Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bond Parameters
Bond Parameters
Uploaded by
sunday omoladeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bond Parameters
Bond Parameters
Uploaded by
sunday omoladeCopyright:
Available Formats
Bond Parameters
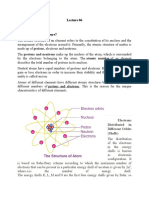
Bond Length: Bond length is defined as the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured by spectroscopic, X-ray diffraction and electron-diffraction
techniques about which you will learn in higher classes. Each atom of the bonded pair contributes to the
bond length. In the case of a covalent bond, the contribution from each atom is called the covalent radius
of that atom. The covalent radius is measured approximately as the radius of an atom’s core which is in
contact with the core of an adjacent atom in a bonded situation. The covalent radius is half of the distance
between two similar atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule. The van der Waals radius
represents the overall size of the atom which includes its valence shell in a non bonded situation. Further,
the van der Waals radius is half of the distance between two similar atoms in separate molecules in a
solid.
Bond Angle: It is defined as the angle between the orbitals containing bonding electron pairs around the
central atom in a molecule/complex ion. Bond angle is expressed in degree which can be experimentally
determined by spectroscopic methods. It gives some idea regarding the distribution of orbitals around the
central atom in a molecule/complex ion and hence it helps us in determining its shape. For example H–
O–H bond angle in water can be represented as under
You might also like
- Electrrob Band StructureDocument9 pagesElectrrob Band StructureTeka KamNo ratings yet
- Method ParametersDocument1 pageMethod Parameterssunday omoladeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties-4Document13 pagesPeriodic Properties-4qweerrNo ratings yet
- Bond ParametersDocument3 pagesBond ParametersQuenneBelocuraNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding IPADDocument4 pagesStructure and Bonding IPADLarissa RubarajNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument22 pagesPeriodic TrendsVasudev M SNo ratings yet
- By AdithyaDocument35 pagesBy AdithyaA SQUARE GAMING DEVIL L7ADILHYANo ratings yet
- Atomic RadiiDocument2 pagesAtomic RadiiVarad VaidyaNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument PresentationmlDocument56 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Presentationmlbala6927No ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentDocument131 pages2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentanathinothandoNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Document17 pages11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Erreneo100% (1)
- Edexcel As Level Chemistry Shapes of Molecules 2019 SpecDocument5 pagesEdexcel As Level Chemistry Shapes of Molecules 2019 Specdrama curiousNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Short Notes by MTHDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding Short Notes by MTHmanthangoel11jeeNo ratings yet
- Ed Lect 3 FinalDocument8 pagesEd Lect 3 FinalAKANKSHA GARGNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 - Conceptos Desarrollo Tarea 1 Gladys Bautista..Document5 pagesTarea 1 - Conceptos Desarrollo Tarea 1 Gladys Bautista..GLADYS BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Study NotesDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- PHSC GR 11 REVISION DOCUMENT APRIL 2022 Collated Final Final PDFDocument66 pagesPHSC GR 11 REVISION DOCUMENT APRIL 2022 Collated Final Final PDFPhilNo ratings yet
- Bonding Essay: IFP Engineering and Science January IntakeDocument6 pagesBonding Essay: IFP Engineering and Science January IntakeGhassan MousaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Band StructureDocument11 pagesElectronic Band StructureinfistudeeeeNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary BondingDocument6 pagesPrimary and Secondary BondingosmondNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends 1. Atomic RadiusDocument4 pagesPeriodic Trends 1. Atomic RadiusJDR JDRNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument94 pagesChemical BondingGagandeep WadhawanNo ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes KhraDocument24 pagesChemistry Notes KhraMohamed WageehNo ratings yet
- Protons,: Electrons Distributed in Different Orbits (Shells)Document17 pagesProtons,: Electrons Distributed in Different Orbits (Shells)Mati Sahab BhattiNo ratings yet
- Class Lecture Atomic Model Conductor SemiconductorDocument8 pagesClass Lecture Atomic Model Conductor SemiconductorRajaul Morshad SaikotNo ratings yet
- # Week 3 NotesDocument13 pages# Week 3 Notestimx123yNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Powered by AIDocument1 pagePowered by AIsoonh jatoiNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lect2b Chemical Properties - Electronic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument54 pages2013 Lect2b Chemical Properties - Electronic Structure and Chemical BondingRatriKiranaPrabaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Bond Valence Method - WikipediaDocument24 pagesBond Valence Method - WikipediaVadivelanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Chemical BondingDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Chemical BondingRavinder singhNo ratings yet
- Topic 3,4,5&6 CH 4 Class 11thDocument3 pagesTopic 3,4,5&6 CH 4 Class 11thLakshaya SainiNo ratings yet
- M4 Check-In Activity 2 CHEM LECDocument3 pagesM4 Check-In Activity 2 CHEM LECjoey pt.2No ratings yet
- 2023 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 1Document5 pages2023 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 1aishwaryasantosh388No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ScriptDocument4 pagesChemical Bonding ScriptAkhil MathewNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table IIDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table IIPrinceblesed EdemNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ashutosh Pandey Chemistry Department MNNIT AllahabadDocument22 pagesDr. Ashutosh Pandey Chemistry Department MNNIT AllahabadbotiwaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bondind and Molecular StructureDocument33 pagesChemical Bondind and Molecular StructureSaadNo ratings yet
- Group Four Write UpDocument11 pagesGroup Four Write Upgodspower odiorNo ratings yet
- Paper of AtomDocument32 pagesPaper of AtomAmelia PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument198 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsRamyasri100% (2)
- Module 6: Physics of Semiconductor Devices Lecture 30: Energy Band DiagramDocument10 pagesModule 6: Physics of Semiconductor Devices Lecture 30: Energy Band Diagramvj.krlambaNo ratings yet
- Band Theory GanDocument29 pagesBand Theory GanRussell TempleNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Shobhit NirwanDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding Shobhit NirwanMinakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Shobhit NirwanDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding Shobhit NirwanGOUTHAMNo ratings yet
- Atomic RadiusDocument2 pagesAtomic Radiusapi-248732283No ratings yet
- Concept Review With Key TermsDocument4 pagesConcept Review With Key TermsWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument12 pagesTerm PaperJunaid Mushtaq100% (1)
- BAND TheoryDocument10 pagesBAND TheoryTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Dative Covalent BondingDocument3 pagesDative Covalent BondingAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- Bonding and ChemistryDocument1 pageBonding and ChemistryAman ChandeNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeometryDocument15 pagesMolecular GeometryArmando Alberto MassingueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Class 11Document17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Class 11Arpan SenNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument26 pagesBand Theory of SolidsDizney Lobaton EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument30 pagesCoordination CompoundsItaakNo ratings yet
- Chem Test RevisionDocument10 pagesChem Test RevisionmaddieNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physical Sciences Revision Document 2024Document79 pagesGrade 11 Physical Sciences Revision Document 2024Yolanda WillsonNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document201 pagesCH 01Khaled OsmanNo ratings yet