Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 Composition of Matter
Unit 2 Composition of Matter
Uploaded by
jhontayson12Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2 Composition of Matter
Unit 2 Composition of Matter
Uploaded by
jhontayson12Copyright:
Available Formats
The earliest recorded discussion of the basic structure of matter
comes from ancient Greek philosophers, the scientists of their day.
Some of them argued that matter is continuous i.e., it could be divided
endlessly into smaller pieces. Others believed that matter is discrete;
i.e., it cannot be infinitely divided.
Democritus (460 - 370 B.C) expressed the belief that all matter
consists of very small, indivisible particles, which he named atomos
(meaning uncuttable or indivisible). He thought of atoms as moving
particles that differed in shape and size which could join together.
According to Democritus matter is discrete.
Aristotle (384 – 322 B.C) argued that matter is divided into smaller
and smaller parts, the division continuous forever without any limit.
He did not believe in microscopic building particles of matter.
Therefore, according to Aristotle, matter is continuous and he believed
that matter consisted of the combinations of fire, earth, air, and water.
What are the two parts of atom?
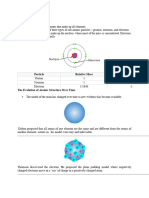
An atom consists of a tiny dense nucleus surrounded by electrons. The
nucleus contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, so
it is positively charged. The electrons are negatively charged. Protons
and neutrons have approximately the same mass and are about 1800
times more massive than an electron. This means that most of the mass
of an atom is in its nucleus. However, most of the volume of an atom is
occupied by its electrons.
Atoms possess internal structure; that is, they are made up of even
smaller particles, which are called subatomic particles.
A subatomic particle is a very small particle that is a building block for atoms.
An atom contains three fundamental sub atomic particles: proton,
electron and neutron. An atom has a definite number of protons,
electrons and neutrons. The structure of the atom describes how these
particles are arranged to make an atom.
The relative charge of a proton is +1. The electron is assigned a
charge of −1. The neutron is assigned zero charge. Since an atom
has equal number of protons and electrons, it is electrically neutral.
A proton has a mass of 1.673 × 10–24 g, and a neutron has a mass of
1.675 × 10–24 g. Thus, a proton and a neutron have almost the same
mass. Since the mass of an electron is very small, 9.109 × 10–28 g,
its mass is assumed to be negligible or approximately zero because
it is ≈ 2000 times less heavier than both the proton and neutron.
All atoms can be identified by the number of protons and neutrons
they contain. The atomic number (Z) of an atom equals the number
of protons in its nucleus. The atomic number is also the number of
electrons that surround the nucleus of a neutral atom.
Atomic number (Z) = Number of protons= number of electrons
Mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and the
number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.Except for the most
common form of hydrogen, which has one proton and no neutrons,
all atomic nuclei contain both protons and neutrons.
Mass number (A) = Number of protons + Number of neutrons.
= Number of Nuetrons + Atomic Number
Proton is equal to the atomic number of atoms.
Number of protons = atomic number (Z)
Electron: The atom is neutral therefore the number of electrons is
equal to the number of protons.
Number of electrons = atomic number (Z) = number of protons
The number of neutrons in an atom is equal to the difference
between the mass number and the atomic number or proton number.
Number of neutrons = Mass number (A) - Number of protons.
Molecules of Elements
A molecule of an element consists of only one type of an atom.
Molecules of elements can be classified as monoatomic, diatomic and
polyatomic.
1. Monoatomic molecules are molecules that contain one atom
of the element. Examples: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn are
monoatomic molecules
2. Diatomic molecules are molecules that contain two atoms of
the element. Examples: O2, H2, F2, Cl2, I2 are diatomic
molecules.
3. Polyatomic molecules are molecules that contain more than
three atoms of the element. Examples: O3, P4 , S8 are polyatomic molecules.
Molecules of compounds
A molecule of a compound always contains two or more atoms of
different elements combined chemically. Water (H2O), ammonia
(NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2), etc. are some examples of molecules of
compounds.
Summary
• Democritus (460-370 BC) introduced the idea that matter consists
of very small indivisible particles called “atoms”.
• The three fundamental subatomic particles are protons, neutrons
and electrons.
• Protons are positively charged.
• Neutrons are chargeless.
• Electrons are negatively charged.
• A proton and a neutron have approximately the same mass; but the
mass of an electron is negligible.
• The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the
nucleus of an atom of the element.
• An atom is electrically neutral because the amount of positive
charge on a proton equals the amount of negative charge on an
electron.
• The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and the
number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
• The number of neutrons in an atom is equal to the difference between
the mass number and the atomic number or proton number.
x A
• An atom is represented by the notation,
in which X is the
symbol of an element Z is the atomic number, and A is the mass
number.
• A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound
that can exist freely in nature.
• Molecules of elements consist of only one type of atoms and can
be classified as monoatomic, diatomic or polyatomic.
• Molecules of compounds consist of two or more different type of
atoms
You might also like
- George Michael - Theology of Hate (2009)Document302 pagesGeorge Michael - Theology of Hate (2009)branx100% (2)
- Community and Communication in Modern Art PDFDocument4 pagesCommunity and Communication in Modern Art PDFAlumno Xochimilco GUADALUPE CECILIA MERCADO VALADEZNo ratings yet
- The British Student's Guide To Obtaining Your Visa To Study at The Islamic University of Madinah v.2Document76 pagesThe British Student's Guide To Obtaining Your Visa To Study at The Islamic University of Madinah v.2Nouridine El KhalawiNo ratings yet
- Grady McMurtry The Millenial Glow Myth and Magic in The Marxist Ethics V 1.0.5 PDFDocument130 pagesGrady McMurtry The Millenial Glow Myth and Magic in The Marxist Ethics V 1.0.5 PDFMoreno KrvavacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ChemistryDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - ChemistryHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDocument51 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDavid PhilemonNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomDocument2 pagesCbse Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomMaa Reddy SanjivNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- GC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions 2 Daltons Atomic TheoryDocument34 pagesGC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions 2 Daltons Atomic TheoryYeri KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic StructureFelix LiandaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Science 1 - 230419 - 164951Document109 pagesElectrical Engineering Science 1 - 230419 - 164951Akogun ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Atoms: 1. Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesAtoms: 1. Atomic Structurecherry shane abanesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument40 pagesAtomic Structure and Interatomic BondingJhomel EberoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Structure of Substance - Lesson - 1Document14 pagesStructure of Substance - Lesson - 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Particles in An AtomDocument8 pagesParticles in An AtomJuliet VillaruelNo ratings yet
- 9.5 Determining The Number of Protons, Electrons, and NeutronsDocument5 pages9.5 Determining The Number of Protons, Electrons, and NeutronsJoana Mae IcoNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument12 pagesAtomatgimale.comNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument6 pagesAtomsshreyaNo ratings yet
- CHAP4 AtomicStructureDocument34 pagesCHAP4 AtomicStructureJex AsupardoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Engineering: Big Stuff (Objects, Etc.)Document27 pagesChemistry and Engineering: Big Stuff (Objects, Etc.)Madhav MakkarNo ratings yet
- Css Atom StructureDocument20 pagesCss Atom StructureHaris AzizNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Atoms: General ChemistryDocument52 pagesElectronic Structure of Atoms: General ChemistryNAM TRƯƠNG HOÀINo ratings yet
- MY3 AtomsDocument6 pagesMY3 AtomserikaNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom-How Atoms DifferDocument11 pagesThe Structure of The Atom-How Atoms DifferRomy G.No ratings yet
- Inside The AtomDocument13 pagesInside The AtomAnita VardhanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom - Boundless ChemistryDocument13 pagesThe Structure of The Atom - Boundless ChemistrySheena Shane CantelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument10 pagesChapter OneMowliid DayibNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2_013153Document8 pagesLesson-2_013153natashalouisse103No ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Notes Physical ChemDocument47 pagesA Level Chemistry Notes Physical ChemSolomon MuwandiNo ratings yet
- Atoms: According To DaltonDocument5 pagesAtoms: According To DaltonSahnaz Mela SandyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 2 - Part 1Document15 pagesChemistry Module 2 - Part 1Francis RecocoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesConcept of Atomic StructureNoor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Description of An AtomDocument32 pagesSession 2-Description of An Atomvalerianphotunatus2002No ratings yet
- Chem Assignment 4Document7 pagesChem Assignment 4ttamNo ratings yet
- Parts of An AtomDocument17 pagesParts of An Atomimmaryam070No ratings yet
- ChemDocument58 pagesChemashwin.sp.004No ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Atomic Structure - 7th STDDocument29 pagesUnit - 4 Atomic Structure - 7th STDthangamuthu baskarNo ratings yet
- CHE101 - Class 03 (Chapter 2)Document44 pagesCHE101 - Class 03 (Chapter 2)Mst. Meherin Jahan 2011229642No ratings yet
- CHEM 2101 Lecture 1 (Atomic Structure)Document4 pagesCHEM 2101 Lecture 1 (Atomic Structure)Asif UddinNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory: A Modern Model of The AtomDocument8 pagesAtomic Theory: A Modern Model of The AtomSophia MartinezNo ratings yet
- AS Atomic StructureDocument34 pagesAS Atomic Structuremadwinyi skeptaNo ratings yet
- Modelos Atómicos: Science 8th Basic Ma. José Espinoza ArellanoDocument45 pagesModelos Atómicos: Science 8th Basic Ma. José Espinoza ArellanoMaría José Espinoza ArellanoNo ratings yet
- 7 - Parts of An AtomDocument14 pages7 - Parts of An Atomprabhjotsaggu1028No ratings yet
- L2-Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument49 pagesL2-Atoms and Atomic Structurekoladejoy49No ratings yet
- Concept of Atomic StructureDocument23 pagesConcept of Atomic StructureMd. Mujahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom (Form 4 Chemistry)Document7 pagesStructure of An Atom (Form 4 Chemistry)Adam NaqibNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 General Chemistry PDFDocument29 pagesUnit 1 General Chemistry PDFchuchu maneNo ratings yet
- Module As Level ChemistryDocument407 pagesModule As Level ChemistryBank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Student Reading: Parts of The AtomDocument12 pagesChapter 4-Student Reading: Parts of The AtomShimmy LimmyNo ratings yet
- ATOMic StructureDocument5 pagesATOMic Structuretalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Week 2Document18 pagesOrganic Chemistry Week 2Nur AmaninaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesAtomic StructurehenryNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure1stDocument34 pagesAtomic Structure1stKayah AzzahratussyifaNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom: Background KnowledgeDocument107 pagesStructure of An Atom: Background KnowledgeTuqir BaabayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lecture PowerpointDocument39 pagesChemistry Lecture Powerpointapi-308666520No ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument8 pagesThe Structure of The AtomAgatha OfrecioNo ratings yet
- Note For EJUDocument18 pagesNote For EJUmr.draungnaingwinNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)Document22 pagesCHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)ogedengbed28No ratings yet
- Structure of Substance - Lesson - 1Document14 pagesStructure of Substance - Lesson - 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2From EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Final ExamDocument3 pagesFinal ExamFaidah PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Fy2023 FWS Budget RequestDocument8 pagesFy2023 FWS Budget RequestinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Top Law Firm in Dubai, UAE - RAALCDocument20 pagesTop Law Firm in Dubai, UAE - RAALCraalc uaeNo ratings yet
- From Lovemaking To Superconsciousness-0shoDocument31 pagesFrom Lovemaking To Superconsciousness-0shoRAGUPATHYNo ratings yet
- Korea IT TimesDocument76 pagesKorea IT TimesDilek KarahocaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document36 pagesChapter 5nsominvz345No ratings yet
- R68 (1) BPI Family V Coscuella PDFDocument2 pagesR68 (1) BPI Family V Coscuella PDFMargarita SisonNo ratings yet
- K-Factor Rated Transformer For Deal With Harmonic Generating LoadsDocument4 pagesK-Factor Rated Transformer For Deal With Harmonic Generating Loadsp41005679No ratings yet
- Just Say No To Big Brother's Smart Meters: The Latest in Bio-Hazard Technology by Orlean KoehleDocument148 pagesJust Say No To Big Brother's Smart Meters: The Latest in Bio-Hazard Technology by Orlean KoehleVen GeanciaNo ratings yet
- Nandan CoffeeDocument18 pagesNandan CoffeegautamNo ratings yet
- Kathmandu Travel GuideDocument7 pagesKathmandu Travel GuidepeepgunNo ratings yet
- Sambo Catalog Torque LimiterDocument2 pagesSambo Catalog Torque LimiterRicNo ratings yet
- Tifr SSRDocument972 pagesTifr SSRAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Law - Lesson 9-10Document8 pagesLaw - Lesson 9-10Stephanie AndalNo ratings yet
- The God in The Flower Pot Mary BarnardDocument4 pagesThe God in The Flower Pot Mary BarnarddianaNo ratings yet
- 4 Week BodyweightDocument76 pages4 Week BodyweightariandapNo ratings yet
- CV Marius Lupoian 12.12.2012 - enDocument5 pagesCV Marius Lupoian 12.12.2012 - enLupoian Florin MariusNo ratings yet
- English 2-3 Class 10Document2 pagesEnglish 2-3 Class 10Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- Coats Tire ChangerDocument32 pagesCoats Tire ChangergomooneyNo ratings yet
- Air Is Allowed To Flow From A Large Reservoir ThroDocument3 pagesAir Is Allowed To Flow From A Large Reservoir Throsid202pkNo ratings yet
- Driscoll WordsDocument55 pagesDriscoll WordsMatthew James DriscollNo ratings yet
- Chapter04.pdf - How To Write A Project Report - ResearchDocument8 pagesChapter04.pdf - How To Write A Project Report - Researchbrownsugar26No ratings yet
- BMW IcebreakersDocument2 pagesBMW IcebreakersdunamisbzNo ratings yet
- Brakes MCQDocument8 pagesBrakes MCQSathistrnpcNo ratings yet
- Tekken Corporation: Company GuideDocument9 pagesTekken Corporation: Company Guidehout rothanaNo ratings yet
- MIJIDocument17 pagesMIJIpranilNo ratings yet