Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drugs For Angina Pectoris (Notes)
Drugs For Angina Pectoris (Notes)
Uploaded by
Angelyca Delgado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesThis document discusses drugs used to treat angina pectoris, a condition where chest pain occurs due to reduced blood flow to the heart. It defines angina pectoris and its underlying cause of coronary artery disease. It describes the two main types of angina - chronic stable angina and Prinzmetal angina - and their pathophysiology. The document then discusses the therapeutic objectives of antianginal drugs which is to restore balance between oxygen supply and demand to the heart. It classifies antianginal drugs into two main categories - vasodilators which increase blood flow and non-vasodilators like beta blockers which decrease oxygen demand on the heart.
Original Description:
Angina Pectoris
Original Title
Drugs for Angina Pectoris (notes)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses drugs used to treat angina pectoris, a condition where chest pain occurs due to reduced blood flow to the heart. It defines angina pectoris and its underlying cause of coronary artery disease. It describes the two main types of angina - chronic stable angina and Prinzmetal angina - and their pathophysiology. The document then discusses the therapeutic objectives of antianginal drugs which is to restore balance between oxygen supply and demand to the heart. It classifies antianginal drugs into two main categories - vasodilators which increase blood flow and non-vasodilators like beta blockers which decrease oxygen demand on the heart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesDrugs For Angina Pectoris (Notes)
Drugs For Angina Pectoris (Notes)
Uploaded by
Angelyca DelgadoThis document discusses drugs used to treat angina pectoris, a condition where chest pain occurs due to reduced blood flow to the heart. It defines angina pectoris and its underlying cause of coronary artery disease. It describes the two main types of angina - chronic stable angina and Prinzmetal angina - and their pathophysiology. The document then discusses the therapeutic objectives of antianginal drugs which is to restore balance between oxygen supply and demand to the heart. It classifies antianginal drugs into two main categories - vasodilators which increase blood flow and non-vasodilators like beta blockers which decrease oxygen demand on the heart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
1 PHARMACOLOGY 2
Drugs for Angina Pectoris
Made by: KAVJ
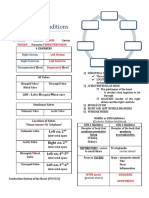
DRUGS FOR ANGINA PECTORIS - Complete damage (Infarction)
o Absence of oxygenation leading to
Angina Pectoris
myocardial necrosis or cell death
- Chest pain o 100% absent oxygen
- Resultant pathologic condition: CAD → Decreased Oxygen → Ischemia → Infarction
o Ischemia
o Infarction
▪ Coronary artery disease
ANGINA PECTORIS
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
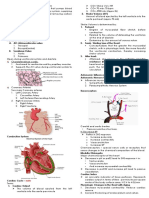
Coronary Artery
- A type of blood vessel that supply oxygenated blood to
the cardiac cells
- Heart pumps and relax because cardiac cells.
- The driving force of cardiac cells for it to pump & relax,
which is oxygen
- Gasoline Station: Coronary Artery
- CHD: obstruction (pagbabara)
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
- Also known as Ischemic Heart Angina Pectoris
Disease; Coronary Heart
Disease - Less oxygen accepted by cardiac cell
- Is a condition where insufficient - Is a characteristic chest pain or discomfort due to
blood flow can occur in one or myocardial ischemia or infarction
more coronary arteries - May be regarded as an expression of a coronary blood
o Only a segment of the supply-demand mismatch
heart is affected - UNDERLYING DISEASE: CAD
(barado)
Types of Angina Pectoris
- Can produce characteristic pain in the chest but pain
may not necessarily occur - Chronic Stable Angina
- Can be temporary, lasting for a few minutes, or Pectoris (CSAP)
permanent leading to death of tissue - Prinzmetal Angina
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
- Not enough blood
(oxygenation)
o Atherosclerosis CHRONIC STABLE ANGINA PECTORIS
▪ Plaque - aka Effort angina,
formation classic angina
made out of - Chest pain lasting for 2-
fats 5 minutes
o Thrombosis - Provoked by physical
▪ Blood clot exertion, emotional
▪ Stationary clot: thrombus stress, exposure to
o Embolism cold, or smoking
▪ Blood clot - No increase in severity,
▪ Travelling clot: embolus duration and frequency
o Vasospasm for the last 1-2 months
- If you rest, it is relieved, no pain will be felt.
Coronary Artery Disease PRINZMETAL ANGINA
MAY RESULT TO: - Also called Variant
Angina; Vasospastic
- Partial damage (Ischemia) Angina; Angina Inversa
o Decreased - Due to transient spasm of
oxygenation of localized portions of the
myocardium but blood vessels, usually
myocardial cells are associated with underlying
still viable atheromas
2 PHARMACOLOGY 2
Drugs for Angina Pectoris
Made by: KAVJ
o Can cause significant myocardial ischemia Classifications of Antianginal Drugs
and pain
o Pain occurs principally at rest, usually I. Vasodilators
unprovoked by physical exertion - Targets the coronary arteries
o Nitrovasodilators
▪ Nitrate/nitrites are converted into
Nitric Oxide
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ANGINA
▪ Nitric oxide activates GC which
- Imbalance between the oxygen requirement of the forms cGMP
heart and the oxygen supplied to it via coronary ▪ cGMP removes phosphate from
vessels MLC-PO4, which leads to relaxation
o Hindi balance ang oxygen supply and oxygen o Calcium Channel Blockers
demand ▪ Blocks L-type calcium channel,
o Supply: Supplier / Coronary artery which leads to relaxation
o Demand: Acceptor / Heart o Dipyridamole - Non-nitrate coronary
vasodilator
- In CSAP ▪ Phosphodiesterase metabolizes
o Because of the effort, you feel the pain = cGMP making it GMP (inactive)
heart pumps faster = more workload = ▪ Phosphodiesterase inhibitor
demands more oxygen ▪ Inhibits the PDE, increase cGMP,
o Coronary arteries cannot give what the relaxation of blood vessel
heart needs → heart feels the pain
(imbalance)
o Myocardial oxygen requirement is not
proportional to coronary blood flow
o Ischemia usually leads to pain, but is some
individuals, not accompanied by pain (“silent”
or “ambulatory” ischemia)
o TOO DEMANDING
- In Variant Angina
o The problem is the vasospasm = low
oxygen supply
o Even no effort/demand, there is pain
o Oxygen delivery decreases as a result of
reversible coronary vasospasm
o LOW SUPPLY OF OXYGEN
II. Non-vasodilator
Therapeutic Objectives of Antianginal Agents o β-adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
- To restore the balance between myocardial O2 supply
and demand
o Decrease O2 demand and increase the
perfusion of ischemic subendocardial tissue:
CSAP
▪ β-blockers
▪ Nitrovasodilators
▪ Ca2+- channel blockers
o Counteract vasospasm and increase O2
supply : Variant Angina
▪ Nitrovasodilators
▪ Ca2+- channel blockers
Beta 1 in the heart:
DRUG ACTION IN ANGINA
- Stimulation
- Decrease myocardial oxygen requirement by
- Increase contraction
decreasing the determinants of oxygen demand
- Gs linked → increase cAMP
o heart rate
o cAMP – responsible for activation of Protein
o ventricular volume
kinase A (PK-A)
o blood pressure
o PK-A facilitates opening of L-type calcium
o contractility
channel
- Increase myocardial oxygen delivery by reversing
coronary artery spasm
3 PHARMACOLOGY 2
Drugs for Angina Pectoris
Made by: KAVJ
o L-type calcium channel will let trigger Other Effects of Nitrates
calcium enter
o Contraction - Nitrates are generally vasodilators
- Relaxation: Increase in cGMP
▪ Very brief ang effect (mabilis lang)
▪ Short lived ang effect
Beta blockers:
▪ Don’t provide clinical benefit
- Competitively block binding of NE to its receptors o Bronchi
o NE cannot bind to B1 receptor o GIT
o No cAMP o Biliary Tract
o L-type calcium channel closes, no entering of o GUT
trigger calcium o Corpus Cavernosum (penile tissue)
o Depression of heart ▪ Vasodilation
▪ More blood goes into the penis →
erection
Nitrovasodilators
- Platelets – decreased aggregation
- Organic Nitrite and Nitrates (R-NO2) o Potentially cause bleeding
o Not significant clinically
- Other effect: Methemoglobinemia
o Observed in using Amyl nitrite
D/I with PDE5 INHIBITORS
o Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors
o In the penile tissue, it degrades and
metabolize cGMP into inactive GMP
MOA:
o cGMP causes erection (dilation)
- Organic nitrates are converted into Nitric oxide by
Nitric oxide synthase, where NO cause increase - SILDENAFIL, TADALAFIL, VARDENAFIL
levels of cGMP → vasodilation (relaxation) o Erectogenic drugs
- Nitroprussides increase NO → increase cGMP → o Block of PDE5 → Increase cGMP → penile
vasodilation erection
- To activate NO synthase, it needs a cofactor - Used in the treatment of Erectile dysfunction
o Groups containing -SH NOTE:
o Thiol-requiring
o PDE5 inhibitors also acts in the blood
vessels like arteries and veins.
Pharmacologic Effects of Nitrates (VASODILATION). Hypotension
o Mas safer ang mga nagc-cause ng
- At regular/ low doses (ISDN 5 mg SL, NTG 0.6 mg SL) erection na local administration. (turok sa
o Used for CSAP penis)
o Effect is PERIPHERAL VENODILATION o It is commonly taken by elderly, they are
o Venodilation: dilation of veins = more more prone to cardiac problems, cardiac
reservoir (capacitance) = less preload = arrest.
less workload = less oxygen
o HEART IS NOT SO DEMANDING o Both nitrates and PDE5 inhibitors cause
▪ Increased peripheral pooling of increase in cGMP levels in the blood
blood vessels.
▪ Decreases preload/venous return
▪ Decreased myocardial wall tension
▪ Decreased O2 requirements and
- Sildenafil (Viagra) potentiates the action of nitrates
reduce tissue pressure
o Severe hypotension and a few myocardial
infarctions have been reported in men taking
- At high doses (High Dose IV Infusion) both drugs
o Used for Prinzmetal
o It is recommended that at least 6 hours pass
o Additional arteriolar and coronary artery between use of a nitrate and the ingestion of
vasodilation
sildenafil
o CA vasodilation = more oxygen supply - Sildenafil also has effects on color vision, causing
▪ Reduced mean arterial pressure
difficulty in blue-green discrimination
▪ Reduce afterload
▪ Diminish O2 requirements
o Men at risk for impotence are aged 50-60
▪ Increased O2 supply
yrs old and above.
4 PHARMACOLOGY 2
Drugs for Angina Pectoris
Made by: KAVJ
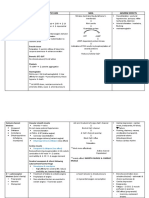
Classes of Nitrovasodilators o Based from the workers that manufactures
bombs, nitrates are API in bombs. If high
I. Very Short-acting (<5-10 minutes)
doses, it is explosive.
o Amyl nitrite – the only nitrite (inhalation)
o Monday, fresh from off, sensitive ang workers
II. Short-acting (10-30 minutes)
sa effects.
o ISDN SL, NTG SL
- Reflex tachycardia
▪ Isosorbide Dinitrate Sublingual
o Felt at high dose nitrate, mask using beta-
▪ Nitroglycerin Sublingual
blockers
III. Intermediate-acting (5-8 hours)
- Postural hypotension
o ISDN tab PO, NTG-SR tab PO
- Nitrite ions oxidize iron atoms of hemoglobin to
▪ Isosorbide Dinitrate tablet taken by
methemoglobin – hypoxia (methemoglobinemia)
mouth
▪ Nitroglycerin Sustained Released
tablet taken by mouth
IV. Long-acting (10-24 hours) Beta-Blockers in Angina
o ISDN-SR tab PO, ISMN tab PO, NTG Beta-Blockers
Transdermal Patches
▪ Isosorbide Dinitrate Sustained - Cardiac depressants and do not act on the blood
Release tablet taken by mouth vessels.
• Isordil - Decreases the heart’s oxygen demand
▪ Isosorbide Mononitrate tablet taken - First line maintenance treatment for CSAP
by mouth o Decrease myocardial oxygen requirement by
• Imdur reducing heart rate, blood pressure and
▪ Nitroglycerin Transdermal patch contractility at rest and during exercise
o Appear to be the most important mechanism
for relief of angina and improved exercise
tolerance
Clinical Uses of Nitrovasodilators
- Prevent reflex tachycardia associated with
- Management of Angina pectoris nitrovasodilators at high doses
o ACS (Acute Coronary Syndrome) – IV o Can reduce the frequency of anginal attack
Infusion - Note: If the patient has on-going angina pectoris,
o CSAP – PO or transdermal NEVER give beta blockers as single agents
o Prinzmetal Angina – IV Infusion + Beta because of compensatory mechanisms that may
Blocker occur.
▪ High dose nitrate: arteriolar
dilation → decrease arterial
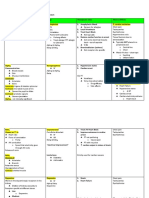
CCBs in Angina
pressure → negative feedback of
baroreceptor → reflex tachycardia Calcium Channel Blockers
(baroreceptor activation) → more
stress in the heart → more oxygen 1. Dihydropyrimidines
needed (demanding) o Acts on the arteries
▪ Combined with beta-blocker, for the 2. Non-Dihydropyrimidines
concealing of reflex tachycardia o Acts in the heart
- Alternative in the Management of Hypertensive - Reduce myocardial oxygen requirements
Emergency – IV Infusion o Verapamil is applied
- Add-on in the Management of CHF o decrease in myocardial contractile force
o ISDN w/ Hydralazine o decrease arterial and intraventricular
o Effective only on African-American px pressure
- Acute Pulmonary Edema (TDDS or SL) - Relieve and prevent the focal coronary artery spasm
o Transdermal delivery system involved in variant angina
o Sublingual o DHPs are used (ending in -dipines)
- Initial Management of Cyanide Poisoning o most effective prophylactic treatment
o Amyl Nitrite CCBs in Angina
- Non-DHP
Adverse Effects of Nitrovasodilators o Verapamil, Diltiazem
o Alternative to beta blockers as maintenance
- Tolerance treatments for CSAP
o Develops when nitrate serum levels are - Long-acting DHP CCBs
sustained over time o Lercanidipine, Lacidipine, Amlodipine
- Vascular Headache o Alternative treatments
o Throbbing headache due to dilation effect - Short-acting DHP CCBs
- Monday Disease o Generally avoided unless for prinzmetal
o Historical (given with beta blockers)
o Headache, tolerance
You might also like
- The Original Backnobber II Tool: User GuideDocument37 pagesThe Original Backnobber II Tool: User GuideAl BnNo ratings yet
- Hematology MCQsDocument84 pagesHematology MCQsHyder Ali84% (19)
- Cardio CH 27 NotesDocument8 pagesCardio CH 27 NotesMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Final RevalidaDocument24 pagesFinal RevalidaKyrajane EsguerraNo ratings yet
- MS Day 1 2Document9 pagesMS Day 1 2Geraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Antinanginal DrugsDocument6 pagesAntinanginal DrugsStefhanie Mae LazaroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ANGINADocument6 pagesReviewer ANGINAytexokrst9No ratings yet
- Short Cardic TabDocument4 pagesShort Cardic TabthackeryuktaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument22 pagesPharmacology NotesJuliann100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemFisco DessereiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Cardio, Snle KsaDocument17 pagesCardio, Snle KsaAa AaNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument14 pagesAngina Pectorisnidhi100% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndromes GAPDocument25 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes GAPhhgangurde9323No ratings yet
- DYSRHYTHMIASDocument15 pagesDYSRHYTHMIASKristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mi PresentationDocument65 pagesMi PresentationJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical NursingMaria TagubaNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument45 pagesAngina PectorisClarisse Biagtan CerameNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Module - Cardiac ConditionsDocument5 pagesCardiac Module - Cardiac ConditionsMarie MNNo ratings yet
- CT_L23_PENYAKIT KARDIOVASKULAR DAPATANDocument12 pagesCT_L23_PENYAKIT KARDIOVASKULAR DAPATAN014 Reshaina ZahratuljannahNo ratings yet
- 401 ReviewerDocument30 pages401 ReviewerSheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DisordersDocument35 pagesCardiac DisordersNaomi Anne AsuntoNo ratings yet
- Final Oral EditedDocument1 pageFinal Oral EditedRey CortezNo ratings yet
- MI SlidesDocument65 pagesMI SlidesJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- 3) Management of IHD (Notes)Document25 pages3) Management of IHD (Notes)Priyanka GosaiNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument7 pagesCoronary Artery Diseasejmar767No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular SystemDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument4 pagesAngina PectorisJohiarra Madanglog TabigneNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Antiagina TTMDocument83 pagesFarmakologi Antiagina TTMEpha Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel BlockersDocument8 pagesCalcium Channel BlockersblankNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document4 pagesActivity 5AngieNo ratings yet
- Med Surg CVD HemaDocument10 pagesMed Surg CVD Hemabekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- Week 29-Angina - MI PDFDocument7 pagesWeek 29-Angina - MI PDFJaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular REVIEWDocument9 pagesCardiovascular REVIEWJezzabel Kyra BadayosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemJenny Torreda100% (1)
- Pharmacology NCLEX ReviewDocument128 pagesPharmacology NCLEX ReviewBritanny NelsonNo ratings yet
- MT MS ArrythmiaDocument3 pagesMT MS ArrythmiaChuchai AmbongNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument23 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionLouise NicoleNo ratings yet
- 5.4 IHD HHD CHF Cor PulmonaleDocument15 pages5.4 IHD HHD CHF Cor PulmonaleMemay velascoNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart Disease (CR)Document11 pagesIschaemic Heart Disease (CR)Banana CakeNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Drugs: Classes Therapeutic Uses MOA Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesAntianginal Drugs: Classes Therapeutic Uses MOA Adverse EffectsNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument40 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromesandi siregarNo ratings yet
- Pathology 1016-Test 2 - Path 4Document3 pagesPathology 1016-Test 2 - Path 4Nicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ABC-CardioDocument7 pagesModule 2 ABC-Cardiomelba040510No ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument59 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- CPT OSCE Reviewer: I, III, V: Case #1Document19 pagesCPT OSCE Reviewer: I, III, V: Case #1manideepreddyNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisPadmanabha T SNo ratings yet
- NorvascDocument1 pageNorvascsoftwareitoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Med SurgDocument7 pagesNCM 112 - Med SurgKierzteen Brianna TaromaNo ratings yet
- Mki 012Document4 pagesMki 012Sinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Blue Print Chapters 15-16 Autonomic NSDocument10 pagesBlue Print Chapters 15-16 Autonomic NSMarisella ReadonNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument33 pagesAngina PectorisRosse Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesPharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemCheryl OrtizNo ratings yet
- Cardio Intensive ReviewDocument40 pagesCardio Intensive ReviewAchilles YbarraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart FailureDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart Failurelynch775100% (2)
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesSudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart Diseasenmyza89No ratings yet
- 4 Chambers of The Heart: Heart Blood Vessels (Arteries and Veins) Blood FlowDocument19 pages4 Chambers of The Heart: Heart Blood Vessels (Arteries and Veins) Blood FlowFilane AntonetteNo ratings yet
- Review On Cardiovascular Diseases: BY: Fidel G. Yongque III, RNDocument20 pagesReview On Cardiovascular Diseases: BY: Fidel G. Yongque III, RNFidel Gimotea Yongque IIINo ratings yet
- L1 - Acute Coronary Syndrome - Yassen AyadDocument22 pagesL1 - Acute Coronary Syndrome - Yassen Ayadmtr325gfNo ratings yet
- Cvspa04 Ihd and MiDocument8 pagesCvspa04 Ihd and MiRobert So JrNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ConditionsDocument15 pagesCardiac ConditionsMariane GumbanNo ratings yet
- Animal ScienceDocument19 pagesAnimal ScienceGel Mi AmorNo ratings yet
- Macrocytosis - What Causes It - Mayo ClinicDocument3 pagesMacrocytosis - What Causes It - Mayo ClinicvmarinelliNo ratings yet
- Kunjungan Sakit Juni 2022Document214 pagesKunjungan Sakit Juni 2022fiqih afandiNo ratings yet
- Session Schedule 20.4.2023Document32 pagesSession Schedule 20.4.2023Aditya RaiNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Importance of Climbers Used in UnanimedicineDocument37 pagesMedicinal Importance of Climbers Used in UnanimedicineKrishnendu RayNo ratings yet
- Oxford Handbook of Geriatric Medicine 3nbsped 0198738382 9780198738381 CompressDocument753 pagesOxford Handbook of Geriatric Medicine 3nbsped 0198738382 9780198738381 CompressNemer Isaeed100% (3)
- 84-Article Text-538-1-10-20201115Document54 pages84-Article Text-538-1-10-20201115Rubilin NitishaNo ratings yet
- TVP 2021 0708 - EarMitesDocument6 pagesTVP 2021 0708 - EarMitesxelexet212No ratings yet
- Cpms College of Nursing: Assignment ON Infection SurveillanceDocument9 pagesCpms College of Nursing: Assignment ON Infection SurveillanceAmy Lalringhluani ChhakchhuakNo ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa Thesis Book Medical Laboratory GeesDocument54 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa Thesis Book Medical Laboratory Geesdhaweeyec12No ratings yet
- Radiology ChantingDocument37 pagesRadiology ChantingKapilNo ratings yet
- Public Health MODULE 7 - Pharmacists, Vaccines, and Public HealthDocument13 pagesPublic Health MODULE 7 - Pharmacists, Vaccines, and Public HealthEmerson John TallodNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Tests Allowing For Imperfect Reference StandardsDocument16 pagesBayesian Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Tests Allowing For Imperfect Reference StandardsYeltsin CastroNo ratings yet
- Pub 004721 PDFDocument42 pagesPub 004721 PDFRenee Jessee Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Colostrum - How Does It Keep Health?Document9 pagesColostrum - How Does It Keep Health?JakirNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Hernia Case FileDocument2 pagesInguinal Hernia Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- UPDRS v1.0 Annotated CRF PDFDocument8 pagesUPDRS v1.0 Annotated CRF PDFAnaaaerobiosNo ratings yet
- ULAT KAMBAL (Pishach Karpas) - Abroma Augusta: A Study On Its Pharmacological Actions From An Ayurvedic PerspectiveDocument7 pagesULAT KAMBAL (Pishach Karpas) - Abroma Augusta: A Study On Its Pharmacological Actions From An Ayurvedic PerspectiveIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Bloodbld 2019003808 CDocument12 pagesBloodbld 2019003808 CBillal BenhaddadNo ratings yet
- Energy Healing TechniquesDocument17 pagesEnergy Healing TechniquesRAMESHBABUNo ratings yet
- The Final FRCA Short Answer Questions - A Practical Study Guide (PDFDrive)Document348 pagesThe Final FRCA Short Answer Questions - A Practical Study Guide (PDFDrive)Andreea0% (1)
- Infectious Diseases: Thea Brabb, Denise Newsome, Andrew Burich, and Martha HanesDocument47 pagesInfectious Diseases: Thea Brabb, Denise Newsome, Andrew Burich, and Martha HanescarlosNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy With EpilepsyDocument40 pagesPregnancy With EpilepsyNaman MishraNo ratings yet
- TMP - 11835-Management of Acute Appendicitis in Adults - UpToDate-1753868369Document20 pagesTMP - 11835-Management of Acute Appendicitis in Adults - UpToDate-1753868369Renata Victoria0% (1)
- Surgery 1 Finals PretestDocument15 pagesSurgery 1 Finals Pretest2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Fisiologia Do EnvelhecimentoDocument2 pagesFisiologia Do EnvelhecimentoLissandro DannyNo ratings yet
- s00431 022 04409 8Document12 pagess00431 022 04409 8Marcela SinisterraNo ratings yet
- A Study About The Relocation of Badjao Community in Totolan 4Document17 pagesA Study About The Relocation of Badjao Community in Totolan 4welpNo ratings yet