Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE2205
EE2205
Uploaded by
Harsh AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Principles of Econometrics 4th Edition Hill Solutions ManualDocument34 pagesPrinciples of Econometrics 4th Edition Hill Solutions Manualcourtneyriceacnmbxqiky100% (13)
- Tech Bulletin 0112 - Creaking Clicking of FrameDocument8 pagesTech Bulletin 0112 - Creaking Clicking of FrameRichard HagleyNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesInvestigatory Projecte_geanga84% (31)
- Global Trends 2030: Alternative WorldsDocument160 pagesGlobal Trends 2030: Alternative WorldsOffice of the Director of National Intelligence97% (29)
- Antenna DvorDocument27 pagesAntenna DvorRhonny AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Conducting Exposures To Daylight Filtered Through Glass: Standard Practice ForDocument5 pagesConducting Exposures To Daylight Filtered Through Glass: Standard Practice ForJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- Liebert Icom User Manual - 00 PDFDocument214 pagesLiebert Icom User Manual - 00 PDFsai krishnaNo ratings yet
- The Ten Commandments What If We Did It God's Way?Document89 pagesThe Ten Commandments What If We Did It God's Way?Isaac AlemanNo ratings yet
- Production of BioethanolDocument43 pagesProduction of BioethanolAniket Chaki100% (4)
- Ee2205 2Document2 pagesEe2205 2Naveen BigShotNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 ModDocument2 pagesAssessment 1 ModSaravana perumalNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer All Questions: Date: Time: 1hourDocument2 pagesInstruction: Answer All Questions: Date: Time: 1hourojwangdan8615No ratings yet
- VL2021220504591 DaDocument2 pagesVL2021220504591 DaDattu GollapinniNo ratings yet
- S T L DDocument12 pagesS T L DMohan Krishna0% (1)
- Practice Problems - 1: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesPractice Problems - 1: Department of Electrical EngineeringMalay Kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic Design (CSE-203) (Makeup)Document2 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic Design (CSE-203) (Makeup)Random ShitNo ratings yet
- QBank DPSD cs2202Document6 pagesQBank DPSD cs2202kunarajNo ratings yet
- BCA I I Digital SystemDocument4 pagesBCA I I Digital SystemAmory Sabri AsmaroNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS NovemberDecember-2020Document1 pageDIGITAL ELECTRONICS NovemberDecember-2020ethanNo ratings yet
- EETE 231 Digital Electronics E 46 Final AssignmentDocument2 pagesEETE 231 Digital Electronics E 46 Final AssignmentERT FAMILY BDNo ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- JanuaryFebruary 2021Document1 pageJanuaryFebruary 2021vishwatejkachu944No ratings yet
- Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pagesDigital Logic DesignShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- EE-342 Digital ElectronicsDocument2 pagesEE-342 Digital ElectronicsDeepesh KumarNo ratings yet
- De As1Document2 pagesDe As1Dr-Tarun ParasharNo ratings yet
- Code - No: 43216: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument1 pageCode - No: 43216: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadKareem KhanNo ratings yet
- Amity University Maharashtra Amity Institute of Information TechnologyDocument2 pagesAmity University Maharashtra Amity Institute of Information TechnologyrevatiNo ratings yet
- DLC Series IaDocument1 pageDLC Series IaAnusha NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem 2012Document2 pagesMid Sem 2012Kshitij GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Junior Paul BalenNo ratings yet
- Assingnment# 1Document8 pagesAssingnment# 1Tayyab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ect203 Scheme 2020Document8 pagesEct203 Scheme 2020ShakiraNo ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignMahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- ECE20022 Assignment Module 1 2 3Document3 pagesECE20022 Assignment Module 1 2 3Nandini PandeyNo ratings yet
- Sub. Code 11: May 2020 Arrear ExaminationDocument2 pagesSub. Code 11: May 2020 Arrear ExaminationSakthiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document3 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashutosh PatilNo ratings yet
- DP-Assignment Brief A1 - UpdatedDocument12 pagesDP-Assignment Brief A1 - UpdatedTân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- DLC Model IDocument2 pagesDLC Model IEEE DEPTNo ratings yet
- Convert Gray Code 101011 Into Its Binary Equivalent. Gray Code: 1 0 1 0 1 1 Binary Code: 1 1 0 0 1 0Document23 pagesConvert Gray Code 101011 Into Its Binary Equivalent. Gray Code: 1 0 1 0 1 1 Binary Code: 1 1 0 0 1 0khadarbasha.n nNo ratings yet
- Ae8501 Ad-Ii Unit Wise QBDocument15 pagesAe8501 Ad-Ii Unit Wise QBpugazhNo ratings yet
- تجميع تست 2Document47 pagesتجميع تست 2fathi123fathi3000No ratings yet
- 9A04401 Switching Theory & Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04401 Switching Theory & Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ia1 DPSDDocument2 pagesIa1 DPSDRaja BenitaNo ratings yet
- EE370 Assignment-IDocument3 pagesEE370 Assignment-ISandeep TomarNo ratings yet
- STLD Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008Document9 pagesSTLD Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008anjaneyulud100% (1)
- Digital Logic Design: Assignment 1 Due Date: 10.12.2020 (Thursday)Document3 pagesDigital Logic Design: Assignment 1 Due Date: 10.12.2020 (Thursday)muktikantaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MicroPDocument9 pagesTutorial MicroPAhmad IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem 2022 MidsemDocument6 pages4th Sem 2022 MidsemAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-2-3 Question Bank DEC 2131004Document2 pagesUnit-1-2-3 Question Bank DEC 2131004Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument3 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoFack AccountNo ratings yet
- 19EC303 DPSD Learners Copy 11 03 24Document56 pages19EC303 DPSD Learners Copy 11 03 24Marshmellow FFNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 7-1Document12 pagesTutorial Sheet 7-1ThejeshVenkataNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - BCD To Excess-3 ConverterDocument6 pagesLab 4 - BCD To Excess-3 Converter213642No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Digital Techniques PDFDocument5 pagesSample Question Paper Digital Techniques PDFAshutosh PatilNo ratings yet
- DLD Ques2Document2 pagesDLD Ques2mahbub mitulNo ratings yet
- 18IT302Document13 pages18IT302SUSEENDRAN VNo ratings yet
- Btech Biomed 4 Sem Digital Electronics Circuit Pbm4i102 2018Document3 pagesBtech Biomed 4 Sem Digital Electronics Circuit Pbm4i102 2018Narinder MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ece DLD Set IiDocument2 pagesEce DLD Set IikisnamohanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Engineering I SemDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Engineering I Semshubhambani45No ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)kenny kannaNo ratings yet
- EE202QDocument7 pagesEE202QBelon Kaler Biyru IINo ratings yet
- FAQs - CS1202 Digital Principles and System DesignDocument13 pagesFAQs - CS1202 Digital Principles and System DesignsridharanchandranNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Attainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorFrom EverandAttainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Endsem May22 EE2201 FinalDocument4 pagesEndsem May22 EE2201 FinalHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- EE2204 Endsem 2022wholeDocument95 pagesEE2204 Endsem 2022wholeHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MSG Sir NotesDocument15 pagesMSG Sir NotesHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem EE2202 Solutions (AS)Document3 pagesMid Sem EE2202 Solutions (AS)Harsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Machines Answer Sheet 2022 DilshadDocument7 pagesMachines Answer Sheet 2022 DilshadHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pedeey: We GaeuuteDocument9 pagesPedeey: We GaeuuteHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Bridgestone Sip ReportDocument44 pagesBridgestone Sip ReportBothra SidharathNo ratings yet
- 921C - Esquematico HidraulicoDocument1 page921C - Esquematico HidraulicoMauricio Gomez GomezNo ratings yet
- Tools Earl LowDocument22 pagesTools Earl Lowjaimecam85No ratings yet
- ASAL Economics Workbook AnswersDocument111 pagesASAL Economics Workbook AnswersMatej Milosavljevic100% (1)
- M408C Chme: M408C Cheat Sheet Final Exameat Sheet Final ExamDocument3 pagesM408C Chme: M408C Cheat Sheet Final Exameat Sheet Final Examjakepatt101No ratings yet
- 74HC00Document9 pages74HC00jnax101No ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument9 pagesResearch ArticleElla Gita SilvianaNo ratings yet
- Abiotic Stress Response in Plants - Physiological Biochemical and Genetic PerspectivesDocument358 pagesAbiotic Stress Response in Plants - Physiological Biochemical and Genetic PerspectivesCarolina Salazar ParraNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication & Testing of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Wind de EctorsDocument61 pagesDesign, Fabrication & Testing of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Wind de EctorsGautham NNo ratings yet
- Digital LA30W Parts CatalogDocument46 pagesDigital LA30W Parts CatalogΓιάννης ΜελετήςNo ratings yet
- Generator Protection Realy Test FormDocument6 pagesGenerator Protection Realy Test Formwaheed bassamiNo ratings yet
- WS01 Slopes Samantha SarahDocument7 pagesWS01 Slopes Samantha SarahSAMANTHA SARAH PURBANo ratings yet
- Philos and Philos Long: Surgical TechniqueDocument38 pagesPhilos and Philos Long: Surgical TechniqueSamuel HarnaenNo ratings yet
- Enprep - 220EC Steel Cu Brass MSDS.Document5 pagesEnprep - 220EC Steel Cu Brass MSDS.LựuLiềuLìNo ratings yet
- FD Fan ID Fan ControlDocument4 pagesFD Fan ID Fan ControlAbhishek Kumar100% (2)
- Ga-G31m-S2l (Rev 1.2)Document33 pagesGa-G31m-S2l (Rev 1.2)Richard Hernandez RuizNo ratings yet
- Elegra Error MessageDocument30 pagesElegra Error MessageLuis Fernando Garcia Sanchez100% (2)
- Classify DEsDocument5 pagesClassify DEsfree_progNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Academy 2016 EDocument56 pagesYaskawa Academy 2016 Ejmorenoh103100% (1)
- Cronologia - Marvel ComicsDocument9 pagesCronologia - Marvel ComicsrafaelasevedosNo ratings yet
- Contridas Charles Daryll Grammar Review Activities Pg1 33Document92 pagesContridas Charles Daryll Grammar Review Activities Pg1 33Charles ContridasNo ratings yet
EE2205
EE2205
Uploaded by
Harsh AgarwalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE2205
EE2205
Uploaded by
Harsh AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
CONFIDENTIAL Ref. No.
: EE2205/ES/2021/05
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, SHIBPUR
B. Tech (EE) 4th Semester Final Examination, May-2021
Digital Electronics (EE2205)
Full Marks: 50 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
(i) Use a single answer-script for all questions
(ii) Answer Qs. No. 1 and ANY THREE full questions from the rest
(iii) All parts of a question MUST be answered in the same place
(iv) Relevant diagram(s) MUST be drawn for each problem
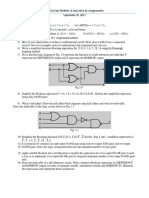
1. (a) Prove the following Boolean Law: A + BC = (A + B).(A + C)
(b) Deduce the Boolean Expression for a full-subtractor. Clearly mention the significance of all
symbols used. Hence, draw the Boolean Logic Circuit for a full subtractor.
(c) An ABCD-to-seven-segment decoder is a combinational circuit that converts a decimal digit in
BCD to an appropriate code for the selection of segment in an indicator used to display the
decimal digit in a familiar form. The seven outputs of the decoder (a, b, c, d, e, f, g) select the
corresponding segments in the display, as shown in Fig. Q1(a). The numeric display chosen to
represent the decimal digit is shown in Fig. Q1(b). Using a truth table and Karnaugh maps, design
the BCD-to-seven-segment decoder, using minimum number of gates. The six invalid
combinations should result in a blank display.
(a) (b)
Fig. Q1
[5 + 5 + 10 = 20]
2. (a) Draw the internal schematic diagram, for a D-type flip-flop, with positive-edge-triggered
architecture, and clearly explain its working. Mention one advantage of this edge-triggered
architecture over master-slave architecture.
(b) Explain the phenomenon of 'contact-bouncing'. How can flip-flops be used as a 'contact de-
bouncer'?
[(2 + 3 + 2) + 3 = 10]
3. (a) With a neat sketch, clearly explain the working of a "Switch-Tail Ring Counter", using four flip-
flops. How many states does this counter have?
(b) Without using any external switch and the minimum number of flip-flops, design a binary counter,
which counts continuously in the following sequence: 0 → 1 → 2 → 4 → 8 → 0 → 1 → .... and so
on (where the decimal nos. given are equivalent decimal value of the binary output). Clearly
explain your steps.
[5 + 5 = 10]
4. (a) "DTL architecture supports wired-AND logic" – Explain the statement with suitable diagrams.
Page 1 of 2
Name of the Paper: Digital Electronics (EE-2205)
Name of the Examination: Final Examination, May-2021
Name of the Paper Setter: S. Dalapati
Signature of the Moderator (with date)
CONFIDENTIAL Ref. No.: EE2205/ES/2021/05
(b) In the circuit, shown in Fig. Q4, the input voltage is
vi, which swings between two levels – 0 and 12 V.
The output voltage is vo. It is assumed that Q will
enter hard saturation if β (= IC/IB) < 10. Determine
mathematically: (i) whether Q is in active zone or
saturation zone when vi = 12 V, and (ii) the levels of
vo for the two input levels of vi. Assume that all
voltages in the figure are with respect to ground
(unless mentioned otherwise) and VBE,sat = 0.8 V and
VCE,sat = 0.2 V.
[5 + 5 = 10] Fig. Q4
5. (a) With a neat sketch, describe the working of a DAC with binary weighted resistors. Mention one
advantage and one disadvantage of this DAC.
(b) A five-bit Digital to Analogue Converter produces an output of 0.4 V for a digital input of 00010.
(i) Find the output for an input of 10001. (ii) What is the resolution of this DAC? (iii) What is the
maximum output, obtainable from this DAC?
[(3 + 2) + (2 + 2 + 1) = 10]
------xxx-------
Page 2 of 2
Name of the Paper: Digital Electronics (EE-2205)
Name of the Examination: Final Examination, May-2021
Name of the Paper Setter: S. Dalapati
Signature of the Moderator (with date)
You might also like
- Principles of Econometrics 4th Edition Hill Solutions ManualDocument34 pagesPrinciples of Econometrics 4th Edition Hill Solutions Manualcourtneyriceacnmbxqiky100% (13)
- Tech Bulletin 0112 - Creaking Clicking of FrameDocument8 pagesTech Bulletin 0112 - Creaking Clicking of FrameRichard HagleyNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesInvestigatory Projecte_geanga84% (31)
- Global Trends 2030: Alternative WorldsDocument160 pagesGlobal Trends 2030: Alternative WorldsOffice of the Director of National Intelligence97% (29)
- Antenna DvorDocument27 pagesAntenna DvorRhonny AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Conducting Exposures To Daylight Filtered Through Glass: Standard Practice ForDocument5 pagesConducting Exposures To Daylight Filtered Through Glass: Standard Practice ForJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- Liebert Icom User Manual - 00 PDFDocument214 pagesLiebert Icom User Manual - 00 PDFsai krishnaNo ratings yet
- The Ten Commandments What If We Did It God's Way?Document89 pagesThe Ten Commandments What If We Did It God's Way?Isaac AlemanNo ratings yet
- Production of BioethanolDocument43 pagesProduction of BioethanolAniket Chaki100% (4)
- Ee2205 2Document2 pagesEe2205 2Naveen BigShotNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 ModDocument2 pagesAssessment 1 ModSaravana perumalNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer All Questions: Date: Time: 1hourDocument2 pagesInstruction: Answer All Questions: Date: Time: 1hourojwangdan8615No ratings yet
- VL2021220504591 DaDocument2 pagesVL2021220504591 DaDattu GollapinniNo ratings yet
- S T L DDocument12 pagesS T L DMohan Krishna0% (1)
- Practice Problems - 1: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesPractice Problems - 1: Department of Electrical EngineeringMalay Kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic Design (CSE-203) (Makeup)Document2 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic Design (CSE-203) (Makeup)Random ShitNo ratings yet
- QBank DPSD cs2202Document6 pagesQBank DPSD cs2202kunarajNo ratings yet
- BCA I I Digital SystemDocument4 pagesBCA I I Digital SystemAmory Sabri AsmaroNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS NovemberDecember-2020Document1 pageDIGITAL ELECTRONICS NovemberDecember-2020ethanNo ratings yet
- EETE 231 Digital Electronics E 46 Final AssignmentDocument2 pagesEETE 231 Digital Electronics E 46 Final AssignmentERT FAMILY BDNo ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- JanuaryFebruary 2021Document1 pageJanuaryFebruary 2021vishwatejkachu944No ratings yet
- Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pagesDigital Logic DesignShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- EE-342 Digital ElectronicsDocument2 pagesEE-342 Digital ElectronicsDeepesh KumarNo ratings yet
- De As1Document2 pagesDe As1Dr-Tarun ParasharNo ratings yet
- Code - No: 43216: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument1 pageCode - No: 43216: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadKareem KhanNo ratings yet
- Amity University Maharashtra Amity Institute of Information TechnologyDocument2 pagesAmity University Maharashtra Amity Institute of Information TechnologyrevatiNo ratings yet
- DLC Series IaDocument1 pageDLC Series IaAnusha NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem 2012Document2 pagesMid Sem 2012Kshitij GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Junior Paul BalenNo ratings yet
- Assingnment# 1Document8 pagesAssingnment# 1Tayyab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ect203 Scheme 2020Document8 pagesEct203 Scheme 2020ShakiraNo ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignMahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- ECE20022 Assignment Module 1 2 3Document3 pagesECE20022 Assignment Module 1 2 3Nandini PandeyNo ratings yet
- Sub. Code 11: May 2020 Arrear ExaminationDocument2 pagesSub. Code 11: May 2020 Arrear ExaminationSakthiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document3 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashutosh PatilNo ratings yet
- DP-Assignment Brief A1 - UpdatedDocument12 pagesDP-Assignment Brief A1 - UpdatedTân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- DLC Model IDocument2 pagesDLC Model IEEE DEPTNo ratings yet
- Convert Gray Code 101011 Into Its Binary Equivalent. Gray Code: 1 0 1 0 1 1 Binary Code: 1 1 0 0 1 0Document23 pagesConvert Gray Code 101011 Into Its Binary Equivalent. Gray Code: 1 0 1 0 1 1 Binary Code: 1 1 0 0 1 0khadarbasha.n nNo ratings yet
- Ae8501 Ad-Ii Unit Wise QBDocument15 pagesAe8501 Ad-Ii Unit Wise QBpugazhNo ratings yet
- تجميع تست 2Document47 pagesتجميع تست 2fathi123fathi3000No ratings yet
- 9A04401 Switching Theory & Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04401 Switching Theory & Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ia1 DPSDDocument2 pagesIa1 DPSDRaja BenitaNo ratings yet
- EE370 Assignment-IDocument3 pagesEE370 Assignment-ISandeep TomarNo ratings yet
- STLD Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008Document9 pagesSTLD Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008anjaneyulud100% (1)
- Digital Logic Design: Assignment 1 Due Date: 10.12.2020 (Thursday)Document3 pagesDigital Logic Design: Assignment 1 Due Date: 10.12.2020 (Thursday)muktikantaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MicroPDocument9 pagesTutorial MicroPAhmad IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem 2022 MidsemDocument6 pages4th Sem 2022 MidsemAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-2-3 Question Bank DEC 2131004Document2 pagesUnit-1-2-3 Question Bank DEC 2131004Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument3 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoFack AccountNo ratings yet
- 19EC303 DPSD Learners Copy 11 03 24Document56 pages19EC303 DPSD Learners Copy 11 03 24Marshmellow FFNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 7-1Document12 pagesTutorial Sheet 7-1ThejeshVenkataNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - BCD To Excess-3 ConverterDocument6 pagesLab 4 - BCD To Excess-3 Converter213642No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Digital Techniques PDFDocument5 pagesSample Question Paper Digital Techniques PDFAshutosh PatilNo ratings yet
- DLD Ques2Document2 pagesDLD Ques2mahbub mitulNo ratings yet
- 18IT302Document13 pages18IT302SUSEENDRAN VNo ratings yet
- Btech Biomed 4 Sem Digital Electronics Circuit Pbm4i102 2018Document3 pagesBtech Biomed 4 Sem Digital Electronics Circuit Pbm4i102 2018Narinder MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ece DLD Set IiDocument2 pagesEce DLD Set IikisnamohanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Engineering I SemDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Engineering I Semshubhambani45No ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)kenny kannaNo ratings yet
- EE202QDocument7 pagesEE202QBelon Kaler Biyru IINo ratings yet
- FAQs - CS1202 Digital Principles and System DesignDocument13 pagesFAQs - CS1202 Digital Principles and System DesignsridharanchandranNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Attainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorFrom EverandAttainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Endsem May22 EE2201 FinalDocument4 pagesEndsem May22 EE2201 FinalHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- EE2204 Endsem 2022wholeDocument95 pagesEE2204 Endsem 2022wholeHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MSG Sir NotesDocument15 pagesMSG Sir NotesHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem EE2202 Solutions (AS)Document3 pagesMid Sem EE2202 Solutions (AS)Harsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Machines Answer Sheet 2022 DilshadDocument7 pagesMachines Answer Sheet 2022 DilshadHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pedeey: We GaeuuteDocument9 pagesPedeey: We GaeuuteHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Bridgestone Sip ReportDocument44 pagesBridgestone Sip ReportBothra SidharathNo ratings yet
- 921C - Esquematico HidraulicoDocument1 page921C - Esquematico HidraulicoMauricio Gomez GomezNo ratings yet
- Tools Earl LowDocument22 pagesTools Earl Lowjaimecam85No ratings yet
- ASAL Economics Workbook AnswersDocument111 pagesASAL Economics Workbook AnswersMatej Milosavljevic100% (1)
- M408C Chme: M408C Cheat Sheet Final Exameat Sheet Final ExamDocument3 pagesM408C Chme: M408C Cheat Sheet Final Exameat Sheet Final Examjakepatt101No ratings yet
- 74HC00Document9 pages74HC00jnax101No ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument9 pagesResearch ArticleElla Gita SilvianaNo ratings yet
- Abiotic Stress Response in Plants - Physiological Biochemical and Genetic PerspectivesDocument358 pagesAbiotic Stress Response in Plants - Physiological Biochemical and Genetic PerspectivesCarolina Salazar ParraNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication & Testing of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Wind de EctorsDocument61 pagesDesign, Fabrication & Testing of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Wind de EctorsGautham NNo ratings yet
- Digital LA30W Parts CatalogDocument46 pagesDigital LA30W Parts CatalogΓιάννης ΜελετήςNo ratings yet
- Generator Protection Realy Test FormDocument6 pagesGenerator Protection Realy Test Formwaheed bassamiNo ratings yet
- WS01 Slopes Samantha SarahDocument7 pagesWS01 Slopes Samantha SarahSAMANTHA SARAH PURBANo ratings yet
- Philos and Philos Long: Surgical TechniqueDocument38 pagesPhilos and Philos Long: Surgical TechniqueSamuel HarnaenNo ratings yet
- Enprep - 220EC Steel Cu Brass MSDS.Document5 pagesEnprep - 220EC Steel Cu Brass MSDS.LựuLiềuLìNo ratings yet
- FD Fan ID Fan ControlDocument4 pagesFD Fan ID Fan ControlAbhishek Kumar100% (2)
- Ga-G31m-S2l (Rev 1.2)Document33 pagesGa-G31m-S2l (Rev 1.2)Richard Hernandez RuizNo ratings yet
- Elegra Error MessageDocument30 pagesElegra Error MessageLuis Fernando Garcia Sanchez100% (2)
- Classify DEsDocument5 pagesClassify DEsfree_progNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Academy 2016 EDocument56 pagesYaskawa Academy 2016 Ejmorenoh103100% (1)
- Cronologia - Marvel ComicsDocument9 pagesCronologia - Marvel ComicsrafaelasevedosNo ratings yet
- Contridas Charles Daryll Grammar Review Activities Pg1 33Document92 pagesContridas Charles Daryll Grammar Review Activities Pg1 33Charles ContridasNo ratings yet