Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kassabr - Care Map 5 - GW
Kassabr - Care Map 5 - GW
Uploaded by
ranakassab7Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Discharge Summary 17 Sep 22Document3 pagesDischarge Summary 17 Sep 22Jomon ThampyNo ratings yet
- Emergency Antibiotic Guide A6 105 1048mm February9 2022Document48 pagesEmergency Antibiotic Guide A6 105 1048mm February9 2022Iain HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument20 pagesCase Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseaseYetTamparong50% (2)
- Portfolio Pat 1Document18 pagesPortfolio Pat 1api-365835586No ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz100% (4)
- Template HXDocument1 pageTemplate HXdawnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BipolarDocument13 pagesDrug Study BipolarrahimsyusophNo ratings yet
- Assessment DiagramDocument1 pageAssessment DiagramHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: University of Southern Mindanao Department of NursingDocument2 pagesDrug Study: University of Southern Mindanao Department of NursingSoleil ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Piptaz DSDocument4 pagesPiptaz DSArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Ursing ARE LAN: College of NursingDocument2 pagesUrsing ARE LAN: College of NursingTsu Wei ChuaNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole PoDocument5 pagesMetronidazole PoFlower Flower FlowerNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument1 pageCefuroxime Drug StudyACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- ms1 PatDocument14 pagesms1 Patapi-364212510No ratings yet
- Vomito PDFDocument2 pagesVomito PDFMauricio RíosNo ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Fundamental Patient Assessment ToolDocument19 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Fundamental Patient Assessment Toolapi-418237167No ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient InformationDocument24 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient Informationapi-315444338No ratings yet
- Pat Revised 9-2014 FundamentalsDocument14 pagesPat Revised 9-2014 Fundamentalsapi-355083078No ratings yet
- 1 Halker Singh Evaluation of Headaches MC Clinical Reviews 2024 CA R SecureDocument62 pages1 Halker Singh Evaluation of Headaches MC Clinical Reviews 2024 CA R Securecadena.astridNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RosillosaDocument4 pagesDrug Study RosillosaJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Takotsubo Syndrome Pathophysiology, Emerging Concepts, and Clinical Implications CirculationDocument1 pageTakotsubo Syndrome Pathophysiology, Emerging Concepts, and Clinical Implications Circulationmarianflacara96No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyMizpah DuculanNo ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient InformationDocument16 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient Informationapi-402496681No ratings yet
- DS AcetaminophenDocument2 pagesDS AcetaminophenSoleil ArcenalNo ratings yet
- NaproxenDocument2 pagesNaproxenDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Pat 2Document19 pagesPat 2api-404415990No ratings yet
- ms1 Pat 2-2Document21 pagesms1 Pat 2-2api-404285262No ratings yet
- GastroenterologyDocument2 pagesGastroenterologyPermis Pour Tous frNo ratings yet
- Pat 1 Medsurg 1Document17 pagesPat 1 Medsurg 1api-354599629No ratings yet
- Balacano, John Glenn BSN-3A: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBalacano, John Glenn BSN-3A: ClassificationDaintyGarciaNo ratings yet
- Ms 1 Pat Marline FaustinDocument18 pagesMs 1 Pat Marline Faustinapi-365764138No ratings yet
- Vaccine Vaccine Vaccine: Prevention StepDocument1 pageVaccine Vaccine Vaccine: Prevention StepNUR AMALIA BINTI ABD. AZIZNo ratings yet
- Pat ms2Document20 pagesPat ms2api-355298006No ratings yet
- Daftar Pasien Baru Bedah Saraf 14 Mei 2019: NO Divisi TGL in Nama U MR Diagnosa R Rencana KS R Problem J KDocument1 pageDaftar Pasien Baru Bedah Saraf 14 Mei 2019: NO Divisi TGL in Nama U MR Diagnosa R Rencana KS R Problem J KFaisal AkbarNo ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient InformationDocument19 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient Informationapi-418237167No ratings yet
- Patient Information Sheet Patient: Doctor: Room: Age: Sex: AllergiesDocument2 pagesPatient Information Sheet Patient: Doctor: Room: Age: Sex: AllergiesLauraysha McMillanNo ratings yet
- Iv Drip IsoxilanDocument1 pageIv Drip IsoxilannierbobierNo ratings yet
- Kristina Nealy ms1 Pat 1 2Document19 pagesKristina Nealy ms1 Pat 1 2api-314372295No ratings yet
- Pat FundiesDocument16 pagesPat Fundiesapi-338998736No ratings yet
- Pat ms1 3 08Document14 pagesPat ms1 3 08api-371817203No ratings yet
- Final Group 2Document29 pagesFinal Group 2minalongjonairaNo ratings yet
- Menpin Drug StudyPenthidineDocument2 pagesMenpin Drug StudyPenthidineVine CastroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagram Format: Example: Ego Integrity Vs Despair, Sense of Satisfaction or FailureDocument1 pageAssessment Diagram Format: Example: Ego Integrity Vs Despair, Sense of Satisfaction or FailureShirley L. CarumbaNo ratings yet
- Pat FundiesDocument18 pagesPat Fundiesapi-355298006No ratings yet
- Hypertension: Prognostic, Diagnostic and Therapeutic AspectsDocument3 pagesHypertension: Prognostic, Diagnostic and Therapeutic AspectsSandwingNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: Medicatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerati ONDocument4 pagesRUG Tudy: Medicatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerati ONGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Medication Indication Contraindicati0N Side Effects Use Caution inDocument17 pagesDrug Study: Medication Indication Contraindicati0N Side Effects Use Caution inAngely Dianne Santiago II100% (2)
- Course in The Ward (April 25-28 Roys)Document9 pagesCourse in The Ward (April 25-28 Roys)Royce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- CNS: Dizzin Ess, Fatigu E, Heada Che, Vertig O,: Tagum Doctors College, IncDocument6 pagesCNS: Dizzin Ess, Fatigu E, Heada Che, Vertig O,: Tagum Doctors College, IncAnne BasilesNo ratings yet
- History FormDocument5 pagesHistory FormYazeed AsrawiNo ratings yet
- Pat Fall 1-1Document17 pagesPat Fall 1-1api-339160012No ratings yet
- PRIETO - Antipsychotic Drug 3Document4 pagesPRIETO - Antipsychotic Drug 3Stiffany PrietoNo ratings yet
- DS-ARF - FINALDocument4 pagesDS-ARF - FINALAlkiana SalardaNo ratings yet
- Patient's Name: Alindajao, Filoteo Diagnosis: CAD Date of Admission: Sex: 58yo Age: Male Height/WeightDocument1 pagePatient's Name: Alindajao, Filoteo Diagnosis: CAD Date of Admission: Sex: 58yo Age: Male Height/WeightButts McgeeNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDSDocument1 pageHIV - AIDSMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoDocument3 pagesDrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledMARIA KIMBERLY S. PINEDANo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Record From Queensland, AustraliaDocument20 pagesPregnancy Record From Queensland, AustraliaPutri AyuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: - 24/june/2020Document1 pageDrug Study: - 24/june/2020daliaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Current Guidelines of Five International Societies On Clostridium Difficile Infection ManagementDocument24 pagesA Comparison of Current Guidelines of Five International Societies On Clostridium Difficile Infection ManagementJulio S. UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic Record TemplateDocument1 pageDrug Therapeutic Record TemplateAubrey Justine GaleonNo ratings yet
- TherapeuticsDocument13 pagesTherapeuticsChecko LatteNo ratings yet
- Sanofi Annual Report 2014Document85 pagesSanofi Annual Report 2014MirzaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Infections: Ickman Setoaji W, DRG., MMDocument66 pagesOdontogenic Infections: Ickman Setoaji W, DRG., MMAmeliza Putri AlindNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- Helicure - Google SearchDocument1 pageHelicure - Google Searchalijan deparNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole PoDocument5 pagesMetronidazole PoFlower Flower FlowerNo ratings yet
- Genital Tract InfectionDocument52 pagesGenital Tract InfectionArvindan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Amphotericin BDocument23 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Amphotericin BElizabeth IdananNo ratings yet
- Brosur Infus-1Document1 pageBrosur Infus-1AKbarNo ratings yet
- Clostridioides Difficile Infection in AdultsDocument28 pagesClostridioides Difficile Infection in AdultsIrina DuceacNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY FOR HYPOKALEMIA Case Study 3Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY FOR HYPOKALEMIA Case Study 3Montero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- STI Treatment WorksheetDocument2 pagesSTI Treatment WorksheetJonas OltmanNo ratings yet
- Myoma Pathophysio, Gordon's NCPDocument13 pagesMyoma Pathophysio, Gordon's NCPicesexy100% (1)
- K46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)Document78 pagesK46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)ayapillaiNo ratings yet
- 2nu03-Group1 Case-Presentation ArmmcpediapmDocument39 pages2nu03-Group1 Case-Presentation ArmmcpediapmCyrus GarciaNo ratings yet
- MollyDocument7 pagesMollyapi-534233456No ratings yet
- M C Q AnaesthesiaDocument7 pagesM C Q Anaesthesiaahmed_anaes1234No ratings yet
- Anti-Protozoal Agents: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIDocument21 pagesAnti-Protozoal Agents: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIHimanshu Barman100% (1)
- Management of Intra-Abdominal InfectionDocument65 pagesManagement of Intra-Abdominal InfectionKamran SherazNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Group 3Document16 pagesModule 8 - Group 3MEDECIELO MELONo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument9 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseSohanInduwaraGamage100% (2)
- Placenta PreviaDocument87 pagesPlacenta PreviaKaye Cueto100% (1)
- نموذج طب بشريDocument11 pagesنموذج طب بشريBassam AlqadasiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ChartsDocument61 pagesAntibiotic Chartspempekplg100% (1)
- Draper 2005Document5 pagesDraper 2005atls jakartaNo ratings yet
Kassabr - Care Map 5 - GW
Kassabr - Care Map 5 - GW
Uploaded by
ranakassab7Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kassabr - Care Map 5 - GW
Kassabr - Care Map 5 - GW
Uploaded by
ranakassab7Copyright:
Available Formats
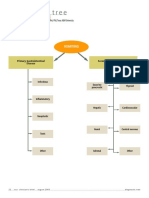
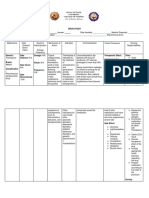
Nifedipine (Procardia chronic medical
XL) 30 mg PO BID condition: cancer Dehydration
Chronic medical condition: HTN
Azilsartan 40mg PO recent severe chronic medical
illness or Diabetes condition: lung KEY
hospitalization disease Patient Demographics:
Tamsulosin (Flomax)
BPH
Pt Initials: GW NANDA
0.4 mg PO BID chronic medical Primary Medical
Urinary retention like Age: 87 Risk Factors
condition: kidney
neurogenic bladder
Infections
Gender: Male
Diagnosis Goal
disease
Ethnicity: white Nursing intervention
Shingles older adult >65
weak immune Code status: Full Pathophysiology Mediactions
recurrent UTI
years old
system due to DOA: 10.20.23 Rationale
aging
AD: No
Paitent's Data
Brimanidine Fall Risk: High Labs and Diagnostics Possible
Glaucoma Allergies: Penicillin Complications
(ALPHAGAN) 0.2%
1drop/eye Isolation: standard Evaluation/modification
Admitting diagnosis: Sepsis and Clinical Manifestation
Dorzolamide HCL- Patient Related=
timolol, one drop/eye Pneumonia Yellow highlight
Erickson's level: Integrity vs
Despair
Sepsis Cefepime 2g/50ml past medical History
Current surgery (NA)
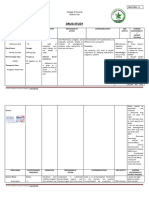
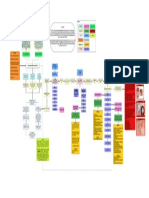
bacteremia MINI NANDA #1: Unstable blood pressure R/T infection, age, and increase
in systolic pressure AEB patient blood pressure is 154/96, patient 2-3 cups
of coffee/day, the patient gets stressed and anxious easily.
Interventions:
Priority problem: Impaired gas exchange R/T decreased lung capacity and decreased 1- administer Azilsartan 40mg PO daily at 9:00.
functional lung tissue AEB, crackles heard at the bases of both lungs, X-ray for the chest release of endotoxins 2- administer Nifedipine 30mg PO BID at 9:00.
shows bilateral atypical pneumonia/atelectasis, CT chest w/o contrast suggests 3- Educate the patient about coffee intake and nonpharmaceutical
pulmonary fibrosis. The patient has edematous lower RLE and LLE. techniques, like guided imagery and deep breathing techniques, to
release of pro- decrease stress and anxiety.
inflammatory: cytokines
Goal: by the end of the shift patient will have improved exchange AEB, the patient will (TNF, IL-1 alpha &
have no signs of respiratory distress or complications, the O2 saturation after each beta, IL-6)
check will be more than 95%, patient will know how to use the incentive spirometer. Mini NANDA #2: risk for DVT R/T unstable blood
activation of: pressure, patient's decreased mobility,
-coagulation system comorbidities, Edema in lower extremities.
Nursing Interventions: -complement system Interventions:
-Kinin system 1- Apply elastic stocking to prevent edema.
-Neutrophil, endothelial and mono- 2- Administer Enoxaparin 80mg SQ daily at 11:00 a.m.
Assessment/intervention: macrophage cell activity 4- Educate the patient to exercise an active range of
1- I: Asses the pulse oximeter reading Q4 hrs and report O2 sat less than 90%. motion in bed.
Rationale: Oxygen saturation of less than 90% can indicate a sign of impaired gas Release of anti-inflammatory cytokines:
-LPS binding protein
exchange and possible complications. The patient might require oxygen -IL-1 receptor antagonist
therapy (Swearingen, 2016, p. 119). Mini NANDA #3: risk of Myocardial Infarction R/T
-IL-10
comorbidities, age, unstable blood pressure.
PR: patient oxygen saturation is 98%. -Nitric acid
Interventions:
2- I: Monitor the patient for signs of respiratory distress. 1- Educate the patient to take blood pressure and heart
Rationale: signs and symptoms of respiratory distress include decreased LOC, endothelial cell every day simultaneously and take them before and after
decreased mental status, restlessness, RR less than 10 breaths per minute, use of dysfunction medication administration.
2- educate the patient to take their blood pressure
accessory muscles, and anxiety (Swearingen, 2016, p. 119).
medication on time.
RR: The patient did not have signs of respiratory distress; his RR was 18, A&OX4, and 3- Educate the patient to eat healthy, decrease fatty food,
he had no signs of anxiety, restlessness, or confusion. tissue microvascular cell programmed free radical and exercise.
hypoxia thrombus adhesion cell death damage
Management/Intervention:
3- I: adminitser Metromidazole (FLAGYL) 500mg IVPB q 8hrs. multiple organ
Rationale: Metronidazole binds and disrupts PNA structure, thereby blocking bacterial nucleic damage
acid synthesis, and early administration of antibiotics decreases inflammation in the lungs
(Skidmore, 2021, p. 846) (Swearingen, 2016, p. 119)
PR: the patient was given Metronidazole (FLAGYL) 500mg IVPB at 11:00.
poor metabolic acidosis 2 or more of SIRS criteria:
4- I: auscultate the patient's breath sounds q2-4 hours or as indicated by the patient's decreased altered mental
capillary thrombocytopenia causes increase fatigue
-Temp 101.3F on admission
urination status
refil lactate
health condition. -WBC count: 18.72k on admission
- Confusion
Rationale: absent or adventitious lung sounds like crackles and wheezing can signal the - HR > 90BPM
nurse about airway obstruction, hypoxia, fluids or air trapping (Swearingen, 2016, p. -RR > 20 breath/min
119).
PR: the patient has a clear lung. Sounds throughout except at the bases where crackles
are heard in the RLL and LLL. decreased UA:
mobility d/t -protein in the urine 30mg/dl - normal<30mg/dl
Hospitalization -Nitrate: positive - normal is negative or trace
Patient education: -WBC UA: 11-20 - normal is 0-5
5- I: Educate the patient on how and why they must use the IS four times/day -RBC UA: 3-5 - normal is 0-2
Lung sounds: Swollen legs (Edema in the -Squamous epithelial: 6-10 - normal is 0-5
Rationale: IS maximizes the expansion of the lungs and alveoli to help resolve the fluids in the -bacteria in urine: few - normal is none seen
Pneumonia Crackles at RLE & LLE) d/t pneumonia
atelectasis caused form pneumonia and mobilizes secretions (Swearingen, 2016, p. 47). lungs
the bases and hospitalization
PR: The patient used the IS two times a day during the 12-hour day of care.
6- I: teach the patient to use non-pharmaceutical techniques, deep breathing, and
listening to music along with exercising and resting periods Increase/unstable
Rationale: non-pharmaceutical breathing techniques decrease anxiety dyspnea and Blood pressure
help facilitate gas exchange (Swearingen, 2016, p. 119-120)
PR: The patient loves to go to the beach with his wife to help helo relax and decrease
stress-related anxiety.
BP: 159/86 Risk for DVT
Evaluation: at the end of the shift, the goal was met. AEB, no signs of complications or
respiratory distress were present, O2 saturation was 98%, a patient used the SI and
knows how to use it, and the reason SI is used. Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
80mg SQ daily at 11:00
If untreated or
unrecognized on
time
Lactate >2mmol/L
References
Hypotension <90/60 septic shock
Harding, M. M., Kwong, J., & Hagler, D. (2020). Lewis’s medical-surgical nursing: assessment and management of clinical problems. Elsevier. HR < 60
McCance, K. L., Huether, S. E., & Rote, N. S. (2019). Pathophysiology: The biologic basis for disease in adults and children. Mosby. MAP<65
Swearingen, P. L. (2016). All-in-one nursing care planning resource: Medical-surgical, pediatric, maternity, and psychiatric-mental health. Elsevier.
Death
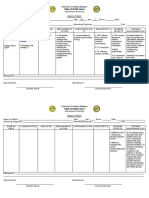
PRIORITY NANDA #1:Infection R/T current diagnosis, age, foreign body invasion causing bacteremia AEB, the temperature on admission of 101.3F, lack of knowledge about infection
causes, WBC count on admission is 18.72k/cmm, neutrophils count on admission was 88%, the patient was dehydrated (tenting skin, forgets to drink fluids).
Goal: at the end of the shift, will have to remain free from signs and symptoms of infection. AEB temperature will stay within a normal range (96-99F), the culture won't be positive for
the pathogen, urine will be yellow, clear, and odorless, the patient will have >500ml of fluids intake by mouth, and patient WBC will be less than 10k, BP will be less than 120/80, Temp
will be less than 99F
Nursing assessment/intervention:
Assessment/Monitoring:
1- I: Assess the patient's vital signs for SIRS criteria q4 hrs and as needed.
Rationale: SIRS criteria can be an early sign to detect infections, and if 2 out of 4 results are abnormal, the patient can develop sepsis (Swearingen, 2016, p.445).
PR: The patient's temperature is 97.8, HR is 77, BP is 108/62, and WBC is 8.5k, and he is alert and oriented x4, with no signs of confusion present.
2- I: assess the patient's mental status, LOC q 4 hours and as needed.
Rationale: LOC questions are a late sign that the patient has an infection, and a quick intervention has to be done if there is an altered LOC as part of SIRS criteria.
PR: the patient could know his name, date of birth, today's date, and why he was at the hospital.
Management/Intervention:
3- I: Administer the patient's antibiotics, Cefepime 2g in 50ml NS IVPB over 30 mins Q12hrs.
Rationale: Cefepime is an antibiotic used to treat UTIs; it inhibits cell wall synthesis by binding to essential PBP to fight infections (Lexicomp, 2023).
PR: Cefepime 2g in 50ml NS IVPB over 30 mins was administered at 15:00.
4- I: adminitser Metromidazole (FLAGYL) 500mg IVPB q 8hrs.
Rationale: Metronidazole binds and disrupts PNA structure, thereby blocking bacterial nucleic acid synthesis (Skidmore, 2021, p. 846)
PR: the patient was given Metronidazole (FLAGYL) 500mg IVPB at 11:00.
Patient Education:
5- I: Collaborate with the PCT to ensure and remind the patient to increase fluid intake.
Rationale: dehydration can increase the risk of infection, and increasing fluid intake can help the body stay hydrated and flush the body.
PR: the patient had 840ml fluids by mouth and 700ml through IV infusion.
6- I: Educate the patient to have probiotics when discharged and not to discontinue his antibiotics when she feels better.
Rationale: Prolonged antibiotic use and/or stopping antibiotics abruptly can kill the normal flora in the body, and that can cause diarrhea and Cdiff (CDAD). Probiotics help restore the
good bacteria in the GI tract (Swearingen, 2016, p. 263).
PR: the patient was not educated about antibiotics use. He will be discharged on 10.21.23. The patient does not take probiotics at home
Evaluation: by the end of the shift, the goal was met AEB, Patient urine remained clear yellow odorless, culture results came out negative, lactate lab results were 1.6, no signs of
confusion present, VS at 16:00 were BP 135/98. Tem was 98.2. HR was 77, and the patient had 840ml of fluids PO (water, juice, coffee).
You might also like
- Discharge Summary 17 Sep 22Document3 pagesDischarge Summary 17 Sep 22Jomon ThampyNo ratings yet
- Emergency Antibiotic Guide A6 105 1048mm February9 2022Document48 pagesEmergency Antibiotic Guide A6 105 1048mm February9 2022Iain HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument20 pagesCase Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseaseYetTamparong50% (2)
- Portfolio Pat 1Document18 pagesPortfolio Pat 1api-365835586No ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz100% (4)
- Template HXDocument1 pageTemplate HXdawnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BipolarDocument13 pagesDrug Study BipolarrahimsyusophNo ratings yet
- Assessment DiagramDocument1 pageAssessment DiagramHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: University of Southern Mindanao Department of NursingDocument2 pagesDrug Study: University of Southern Mindanao Department of NursingSoleil ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Piptaz DSDocument4 pagesPiptaz DSArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Ursing ARE LAN: College of NursingDocument2 pagesUrsing ARE LAN: College of NursingTsu Wei ChuaNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole PoDocument5 pagesMetronidazole PoFlower Flower FlowerNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument1 pageCefuroxime Drug StudyACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- ms1 PatDocument14 pagesms1 Patapi-364212510No ratings yet
- Vomito PDFDocument2 pagesVomito PDFMauricio RíosNo ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Fundamental Patient Assessment ToolDocument19 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Fundamental Patient Assessment Toolapi-418237167No ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient InformationDocument24 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient Informationapi-315444338No ratings yet
- Pat Revised 9-2014 FundamentalsDocument14 pagesPat Revised 9-2014 Fundamentalsapi-355083078No ratings yet
- 1 Halker Singh Evaluation of Headaches MC Clinical Reviews 2024 CA R SecureDocument62 pages1 Halker Singh Evaluation of Headaches MC Clinical Reviews 2024 CA R Securecadena.astridNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RosillosaDocument4 pagesDrug Study RosillosaJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Takotsubo Syndrome Pathophysiology, Emerging Concepts, and Clinical Implications CirculationDocument1 pageTakotsubo Syndrome Pathophysiology, Emerging Concepts, and Clinical Implications Circulationmarianflacara96No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyMizpah DuculanNo ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient InformationDocument16 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient Informationapi-402496681No ratings yet
- DS AcetaminophenDocument2 pagesDS AcetaminophenSoleil ArcenalNo ratings yet
- NaproxenDocument2 pagesNaproxenDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Pat 2Document19 pagesPat 2api-404415990No ratings yet
- ms1 Pat 2-2Document21 pagesms1 Pat 2-2api-404285262No ratings yet
- GastroenterologyDocument2 pagesGastroenterologyPermis Pour Tous frNo ratings yet
- Pat 1 Medsurg 1Document17 pagesPat 1 Medsurg 1api-354599629No ratings yet
- Balacano, John Glenn BSN-3A: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBalacano, John Glenn BSN-3A: ClassificationDaintyGarciaNo ratings yet
- Ms 1 Pat Marline FaustinDocument18 pagesMs 1 Pat Marline Faustinapi-365764138No ratings yet
- Vaccine Vaccine Vaccine: Prevention StepDocument1 pageVaccine Vaccine Vaccine: Prevention StepNUR AMALIA BINTI ABD. AZIZNo ratings yet
- Pat ms2Document20 pagesPat ms2api-355298006No ratings yet
- Daftar Pasien Baru Bedah Saraf 14 Mei 2019: NO Divisi TGL in Nama U MR Diagnosa R Rencana KS R Problem J KDocument1 pageDaftar Pasien Baru Bedah Saraf 14 Mei 2019: NO Divisi TGL in Nama U MR Diagnosa R Rencana KS R Problem J KFaisal AkbarNo ratings yet
- University of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient InformationDocument19 pagesUniversity of South Florida College of Nursing: Msi & Msii Patient Assessment Tool 1 Patient Informationapi-418237167No ratings yet
- Patient Information Sheet Patient: Doctor: Room: Age: Sex: AllergiesDocument2 pagesPatient Information Sheet Patient: Doctor: Room: Age: Sex: AllergiesLauraysha McMillanNo ratings yet
- Iv Drip IsoxilanDocument1 pageIv Drip IsoxilannierbobierNo ratings yet
- Kristina Nealy ms1 Pat 1 2Document19 pagesKristina Nealy ms1 Pat 1 2api-314372295No ratings yet
- Pat FundiesDocument16 pagesPat Fundiesapi-338998736No ratings yet
- Pat ms1 3 08Document14 pagesPat ms1 3 08api-371817203No ratings yet
- Final Group 2Document29 pagesFinal Group 2minalongjonairaNo ratings yet
- Menpin Drug StudyPenthidineDocument2 pagesMenpin Drug StudyPenthidineVine CastroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagram Format: Example: Ego Integrity Vs Despair, Sense of Satisfaction or FailureDocument1 pageAssessment Diagram Format: Example: Ego Integrity Vs Despair, Sense of Satisfaction or FailureShirley L. CarumbaNo ratings yet
- Pat FundiesDocument18 pagesPat Fundiesapi-355298006No ratings yet
- Hypertension: Prognostic, Diagnostic and Therapeutic AspectsDocument3 pagesHypertension: Prognostic, Diagnostic and Therapeutic AspectsSandwingNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: Medicatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerati ONDocument4 pagesRUG Tudy: Medicatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerati ONGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Medication Indication Contraindicati0N Side Effects Use Caution inDocument17 pagesDrug Study: Medication Indication Contraindicati0N Side Effects Use Caution inAngely Dianne Santiago II100% (2)
- Course in The Ward (April 25-28 Roys)Document9 pagesCourse in The Ward (April 25-28 Roys)Royce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- CNS: Dizzin Ess, Fatigu E, Heada Che, Vertig O,: Tagum Doctors College, IncDocument6 pagesCNS: Dizzin Ess, Fatigu E, Heada Che, Vertig O,: Tagum Doctors College, IncAnne BasilesNo ratings yet
- History FormDocument5 pagesHistory FormYazeed AsrawiNo ratings yet
- Pat Fall 1-1Document17 pagesPat Fall 1-1api-339160012No ratings yet
- PRIETO - Antipsychotic Drug 3Document4 pagesPRIETO - Antipsychotic Drug 3Stiffany PrietoNo ratings yet
- DS-ARF - FINALDocument4 pagesDS-ARF - FINALAlkiana SalardaNo ratings yet
- Patient's Name: Alindajao, Filoteo Diagnosis: CAD Date of Admission: Sex: 58yo Age: Male Height/WeightDocument1 pagePatient's Name: Alindajao, Filoteo Diagnosis: CAD Date of Admission: Sex: 58yo Age: Male Height/WeightButts McgeeNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDSDocument1 pageHIV - AIDSMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoDocument3 pagesDrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledMARIA KIMBERLY S. PINEDANo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Record From Queensland, AustraliaDocument20 pagesPregnancy Record From Queensland, AustraliaPutri AyuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: - 24/june/2020Document1 pageDrug Study: - 24/june/2020daliaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Current Guidelines of Five International Societies On Clostridium Difficile Infection ManagementDocument24 pagesA Comparison of Current Guidelines of Five International Societies On Clostridium Difficile Infection ManagementJulio S. UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic Record TemplateDocument1 pageDrug Therapeutic Record TemplateAubrey Justine GaleonNo ratings yet
- TherapeuticsDocument13 pagesTherapeuticsChecko LatteNo ratings yet
- Sanofi Annual Report 2014Document85 pagesSanofi Annual Report 2014MirzaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Infections: Ickman Setoaji W, DRG., MMDocument66 pagesOdontogenic Infections: Ickman Setoaji W, DRG., MMAmeliza Putri AlindNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- Helicure - Google SearchDocument1 pageHelicure - Google Searchalijan deparNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole PoDocument5 pagesMetronidazole PoFlower Flower FlowerNo ratings yet
- Genital Tract InfectionDocument52 pagesGenital Tract InfectionArvindan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Amphotericin BDocument23 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Amphotericin BElizabeth IdananNo ratings yet
- Brosur Infus-1Document1 pageBrosur Infus-1AKbarNo ratings yet
- Clostridioides Difficile Infection in AdultsDocument28 pagesClostridioides Difficile Infection in AdultsIrina DuceacNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY FOR HYPOKALEMIA Case Study 3Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY FOR HYPOKALEMIA Case Study 3Montero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- STI Treatment WorksheetDocument2 pagesSTI Treatment WorksheetJonas OltmanNo ratings yet
- Myoma Pathophysio, Gordon's NCPDocument13 pagesMyoma Pathophysio, Gordon's NCPicesexy100% (1)
- K46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)Document78 pagesK46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)ayapillaiNo ratings yet
- 2nu03-Group1 Case-Presentation ArmmcpediapmDocument39 pages2nu03-Group1 Case-Presentation ArmmcpediapmCyrus GarciaNo ratings yet
- MollyDocument7 pagesMollyapi-534233456No ratings yet
- M C Q AnaesthesiaDocument7 pagesM C Q Anaesthesiaahmed_anaes1234No ratings yet
- Anti-Protozoal Agents: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIDocument21 pagesAnti-Protozoal Agents: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIHimanshu Barman100% (1)
- Management of Intra-Abdominal InfectionDocument65 pagesManagement of Intra-Abdominal InfectionKamran SherazNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Group 3Document16 pagesModule 8 - Group 3MEDECIELO MELONo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument9 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseSohanInduwaraGamage100% (2)
- Placenta PreviaDocument87 pagesPlacenta PreviaKaye Cueto100% (1)
- نموذج طب بشريDocument11 pagesنموذج طب بشريBassam AlqadasiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ChartsDocument61 pagesAntibiotic Chartspempekplg100% (1)
- Draper 2005Document5 pagesDraper 2005atls jakartaNo ratings yet