Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earthing Protection System Explained
Earthing Protection System Explained
Uploaded by
abuzar125330 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesEarthing protection, also known as grounding protection or a grounding system, provides a safe path for electrical currents to flow into the ground. It prevents electric shocks, fires, and equipment damage. A proper grounding system includes a grounding electrode buried in the earth, grounding conductors connecting equipment to the electrode, and consideration of soil conditions and electrical system layout. An effective grounding system is crucial for safety and protects both people and equipment from faults and lightning strikes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEarthing protection, also known as grounding protection or a grounding system, provides a safe path for electrical currents to flow into the ground. It prevents electric shocks, fires, and equipment damage. A proper grounding system includes a grounding electrode buried in the earth, grounding conductors connecting equipment to the electrode, and consideration of soil conditions and electrical system layout. An effective grounding system is crucial for safety and protects both people and equipment from faults and lightning strikes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesEarthing Protection System Explained
Earthing Protection System Explained
Uploaded by
abuzar12533Earthing protection, also known as grounding protection or a grounding system, provides a safe path for electrical currents to flow into the ground. It prevents electric shocks, fires, and equipment damage. A proper grounding system includes a grounding electrode buried in the earth, grounding conductors connecting equipment to the electrode, and consideration of soil conditions and electrical system layout. An effective grounding system is crucial for safety and protects both people and equipment from faults and lightning strikes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
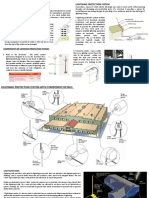
Earthing Protection System Explained
Earthing protection, also known as grounding protection or grounding system, is a
crucial aspect of electrical and structural safety. It involves providing a low-resistance
path for electrical currents to flow safely into the ground, thereby preventing electric
shocks, fires, and equipment damage.
Here's a breakdown of the key components and concepts related to earthing
protection:
1. Grounding Electrode: This is a metal rod, plate, or other conductive structure
that is buried in the ground and serves as the connection point between the
electrical system and the earth. Common grounding electrodes include copper
rods, copper-clad steel rods, and grounding plates.
2. Grounding Conductor: This is a conductor (usually made of copper or
aluminum) that connects electrical equipment, systems, or components to the
grounding electrode. It provides a low-resistance path for fault currents to flow
into the ground, ensuring the safety of the electrical system and preventing the
buildup of dangerous voltages.
3. Grounding Busbar: In larger electrical systems, a grounding busbar may be
used to consolidate multiple grounding conductors and provide a centralized
point for connecting to the grounding electrode.
4. Grounding System Design: Proper design of the grounding system is essential
to ensure effective protection. Factors such as soil resistivity, the type of
grounding electrode used, and the layout of the electrical system must be
considered to achieve adequate grounding.
5. Grounding for Lightning Protection: In addition to providing protection
against electrical faults, grounding systems are also essential for lightning
protection. Lightning rods, surge protectors, and other lightning protection
devices are connected to the grounding system to safely dissipate lightning
strikes into the ground.
6. Safety Grounding: In electrical systems, grounding is used to provide a
reference point for voltage measurements and to safely discharge static
electricity. All exposed metal parts of electrical equipment and enclosures
should be bonded to the grounding system to prevent electric shocks.
7. Fault Protection: Grounding plays a critical role in fault protection by providing
a low-impedance path for fault currents to flow, allowing protective devices
such as circuit breakers and fuses to quickly detect and interrupt faults.
Overall, proper earthing protection is essential for ensuring the safety, reliability, and
performance of electrical systems. It helps protect against electric shocks, equipment
damage, and fire hazards, making it a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering and
building safety codes and standards.
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Lilyum / Lilyum Bym: Lilyum Operator'S ManualDocument96 pagesLilyum / Lilyum Bym: Lilyum Operator'S ManualNassima BELIL100% (2)
- Applying Grounding and Shielding For Instrumentation PDFDocument44 pagesApplying Grounding and Shielding For Instrumentation PDFAnonymous zdCUbW8HfNo ratings yet
- Earthing in Industrial and Pharmaceutical PlantsDocument28 pagesEarthing in Industrial and Pharmaceutical PlantsBrayden Chetty100% (1)
- Protection of SubstationDocument21 pagesProtection of SubstationARVIND100% (3)
- 45 - Altivar 61 Plus Variable Speed DrivesDocument130 pages45 - Altivar 61 Plus Variable Speed Drivesabdul aziz alfiNo ratings yet
- Lightning Protection System ExplainedDocument2 pagesLightning Protection System Explainedabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Power System Protection: Submitted To: Jamil Ahmad KhanDocument5 pagesPower System Protection: Submitted To: Jamil Ahmad KhanHasnain KhanNo ratings yet
- Guia Soluciones Parque FotovoltaicoDocument18 pagesGuia Soluciones Parque FotovoltaicoEnrique MirandaNo ratings yet
- Lightning Proection System1Document2 pagesLightning Proection System1Pratheep SelvakumaranNo ratings yet
- Elec 104 Ni KylleDocument2 pagesElec 104 Ni KylleKylle Bryan AranceNo ratings yet
- GroundingDocument32 pagesGroundingcharleselitb92100% (2)
- Earthing SystemDocument5 pagesEarthing SystemFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Lightning Protection For Farms: This Fact Sheet CoversDocument4 pagesLightning Protection For Farms: This Fact Sheet Coversamir11601No ratings yet
- Plate Earthing For Electrical AppliancesDocument8 pagesPlate Earthing For Electrical AppliancesYash BhowateNo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument5 pagesEarthing SystemNUR FATHIAH BINTI ABDUL HALIM STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Protection of SubstationDocument21 pagesProtection of Substationkvramanan_1100% (1)
- 9 Recommended Practices For GroundingDocument15 pages9 Recommended Practices For GroundingMuhammed Mekki100% (1)
- 9 Recommended Practices For GroundingDocument6 pages9 Recommended Practices For Groundingsikander843562No ratings yet
- Earthing CalculationDocument88 pagesEarthing CalculationRamesh Epili100% (18)
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportsazildiwan9No ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose of Protective Device?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of Protective Device?Esai StephenNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document15 pagesPresentation 10vica.babate.cocNo ratings yet
- 204 Electrical Fire HazardsDocument7 pages204 Electrical Fire HazardsGyanendra Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- 9 Recommended Practices For Grounding: Basis For Safety and Power QualityDocument11 pages9 Recommended Practices For Grounding: Basis For Safety and Power QualityPrabu Baskaran100% (1)
- Earthing CalculationDocument91 pagesEarthing CalculationRamji RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Protection of SubstationDocument21 pagesProtection of SubstationDivyanshu Agarwal50% (2)
- BC BmuDocument3 pagesBC BmuDevyani JainNo ratings yet
- ILDC GroundingBondingSurgeprotectionDocument6 pagesILDC GroundingBondingSurgeprotectionADRIANA ESCOBAR HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Deshaunie SullivanDocument17 pagesDeshaunie SullivanK KgfdfNo ratings yet
- Guide To ProtectionDocument32 pagesGuide To ProtectionpjaengjaikulNo ratings yet
- EE410 Introduction To Electrical Design For Cathodic Protection SystemsDocument30 pagesEE410 Introduction To Electrical Design For Cathodic Protection SystemsHassenLNo ratings yet
- ECE589 ProjectDocument9 pagesECE589 ProjectAyoub MondoNo ratings yet
- Data Center ProtectionDocument5 pagesData Center ProtectionGia BảoNo ratings yet
- 3a What Is EarthingDocument2 pages3a What Is EarthingMichael WheelerNo ratings yet
- Material and Description Pictur1Document3 pagesMaterial and Description Pictur1raphaelchriatopherNo ratings yet
- Dara Amelia Ula-D3 TL 2a-07Document3 pagesDara Amelia Ula-D3 TL 2a-07Dara AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Tes T 111 02R0 PDFDocument35 pagesTes T 111 02R0 PDFMohammad Abo AliNo ratings yet
- Tools and Equipment in ElectricityDocument19 pagesTools and Equipment in ElectricityJoane MedallaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document45 pagesChapter - 1Rajendra Prasad ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Protection Devices1Document45 pagesProtection Devices1sivaNo ratings yet
- Ee 322 Bsee3 Panes Von Andrae Research WorkDocument6 pagesEe 322 Bsee3 Panes Von Andrae Research WorkVon Andrae A PanesNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Electrical Grounding, 1st Edition, 1999-EricoDocument134 pagesPractical Guide To Electrical Grounding, 1st Edition, 1999-EricoFABIANO FREIRE DA SILVANo ratings yet
- Analysis of Electrical Grounding Design of Substation and Lines - Journal PublishedDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Electrical Grounding Design of Substation and Lines - Journal PublishedJames UjamNo ratings yet
- Finals Module 1 2 Avt 4232Document54 pagesFinals Module 1 2 Avt 4232angeloNo ratings yet
- EE137Document7 pagesEE137John Patrick CeldaNo ratings yet
- Earthing System: Objectives of Electrical EarthingDocument1 pageEarthing System: Objectives of Electrical EarthingredfordNo ratings yet
- Types of Safety Devices: 1. FuseDocument4 pagesTypes of Safety Devices: 1. FuseMuhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Celda - Ee137 - Home Act 1Document7 pagesCelda - Ee137 - Home Act 1John Patrick CeldaNo ratings yet
- Cad Electrical QuestionDocument1 pageCad Electrical QuestionMathavan MNo ratings yet
- EMIT Unit8Document9 pagesEMIT Unit8PKNo ratings yet
- Overvoltage Protection Design For Photovoltaic Panels and SystemsDocument2 pagesOvervoltage Protection Design For Photovoltaic Panels and SystemsEmir JusićNo ratings yet
- ELEC9713-11 Lec07 EarthingDocument54 pagesELEC9713-11 Lec07 Earthinggolu100% (1)
- Early Streamer Emission TechnologyDocument10 pagesEarly Streamer Emission Technologyhoangan15No ratings yet
- 8 DEE 1 EARTHING CompleteDocument13 pages8 DEE 1 EARTHING Completesammychesoli4No ratings yet
- Lightning ProtectionDocument7 pagesLightning ProtectionShiv Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- 5 Protection Against The Effects of LightningDocument5 pages5 Protection Against The Effects of LightningDayaniGiraldoAizalesNo ratings yet
- Module - 3: Switches and FusesDocument53 pagesModule - 3: Switches and FusesdemokykNo ratings yet
- Earthing and Lightning Proetction SystemsDocument19 pagesEarthing and Lightning Proetction SystemsAr. Soumya P SNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Earthing Systems and Lightning ProtectionDocument7 pagesChapter Four Earthing Systems and Lightning Protectionyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- NFPA Summary LIGHTENING ARRESTORSDocument3 pagesNFPA Summary LIGHTENING ARRESTORSParas VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Earthing (19.07.2016)Document18 pagesEarthing (19.07.2016)Anshul TayalNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument2 pagesTypes of Transformersabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Types of EarthingDocument2 pagesTypes of Earthingabuzar12533No ratings yet
- A Block Flow DiagramDocument2 pagesA Block Flow Diagramabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Ampere's Law and Couloumb's LawDocument2 pagesAmpere's Law and Couloumb's Lawabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's Lawabuzar12533No ratings yet
- VFDDocument2 pagesVFDabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Space HeaterDocument1 pageSpace Heaterabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Motor DetailsDocument1 pageMotor Detailsabuzar12533No ratings yet
- GeneratorDocument1 pageGeneratorabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Exercise 14Document8 pagesExercise 14mjovicaNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger Rs-1000: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument32 pagesBattery Charger Rs-1000: Downloaded From Manuals Search Engineice_coldNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Air University 1st Progress Presentation - FYP - II (Session 2016-20)Document6 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Computer Engineering Air University 1st Progress Presentation - FYP - II (Session 2016-20)atiqakbar1No ratings yet
- Parts of TransformerDocument4 pagesParts of TransformerAkanksha SoodNo ratings yet
- DLL Aug 8 Discovery of EM WavesDocument4 pagesDLL Aug 8 Discovery of EM WavesHelen Grace Llemos Cabalag100% (3)
- AE MCQs CombinedDocument45 pagesAE MCQs Combinedmuthoju sandeepNo ratings yet
- Diodes Applications: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis NashelskyDocument23 pagesDiodes Applications: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelskyasiri201912No ratings yet
- A Bridgeless Totem-Pole Interleaved PFC Converter For Plug-In Electric Vehicles PDFDocument4 pagesA Bridgeless Totem-Pole Interleaved PFC Converter For Plug-In Electric Vehicles PDFLeMeniz InfotechNo ratings yet
- Trench Bushings Cot 24kv To 550kvDocument24 pagesTrench Bushings Cot 24kv To 550kvdsanmi0% (1)
- Chapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsDocument13 pagesChapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsShara TayonaNo ratings yet
- Brosur Line Post InsulatorDocument2 pagesBrosur Line Post InsulatorHizbul MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges Part-2Document20 pagesMoving Charges Part-2likhithNo ratings yet
- Solaredge Extended Power Three Phase Inverters: For Delta Grids (Belgium, Norway, Taiwan & Philippines)Document2 pagesSolaredge Extended Power Three Phase Inverters: For Delta Grids (Belgium, Norway, Taiwan & Philippines)Shantanu RoyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument6 pagesExperiment 5 Maximum Power Transfer TheoremronakNo ratings yet
- Ge Iav52Document38 pagesGe Iav52MFOBLLLLLLLNo ratings yet
- 1769 Ob32tDocument24 pages1769 Ob32tHilder Ramirez PuellesNo ratings yet
- Flip Flop PDFDocument5 pagesFlip Flop PDFarevazhagunvcNo ratings yet
- 3 G 3 JVDocument6 pages3 G 3 JVDejan AćimovićNo ratings yet
- HVAC, PHE & FF Eqpt - Elect LoadDocument13 pagesHVAC, PHE & FF Eqpt - Elect LoadSaurabh DwivediNo ratings yet
- XEROX Phaser 6300, 6350, 6360 Parts List, Service ManualDocument564 pagesXEROX Phaser 6300, 6350, 6360 Parts List, Service ManualDaniel Christopher HargettNo ratings yet
- MEX MEXICO CITY Anatole France 26 31333 ENGDocument40 pagesMEX MEXICO CITY Anatole France 26 31333 ENGjose ruben jimenezNo ratings yet
- 7600-S-3-RJS Series - Kit Selection Guide: KV In. (MM)Document3 pages7600-S-3-RJS Series - Kit Selection Guide: KV In. (MM)Jalal AlbadriNo ratings yet
- Ratings GuideDocument36 pagesRatings Guidegigo_dream0% (1)
- Hormann Lineamatic Gate OperatorsDocument46 pagesHormann Lineamatic Gate Operatorsineskhiari2204No ratings yet
- A 1-Eel306Document21 pagesA 1-Eel306Siddhartha DasNo ratings yet
- NR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocument6 pagesNR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Modbus Protocol Start Address Hex Ø Ø Ø: Input RegistersDocument8 pagesModbus Protocol Start Address Hex Ø Ø Ø: Input RegistersMannNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Models 4370 R1800 RecorderDocument129 pagesInstruction Manual: Models 4370 R1800 RecordermihaiisvoranuNo ratings yet