNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Combined LoadingDocument51 pagesChapter 8 - Combined Loadingfaiz fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Structural CalculationDocument20 pagesStructural CalculationOmr'GzmnNo ratings yet
- Ahts ProjectDocument39 pagesAhts ProjectSurya Chala PraveenNo ratings yet
- 5.a ME8539 - Question PaperDocument3 pages5.a ME8539 - Question PapersowthaminiNo ratings yet
- 1A - OCC and Load Characteristics of A Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDocument4 pages1A - OCC and Load Characteristics of A Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorAkash MNo ratings yet
- r5310305 Design of Machine Members IDocument1 pager5310305 Design of Machine Members IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- RCD Lecture 4 PDF 2Document19 pagesRCD Lecture 4 PDF 2Paul Zaivan RoldanNo ratings yet
- Open Book Test AnwsersDocument5 pagesOpen Book Test Anwsersإبراهيم مرجاويNo ratings yet
- Railway BridgeDocument21 pagesRailway BridgeAzzahra BilqisNo ratings yet
- 2019物理習題第9回Document6 pages2019物理習題第9回廖亮鈞No ratings yet
- Rr310204-Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageRr310204-Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument22 pagesExercisessiakeehoNo ratings yet
- Pe SS Final Ex 2010Document4 pagesPe SS Final Ex 2010Saif UddinNo ratings yet
- GTP 145 KV CBDocument3 pagesGTP 145 KV CBVipul HavaleNo ratings yet
- Is 6938Document13 pagesIs 6938Dhanashri Patil100% (1)
- Question PapersDocument89 pagesQuestion PapersDreamer ChavanNo ratings yet
- Job 8Document3 pagesJob 8M Usama TabassumNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationFrom EverandShape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination in MAPEH 2019 2020Document5 pages2nd Quarter Examination in MAPEH 2019 2020MinaYaguelValenzuela100% (1)
- Preseason Resistance Training For FootballDocument4 pagesPreseason Resistance Training For FootballSeyfullah DumazNo ratings yet
- Datta WorkOut Upper Lower 2Document27 pagesDatta WorkOut Upper Lower 2designfordummyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Daily Activities: Pair Work. Take Turns. Now Talk About Your Busiest Day of The WeekDocument5 pagesUnit 7 Daily Activities: Pair Work. Take Turns. Now Talk About Your Busiest Day of The WeekWindi MeliyanaNo ratings yet
- Boo OoksDocument3 pagesBoo Ookssiaogila0% (1)
- DBD Week 1 Day 1 - LegsDocument5 pagesDBD Week 1 Day 1 - LegsSaw Min ThuNo ratings yet
- English For Starters 8 - SBDocument100 pagesEnglish For Starters 8 - SBRenz Louie LedseyNo ratings yet
- Pe10 q1 Mod1 Lifestyleandweightmanagement v5Document30 pagesPe10 q1 Mod1 Lifestyleandweightmanagement v5regiegetalla7No ratings yet
- Lower Back Pains ExercisesDocument13 pagesLower Back Pains ExercisesArlhona Juana RagoNo ratings yet
- 31 Hardcore Work Out Finishers FinalDocument24 pages31 Hardcore Work Out Finishers FinalMaxim Borodin90% (10)
- Olymp20159 10dashanrDocument5 pagesOlymp20159 10dashanrHratsin PoghosyanNo ratings yet
- The Tight Tan Slacks of Dezso BanDocument7 pagesThe Tight Tan Slacks of Dezso BanCD KHUTIYALENo ratings yet
- Long WireDocument4 pagesLong Wirelu1agpNo ratings yet
- MUHS BPTH I Year Amended 180609Document22 pagesMUHS BPTH I Year Amended 180609Kumar G PalaniNo ratings yet
- Can Cannot ExerciseDocument4 pagesCan Cannot ExerciseRezky TarihoranNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Q2 M1 PDFDocument40 pagesMapeh 10 Q2 M1 PDFzenqdumbasfNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Look and write: Bài Tập Cơ BảnDocument8 pagesExercise 1: Look and write: Bài Tập Cơ BảnKhánh Linh NghiêmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Visakh A SNo ratings yet
- Part I - Content Update: in The BeginningDocument11 pagesPart I - Content Update: in The BeginningEarshad Shinichi IIINo ratings yet
- Speed Dating TDocument5 pagesSpeed Dating TЛілія ТютінаNo ratings yet
- New-Module-2-PEH 12-Outdoor Reacreational ActivitiesDocument9 pagesNew-Module-2-PEH 12-Outdoor Reacreational ActivitiesJohnlloyd MontierroNo ratings yet
- Mco 6100.14Document9 pagesMco 6100.14guimonteirotereNo ratings yet
- Summary Pathfit 1Document3 pagesSummary Pathfit 1Cham ZapataNo ratings yet
- Health Is Wealth: Basic ProfileDocument18 pagesHealth Is Wealth: Basic ProfilekristhelynNo ratings yet
- Sanatate KineticaDocument14 pagesSanatate KineticacrinaconstantNo ratings yet
- 2021 Rincon, PHYSICAL THERAPY TREATMENT IN A PARA-POWERLIFTING AND PARA-SWIMMING ATHLETE WITH ACHONDROPLASIA. CASE REPORTDocument10 pages2021 Rincon, PHYSICAL THERAPY TREATMENT IN A PARA-POWERLIFTING AND PARA-SWIMMING ATHLETE WITH ACHONDROPLASIA. CASE REPORTdanielalejandrorin04No ratings yet