Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DFMEA Rating Table v01
DFMEA Rating Table v01
Uploaded by
Balakumaran Murugesan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesThis document contains tables for rating the severity (S) and occurrence (O) of potential failures in a DFMEA (Design Failure Mode Effects Analysis).
The severity table rates the effects of potential failures from 1-10 based on their impact, such as safety, compliance, or vehicle function.
The occurrence table provides criteria for rating the likelihood of potential failure causes from 1-10 based on factors like design experience, testing, standards, and prevention controls.
Original Description:
Original Title
DFMEA_rating_table_v01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains tables for rating the severity (S) and occurrence (O) of potential failures in a DFMEA (Design Failure Mode Effects Analysis).
The severity table rates the effects of potential failures from 1-10 based on their impact, such as safety, compliance, or vehicle function.
The occurrence table provides criteria for rating the likelihood of potential failure causes from 1-10 based on factors like design experience, testing, standards, and prevention controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesDFMEA Rating Table v01
DFMEA Rating Table v01
Uploaded by
Balakumaran MurugesanThis document contains tables for rating the severity (S) and occurrence (O) of potential failures in a DFMEA (Design Failure Mode Effects Analysis).
The severity table rates the effects of potential failures from 1-10 based on their impact, such as safety, compliance, or vehicle function.
The occurrence table provides criteria for rating the likelihood of potential failure causes from 1-10 based on factors like design experience, testing, standards, and prevention controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Cubonic-internal/external DFMEA Rating table Version 01
Remark to confidentiality Title Template version
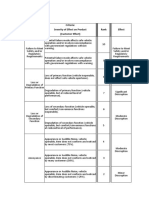
1. DFMEA Severity table
Product General Evaluation Criteria Severity (S)
Blank until
Potential Failure Effects rated according to the criteria below.
filled in by user
Corporate or
S Effect Severity criteria Product Line
Examples
Affects safe operation of the vehicle and/or other
10 vehicles, the health of driver or passenger(s) or
Very high
road users or pedestrians.
9 Noncompliance with regulations.
Loss of primary vehicle function necessary for normal
8
driving during expected service life.
High
Degradation of primary vehicle function necessary
7
for normal driving during expected service life.
6 Loss of secondary vehicle function.
5 Degradation of secondary vehicle function.
Moderate
Very objectionable appearance, sound, vibration,
4
harshness, or haptics.
Moderately objectionable appearance, sound,
3
vibration, harshness, or haptics.
Low
Slightly objectionable appearance, sound,
2
vibration, harshness, or haptics.
1 Very low No discernible effect.
Cubonic GmbH – all rights reserved
Page 1 of 4
CUBONIC-internal/external DFMEA Rating table Version 01
Remark to confidentiality Title Template version
2. DFMEA occurrence table
Occurrence Potential (O) for the Product
Potential Failure Causes rated according to the criteria below. Consider Blank until
Product Experience and Prevention Controls when determining the best filled in by
Occurrence estimate (Qualitative rating). user
Prediction
of Occurrence
O Failure Occurrence criteria - DFMEA criteria -
Cause DFMEA
Occurring
First application of new technology anywhere without
operating experience and/or under uncontrolled
operating conditions. No product verification and/or
Extremely validation experience.
10
high
Standards do not exist and best practices have not yet
been determined. Prevention controls not able to predict
field performance or do not exist.
First use of design with technical innovations or materials
within the company. New application or change in duty
cycle / operating conditions. No product verification and/or
9 validation experience.
Prevention controls not targeted to identify performance
to specific requirements.
Very high First use of design with technical innovations or materials
on a new application. New application or change in duty
cycle / operating conditions. No product verification and/or
validation experience.
8
Few existing standards and best practices, not directly
applicable for this design. Prevention controls not a
reliable indicator of field performance.
New design based on similar technology and materials.
New application or change in duty cycle / operating
conditions. No product verification and/or validation
experience.
7
Standards, best practices, and design rules apply to the
baseline design, but not the innovations. Prevention
controls provide limited indication of performance
High
Similar to previous designs, using existing technology and
materials. Similar application, with changes in duty cycle
or operating conditions. Previous testing or field
experience.
6
Standards and design rules exist but are insufficient to
ensure that the failure cause will not occur. Prevention
controls provide some ability to prevent a failure cause.
CUBONIC GmbH – all rights reserved
Page 2 of 4
CUBONIC-internal/external DFMEA Rating table Version 01
Remark to confidentiality Title Template version
Occurrence Potential (O) for the Product
Potential Failure Causes rated according to the criteria below. Consider Blank until
Product Experience and Prevention Controls when determining the best filled in by
Occurrence estimate (Qualitative rating). user
Prediction
of Occurrence
O Failure Occurrence criteria - DFMEA criteria -
Cause DFMEA
Occurring
Detail changes to previous design, using proven
technology and materials. Similar application, duty cycle
or operating conditions. Previous testing or field
experience, or new design with some test experience
related to the failure.
5
Design addresses lessons learned from previous designs.
Best Practices re-evaluated for this design but have not
yet been proven. Prevention controls capable of finding
deficiencies in the product related to the failure cause and
Moderate
provide some indication of performance.
Almost identical design with short-term field exposure.
Similar application, with minor change in duty cycle or
operating conditions. Previous testing or field experience.
4 Predecessor design and changes for new design conform
to best practices, standards, and specifications. Prevention
controls capable of finding deficiencies in the product
related to the failure cause and indicate likely design
conformance.
Detail changes to known design (same application, with
minor change in duty cycle or operating conditions) and
testing or field experience under comparable operating
conditions, or new design with successfully completed test
procedure.
3 Low
Design expected to conform to Standards and Best
Practices, considering Lessons Learned from previous
designs. Prevention controls capable of finding
deficiencies in the product related to the failure cause and
predict conformance of production design.
Almost identical mature design with long term field
exposure. Same application, with comparable duty cycle
and operating conditions. Testing or field experience
under comparable operating conditions.
2 Very low Design expected to conform to standards and best
practices, considering Lessons Learned from previous
designs, with significant margin of confidence. Prevention
controls capable of finding deficiencies in the product
related to the failure cause and indicate confidence in
design conformance.
Extremely Failure eliminated through prevention control and failure
1
low cause is not possible by design
Product Experience: History of product usage within the company (Novelty of design, application or use case).
Results of already completed detection controls provide experience with the design.
Prevention Controls: Use of Best Practices for product design, Design Rules, Company Standards, Lessons
Learned, Industry Standards, Material Specifications, Government Regulations and effectiveness of prevention
oriented analytical tools including Computer Aided Engineering, Math Modeling, Simulation Studies,
Tolerance Stacks and Design Safety Margins
Note: O 10, 9, 8, 7 can drop based on product validation activities.
CUBONIC GmbH – all rights reserved
Page 3 of 4
CUBONIC-internal/external DFMEA Rating table Version 01
Remark to confidentiality Title Template version
3. DFMEA Detection table
Detection Potential (D) for the Validation of the Product Design
Blank until
Detection Controls rated according to Detection Method Maturity and
filled in by
Opportunity for Detection.
user
Corporate or
Ability to Opportunity for
D Detection method maturity product line
detect detection
examples
Test method not
10 Test procedure yet to be developed.
defined
Very low Test method not designed Pass-Fail, Test-to-
9 specifically to detect failure mode or Fail, Degradation
cause. Testing
Pass-Fail, Test-to-
8 New test method; not proven. Fail, Degradation
Low
Testing
7 Proven test method for verification of Pass-Fail Testing
6 functionality or validation of Test-to-Failure
performance, quality, reliability and
durability; planned timing is later in
Moderate the product development cycle such Degradation
5
that test failures may result in Testing
production delays for re-design
and/or re-tooling.
4 Proven test method for verification of Pass-Fail Testing
3 functionality or validation of Test-to-Failure
performance, quality, reliability and
High
durability; planned timing is Degradation
2
sufficient to modify production tools Testing
before release for production.
Prior testing confirmed that failure mode or cause
1 Very high cannot occur, or detection methods proven to always
detect the failure mode or failure cause.
CUBONIC GmbH – all rights reserved
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Assignment On Business PlanDocument28 pagesAssignment On Business PlanShantanu Das85% (62)
- AIAG and VDA FMEA Handbook Apr 4 2019-1Document16 pagesAIAG and VDA FMEA Handbook Apr 4 2019-1Rudiney Trombetta88% (16)
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1William ChinNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE FOR OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL - Pharmaceutical GuidanceDocument7 pagesTEMPLATE FOR OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL - Pharmaceutical GuidanceMSL India100% (2)
- Reverse FMEA PSADocument53 pagesReverse FMEA PSABES100% (9)
- The Complete Response Function and System Parameters For A Loudspeaker With Passive Radiator PDFDocument17 pagesThe Complete Response Function and System Parameters For A Loudspeaker With Passive Radiator PDFMajo JaimesNo ratings yet
- Fmea ProcessDocument25 pagesFmea ProcessEmperor89100% (1)
- FMEA Process Training MaterialDocument38 pagesFMEA Process Training MaterialDearRed FrankNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis Severity RatingDocument5 pagesFailure Mode and Effect Analysis Severity RatingRemus CicuNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: DesignDocument33 pagesFailure Mode and Effect Analysis: Designವಿಕಾಸ ಏಕನಾಥಭಟ್ಟNo ratings yet
- DFMEArefcard PDFDocument2 pagesDFMEArefcard PDFIgor PNo ratings yet
- SMMT AQMS FMEA Alignment AIAG and VDA - en PDFDocument32 pagesSMMT AQMS FMEA Alignment AIAG and VDA - en PDFNilton de OliveraNo ratings yet
- 7 FMEA NewDocument38 pages7 FMEA NewrakeshNo ratings yet
- RPN RankingsDocument5 pagesRPN RankingsThế PhongNo ratings yet
- TQM Live Lecture 11 Apr 2021 1618022055727Document27 pagesTQM Live Lecture 11 Apr 2021 1618022055727Kumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 203 LSS Gbo - FmeaDocument47 pages203 LSS Gbo - FmeaRocker byNo ratings yet
- "Fmea & Case Study": Kelompok: Rohmat Setiawan Titin NuryawatiDocument41 pages"Fmea & Case Study": Kelompok: Rohmat Setiawan Titin Nuryawatirohmat_setiawan77No ratings yet
- The 7 Steps of Process-FMEA: Step 1: Planning and PreparationDocument2 pagesThe 7 Steps of Process-FMEA: Step 1: Planning and PreparationTarun PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- QSP 14 Fmea Procedure - 01Document7 pagesQSP 14 Fmea Procedure - 01kmvimal36No ratings yet
- Perfecto Test Coverage Guide Spring 22Document22 pagesPerfecto Test Coverage Guide Spring 22Vanja Kovač GajićNo ratings yet
- Sevrity Reating Table Old & NewDocument26 pagesSevrity Reating Table Old & NewSibaram DasNo ratings yet
- Risk ReductionDocument58 pagesRisk Reductionmartin_746No ratings yet
- Module III Lec3Document10 pagesModule III Lec3Surajit SahaNo ratings yet
- FMEA ProcessDocument7 pagesFMEA ProcessRANJITHNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad SabriDocument42 pagesFailure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad Sabricalvin100% (1)
- Failure Modes & Effects Analysis: Project Activities in Which The FMEA Is UsefulDocument10 pagesFailure Modes & Effects Analysis: Project Activities in Which The FMEA Is Usefulpajaro1111111No ratings yet
- Fmea Notes-1Document6 pagesFmea Notes-1sagarvadhel78No ratings yet
- Design and Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (Dfmea & Pfmea)Document19 pagesDesign and Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (Dfmea & Pfmea)Mohammed KassemNo ratings yet
- Xfmea Report Sample - Design FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsDocument6 pagesXfmea Report Sample - Design FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsVilas m ChinkeNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Tester Foundation Level CTFLDocument80 pagesLec 3 Tester Foundation Level CTFLPhilip WagihNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis of Hotwell System Motor Operated Butterfly ValveDocument19 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis of Hotwell System Motor Operated Butterfly ValveBalan SelvanNo ratings yet
- Testing & SDLC BasicsDocument23 pagesTesting & SDLC BasicsSandeep BennyNo ratings yet
- 20bba0194 TQM Da 1 FmeaDocument9 pages20bba0194 TQM Da 1 Fmeavani sureshNo ratings yet
- EMT 480 Reliability & Failure AnalysisDocument38 pagesEMT 480 Reliability & Failure AnalysisK ULAGANATHANNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of TestingDocument95 pagesFundamentals of TestingAlexandru Si Larisa Serb-Alexe100% (1)
- FMEA: Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocument24 pagesFMEA: Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisAlvaro CotaquispeNo ratings yet
- Severity, Occurrence, and Detection Criteria For Design FMEADocument2 pagesSeverity, Occurrence, and Detection Criteria For Design FMEAtejashraj93No ratings yet
- Touchless Testing PlatformDocument9 pagesTouchless Testing PlatformPrasanna KrishnaNo ratings yet
- DfmeaDocument13 pagesDfmeaAshisNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisDocument5 pagesFailure Mode and Effects AnalysisSamantha IsabelNo ratings yet
- SeverityDocument10 pagesSeverityVijayamalar AmruthalingamNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument25 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysislokelooksNo ratings yet
- Preview ANSI+ASQ+Z1.4-2003+ (R2013)Document8 pagesPreview ANSI+ASQ+Z1.4-2003+ (R2013)mlk1971No ratings yet
- FMEA Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument61 pagesFMEA Failure Mode Effect AnalysisAbhijeet RandhirNo ratings yet
- 7-Step Pocket GuideDocument2 pages7-Step Pocket Guidesutra01No ratings yet
- Test Force Faq'S: 1. What Is Alpha Testing?Document8 pagesTest Force Faq'S: 1. What Is Alpha Testing?Sandeep PulipatiNo ratings yet
- Perfecto State Test Automation 23Document11 pagesPerfecto State Test Automation 23stephaniehe8080No ratings yet
- 8 Process Safety Awareness PresentationDocument27 pages8 Process Safety Awareness PresentationVincent Magtibay67% (3)
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document23 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Anthony Mc CormackNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Fundamentals of Software TestingDocument37 pagesUnit 1: Fundamentals of Software Testingkarishma10No ratings yet
- FMEA HandbookDocument1 pageFMEA Handbookavinashchauhan2695No ratings yet
- Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis DfmeaDocument14 pagesDesign Failure Mode and Effects Analysis DfmeasdNo ratings yet
- Supplier Audit Check SheetDocument5 pagesSupplier Audit Check SheetMotive Post100% (2)
- PFMEA Ranking Table Rating Criteria Action GuidelineDocument10 pagesPFMEA Ranking Table Rating Criteria Action GuidelineEnrico Miguel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Equipment QualificationDocument28 pagesEquipment Qualificationswapnil_ballal63% (8)
- IPC-TM-650 Test Methods ManualDocument1 pageIPC-TM-650 Test Methods ManualHarish MahadevanNo ratings yet
- PFMEA RankingDocument1 pagePFMEA RankingSachin KumbharNo ratings yet
- Table P1 For Severity RatingDocument2 pagesTable P1 For Severity RatingAhmad Bin Ismail KhanNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Basic NotesDocument18 pagesSoftware Testing Basic NotesgunachandravarmaNo ratings yet
- Process Safety AwarenessDocument19 pagesProcess Safety AwarenessiekazalyNo ratings yet
- Effective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisFrom EverandEffective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Debugging Playbook: System Testing, Error Localization, And Vulnerability RemediationFrom EverandDebugging Playbook: System Testing, Error Localization, And Vulnerability RemediationNo ratings yet
- Supplier FAI PlanDocument1 pageSupplier FAI PlanBalakumaran MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis - Design (Dfmea)Document14 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis - Design (Dfmea)Balakumaran MurugesanNo ratings yet
- PFMEA-FIST Patch Splice TrayDocument12 pagesPFMEA-FIST Patch Splice TrayBalakumaran MurugesanNo ratings yet
- OSPL170144-PPR Report Budi-S Splice Up To 24 With Standard Pins With Feeder Cable KitDocument10 pagesOSPL170144-PPR Report Budi-S Splice Up To 24 With Standard Pins With Feeder Cable KitBalakumaran MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Moudling Operation GSIC Process: MouldingDocument13 pagesMoudling Operation GSIC Process: MouldingBalakumaran MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Moudling Operation GSIC Process: MouldingDocument13 pagesMoudling Operation GSIC Process: MouldingBalakumaran MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Manual-4RY8812 Version 2.0Document36 pagesManual-4RY8812 Version 2.0Katty MenaNo ratings yet
- 2PAA110154-610 A en System 800xa 6.1 Operator Workplace Support For Mobile DeviceDocument180 pages2PAA110154-610 A en System 800xa 6.1 Operator Workplace Support For Mobile Deviceershivkumar2002No ratings yet
- Mainly Designing SkeDocument22 pagesMainly Designing Skeapi-619135742No ratings yet
- Autosar Memory Stack (Memstack)Document21 pagesAutosar Memory Stack (Memstack)Marute ChavanNo ratings yet
- De005827 CBDC White Paper Final PagesDocument26 pagesDe005827 CBDC White Paper Final PagesAdil SadikiNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Survey On Authentication and Secure Key Management in Internet of ThingsDocument31 pagesA Comprehensive Survey On Authentication and Secure Key Management in Internet of ThingsEmmanuel Kayode FasinaNo ratings yet
- Hive Installation On WindowsDocument21 pagesHive Installation On WindowsSrinath YasamNo ratings yet
- AMDVBFLASH User Guide NDADocument12 pagesAMDVBFLASH User Guide NDADanej DoberšekNo ratings yet
- SID-2015-Tutorial 3-Ruaumoko and Dynaplot in Batch ModeDocument26 pagesSID-2015-Tutorial 3-Ruaumoko and Dynaplot in Batch ModeDiego RojasNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Harman/kardonDocument229 pagesService Manual: Harman/kardonSang NhNo ratings yet
- Sofimshc 1Document109 pagesSofimshc 1Chris LumyNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Research Aims and ObjectivesDocument7 pagesDissertation Research Aims and ObjectivesHelpWritingACollegePaperCanada100% (1)
- Lecture 8: Gradient Descent and Logistic RegressionDocument39 pagesLecture 8: Gradient Descent and Logistic RegressionAshish JainNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-21-25Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-21-25Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Api 5CDocument12 pagesApi 5CRakefsNo ratings yet
- Online FDP - Civil Engg-VIT ChennaiDocument2 pagesOnline FDP - Civil Engg-VIT ChennaiDharmesh DharmaNo ratings yet
- Format of Ielts General Training LettersDocument24 pagesFormat of Ielts General Training LettersmanwinderNo ratings yet
- Extract Files in FinaleDocument6 pagesExtract Files in FinaleAngela GohNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing: Introductory MaterialDocument30 pagesIP Addressing: Introductory MaterialJoby PaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To World Class ManufacturingDocument6 pagesIntroduction To World Class ManufacturinganurajNo ratings yet
- As An AI Language ModelDocument2 pagesAs An AI Language ModelAlfred TaimoniNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Computer Networks - Nibusinessinfo - Co.ukDocument2 pagesBenefits of Computer Networks - Nibusinessinfo - Co.ukMike MikkelsenNo ratings yet
- Practice6 CSDocument12 pagesPractice6 CS87shf2xx2jNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 HTML ManualDocument3 pagesLab 8 HTML ManualMisbah UllahNo ratings yet
- ST332B Adsl2+Document28 pagesST332B Adsl2+Juan Manuel Martinez AlbaceteNo ratings yet
- XCOM User GuideDocument33 pagesXCOM User GuideAnonymous ljkiyqJt8MNo ratings yet
- Image Captionbot For Assistive TechnologyDocument3 pagesImage Captionbot For Assistive TechnologyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet