Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DTM - Demographic Transition Model
DTM - Demographic Transition Model
Uploaded by
JP Model 14-V5-MKMSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DTM - Demographic Transition Model
DTM - Demographic Transition Model
Uploaded by
JP Model 14-V5-MKMSCopyright:
Available Formats
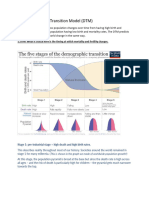
DTM – demographic transition model
The demographic transition model shows population change over time. It studies how birth rate and
death rate affect the total population of a country.
Watch the link below and describe each characteristics of each stage in DTM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l1_KBTk5FhQ
Stage 1 describes a period prior to the Industrial Revolution in 1750 where a majority of the human
population was. This is a period of constant conflict between human nations, tribes and groups that also
had a lack of access to more advanced forms of medication and vaccines. This sees death rates and birth
rates swing up and down constantly.
Stage 2 describes the period after the 1750’s where more advanced form of medication eliminates more
simply treated diseases like the common cold from being all too deadly. This sees a steady level of birth
rates and rapidly falling death rates.
Stage 3 is best compared to the period during the 1930’s to 50’s and over, which sees a rapid increase of
urbanization that dates back to the Victorian era prior to the First World War which sees a continued
decrease in deaths but now also births caused by factors such as urbanization alongside economic
booms in nations such as the U.S. in the 50’s and 60’s with a mind change too whilst maintaining the
same medicinal development.
Stage 4 sees low to no growth which is common amongst developed and High Income Countries today.
This sees the death rate and birth rate equalize with one another but on a much higher scale than Stage
1 seeing low deaths and low births meaning a steady but now massive population that ages overtime.
This is caused by urbanization and women being given more opportunities to join the workforce and the
such which leads to less of a will to be a housewife and deal with children.
Stage 5 is a stage that most countries have not reached but are reaching slowly such as Japan and Russia
(Although Russia’s reasons are much different than Japans) which sees the death rate be higher than the
birth rate. This can be attributed to factors such as an ageing population meaning less and less people
can or will reproduce leading to burdens on the few youths of society.
You might also like
- World Population Growth - World Bank ReportDocument6 pagesWorld Population Growth - World Bank ReportShaina SmallNo ratings yet
- Contemporary 2023 FinalsDocument31 pagesContemporary 2023 Finalsjrmv0902No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory of Demographic TransitionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To The Theory of Demographic Transitionela afrinNo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument3 pagesGlobal Demographykrbedes.pboxNo ratings yet
- Demographic TransitionDocument19 pagesDemographic TransitionIsha BalangueNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Demographic Transition (With Criticisms) : (A Critique About Population Growth)Document6 pagesThe Theory of Demographic Transition (With Criticisms) : (A Critique About Population Growth)Liezl LachicaNo ratings yet
- The Demographic Transition Model NoteDocument4 pagesThe Demographic Transition Model NoteJamal MollaNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transformation: Rubina Waseem Preston UniversityDocument46 pagesDemographic Transformation: Rubina Waseem Preston UniversityKiran KareemNo ratings yet
- Paper6 PDFDocument24 pagesPaper6 PDFzamaxxNo ratings yet
- PSW S 12078 PDFP Study Notes 2Document61 pagesPSW S 12078 PDFP Study Notes 2TREESANo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument18 pagesGlobal Demographyortegamaryann15No ratings yet
- Demographic TransitionDocument5 pagesDemographic TransitionreddishpinkNo ratings yet
- Demograpy and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesDemograpy and DevelopmentAditya GogoiNo ratings yet
- Population ExplosionDocument5 pagesPopulation Explosionprince robert bhairaviNo ratings yet
- Population PT 2 - Demographic TransitionDocument13 pagesPopulation PT 2 - Demographic TransitionTow anaNo ratings yet
- Critically Examine The Relevance of Demographic Transition Theory Explaining Population Growth in NigeriaDocument12 pagesCritically Examine The Relevance of Demographic Transition Theory Explaining Population Growth in NigeriaUzoma FrancisNo ratings yet
- Global Demography ReportDocument19 pagesGlobal Demography ReportSamantha Isabel Villaruel ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Global Demography CompressesDocument6 pagesGlobal Demography CompressesDianneNo ratings yet
- GEO303 Unit 4 LecDocument47 pagesGEO303 Unit 4 LecSahil PrasharNo ratings yet
- DTM HandoutDocument2 pagesDTM Handoutq6dc466k8bNo ratings yet
- The Demographic TransitionDocument6 pagesThe Demographic TransitionUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- The Demographic Transition Three Centuries of Fundamental Change - LeeDocument25 pagesThe Demographic Transition Three Centuries of Fundamental Change - LeeAihsirtAledZurcNo ratings yet
- World Population Growth: Countries Plummeting After World War IIDocument6 pagesWorld Population Growth: Countries Plummeting After World War IIJex DeyNo ratings yet
- Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentDocument57 pagesPopulation Growth and Economic DevelopmentTasnim Hosna100% (1)
- Global Demograph1Document20 pagesGlobal Demograph1Mir AqibNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition PowerPointDocument63 pagesDemographic Transition PowerPointTechnoShindoNo ratings yet
- Government Postgraduate College Samanabad FaisalabadDocument9 pagesGovernment Postgraduate College Samanabad FaisalabadMubeen AhmadNo ratings yet
- 4.1 & 4.2 Population Growth and Eco. Devt.-Demographic Transition Etc.-1Document7 pages4.1 & 4.2 Population Growth and Eco. Devt.-Demographic Transition Etc.-1rakesh naskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Ubcv2)Document8 pagesChapter 3 (Ubcv2)Janea GarciaNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition Model 2Document12 pagesDemographic Transition Model 2muhammad.faisal.ghulam.mustafa37No ratings yet
- Demography N MCH NotesDocument12 pagesDemography N MCH Notesjyotshna sahooNo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument3 pagesGlobal DemographyFaizal Usop PatikamanNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition TheoryDocument4 pagesDemographic Transition TheoryanshikchaurasiyaanshNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument15 pagesENGLISHElen. UnusyanNo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument27 pagesGlobal DemographyMaria MagisaNo ratings yet
- Demography Final Handout CorrectedDocument20 pagesDemography Final Handout Correctedmadanlal sainiNo ratings yet
- The Following Will Be Your Quiz #5 On The Topic DemographyDocument3 pagesThe Following Will Be Your Quiz #5 On The Topic DemographyRafael DelapeñaNo ratings yet
- Global Demography: Submitted By: John Kenneth M. ReyesDocument16 pagesGlobal Demography: Submitted By: John Kenneth M. ReyesJoshua CristobalNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Programming Theory and AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesNonlinear Programming Theory and AlgorithmsOmar Garcia FloresNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Population: Lea RN in G Obj Ectiv EsDocument28 pages15.2 Population: Lea RN in G Obj Ectiv Esshahida hassanNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition ModelDocument6 pagesDemographic Transition ModelJenn RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Types of Population PyramidDocument4 pagesTypes of Population PyramidEleonor Morales50% (2)
- The Demographic Transition Model 1Document2 pagesThe Demographic Transition Model 1TM_ButlerNo ratings yet
- Causes and Cons of DemoTransDocument22 pagesCauses and Cons of DemoTransitsmeryanNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition USA 2015Document1 pageDemographic Transition USA 2015caitlynstarkey123No ratings yet
- The Demographic TransitionDocument24 pagesThe Demographic TransitionShane Aliyah S. FermoNo ratings yet
- Population ExplotionDocument25 pagesPopulation ExplotionhasanNo ratings yet
- Population Evaluation and FutureDocument2 pagesPopulation Evaluation and FutureDéboraFernandesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Ge3Document3 pagesLesson 11 Ge3DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Population Dynamics & Processes: Birth, or Fertility, RatesDocument9 pagesPopulation Dynamics & Processes: Birth, or Fertility, RatesSamantha Ann T. TirthdasNo ratings yet
- Population Grow ChinaDocument3 pagesPopulation Grow ChinaLexi HabifNo ratings yet
- 4 TCW Chapter 4 Global Demography, Migration, and Global CitiesDocument18 pages4 TCW Chapter 4 Global Demography, Migration, and Global CitiesMiya LaideNo ratings yet
- Set 9 - Demographic Transition - LeeDocument38 pagesSet 9 - Demographic Transition - LeeAsnadenNo ratings yet
- DEMOGRAPHY Lee (2003) Journal of Economic Perspectives-1Document32 pagesDEMOGRAPHY Lee (2003) Journal of Economic Perspectives-1Jhon Luansing JarinaNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition HandoutDocument4 pagesDemographic Transition Handoutsalamgp21No ratings yet
- Economic Development and The Demographic Transition: The Role of Cumulative CausalityDocument39 pagesEconomic Development and The Demographic Transition: The Role of Cumulative CausalitySaira BalochNo ratings yet
- Name: Krishna Parnami Batch 1 Ba LLB (Spe - Energy) Semester 1 Roll Number: 53 SAP ID: 500061262 Topic: Demographic TranisitionDocument14 pagesName: Krishna Parnami Batch 1 Ba LLB (Spe - Energy) Semester 1 Roll Number: 53 SAP ID: 500061262 Topic: Demographic Tranisitionajay narwalNo ratings yet
- A TCWQDocument5 pagesA TCWQJunelyn QuimboNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 2024Document14 pagesPaper 1 2024JP Model 14-V5-MKMSNo ratings yet
- Ozone Loss ReviewDocument1 pageOzone Loss ReviewJP Model 14-V5-MKMSNo ratings yet
- ESS Species Diversity BodogolDocument5 pagesESS Species Diversity BodogolJP Model 14-V5-MKMSNo ratings yet
- Soil Texture Triangle WorksheetDocument2 pagesSoil Texture Triangle WorksheetJP Model 14-V5-MKMSNo ratings yet