Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a Sol e
OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a Sol e
Uploaded by
林俊佑Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Airway Management - AdultDocument13 pagesAirway Management - AdultD M Shawkot HossainNo ratings yet
- NCM 2nd Ce 4a04a Sol eDocument9 pagesNCM 2nd Ce 4a04a Sol eapi-517118868No ratings yet
- Notes - Functions 1Document12 pagesNotes - Functions 1shawnkao20021024No ratings yet
- FunctionDocument9 pagesFunctioncayleewong1115No ratings yet
- Purcell Edisi 9 Bab 15Document14 pagesPurcell Edisi 9 Bab 15Alderine KuswardhaniNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument92 pagesIntegralesAbel LopezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Phase 1Document269 pagesMathematics - Phase 1Sarthak AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document25 pagesChapter 20Anoushka KharbandaNo ratings yet
- Limits PDFDocument60 pagesLimits PDFVishwas JainNo ratings yet
- Function ProjectDocument2 pagesFunction ProjectcailannevilleNo ratings yet
- Function (Theory + Exercise)Document87 pagesFunction (Theory + Exercise)Ayushi Chandel 12-C,53No ratings yet
- Lectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsDocument7 pagesLectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsLaluNo ratings yet
- Caie As Maths 9709 Pure 1 v1Document13 pagesCaie As Maths 9709 Pure 1 v1AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Dy DXDocument4 pagesDy DXnely coniNo ratings yet
- Bmevening - Batch 2016-19: Optimization Using Calculus: Dipankar Bose May 30, 2016Document2 pagesBmevening - Batch 2016-19: Optimization Using Calculus: Dipankar Bose May 30, 2016Zia AhmadNo ratings yet
- Solution of DE HW1Document4 pagesSolution of DE HW1Abegail LorillaNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level: MATHS (9709)Document13 pagesCaie As Level: MATHS (9709)MichelleNo ratings yet
- Calculus Week 1Document6 pagesCalculus Week 1Kuzey GülerNo ratings yet
- Second Order ODE UWSDocument17 pagesSecond Order ODE UWSnirakaru123No ratings yet
- Definition: Limit of A Function F (X) Is Said To Exist, As X A WhenDocument21 pagesDefinition: Limit of A Function F (X) Is Said To Exist, As X A WhenDilkhushNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Precalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Precalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFkyackvicary.n62kje100% (13)
- Lec 2Document7 pagesLec 2t86qpd68z6No ratings yet
- Convex Functions: See P. 10 of The Handout On Preliminary MaterialDocument20 pagesConvex Functions: See P. 10 of The Handout On Preliminary MaterialClaribel Paola Serna CelinNo ratings yet
- General MathematicsDocument10 pagesGeneral MathematicsKinect Nueva EcijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: One-To-One and Inverse Functions Content Standard Performance StandardDocument9 pagesChapter 3: One-To-One and Inverse Functions Content Standard Performance StandardWon YudingzNo ratings yet
- Student BK Alg2-Sect11 1Document68 pagesStudent BK Alg2-Sect11 1Xiaoxu MaNo ratings yet
- (18144) Sheet 01 Limit Continuity and Derivability BDocument118 pages(18144) Sheet 01 Limit Continuity and Derivability Bmanu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Differential EquationDocument2 pagesHomogeneous Differential EquationAtif BaigNo ratings yet
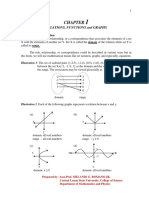
- Chapter 1relations Functions and GraphsDocument18 pagesChapter 1relations Functions and GraphsDafer M. EnrijoNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document402 pagesBook 1Kishor Kumar KNo ratings yet
- Tangents and Normal HintsDocument4 pagesTangents and Normal HintsShantanu BhosaleNo ratings yet
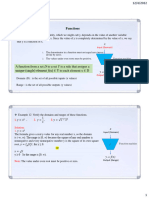
- H - NA RA ( ) A A H - NA ( ) RA Dim ( ) Dim RA RADocument1 pageH - NA RA ( ) A A H - NA ( ) RA Dim ( ) Dim RA RApearl301010No ratings yet
- Proof of The Riemann Hypothesis: Björn Tegetmeyer 16.01.2022Document6 pagesProof of The Riemann Hypothesis: Björn Tegetmeyer 16.01.2022Ta BarNo ratings yet
- Function - PlacematsDocument4 pagesFunction - PlacematsRomadel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- CollegeAlgebra Chapter6 Functions IMG 20140923 0001Document21 pagesCollegeAlgebra Chapter6 Functions IMG 20140923 0001Planning OfficeNo ratings yet
- Functions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterDocument9 pagesFunctions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterHussein JaberNo ratings yet
- Dirac Delta FunctionDocument3 pagesDirac Delta FunctionAmit GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument62 pagesChapter IIKamalpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Math425 Probability FINAL-Exam SOLUTIONS Fall04Document6 pagesMath425 Probability FINAL-Exam SOLUTIONS Fall04mojarramanNo ratings yet
- Linearzition 02Document2 pagesLinearzition 02fatma shahoutNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IDocument10 pagesDifferential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IIndranil KutheNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IDocument10 pagesDifferential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IKaiash M YNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document13 pagesLecture 6Jitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- MC Bus Introtodiff 2009 1Document2 pagesMC Bus Introtodiff 2009 1Francis BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LimitsDocument19 pagesChapter 1 LimitsIrsyadNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations ReviewDocument20 pagesDifferential Equations Reviewsaimom sarkerNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Sample 1Document58 pagesVol 2 Sample 1VADAPALLY PRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document39 pagesChapter 8FitsumNo ratings yet
- Do Now: Complete The Chart For Each Linear Equation. y X - 2 y 2x + 3Document16 pagesDo Now: Complete The Chart For Each Linear Equation. y X - 2 y 2x + 3Riza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Lec4 Convexity and The Arithmetic-Geometric Mean InequalityDocument6 pagesChap2 Lec4 Convexity and The Arithmetic-Geometric Mean InequalityUzair AslamNo ratings yet
- Isra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111Document26 pagesIsra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111syeda zainabNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions: EE263 Autumn 2015 S. Boyd and S. LallDocument7 pagesLinear Functions: EE263 Autumn 2015 S. Boyd and S. LallMouliNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesPrecalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions ManualAndrewLopezcaydk100% (12)
- Math 220, Practice Problems For The Final Exam.: N N N NDocument4 pagesMath 220, Practice Problems For The Final Exam.: N N N NAllenNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Derivates. No Solutions. UC3M. Math For EconomicsDocument3 pagesHigher Order Derivates. No Solutions. UC3M. Math For EconomicsjNo ratings yet
- Arnold's Trivium 1991 PDFDocument10 pagesArnold's Trivium 1991 PDFKristine Rose VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3ziadadjili7No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Complex VariablesDocument30 pagesChapter 4 - Complex Variableser.rahul.2k22No ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b Sol E-1Document10 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12d Sol E-1Document19 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12d Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e Sol E-1Document18 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv2 E-1Document4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12c lv2 E-1Document4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12c lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12a Sol E-1Document13 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12a Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B07 7b Sol eDocument6 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B07 7b Sol e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b lv2 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv1 E-1Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv1 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f Sol E-1Document14 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- 2019 Mock Exam P1 Part A QABDocument8 pages2019 Mock Exam P1 Part A QAB林俊佑No ratings yet
- OJM DSETraining Basic Algebra I eDocument6 pagesOJM DSETraining Basic Algebra I e林俊佑No ratings yet
- 2019 Mock Exam P3 Part A QABDocument12 pages2019 Mock Exam P3 Part A QAB林俊佑No ratings yet
- OJM Geo&StatPractice 2 e SolDocument3 pagesOJM Geo&StatPractice 2 e Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e ExamDocument7 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e Exam林俊佑No ratings yet
- OJM DSETraining Rectangular Coordinate System I eDocument5 pagesOJM DSETraining Rectangular Coordinate System I e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e SuppExDocument17 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e SuppEx林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e Ex2CDocument11 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e Ex2C林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv1Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a SolDocument8 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b Sol eDocument7 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b Sol e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a lv2 eDocument4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a lv2 e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b SolDocument8 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b lv1 eDocument3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b lv1 e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- Bookmyshow Balanced ScorecardDocument3 pagesBookmyshow Balanced ScorecardSirsha PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Enviornmental Conservation in Ancient IndiaDocument4 pagesEnviornmental Conservation in Ancient Indiaashim royNo ratings yet
- Indesign TutotialDocument6 pagesIndesign TutotialDaniel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- How To Find A PHD Supervisor at Koç UniversityDocument3 pagesHow To Find A PHD Supervisor at Koç UniversityHam NciNo ratings yet
- TarotDocument3 pagesTarotDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Manual Servicio bv29Document123 pagesManual Servicio bv29newplayer12100% (1)
- Apps Month Messenger Abril Apps Enero Febrero Facebook Whassap Instagram Messenger Teams Zoom Netflix SnapchatDocument168 pagesApps Month Messenger Abril Apps Enero Febrero Facebook Whassap Instagram Messenger Teams Zoom Netflix SnapchatMariana TorresNo ratings yet
- Physics Exercise 3Document19 pagesPhysics Exercise 3Law Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- Godrej Sheet OPCDocument1,074 pagesGodrej Sheet OPCAmresh Kumar KanthNo ratings yet
- Artifacts in HistopathologyDocument8 pagesArtifacts in Histopathologysyed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Corporate BrochureDocument28 pagesCorporate BrochureVijay KambleNo ratings yet
- Reading Response Rubric: Accurately DemonstratesDocument1 pageReading Response Rubric: Accurately DemonstratesElenaNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Scientific Management (PDFDrive)Document152 pagesThe Principles of Scientific Management (PDFDrive)Renato Sukno RojasNo ratings yet
- Priemus, Zonneveld - What Are Corridors and What Are The Issues. Introduction To Special Issue - The Governance of CorridorsDocument11 pagesPriemus, Zonneveld - What Are Corridors and What Are The Issues. Introduction To Special Issue - The Governance of CorridorsBrankoNo ratings yet
- Ayurvision - e Book - 2011Document124 pagesAyurvision - e Book - 2011drmsk100% (4)
- Notes-OscillationsDocument9 pagesNotes-OscillationsMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Project MusthafaDocument64 pagesProject MusthafaMusthafa CkNo ratings yet
- Pacun Research Design 7Document17 pagesPacun Research Design 7Kevin RamosNo ratings yet
- Grammar File2Document2 pagesGrammar File2AlejandroNo ratings yet
- 2013 USMS High Performance Camp BrochureDocument2 pages2013 USMS High Performance Camp BrochureCokie LepinskiNo ratings yet
- Daily Irradiance Data: PVGIS-5 Geo-Temporal Irradiation DatabaseDocument1 pageDaily Irradiance Data: PVGIS-5 Geo-Temporal Irradiation DatabaseJasmina F.No ratings yet
- Savings PlansDocument39 pagesSavings Plansfrsantos123No ratings yet
- The Definitive Guide To Ielts Academic: Preparation and PracticeDocument3 pagesThe Definitive Guide To Ielts Academic: Preparation and PracticeShaurya AryaNo ratings yet
- Surfacing of 3.25% Nickel Steel With Inconel 625 by The Gas Metal Arc Welding-Pulsed Arc ProcessDocument8 pagesSurfacing of 3.25% Nickel Steel With Inconel 625 by The Gas Metal Arc Welding-Pulsed Arc ProcessMoses_JakkalaNo ratings yet
- China Heavy Equipments and Its SpecsDocument11 pagesChina Heavy Equipments and Its SpecsLuis Thethird BuotNo ratings yet
- Office365 Exchange Online Module5 Client AccessDocument176 pagesOffice365 Exchange Online Module5 Client Accessgator9No ratings yet
- Zymark XP ManualDocument232 pagesZymark XP ManualcurtisvaleroNo ratings yet
- Dummy Block Lubrication Best PracticesDocument6 pagesDummy Block Lubrication Best PracticesLeonel Velasquez100% (1)
- 2-2-Parallel-Distributed ComputingDocument2 pages2-2-Parallel-Distributed ComputingJathin DarsiNo ratings yet
OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a Sol e
OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a Sol e
Uploaded by
林俊佑Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a Sol e
OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a Sol e
Uploaded by
林俊佑Copyright:
Available Formats
Senior Secondary Oxford Mathematics for the New Century 4A
Basic Knowledge of Functions
4
Consolidation Exercise Solution
Consolidation Exercise 4A 10. ∵ The value of 12 – x under the radical sign
1. ∵ V is a function of d. cannot be negative.
∴ d is the independent variable and V is the ∴ 12 – x 0
dependent variable. x 12
∴ The domain is all real numbers smaller than
2. ∵ C is a function of w.
or equal to 12.
∴ w is the independent variable and C is the
dependent variable.
11. Each value of x has one (and only one)
3. The domain is all real numbers. corresponding value of y.
∴ y is a function of x.
4. The domain is all real numbers.
12. When x = 0, there is more than one corresponding
5. The domain is all real numbers.
value of y (2, 1 and 2).
∴ y is not a function of x.
6. ∵ The value of the denominator x – 7 cannot be 0.
∴ x – 7 0
13. Each value of x has one (and only one)
x7
corresponding value of y.
∴ The domain is all real numbers except 7.
∴ y is a function of x.
7. ∵ The value of the denominator 2 + x cannot be 0.
14. Each value of x has one (and only one)
∴ 2+x0
corresponding value of y.
x –2 ∴ y is a function of x.
∴ The domain is all real numbers except –2.
15. (a) For each value of x, there is one
8. ∵ The value of x – 8 under the radical sign
corresponding value of y.
cannot be negative.
(b) Each value of x has one (and only one)
∴ x–80
corresponding value of y.
x8
∴ y is a function of x.
∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than
or equal to 8. 16. Each value of x has one (and only one)
corresponding value of y.
9. ∵ The value of x + 11 under the radical sign
∴ y is a function of x.
cannot be negative.
∴ x + 11 0 17. When x = 0, there is more than one corresponding
x –11 value of y (2 and 3).
∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than ∴ y is not a function of x.
or equal to –11.
© Oxford University Press 2023 1 4A04 Consolidation Exercise 4A Solution
Senior Secondary Oxford Mathematics for the New Century 4A
18. Each value of x has one (and only one) (e) (i) When x = 1, y2 = 3(1)
corresponding value of y. y2 = 3
∴ y is a function of x. y = 3
When x = 2, y2 = 3(2)
19. (a) (i) When x = 1, y = 2(1) + 7 = 5; y2 = 6
when x = 2, y = 2(2) + 7 = 3; y = 6
when x = 3, y = 2(3) + 7 = 1; When x = 3, y2 = 3(3)
when x = 4, y = 2(4) + 7 = 1, etc. y2 = 9
∴ For each value of x, there is one y = 3
corresponding value of y. When x = 4, y2 = 3(4)
(ii) From (a)(i), y is a function of x. y2 = 12
(b) (i) When x = 1, y = 12 + 8 = 9; y = 12 , etc.
when x = 2, y = 22 + 8 = 12; ∴ For each value of x (where x > 0),
when x = 3, y = 32 + 8 = 17; there are two corresponding values
when x = 4, y = 42 + 8 = 24, etc. of y.
∴ For each value of x, there is one (ii) From (e)(i), y is not a function of x.
corresponding value of y. (f) (i) When x = 1, y = 2(1) = 2 ;
(ii) From (b)(i), y is a function of x. when x = 2, y = 2( 2) = 2;
(c) (i) When x = 1, y = 3 5(1)2 = 2; when x = 3, y = 2(3) = 6 ;
when x = 2, y = 3 5(2)2 = 17; when x = 4, y = 2( 4) = 8 , etc.
when x = 3, y = 3 5(3)2 = 42; ∴ For each value of x (where x > 0),
when x = 4, y = 3 5(4)2 = 77, etc. there is one corresponding value of y.
∴ For each value of x, there is one (ii) From (f)(i), y is a function of x.
corresponding value of y.
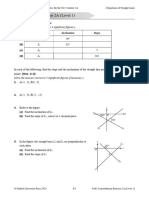
20. (a) y
(ii) From (c)(i), y is a function of x. vertical line
7
(d) (i) When x = 1, y = = 7;
1
7 a
when x = 2, y = ; O
x
2 b
7
when x = 3, y = ; Each vertical line intersects the graph at only
3
7 one point.
when x = 4, y = , etc.
4 ∴ y is a function of x.
∴ For each value of x (where x 0), (b) y
vertical line
there is one corresponding value of y.
(ii) From (d)(i), y is a function of x.
O a x
b
A vertical line intersects the graph at two points.
∴ y is not a function of x.
© Oxford University Press 2023 2 4A04 Consolidation Exercise 4A Solution
Senior Secondary Oxford Mathematics for the New Century 4A
(c) y 26. ∵ The value of 7x + 4 under the radical sign
vertical line
x
cannot be negative.
∴ 7x + 4 0
a 4
O b
x x
7
A vertical line intersectsy the graph at three ∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than
4
points. or equal to .
7
∴ y is not a function of x.
27. ∵ x2 0
21. ∵ The value of the denominator 5 – 4x cannot be 0. ∴ x2 + 3 3
∴ 5 – 4x 0 The value of x2 + 3 under the radical sign will not
5
x be negative for any real number x.
4
∴ The domain is all real numbers.
5
∴ The domain is all real numbers except .
4
28. For the denominator x 9 , the value of x + 9
must be positive.
22. ∵ x2 0
∴ x+9>0
∴ x2 + 1 1
x > –9
The value of the denominator x2 + 1 will not be 0
∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than –9.
for any real number x.
∴ The domain is all real numbers. 29. For the denominator x 4 , the value of x – 4
must be positive.
23. ∵ The value of the denominator x + 3 cannot be 0. ∴ x–4>0
∴ x+30 x>4
x –3 ∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than 4.
∴ The domain is all real numbers except –3.
30. For the denominator 3x 2 , the value of
24. ∵ The value of the denominator 8 – 2x cannot be 0. –3x + 2 must be positive.
∴ 8 – 2x 0 ∴ –3x + 2 > 0
x4 2
x<
∴ The domain is all real numbers except 4. 3
2
∴ The domain is all real numbers smaller than .
3
25. ∵ The value of 2 – 9x under the radical sign
cannot be negative. 31. For x(x – 3) = 0,
∴ 2 – 9x 0 x = 0 or x = 3
2 ∵ The value of the denominator x(x – 3) cannot
x
9 be 0.
∴ The domain is all real numbers smaller than
∴ x(x – 3) 0
2
or equal to . x 0 and x 3
9
∴ The domain is all real numbers except 0 and 3.
© Oxford University Press 2023 3 4A04 Consolidation Exercise 4A Solution
Senior Secondary Oxford Mathematics for the New Century 4A
32. For x2 + 8x = 0, 36. For 2x2 – 9x – 5 = 0,
x(x + 8) = 0 (2x + 1)(x – 5) = 0
x = 0 or x = –8 1
x=
or x = 5
∵ The value of the denominator x + 8x cannot
2 2
∵ The value of the denominator 2x2 – 9x – 5
be 0.
cannot be 0.
∴ x2 + 8x 0
∴ 2x2 – 9x – 5 0
x 0 and x –8
1
∴ The domain is all real numbers except 0 and –8. x and x 5
2
1
∴ The domain is all real numbers except
33. For x – 9 = 0,
2
2
(x + 3)(x – 3) = 0 and 5.
x = –3 or x = 3
∵ The value of the denominator x2 – 9 cannot 1
37. For , the value of the denominator x cannot be 0,
be 0. x
i.e. x 0.
∴ x2 – 9 0
For x , the value of x under the radical sign
x –3 and x 3
cannot be negative, i.e. x 0.
∴ The domain is all real numbers except –3 and 3.
∴ x>0
∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than 0.
34. For x2 + 5x – 6 = 0,
(x + 6)(x – 1) = 0 38. For x , the value of x under the radical sign
x = –6 or x = 1 cannot be negative, i.e. x 0.
∵ The value of the denominator x2 + 5x – 6 1
For , the value of the denominator x – 1
cannot be 0. x 1
∴ x2 + 5x – 6 0 cannot be 0, i.e. x 1.
x –6 and x 1 ∴ x 0 and x 1
∴ The domain is all real numbers except –6 and 1. ∴ The domain is all real numbers greater than
or equal to 0 except 1.
35. For x2 + 8x + 16 = 0,
(x + 4)2 = 0 39. (a) x 3 2 1 0
x = –4 (repeated) y 0 1 2 3
∵ The value of the denominator x + 8x + 16 2
(b) ∵ (3 , 0) lies on the graph.
cannot be 0. ∴ 0 = m(3) + 3
∴ x + 8x + 16 0
2
3m = 3
x –4 m = 1
∴ The domain is all real numbers except –4.
© Oxford University Press 2023 4 4A04 Consolidation Exercise 4A Solution
Senior Secondary Oxford Mathematics for the New Century 4A
40. (a) x 0 1 2 3 4 44. (a) When n = 1 000, C = 203.
203 = 3 + k(1 000)
y 3 1 1 3 7
1 000k = 200
(b) ∵ (1 , –1) lies on the graph.
k = 0.2
∴ 1 = 12 – p(1) – 3
(b) From (a), C = 3 + 0.2n.
1 = p – 4
When n = 6 500,
p = 3
C = 3 + 0.2(6 500)
41. ∵ (1 , 5) lies on the graph. = 1 303
∴ 5 = a(1)2 – 1 – 5 ∴ The cost of copying a document with
a=1 6 500 pages is $1 303.
(c) When C = 725.5,
42. (a) When x = 4, y = 2. 725.5 = 3 + 0.2n
∴ 2 = k(4) – 6 0.2n = 722.5
4k = 8 n = 3 612.5
k = 2 ∵ n must be an integer.
(b) From (a), y = –2x – 6. ∴ The cost of copying a document cannot
When x = 4, be exactly $725.5.
y = 2(4) – 6 ∴ The claim is disagreed.
= 14
(c) When y = 11, 45. (a) When h = 0.8, T = 19.8.
11 = 2x – 6 19.8 = a – 6.5(0.8)
2x = 17 a = 25
17 (b) From (a), T = 25 – 6.5h.
x= When h = 3,
2
T = 25 – 6.5(3)
43. (a) When x = 3, y = 11. = 5.5
11 = (3) + r(3) – 4
2
∴ When the height above sea level is 3 km,
3r = 6 the temperature is 5.5C.
r = 2 (c) When T = 0,
(b) From (a), y = x2 – 2x – 4. 0 = 25 – 6.5h
When x = 2, 6.5h = 25
11
y = 22 – 2(2) – 4 h =3
13
= –4
<4
(c) When y = 20, ∴ It is possible that the corresponding
20 = x2 – 2x – 4 temperature is exactly 0C.
x – 2x – 24 = 0
2
(x + 4)(x – 6) = 0
x = –4 or 6
© Oxford University Press 2023 5 4A04 Consolidation Exercise 4A Solution
Senior Secondary Oxford Mathematics for the New Century 4A
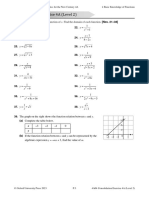
46. (a) From the graph, when x = 0, y = ‒3. 47. (a) From the graph, when x = 0, y = 50.
∴ ‒3 = a(0) + b ∴ 50 = T + P(0)
b = ‒3 T = 50
(b) y (b) y
8 1 500
6 1 250
y = ax + b
4 1 000
2 750
x 500
–2 0 2 4 6
–2 250
–4 x
0
5 10 15 20
–6
From the graph, when x = 10,
–8 y = 800
From (a), y = 50 + Px.
From the graph, when x = 4, y = 5. Substitute x = 10 and y = 800 into
From (a), y = ax ‒ 3. y = 50 + Px.
∴ 5 = a(4) ‒ 3 800 = 50 + P(10)
8 = 4a 10P = 750
a=2 P = 75
(c) From (a) and (b), y = 2x ‒ 3. (c) From (a) and (b), y = 50 + 75x.
When y = 13, When y = 1 850,
13 = 2x ‒ 3 1 850 = 50 + 75x
16 = 2x 1 800 = 75x
x=8 x = 24
∴ The number of dresses that she ordered
is 24.
© Oxford University Press 2023 6 4A04 Consolidation Exercise 4A Solution
You might also like
- Airway Management - AdultDocument13 pagesAirway Management - AdultD M Shawkot HossainNo ratings yet
- NCM 2nd Ce 4a04a Sol eDocument9 pagesNCM 2nd Ce 4a04a Sol eapi-517118868No ratings yet
- Notes - Functions 1Document12 pagesNotes - Functions 1shawnkao20021024No ratings yet
- FunctionDocument9 pagesFunctioncayleewong1115No ratings yet
- Purcell Edisi 9 Bab 15Document14 pagesPurcell Edisi 9 Bab 15Alderine KuswardhaniNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument92 pagesIntegralesAbel LopezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Phase 1Document269 pagesMathematics - Phase 1Sarthak AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document25 pagesChapter 20Anoushka KharbandaNo ratings yet
- Limits PDFDocument60 pagesLimits PDFVishwas JainNo ratings yet
- Function ProjectDocument2 pagesFunction ProjectcailannevilleNo ratings yet
- Function (Theory + Exercise)Document87 pagesFunction (Theory + Exercise)Ayushi Chandel 12-C,53No ratings yet
- Lectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsDocument7 pagesLectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsLaluNo ratings yet
- Caie As Maths 9709 Pure 1 v1Document13 pagesCaie As Maths 9709 Pure 1 v1AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Dy DXDocument4 pagesDy DXnely coniNo ratings yet
- Bmevening - Batch 2016-19: Optimization Using Calculus: Dipankar Bose May 30, 2016Document2 pagesBmevening - Batch 2016-19: Optimization Using Calculus: Dipankar Bose May 30, 2016Zia AhmadNo ratings yet
- Solution of DE HW1Document4 pagesSolution of DE HW1Abegail LorillaNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level: MATHS (9709)Document13 pagesCaie As Level: MATHS (9709)MichelleNo ratings yet
- Calculus Week 1Document6 pagesCalculus Week 1Kuzey GülerNo ratings yet
- Second Order ODE UWSDocument17 pagesSecond Order ODE UWSnirakaru123No ratings yet
- Definition: Limit of A Function F (X) Is Said To Exist, As X A WhenDocument21 pagesDefinition: Limit of A Function F (X) Is Said To Exist, As X A WhenDilkhushNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Precalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Precalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFkyackvicary.n62kje100% (13)
- Lec 2Document7 pagesLec 2t86qpd68z6No ratings yet
- Convex Functions: See P. 10 of The Handout On Preliminary MaterialDocument20 pagesConvex Functions: See P. 10 of The Handout On Preliminary MaterialClaribel Paola Serna CelinNo ratings yet
- General MathematicsDocument10 pagesGeneral MathematicsKinect Nueva EcijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: One-To-One and Inverse Functions Content Standard Performance StandardDocument9 pagesChapter 3: One-To-One and Inverse Functions Content Standard Performance StandardWon YudingzNo ratings yet
- Student BK Alg2-Sect11 1Document68 pagesStudent BK Alg2-Sect11 1Xiaoxu MaNo ratings yet
- (18144) Sheet 01 Limit Continuity and Derivability BDocument118 pages(18144) Sheet 01 Limit Continuity and Derivability Bmanu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Differential EquationDocument2 pagesHomogeneous Differential EquationAtif BaigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1relations Functions and GraphsDocument18 pagesChapter 1relations Functions and GraphsDafer M. EnrijoNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document402 pagesBook 1Kishor Kumar KNo ratings yet
- Tangents and Normal HintsDocument4 pagesTangents and Normal HintsShantanu BhosaleNo ratings yet
- H - NA RA ( ) A A H - NA ( ) RA Dim ( ) Dim RA RADocument1 pageH - NA RA ( ) A A H - NA ( ) RA Dim ( ) Dim RA RApearl301010No ratings yet
- Proof of The Riemann Hypothesis: Björn Tegetmeyer 16.01.2022Document6 pagesProof of The Riemann Hypothesis: Björn Tegetmeyer 16.01.2022Ta BarNo ratings yet
- Function - PlacematsDocument4 pagesFunction - PlacematsRomadel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- CollegeAlgebra Chapter6 Functions IMG 20140923 0001Document21 pagesCollegeAlgebra Chapter6 Functions IMG 20140923 0001Planning OfficeNo ratings yet
- Functions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterDocument9 pagesFunctions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterHussein JaberNo ratings yet
- Dirac Delta FunctionDocument3 pagesDirac Delta FunctionAmit GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument62 pagesChapter IIKamalpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Math425 Probability FINAL-Exam SOLUTIONS Fall04Document6 pagesMath425 Probability FINAL-Exam SOLUTIONS Fall04mojarramanNo ratings yet
- Linearzition 02Document2 pagesLinearzition 02fatma shahoutNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IDocument10 pagesDifferential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IIndranil KutheNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IDocument10 pagesDifferential Equations 6: Phy310 - Mathematical Methods For Physicists IKaiash M YNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document13 pagesLecture 6Jitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- MC Bus Introtodiff 2009 1Document2 pagesMC Bus Introtodiff 2009 1Francis BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LimitsDocument19 pagesChapter 1 LimitsIrsyadNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations ReviewDocument20 pagesDifferential Equations Reviewsaimom sarkerNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Sample 1Document58 pagesVol 2 Sample 1VADAPALLY PRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document39 pagesChapter 8FitsumNo ratings yet
- Do Now: Complete The Chart For Each Linear Equation. y X - 2 y 2x + 3Document16 pagesDo Now: Complete The Chart For Each Linear Equation. y X - 2 y 2x + 3Riza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Lec4 Convexity and The Arithmetic-Geometric Mean InequalityDocument6 pagesChap2 Lec4 Convexity and The Arithmetic-Geometric Mean InequalityUzair AslamNo ratings yet
- Isra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111Document26 pagesIsra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111syeda zainabNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions: EE263 Autumn 2015 S. Boyd and S. LallDocument7 pagesLinear Functions: EE263 Autumn 2015 S. Boyd and S. LallMouliNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesPrecalculus Real Mathematics Real People 7th Edition Larson Solutions ManualAndrewLopezcaydk100% (12)
- Math 220, Practice Problems For The Final Exam.: N N N NDocument4 pagesMath 220, Practice Problems For The Final Exam.: N N N NAllenNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Derivates. No Solutions. UC3M. Math For EconomicsDocument3 pagesHigher Order Derivates. No Solutions. UC3M. Math For EconomicsjNo ratings yet
- Arnold's Trivium 1991 PDFDocument10 pagesArnold's Trivium 1991 PDFKristine Rose VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3ziadadjili7No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Complex VariablesDocument30 pagesChapter 4 - Complex Variableser.rahul.2k22No ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b Sol E-1Document10 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12d Sol E-1Document19 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12d Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e Sol E-1Document18 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv2 E-1Document4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12c lv2 E-1Document4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12c lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12a Sol E-1Document13 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12a Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B07 7b Sol eDocument6 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B07 7b Sol e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b lv2 E-1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12b lv2 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv1 E-1Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12e lv1 E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f Sol E-1Document14 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4B12 12f Sol E-1林俊佑No ratings yet
- 2019 Mock Exam P1 Part A QABDocument8 pages2019 Mock Exam P1 Part A QAB林俊佑No ratings yet
- OJM DSETraining Basic Algebra I eDocument6 pagesOJM DSETraining Basic Algebra I e林俊佑No ratings yet
- 2019 Mock Exam P3 Part A QABDocument12 pages2019 Mock Exam P3 Part A QAB林俊佑No ratings yet
- OJM Geo&StatPractice 2 e SolDocument3 pagesOJM Geo&StatPractice 2 e Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e ExamDocument7 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e Exam林俊佑No ratings yet
- OJM DSETraining Rectangular Coordinate System I eDocument5 pagesOJM DSETraining Rectangular Coordinate System I e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e SuppExDocument17 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e SuppEx林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e Ex2CDocument11 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e Ex2C林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv1Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a lv1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a SolDocument8 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2a Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2c lv1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b Sol eDocument7 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b Sol e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a lv2 eDocument4 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a lv2 e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b SolDocument8 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b lv1 eDocument3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4b lv1 e林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv1Document2 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv1林俊佑No ratings yet
- OSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv2Document3 pagesOSM ConsolEx 4A02 2b lv2林俊佑No ratings yet
- Bookmyshow Balanced ScorecardDocument3 pagesBookmyshow Balanced ScorecardSirsha PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Enviornmental Conservation in Ancient IndiaDocument4 pagesEnviornmental Conservation in Ancient Indiaashim royNo ratings yet
- Indesign TutotialDocument6 pagesIndesign TutotialDaniel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- How To Find A PHD Supervisor at Koç UniversityDocument3 pagesHow To Find A PHD Supervisor at Koç UniversityHam NciNo ratings yet
- TarotDocument3 pagesTarotDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Manual Servicio bv29Document123 pagesManual Servicio bv29newplayer12100% (1)
- Apps Month Messenger Abril Apps Enero Febrero Facebook Whassap Instagram Messenger Teams Zoom Netflix SnapchatDocument168 pagesApps Month Messenger Abril Apps Enero Febrero Facebook Whassap Instagram Messenger Teams Zoom Netflix SnapchatMariana TorresNo ratings yet
- Physics Exercise 3Document19 pagesPhysics Exercise 3Law Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- Godrej Sheet OPCDocument1,074 pagesGodrej Sheet OPCAmresh Kumar KanthNo ratings yet
- Artifacts in HistopathologyDocument8 pagesArtifacts in Histopathologysyed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Corporate BrochureDocument28 pagesCorporate BrochureVijay KambleNo ratings yet
- Reading Response Rubric: Accurately DemonstratesDocument1 pageReading Response Rubric: Accurately DemonstratesElenaNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Scientific Management (PDFDrive)Document152 pagesThe Principles of Scientific Management (PDFDrive)Renato Sukno RojasNo ratings yet
- Priemus, Zonneveld - What Are Corridors and What Are The Issues. Introduction To Special Issue - The Governance of CorridorsDocument11 pagesPriemus, Zonneveld - What Are Corridors and What Are The Issues. Introduction To Special Issue - The Governance of CorridorsBrankoNo ratings yet
- Ayurvision - e Book - 2011Document124 pagesAyurvision - e Book - 2011drmsk100% (4)
- Notes-OscillationsDocument9 pagesNotes-OscillationsMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Project MusthafaDocument64 pagesProject MusthafaMusthafa CkNo ratings yet
- Pacun Research Design 7Document17 pagesPacun Research Design 7Kevin RamosNo ratings yet
- Grammar File2Document2 pagesGrammar File2AlejandroNo ratings yet
- 2013 USMS High Performance Camp BrochureDocument2 pages2013 USMS High Performance Camp BrochureCokie LepinskiNo ratings yet
- Daily Irradiance Data: PVGIS-5 Geo-Temporal Irradiation DatabaseDocument1 pageDaily Irradiance Data: PVGIS-5 Geo-Temporal Irradiation DatabaseJasmina F.No ratings yet
- Savings PlansDocument39 pagesSavings Plansfrsantos123No ratings yet
- The Definitive Guide To Ielts Academic: Preparation and PracticeDocument3 pagesThe Definitive Guide To Ielts Academic: Preparation and PracticeShaurya AryaNo ratings yet
- Surfacing of 3.25% Nickel Steel With Inconel 625 by The Gas Metal Arc Welding-Pulsed Arc ProcessDocument8 pagesSurfacing of 3.25% Nickel Steel With Inconel 625 by The Gas Metal Arc Welding-Pulsed Arc ProcessMoses_JakkalaNo ratings yet
- China Heavy Equipments and Its SpecsDocument11 pagesChina Heavy Equipments and Its SpecsLuis Thethird BuotNo ratings yet
- Office365 Exchange Online Module5 Client AccessDocument176 pagesOffice365 Exchange Online Module5 Client Accessgator9No ratings yet
- Zymark XP ManualDocument232 pagesZymark XP ManualcurtisvaleroNo ratings yet
- Dummy Block Lubrication Best PracticesDocument6 pagesDummy Block Lubrication Best PracticesLeonel Velasquez100% (1)
- 2-2-Parallel-Distributed ComputingDocument2 pages2-2-Parallel-Distributed ComputingJathin DarsiNo ratings yet