Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect
Uploaded by
lenard.dongsalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 100 Years of Einstein's Photoelectric EffectDocument16 pages100 Years of Einstein's Photoelectric EffectsumivrindavanNo ratings yet
- DPI BioChar in Horticulture PDFDocument104 pagesDPI BioChar in Horticulture PDFManuel Martínez SotillosNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect UsesDocument2 pagesPhotoelectric Effect UsesAbhishek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heinrich Rudolf HertzDocument2 pagesHeinrich Rudolf HertzChinmay VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect PresentationDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric Effect PresentationXofoNo ratings yet
- Mera LaundaDocument22 pagesMera LaundaThe SeekerNo ratings yet
- 1921 Nobel Prize Winner of PhysicsDocument5 pages1921 Nobel Prize Winner of PhysicsRida RubabNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric EffectDocument4 pagesPhoto Electric EffectSamiul SeikhNo ratings yet
- Physics Photoelectric ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics Photoelectric ProjectAnonymous 3CivXAHALi100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument17 pagesPhotoelectric Effectvprogamer06No ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument19 pagesPhy ProjectGopi SowryNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument27 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaneezabdul2003100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSAMIR BEHERANo ratings yet
- Photoelectric e-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesPhotoelectric e-WPS OfficeA HNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric Effect - Britannica Online EncyclopediaAyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Photoelectric Effect: Noble International SchoolDocument22 pagesTopic: Photoelectric Effect: Noble International SchoolAnmol SinghalNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthandy moseyNo ratings yet
- Project On Photoelectric Effect Class 12Document24 pagesProject On Photoelectric Effect Class 12fizakouser1216100% (4)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric EffectGlay Cabañero TacanayNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument10 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSouvik BaruaNo ratings yet
- Physics T SafdarDocument17 pagesPhysics T SafdarSAFDAR HafizNo ratings yet
- Presentation of The Photoelectric EffectDocument16 pagesPresentation of The Photoelectric EffectJulia Marie AshelyNo ratings yet
- Fotoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesFotoelectric EffectDavid IssaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect L29Document10 pagesPhotoelectric Effect L29John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- The Photoelectric Effect DiapositivasDocument13 pagesThe Photoelectric Effect DiapositivasJuan David VillabonaNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument35 pagesContentshruthiandsridharNo ratings yet
- Blue Professional Background Paper Border A4 - 20231101 - 192456 - 0000Document11 pagesBlue Professional Background Paper Border A4 - 20231101 - 192456 - 0000bhabak0024No ratings yet
- History of Photoelectric Effect 4Document2 pagesHistory of Photoelectric Effect 4api-643290276No ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument10 pagesModern PhysicsMohammad Rashik ZamanNo ratings yet
- Phy Jan's ProjectDocument34 pagesPhy Jan's ProjectSakthiiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project 2023 2024 - RearrangedDocument27 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 2023 2024 - Rearrangedbabitaakkal709No ratings yet
- Project Title Exploring The Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesProject Title Exploring The Photoelectric Effectakash dasNo ratings yet
- Physics PWDocument16 pagesPhysics PWnimeshshresthatecesNo ratings yet
- QPhysics-Lab 1 - Photoelectric EffectDocument2 pagesQPhysics-Lab 1 - Photoelectric EffectEvariste MigaboNo ratings yet
- Phy 105 Photon TheoryDocument19 pagesPhy 105 Photon TheoryjaysonNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument22 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthemnphysic91No ratings yet
- CONTENTDocument9 pagesCONTENTAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric EffectUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric Effect NotesDocument11 pagesPhoto Electric Effect NotesChitransh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Wa0151Document26 pagesWa0151Kamalesh 354No ratings yet
- Laporan Unit 3 AyangDocument28 pagesLaporan Unit 3 AyangMurphy LinxNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric EffectDocument8 pagesPhoto Electric EffectRahul SoodNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument17 pagesSolar Energyapi-546410997No ratings yet
- 08. ОБЩАЯ ЭФИРОДИНАМИКА - Ацюковский В.А. (2) (1) -300-578Document279 pages08. ОБЩАЯ ЭФИРОДИНАМИКА - Ацюковский В.А. (2) (1) -300-578Yahya ShukurovNo ratings yet
- Photo Volaic EffectDocument2 pagesPhoto Volaic EffectMohammed Javeed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect1Document42 pagesPhotoelectric Effect1Pearl Shane DomingoNo ratings yet
- PhotoelectricDocument1 pagePhotoelectricazhar baig azharNo ratings yet
- تقرير الانكليزي - مصطفى خالد - فيزياءDocument3 pagesتقرير الانكليزي - مصطفى خالد - فيزياءمصطفى خالدNo ratings yet
- MODERN PHYSICS 1 Dual Nature and AtomsDocument4 pagesMODERN PHYSICS 1 Dual Nature and AtomsAkash tech. videoNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesPhotoelectric EffectRivu BasuNo ratings yet
- SC ProjtDocument1 pageSC ProjtStudy Centre IGNOUNo ratings yet
- Physical Effects Employed For Signal TransductionDocument24 pagesPhysical Effects Employed For Signal TransductionrimalisaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument31 pagesChapter 11 - Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterAtharva MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction of Modern Physics and Theory of Special Relativity 3 MuhammaDocument13 pages1 Introduction of Modern Physics and Theory of Special Relativity 3 MuhammaIlmu AnNo ratings yet
- Photoeletric EffectDocument20 pagesPhotoeletric EffectAkash DeepNo ratings yet
- ..Mona SediqDocument28 pages..Mona Sediqمحمد عامر الحكيميNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Sensors Part-2Document39 pagesUnit-1 Sensors Part-217 CSE Lokesh VNo ratings yet
- Quantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsFrom EverandQuantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- GATE 2018 SolutionDocument27 pagesGATE 2018 SolutionSubhajit PaulNo ratings yet
- CHEM 210 CH05 Stereochemistry IIDocument6 pagesCHEM 210 CH05 Stereochemistry IIHelm weuttNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Chap 2 ChemDocument15 pagesAtomic Structure Chap 2 ChemSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Palintestphotometer 8000Document2 pagesPalintestphotometer 8000Mestawot GirmaNo ratings yet
- SertralineDocument5 pagesSertralinePapaindoNo ratings yet
- Ford Transit VM 2006 2013 Workshop Manual 9Document1 pageFord Transit VM 2006 2013 Workshop Manual 9mail4281No ratings yet
- Poisons Their Isolation Identification PDFDocument156 pagesPoisons Their Isolation Identification PDFaftredgh0% (1)
- Study On Behaviour of Geopolymer Concrete Column: Shiva Kumar K.K.V, M. Prakash and Satyanarayanan K.SDocument4 pagesStudy On Behaviour of Geopolymer Concrete Column: Shiva Kumar K.K.V, M. Prakash and Satyanarayanan K.SjjNo ratings yet
- FME 522 THERMODYNAMICS V-Section I NotesDocument26 pagesFME 522 THERMODYNAMICS V-Section I NotesKatesh GumaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biological MS and Proteomics Carr 5 15 PDFDocument43 pagesFundamentals of Biological MS and Proteomics Carr 5 15 PDFCarlos Julio Nova LopezNo ratings yet
- Ice Cream AAKDocument12 pagesIce Cream AAKRobert RossNo ratings yet
- MLP PCMB Schedule For 22-23Document9 pagesMLP PCMB Schedule For 22-23Abdus SamadNo ratings yet
- Combipac Section IiiDocument11 pagesCombipac Section IiiMohammed Sultan SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- D 2152 - 95 - Rdixntitotu - PDFDocument4 pagesD 2152 - 95 - Rdixntitotu - PDFAndre CasteloNo ratings yet
- Similac® Human Milk Fortifier PowderDocument4 pagesSimilac® Human Milk Fortifier PowderEnzeru BDNo ratings yet
- How To Disperse and Stabili..Document12 pagesHow To Disperse and Stabili..tusharmechem100% (4)
- Bioresource TechnologyDocument7 pagesBioresource TechnologydevimeggaNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of Honeycomb Structure With Variation of Cell SizeDocument3 pagesModal Analysis of Honeycomb Structure With Variation of Cell Sizeprateekg92No ratings yet
- Hernandez - Activity 8Document3 pagesHernandez - Activity 8Ma Lourdes Diona HernandezNo ratings yet
- Coumarin-Based Small-Molecule Fluorescent Chemosensors PDFDocument117 pagesCoumarin-Based Small-Molecule Fluorescent Chemosensors PDFJEYMY SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Chiller Modelos - YK PDFDocument72 pagesChiller Modelos - YK PDFRenanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Himanshu Aggarwal0% (1)
- Tenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINALDocument1 pageTenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINALsanderssebastianNo ratings yet
- Chem 345 - Organic Reactions Chapter 17: Prepared by José Laboy, MSDocument1 pageChem 345 - Organic Reactions Chapter 17: Prepared by José Laboy, MSsridhar ramanaNo ratings yet
- Density of Steel For Ultrasonic TestingDocument3 pagesDensity of Steel For Ultrasonic TestingGaurav ChopraNo ratings yet
- Australian Standard: Structural Steel Hollow SectionsDocument26 pagesAustralian Standard: Structural Steel Hollow SectionsroscillaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Isophorone DiisocyanateDocument6 pagesMSDS Isophorone DiisocyanateIzzuddin IsmailNo ratings yet
- TabletDocument37 pagesTabletPranjul ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect
Uploaded by
lenard.dongsalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect
Uploaded by
lenard.dongsalCopyright:
Available Formats
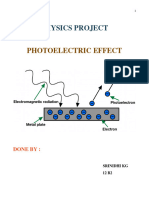
The
photoelectric
effect was first
introduced by
Wilhelm Ludwig
Franz Hallwachs
in the year 1887,
and the
experimental
verification was
done by
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Einstein’s Contributions towards the
Photoelectric Effect
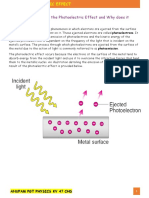
The photoelectric effect is the
process that involves the
ejection or release of electrons
from the surface of materials
(generally a metal) when light
falls on them. The photoelectric
effect is an important concept
that enables us to clearly understand the quantum nature of
light and electrons.
What is photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect is phenomenon of
metals releasing electrons when they are
exposed to light of the appropriate frequency
is called the photoelectric effect, and the
electrons emitted during the process are
called photoelectrons. Today, we study the
photoelectric effect as a phenomenon that
involves a material absorbing
electromagnetic radiation and releasing
electrically charged particles.
Principle of the Photoelectric Effect
The law of conservation of energy forms the
basis for the photoelectric effect.
Application of Photoelectric Effect
Used to generate electricity in solar panels.
These panels contain metal combinations
that allow electricity generation from a wide
range of wavelengths.
Digital cameras can detect and record light
because they have photoelectric sensors that
respond to different colors of light.
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS):
This technique uses X-rays to irradiate a
surface and measure the kinetic energies of
the emitted electrons. Important aspects of
the chemistry of a surface can be obtained,
such as elemental composition, chemical
composition, the empirical formula of
compounds and chemical state.
Night vision devices are based on this effect.
You might also like
- 100 Years of Einstein's Photoelectric EffectDocument16 pages100 Years of Einstein's Photoelectric EffectsumivrindavanNo ratings yet
- DPI BioChar in Horticulture PDFDocument104 pagesDPI BioChar in Horticulture PDFManuel Martínez SotillosNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect UsesDocument2 pagesPhotoelectric Effect UsesAbhishek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heinrich Rudolf HertzDocument2 pagesHeinrich Rudolf HertzChinmay VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect PresentationDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric Effect PresentationXofoNo ratings yet
- Mera LaundaDocument22 pagesMera LaundaThe SeekerNo ratings yet
- 1921 Nobel Prize Winner of PhysicsDocument5 pages1921 Nobel Prize Winner of PhysicsRida RubabNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric EffectDocument4 pagesPhoto Electric EffectSamiul SeikhNo ratings yet
- Physics Photoelectric ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics Photoelectric ProjectAnonymous 3CivXAHALi100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument17 pagesPhotoelectric Effectvprogamer06No ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument19 pagesPhy ProjectGopi SowryNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument27 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaneezabdul2003100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSAMIR BEHERANo ratings yet
- Photoelectric e-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesPhotoelectric e-WPS OfficeA HNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric Effect - Britannica Online EncyclopediaAyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Photoelectric Effect: Noble International SchoolDocument22 pagesTopic: Photoelectric Effect: Noble International SchoolAnmol SinghalNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthandy moseyNo ratings yet
- Project On Photoelectric Effect Class 12Document24 pagesProject On Photoelectric Effect Class 12fizakouser1216100% (4)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric EffectGlay Cabañero TacanayNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument10 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSouvik BaruaNo ratings yet
- Physics T SafdarDocument17 pagesPhysics T SafdarSAFDAR HafizNo ratings yet
- Presentation of The Photoelectric EffectDocument16 pagesPresentation of The Photoelectric EffectJulia Marie AshelyNo ratings yet
- Fotoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesFotoelectric EffectDavid IssaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect L29Document10 pagesPhotoelectric Effect L29John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- The Photoelectric Effect DiapositivasDocument13 pagesThe Photoelectric Effect DiapositivasJuan David VillabonaNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument35 pagesContentshruthiandsridharNo ratings yet
- Blue Professional Background Paper Border A4 - 20231101 - 192456 - 0000Document11 pagesBlue Professional Background Paper Border A4 - 20231101 - 192456 - 0000bhabak0024No ratings yet
- History of Photoelectric Effect 4Document2 pagesHistory of Photoelectric Effect 4api-643290276No ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument10 pagesModern PhysicsMohammad Rashik ZamanNo ratings yet
- Phy Jan's ProjectDocument34 pagesPhy Jan's ProjectSakthiiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project 2023 2024 - RearrangedDocument27 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 2023 2024 - Rearrangedbabitaakkal709No ratings yet
- Project Title Exploring The Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesProject Title Exploring The Photoelectric Effectakash dasNo ratings yet
- Physics PWDocument16 pagesPhysics PWnimeshshresthatecesNo ratings yet
- QPhysics-Lab 1 - Photoelectric EffectDocument2 pagesQPhysics-Lab 1 - Photoelectric EffectEvariste MigaboNo ratings yet
- Phy 105 Photon TheoryDocument19 pagesPhy 105 Photon TheoryjaysonNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument22 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthemnphysic91No ratings yet
- CONTENTDocument9 pagesCONTENTAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric EffectUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric Effect NotesDocument11 pagesPhoto Electric Effect NotesChitransh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Wa0151Document26 pagesWa0151Kamalesh 354No ratings yet
- Laporan Unit 3 AyangDocument28 pagesLaporan Unit 3 AyangMurphy LinxNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric EffectDocument8 pagesPhoto Electric EffectRahul SoodNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument17 pagesSolar Energyapi-546410997No ratings yet
- 08. ОБЩАЯ ЭФИРОДИНАМИКА - Ацюковский В.А. (2) (1) -300-578Document279 pages08. ОБЩАЯ ЭФИРОДИНАМИКА - Ацюковский В.А. (2) (1) -300-578Yahya ShukurovNo ratings yet
- Photo Volaic EffectDocument2 pagesPhoto Volaic EffectMohammed Javeed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect1Document42 pagesPhotoelectric Effect1Pearl Shane DomingoNo ratings yet
- PhotoelectricDocument1 pagePhotoelectricazhar baig azharNo ratings yet
- تقرير الانكليزي - مصطفى خالد - فيزياءDocument3 pagesتقرير الانكليزي - مصطفى خالد - فيزياءمصطفى خالدNo ratings yet
- MODERN PHYSICS 1 Dual Nature and AtomsDocument4 pagesMODERN PHYSICS 1 Dual Nature and AtomsAkash tech. videoNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesPhotoelectric EffectRivu BasuNo ratings yet
- SC ProjtDocument1 pageSC ProjtStudy Centre IGNOUNo ratings yet
- Physical Effects Employed For Signal TransductionDocument24 pagesPhysical Effects Employed For Signal TransductionrimalisaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument31 pagesChapter 11 - Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterAtharva MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction of Modern Physics and Theory of Special Relativity 3 MuhammaDocument13 pages1 Introduction of Modern Physics and Theory of Special Relativity 3 MuhammaIlmu AnNo ratings yet
- Photoeletric EffectDocument20 pagesPhotoeletric EffectAkash DeepNo ratings yet
- ..Mona SediqDocument28 pages..Mona Sediqمحمد عامر الحكيميNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Sensors Part-2Document39 pagesUnit-1 Sensors Part-217 CSE Lokesh VNo ratings yet
- Quantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsFrom EverandQuantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- GATE 2018 SolutionDocument27 pagesGATE 2018 SolutionSubhajit PaulNo ratings yet
- CHEM 210 CH05 Stereochemistry IIDocument6 pagesCHEM 210 CH05 Stereochemistry IIHelm weuttNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Chap 2 ChemDocument15 pagesAtomic Structure Chap 2 ChemSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Palintestphotometer 8000Document2 pagesPalintestphotometer 8000Mestawot GirmaNo ratings yet
- SertralineDocument5 pagesSertralinePapaindoNo ratings yet
- Ford Transit VM 2006 2013 Workshop Manual 9Document1 pageFord Transit VM 2006 2013 Workshop Manual 9mail4281No ratings yet
- Poisons Their Isolation Identification PDFDocument156 pagesPoisons Their Isolation Identification PDFaftredgh0% (1)
- Study On Behaviour of Geopolymer Concrete Column: Shiva Kumar K.K.V, M. Prakash and Satyanarayanan K.SDocument4 pagesStudy On Behaviour of Geopolymer Concrete Column: Shiva Kumar K.K.V, M. Prakash and Satyanarayanan K.SjjNo ratings yet
- FME 522 THERMODYNAMICS V-Section I NotesDocument26 pagesFME 522 THERMODYNAMICS V-Section I NotesKatesh GumaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biological MS and Proteomics Carr 5 15 PDFDocument43 pagesFundamentals of Biological MS and Proteomics Carr 5 15 PDFCarlos Julio Nova LopezNo ratings yet
- Ice Cream AAKDocument12 pagesIce Cream AAKRobert RossNo ratings yet
- MLP PCMB Schedule For 22-23Document9 pagesMLP PCMB Schedule For 22-23Abdus SamadNo ratings yet
- Combipac Section IiiDocument11 pagesCombipac Section IiiMohammed Sultan SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- D 2152 - 95 - Rdixntitotu - PDFDocument4 pagesD 2152 - 95 - Rdixntitotu - PDFAndre CasteloNo ratings yet
- Similac® Human Milk Fortifier PowderDocument4 pagesSimilac® Human Milk Fortifier PowderEnzeru BDNo ratings yet
- How To Disperse and Stabili..Document12 pagesHow To Disperse and Stabili..tusharmechem100% (4)
- Bioresource TechnologyDocument7 pagesBioresource TechnologydevimeggaNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of Honeycomb Structure With Variation of Cell SizeDocument3 pagesModal Analysis of Honeycomb Structure With Variation of Cell Sizeprateekg92No ratings yet
- Hernandez - Activity 8Document3 pagesHernandez - Activity 8Ma Lourdes Diona HernandezNo ratings yet
- Coumarin-Based Small-Molecule Fluorescent Chemosensors PDFDocument117 pagesCoumarin-Based Small-Molecule Fluorescent Chemosensors PDFJEYMY SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Chiller Modelos - YK PDFDocument72 pagesChiller Modelos - YK PDFRenanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Himanshu Aggarwal0% (1)
- Tenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINALDocument1 pageTenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINALsanderssebastianNo ratings yet
- Chem 345 - Organic Reactions Chapter 17: Prepared by José Laboy, MSDocument1 pageChem 345 - Organic Reactions Chapter 17: Prepared by José Laboy, MSsridhar ramanaNo ratings yet
- Density of Steel For Ultrasonic TestingDocument3 pagesDensity of Steel For Ultrasonic TestingGaurav ChopraNo ratings yet
- Australian Standard: Structural Steel Hollow SectionsDocument26 pagesAustralian Standard: Structural Steel Hollow SectionsroscillaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Isophorone DiisocyanateDocument6 pagesMSDS Isophorone DiisocyanateIzzuddin IsmailNo ratings yet
- TabletDocument37 pagesTabletPranjul ShrivastavaNo ratings yet