Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management Science
Management Science
Uploaded by
kennethespadero000 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesManagement Science involves applying quantitative methods and mathematical models to analyze complex problems and help organizations make optimal decisions. It includes techniques such as decision analysis, optimization, simulation, forecasting, inventory management, project management, queuing theory, game theory, and financial modeling. These techniques help organizations maximize profits, minimize costs, improve processes, predict trends, and allocate resources efficiently.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentManagement Science involves applying quantitative methods and mathematical models to analyze complex problems and help organizations make optimal decisions. It includes techniques such as decision analysis, optimization, simulation, forecasting, inventory management, project management, queuing theory, game theory, and financial modeling. These techniques help organizations maximize profits, minimize costs, improve processes, predict trends, and allocate resources efficiently.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesManagement Science
Management Science
Uploaded by
kennethespadero00Management Science involves applying quantitative methods and mathematical models to analyze complex problems and help organizations make optimal decisions. It includes techniques such as decision analysis, optimization, simulation, forecasting, inventory management, project management, queuing theory, game theory, and financial modeling. These techniques help organizations maximize profits, minimize costs, improve processes, predict trends, and allocate resources efficiently.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE (BSA2)
Management Science is the application of scientific and mathematical principles, models, and
techniques to analyze and solve decision-making and operational problems in organizations. It
involves the systematic use of quantitative methods to address complex issues, make informed
choices, and improve processes and outcomes.
Scope of Management Science:
1. Decision Analysis: Management Science helps organizations make better decisions by
providing tools and models for evaluating various alternatives, assessing risks, and choosing
the most optimal course of action. Decision analysis includes techniques like decision trees,
utility theory, and multi-criteria decision analysis.
2. Optimization: Optimization is a core component of Management Science, involving the
search for the best possible solution among a set of feasible alternatives. Linear and
nonlinear programming, integer programming, and dynamic programming are some of the
optimization techniques used to maximize or minimize objectives such as profit, cost, or
resource utilization.
3. Simulation: Simulation modeling is used to mimic real-world systems and processes in a
computerized environment. It allows organizations to experiment with different scenarios
and assess the impact of changes before implementing them in the real world. Monte Carlo
simulation and discrete event simulation are commonly used techniques.
4. Forecasting: Management Science includes various methods for predicting future trends and
outcomes. Time series analysis, regression analysis, and forecasting models help
organizations make informed decisions by understanding historical data and predicting
future patterns.
5. Inventory and Supply Chain Management: Management Science plays a crucial role in
optimizing inventory levels, managing supply chains, and improving logistics. Techniques like
the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model and the Bullwhip effect analysis help
organizations minimize costs and improve the flow of goods and services.
6. Project Management: Project management tools and techniques, such as Critical Path
Analysis (CPA) and Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), are part of
Management Science. They aid in planning, scheduling, and controlling projects to ensure
they are completed on time and within budget.
7. Queuing Theory: Queuing theory deals with the study of waiting lines and helps
organizations optimize service processes by minimizing customer wait times and resource
utilization. It is commonly applied in areas like customer service, call centers, and
healthcare.
8. Game Theory: Game theory is used to analyze strategic interactions between decision-
makers and competitors. It helps organizations make decisions in situations where the
outcome depends on the choices of multiple parties.
9. Financial Modeling: Management Science is also applied in finance to build models for
portfolio optimization, risk assessment, and investment analysis, among other areas.
10. Healthcare and Public Policy: In healthcare and public policy, Management Science is used
to optimize resource allocation, healthcare delivery, and policy formulation. It aids in
addressing issues like hospital resource allocation, disease modeling, and vaccination
strategies.
Quantitative techniques play a crucial role in decision-making across various fields and industries.
These techniques involve the use of numerical data, mathematical models, and statistical analysis to
support decision-making processes. Here are some key ways in which quantitative techniques are
used in decision-making:
1. Data Analysis and Interpretation: Quantitative techniques enable organizations to collect,
analyze, and interpret large datasets. This helps in gaining insights into trends, patterns, and
relationships within the data, which can inform decision-making.
2. Risk Assessment: Quantitative methods are often employed to assess and quantify risks
associated with different courses of action. This is particularly important in financial
planning, project management, and investment decisions.
3. Forecasting: Businesses use quantitative techniques for forecasting future trends and
outcomes. This can involve time series analysis, regression analysis, and other statistical
methods to make predictions about sales, demand, and market trends.
4. Optimization: Quantitative techniques are used to find optimal solutions to complex
problems. Linear programming, integer programming, and nonlinear programming are
examples of methods used to optimize resource allocation, production schedules, and
supply chain management.
5. Cost-Benefit Analysis: Quantitative analysis helps in evaluating the costs and benefits of
various alternatives. Decision-makers can compare different options and choose the one
that offers the best balance between costs and benefits.
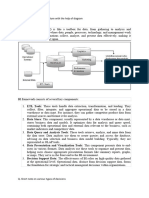
6. Decision Support Systems: Quantitative models are often integrated into decision support
systems (DSS), which assist managers in making informed decisions by providing them with
data-driven insights and scenario analysis.
7. Quality Control: In manufacturing and service industries, statistical process control (SPC) and
other quantitative techniques are used to monitor and improve the quality of products and
services.
8. Market Research: Quantitative methods, such as surveys and experiments, are used to
gather data on customer preferences, market trends, and consumer behavior. This
information is vital for product development and marketing strategies.
9. Portfolio Management: In finance, quantitative techniques are employed for portfolio
optimization and risk management. Investors use mathematical models to allocate assets in
a way that maximizes returns while managing risk.
10. Performance Evaluation: Quantitative metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are
used to assess the performance of individuals, teams, and organizations. These metrics
provide objective data for performance reviews and decision-making related to promotions,
resource allocation, and strategic planning.
11. Simulation and Modeling: Decision-makers can create models and run simulations to test
different scenarios and assess their potential outcomes. This is especially useful in complex
systems where real-world experimentation is costly or impractical.
12. Inventory Management: Quantitative techniques help in determining optimal inventory
levels, reorder points, and order quantities to minimize carrying costs while ensuring
product availability.
You might also like
- Affidavit of Authentication in Compliance With Rules On Electronic EvidenceDocument1 pageAffidavit of Authentication in Compliance With Rules On Electronic EvidenceGP Buhangin100% (9)
- Quantitative Techniques in Decision MakingDocument59 pagesQuantitative Techniques in Decision MakingLore Jie Mellizas100% (8)
- 3 BHK Plan-Model PDFDocument1 page3 BHK Plan-Model PDFSalahuddin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Management Science (Introduction)Document15 pagesManagement Science (Introduction)rhrrakibforayeziNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To Operation ResearchDocument9 pagesIntoduction To Operation Researchkushagrajaiswal.nestNo ratings yet
- Optimization Methods TheoryDocument28 pagesOptimization Methods Theorykd vlogsNo ratings yet
- 105 - Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDocument21 pages105 - Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsMycareer RamNo ratings yet
- Management ScienceDocument2 pagesManagement ScienceTheo John TalleNo ratings yet
- Operation Research by ADDocument36 pagesOperation Research by ADDaniyal AwanNo ratings yet
- Assignment in MathDocument4 pagesAssignment in Mathjulie anne mae mendozaNo ratings yet
- MBA201 OptimizationModelsforBDDocument56 pagesMBA201 OptimizationModelsforBD9801ashuNo ratings yet
- The Tools of Management ScienceDocument3 pagesThe Tools of Management ScienceSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- QT1Document2 pagesQT1Shweta GaurNo ratings yet
- Operation AnalyticsDocument62 pagesOperation Analyticssanjit kadneNo ratings yet
- Operations 1Document12 pagesOperations 1INCOGNITONo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDocument36 pagesQuantitative Techniques in Businesstalha mudassirNo ratings yet
- Statistical Techniques For Management Decision MakingDocument4 pagesStatistical Techniques For Management Decision MakingDrRitesh Patel67% (3)
- Operation Research Notes For PDF Contatc Me at HTTPS://WWW - Youtube.com/@kdpandharam #Nagpuruniversity #MBADocument7 pagesOperation Research Notes For PDF Contatc Me at HTTPS://WWW - Youtube.com/@kdpandharam #Nagpuruniversity #MBAMBA EngineerNo ratings yet
- FBAS Chap1Document8 pagesFBAS Chap1chibiNo ratings yet
- QTDM-1 PranaviDocument7 pagesQTDM-1 PranavipranaviNo ratings yet
- IBM Imp QuestionsDocument5 pagesIBM Imp Questionselegant.sksNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument15 pagesDecision MakingDr Umesh RajopadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument6 pagesUnit IArushi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document7 pagesUnit 1narutomoogrNo ratings yet
- Operational ResearchsDocument5 pagesOperational ResearchsDaniyal AwanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Tec Assignment 1Document6 pagesQuantitative Tec Assignment 1tage008No ratings yet
- Ba Unit 3 and 4Document30 pagesBa Unit 3 and 4Mythili SNo ratings yet
- Om 11Document16 pagesOm 11गब्बर जाटNo ratings yet
- Involves The Use of Quantitative Techniques, Such As Statistics, Information Models, and Computer Simulations, To Improve Decision MakingDocument2 pagesInvolves The Use of Quantitative Techniques, Such As Statistics, Information Models, and Computer Simulations, To Improve Decision Makingsssmitali53No ratings yet
- ModellingDocument4 pagesModellingltghunga5No ratings yet
- Business Analytics Batch 3-New1 - (Latest) - 0Document13 pagesBusiness Analytics Batch 3-New1 - (Latest) - 0uma.mba9920No ratings yet
- Management Science AutosavedDocument24 pagesManagement Science AutosavedRoncesvalles Geneva U.No ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: Md. Atiqur Rahman KhanDocument23 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: Md. Atiqur Rahman KhanFuadNo ratings yet
- Management Science Ouput 4 PDFDocument4 pagesManagement Science Ouput 4 PDFMyles Ninon LazoNo ratings yet
- Pa 202 Nov 12 AssignmentDocument3 pagesPa 202 Nov 12 AssignmentDebbie Valdehueza MercadoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business AnalyticsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Business AnalyticsTulasiram KandulaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Operations and Decisions MakingDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 2 Operations and Decisions Makingiamjean CortezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business AnalyticsDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Business AnalyticsMerlajoy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management and TQM: (CBME 1)Document5 pagesOperations Management and TQM: (CBME 1)AnggeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1Saurabh KUMARNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument13 pagesIntroductioneunice IlakizaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analytics TrainingDocument49 pagesFinancial Analytics Trainingayaankhan2307sreNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document8 pagesActivity 1Cha Eun WooNo ratings yet
- Bi Unit 1 PDFDocument38 pagesBi Unit 1 PDFAnuja GanjikarNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Notes1Document1 pageManagement Accounting Notes1GODFREY SIDWAKANo ratings yet
- OR Unit 1Document16 pagesOR Unit 1sakshi narayanNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTIONS AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT QnA AnsDocument14 pagesPRODUCTIONS AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT QnA AnsAbhishek MandalNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Business AnalyticsDocument11 pagesReviewer Business AnalyticsDaniel JadeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 HalfDocument8 pagesUnit 1 HalfSHIVANo ratings yet
- BBA 202 Business AnalyticsDocument52 pagesBBA 202 Business Analyticssatyam ranaNo ratings yet
- BI AssignmentDocument7 pagesBI AssignmentbhlmallahNo ratings yet
- Operations Researchfirst PartDocument6 pagesOperations Researchfirst Partzekariyas melleseNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology QuizDocument19 pagesResearch Methodology Quizpranav.gugaleNo ratings yet
- Management Notes1Document2 pagesManagement Notes1GODFREY SIDWAKANo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques 1Document6 pagesQuantitative Techniques 1rahulravi4u50% (2)
- 01 Business IntelligenceDocument16 pages01 Business IntelligencetovilasNo ratings yet
- QTDM 2Document3 pagesQTDM 2pranaviNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management - EditedDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Management - EditedMaina PeterNo ratings yet
- Quantitative School of MGT Assignment PrantoDocument6 pagesQuantitative School of MGT Assignment Prantopranto shuvoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1:: Overview of Quantitative MethodsDocument6 pagesLesson 1:: Overview of Quantitative MethodsMaweh SingcaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics: Leveraging Data for Insights and Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Analytics: Leveraging Data for Insights and Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Model Evaluation: Evaluating the Performance and Accuracy of Data Warehouse ModelsFrom EverandModel Evaluation: Evaluating the Performance and Accuracy of Data Warehouse ModelsNo ratings yet
- Paper - Google ScholarDocument2 pagesPaper - Google ScholarJJJJ TarkaNo ratings yet
- Sourabh Dixit C.V .Docs - 2Document2 pagesSourabh Dixit C.V .Docs - 2sdNo ratings yet
- Bachelor Thesis Cloud Computing PDFDocument4 pagesBachelor Thesis Cloud Computing PDFcatherineaguirresaltlakecity100% (2)
- Reading 2 Non-Parametric Approaches - AnswersDocument5 pagesReading 2 Non-Parametric Approaches - AnswersDivyansh ChandakNo ratings yet
- Geriatric-Medi BotDocument38 pagesGeriatric-Medi Bot4402 Ajesh RNo ratings yet
- Bare Overhead TransDocument174 pagesBare Overhead TransWilmer SuarezNo ratings yet
- MIS E-ContentDocument96 pagesMIS E-ContentManoj Kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Energy Management in Smart Buildings.: G. V. Acharya. Institutes of Engineering & Technology Shelu, KarjatDocument10 pagesEnergy Management in Smart Buildings.: G. V. Acharya. Institutes of Engineering & Technology Shelu, Karjatyashwantm2004No ratings yet
- Hotel Management System: Software Engineering Lab. 3rd SemesterDocument15 pagesHotel Management System: Software Engineering Lab. 3rd SemesterMuhammad AbuzarNo ratings yet
- English Task 2Document10 pagesEnglish Task 2Jordy Aprillianza BudiangNo ratings yet
- MR S's Mega Revision Pack 1 (1) - 240407 - 105850Document166 pagesMR S's Mega Revision Pack 1 (1) - 240407 - 105850Rayalakshmi RajyalakshmiNo ratings yet
- 907 1TDSDocument2 pages907 1TDSJainam Shah100% (1)
- Matlab Manual Cse DeptDocument65 pagesMatlab Manual Cse DeptAbinash MohantyNo ratings yet
- MED220 Chapter 3Document6 pagesMED220 Chapter 3CESAR ESGUERRANo ratings yet
- Project Overview Template - Candidate Package - Group Work Challenge - TMP Fall 2022 - AIESEC in FHN 2223Document40 pagesProject Overview Template - Candidate Package - Group Work Challenge - TMP Fall 2022 - AIESEC in FHN 2223k60.2114110143No ratings yet
- NCP-DS MyDocument23 pagesNCP-DS Myblackmamba etti jeanNo ratings yet
- What Are The Essential Requirements For Unattended Machinery Space (UMS) ShipDocument10 pagesWhat Are The Essential Requirements For Unattended Machinery Space (UMS) ShipstamatisNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Colour CalibrationDocument4 pages3.4 Colour Calibrationanandiyer01No ratings yet
- Smart Dustbin Vigilant System Using GSM and Arduino UnoDocument4 pagesSmart Dustbin Vigilant System Using GSM and Arduino UnoClean 91No ratings yet
- Gantt Chart Work ScheduleDocument2 pagesGantt Chart Work Schedulefarah aizarNo ratings yet
- Multi-Station Analysis of Surface Wave DispersionDocument10 pagesMulti-Station Analysis of Surface Wave DispersionChih-Ping LinNo ratings yet
- Tpack Module 2 Project - Kylie RussellDocument4 pagesTpack Module 2 Project - Kylie Russellapi-509237317No ratings yet
- Topic: Research On The Effects of Social Network Tiktok On Today'S YouthDocument2 pagesTopic: Research On The Effects of Social Network Tiktok On Today'S YouthNam HoàngNo ratings yet
- Climaveneta FOCS Water 2602Document1 pageClimaveneta FOCS Water 2602nomi1873No ratings yet
- Kioti Daedong DK751 (C), DK901 (C), DK753 (C), DK903 (C) Tractors Service ManualDocument19 pagesKioti Daedong DK751 (C), DK901 (C), DK753 (C), DK903 (C) Tractors Service ManualLisakolyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Online Voting System 1Document52 pagesIntroduction To Online Voting System 1Swaragini PatilNo ratings yet
- SCLMDocument45 pagesSCLMkeerthana chandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Online Voting SystemDocument26 pagesOnline Voting SystemVenkatesh Hanumandla96% (27)