Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Year-7-Forces Questions t-3
Year-7-Forces Questions t-3
Uploaded by
christal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis fact sheet provides information about different types of forces including gravity, weight, friction, and air resistance. It defines key terms like balanced and unbalanced forces, and how they affect stationary and moving objects. Equations for speed are given as speed equals distance divided by time, with examples of calculating speed from values of distance and time. Standard units for measuring force as newtons and speed as meters per second are also stated.
Original Description:
Original Title
Year-7-Forces questions t-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis fact sheet provides information about different types of forces including gravity, weight, friction, and air resistance. It defines key terms like balanced and unbalanced forces, and how they affect stationary and moving objects. Equations for speed are given as speed equals distance divided by time, with examples of calculating speed from values of distance and time. Standard units for measuring force as newtons and speed as meters per second are also stated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesYear-7-Forces Questions t-3
Year-7-Forces Questions t-3
Uploaded by
christalThis fact sheet provides information about different types of forces including gravity, weight, friction, and air resistance. It defines key terms like balanced and unbalanced forces, and how they affect stationary and moving objects. Equations for speed are given as speed equals distance divided by time, with examples of calculating speed from values of distance and time. Standard units for measuring force as newtons and speed as meters per second are also stated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Year 7 Forces fact sheet
Types of force
1. Forces are …. and ….. Forces are pushes and pulls
2. What are the units for force? N (Newton)
3. Name the force which pulls objects towards
Gravity
the centre of the Earth
4. Name the force which objects have because of
Weight
gravity
5. Name the force which pushes a car forwards Driving force
6. Name the force that occurs when 2 objects
Friction
are rubbed together
7. Name the force which slows down an object
Air resistance
when it is travelling through air
Balanced and unbalanced forces
1. What will happen to the stationary box?
It will stay where it is
2. What will happen to the stationary box?
It will move to the left
3. What will happen to the stationary box?
It will move to the right
4. What will happen to the stationary box?
It will move down
Year 7 Forces fact sheet
5. What happens to a stationary object when
It stays still
the forces are balanced?
6. What happens to a stationary object when It starts to move or change
the forces are unbalanced? shape
7. What happens to a moving object when the It carries on moving at the same
forces are balanced? speed and in the same direction
8. What happens to a moving object when the It changes speed, stops moving
forces are unbalanced? or changes direction
9. What do we call the overall force acting on an
Resultant force
object?
Friction
1. When would objects experience friction? When they are rubbed together
Walking (so you don’t slip
2. Describe a situation where friction is useful over)
When a car stops
Car tyres getting worn
3. Describe a situation where friction is not
Ice skating when you want
useful
to go fast
Air resistance
1. When would objects experience air When they are moving
resistance? through the air
2. Describe a situation where air resistance is When you want to slow down,
useful e.g. a parachute
When you don’t want to slow
3. Describe a situation where air resistance is
down, e.g. driving, cycling, or
not useful
fast sport
Speed
1. Speed = ________ ÷ __________ Speed = distance ÷ time
2. What is the standard unit for speed? m/s (‘meters per second’)
3. The faster your speed the longer/ shorter
Shorter
your journey time
Speed = distance ÷ time
4. An object travels 10m in 5 seconds. Calculate
= 10 ÷ 5
its speed
= 2 m/s
Speed = distance ÷ time
5. An object travels 30m in 10 seconds.
= 30 ÷ 10
Calcualte its speed
= 3 m/s
Speed = distance ÷ time
6. An object travels 27m in 3 seconds. Calcualte
= 27 ÷ 3
its speed
= 9 m/s
Year 7 Forces fact sheet
You might also like
- Forces and Motion Reading WorksheetDocument7 pagesForces and Motion Reading WorksheetAbbes Mohammed Zoheir0% (2)
- Report No. 1Document11 pagesReport No. 1Alex QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionDenjie Magrimbao100% (1)
- Personal Best A1 Unit 8 Reading TestDocument3 pagesPersonal Best A1 Unit 8 Reading TestLuis Fernando Osorio SanchezNo ratings yet
- Midterms Physics ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterms Physics Reviewermobilegaming2231No ratings yet
- Integrated Science: Quarter 2: Force, Motion and Energy Module 3: The Laws of MotionDocument11 pagesIntegrated Science: Quarter 2: Force, Motion and Energy Module 3: The Laws of MotionRonnelMananganCorpuzNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Key NotesDocument12 pagesSPM Physics Key NotesAce Cheah Mun ChunNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q1 Week 1Document12 pagesScience 8 Q1 Week 1Alyssa Gomez100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: Isaac Newton To The StudentsDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: Isaac Newton To The StudentsreslieNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion: SDO Rizal All Rights ReservedDocument24 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion: SDO Rizal All Rights ReservedVictorino Victorino ButronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IGCSE - Edit - 2 - 27 April 2018 (No Comments)Document14 pagesChapter 1 IGCSE - Edit - 2 - 27 April 2018 (No Comments)Najia UmarNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Study Guide - Student-SantiagoSerranoBalzaDocument5 pagesForce and Motion Study Guide - Student-SantiagoSerranoBalzasawgumNo ratings yet
- Chapter': 2.1 Analysing Linear MotionDocument5 pagesChapter': 2.1 Analysing Linear MotionkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: Air Resistance and Terminal Velocity: What You Need To KnowDocument5 pagesLesson 8: Air Resistance and Terminal Velocity: What You Need To KnowKumar GankaNo ratings yet
- Physics 9 Starter PackDocument14 pagesPhysics 9 Starter PackbraindeadNo ratings yet
- JPC冲刺班讲义Document19 pagesJPC冲刺班讲义huangzhouexportNo ratings yet
- Foundational Physics Midterm ReviewDocument4 pagesFoundational Physics Midterm ReviewMichael ClarkNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet, Friction and Kinds of FrictionDocument6 pagesActivity Sheet, Friction and Kinds of FrictionLV BENDANANo ratings yet
- 2023 9th Class SolutionDocument15 pages2023 9th Class SolutionSowmiya NadarNo ratings yet
- Motion PuzzlesDocument2 pagesMotion PuzzlesSuresh Arulraj100% (1)
- Class 9 Sci Topic 1 - Laws of Motion - Notes - Awatade ClassesDocument7 pagesClass 9 Sci Topic 1 - Laws of Motion - Notes - Awatade ClassesRamkrishnahari RaskarNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Advance PhysicsDocument29 pagesNewtons Law Advance PhysicsAaliyah CarlobosNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument79 pagesForcesStephanie Joyce De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument2 pagesMotionmaryglynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 First Law of MotionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 First Law of MotionPeter Osorio McNinchNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Q3 WK 1-2 LASDocument24 pagesSCIENCE Q3 WK 1-2 LASAnaLizaD.SebastianNo ratings yet
- School Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesSchool Lesson PlanprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan G8 Q1 WK 1 D4Document11 pagesDaily Lesson Plan G8 Q1 WK 1 D4Marissa GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument1 pageNewton's First LawSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter LAS in Science 6Document4 pages3rd Quarter LAS in Science 6Michael Edward De VillaNo ratings yet
- Newton Force Law of MotionDocument25 pagesNewton Force Law of MotionUjjal BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Scie 6 Q3 W2Document10 pagesScie 6 Q3 W2John Rich CaidicNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Motion For Grade 8Document33 pagesNewtons Law of Motion For Grade 8janice alquizar100% (1)
- Chapter4 - Section1 PhysicsDocument4 pagesChapter4 - Section1 PhysicsHope MazzuchiNo ratings yet
- PH 11 CHP 4Document2 pagesPH 11 CHP 4Kasim hemdenNo ratings yet
- Darlene Kharell Cuizon Quarter 1 Module 1 NEWTONS FIRST LAW OF MOTIONDocument8 pagesDarlene Kharell Cuizon Quarter 1 Module 1 NEWTONS FIRST LAW OF MOTIONJhoanna Elaine CuizonNo ratings yet
- KPK Board Conceptual Questions 9th ClassDocument18 pagesKPK Board Conceptual Questions 9th ClassWaleed Nasir100% (4)
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Law of Inertia and Law of AccelerationDocument4 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: Law of Inertia and Law of AccelerationEileen NagaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 9-13Document2 pagesScience Chapter 9-13Prakahsh BajajNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8TH Final PracticeDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 8TH Final Practicemarinadencheva09No ratings yet
- Science9 - Q4 - M3 Impulse and MomentumDocument14 pagesScience9 - Q4 - M3 Impulse and MomentumArcee TogyNo ratings yet
- English Medium (Science) Grade 10-Unit Test 4Document6 pagesEnglish Medium (Science) Grade 10-Unit Test 4elissa yohanNo ratings yet
- Newtons LawsDocument28 pagesNewtons LawsLeah Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- NEW P2 Revision Guide HigherDocument66 pagesNEW P2 Revision Guide Higherdiane hoyles100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Laws of Motion: AnswerDocument6 pagesChapter 1. Laws of Motion: AnswerARJUUUUUUUUUUNNo ratings yet
- Test Question For TOSDocument2 pagesTest Question For TOSCylc Clarence CalubingNo ratings yet
- Scince I Notes Part 8 Oct (Revised)Document16 pagesScince I Notes Part 8 Oct (Revised)SANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument42 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionJeffrey De BelenNo ratings yet
- 3RD Monthly Exam - 2024Document9 pages3RD Monthly Exam - 2024Daisy Joy LacandazoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Monthly ExaminationDocument6 pages3rd Monthly ExaminationDaisy Joy LacandazoNo ratings yet
- Newton - S Laws of MotionDocument64 pagesNewton - S Laws of MotionRiss CalmaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLL OlibaDocument4 pagesScience 6 DLL OlibaclaudineNo ratings yet
- Mdcat: PhysicsDocument29 pagesMdcat: PhysicsSayaamNo ratings yet
- Ncert Secrets #2: Laws of Motion & FrictionDocument11 pagesNcert Secrets #2: Laws of Motion & FrictionNeerav AhujaNo ratings yet
- Forces PDFDocument32 pagesForces PDFwaldilopezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ProjectDocument2 pagesUnit 1 ProjectTyrique GoldenNo ratings yet
- Newtonslawsofmotion 090903174139 Phpapp01Document34 pagesNewtonslawsofmotion 090903174139 Phpapp01meccayllasunio5No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument33 pagesNewtons Laws of Motionapi-237070241No ratings yet
- Friction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandFriction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- From Falling Apples to the Universe: A Guide for New Perspectives on Gravity and GravitationFrom EverandFrom Falling Apples to the Universe: A Guide for New Perspectives on Gravity and GravitationNo ratings yet
- DarkparisDocument1 pageDarkparischristalNo ratings yet
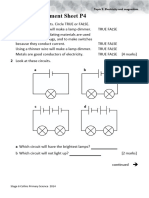
- TG6AssessmentSheet P03Document2 pagesTG6AssessmentSheet P03christalNo ratings yet
- TG6AssessmentSheet P04Document2 pagesTG6AssessmentSheet P04christalNo ratings yet
- For Each Question, Choose The Correct Answer.: Practice K (A2) Li 29 Listening Part 1 Questions 1-5Document5 pagesFor Each Question, Choose The Correct Answer.: Practice K (A2) Li 29 Listening Part 1 Questions 1-5christalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10.8: James Joule's ThermometerDocument2 pagesWorksheet 10.8: James Joule's ThermometerchristalNo ratings yet
- CAE Test 1. QUESTDocument3 pagesCAE Test 1. QUESTchristalNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science Practice TestDocument28 pagesGrade 5 Science Practice Testchristal100% (1)
- Galaxy WorksheetDocument2 pagesGalaxy WorksheetchristalNo ratings yet
- Speech, Tenses KeyDocument9 pagesSpeech, Tenses KeychristalNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table 2Document2 pagesThe Periodic Table 2christalNo ratings yet
- TG6AssessmentSheet C01Document1 pageTG6AssessmentSheet C01christalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document24 pagesUnit 5christal100% (1)
- Structure of The EarthDocument13 pagesStructure of The EarthchristalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet U2.4Document2 pagesWorksheet U2.4christalNo ratings yet
- Practice 18Document29 pagesPractice 18christalNo ratings yet
- Reversible ChangesDocument16 pagesReversible ChangeschristalNo ratings yet
- G5 ScienceDocument1 pageG5 SciencechristalNo ratings yet
- Riddles For Kids PDFDocument3 pagesRiddles For Kids PDFchristalNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary RainforestDocument1 pageVocabulary RainforestchristalNo ratings yet
- Worksheets The-Solar-System-And-BeyondDocument24 pagesWorksheets The-Solar-System-And-BeyondchristalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Year 8Document7 pagesChemical Reactions Year 8christalNo ratings yet
- 2022 TestDocument32 pages2022 TestchristalNo ratings yet
- Electricity Sec-2, 16.12.2022.Document11 pagesElectricity Sec-2, 16.12.2022.christalNo ratings yet
- Plant StructureDocument1 pagePlant StructurechristalNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy!Document4 pagesHeat Energy!christalNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument9 pagesForceschristalNo ratings yet
- U8 Ans Workbook 2Document2 pagesU8 Ans Workbook 2christalNo ratings yet
- Notes PlantDocument3 pagesNotes PlantchristalNo ratings yet
- Moment of A ForceDocument3 pagesMoment of A ForcechristalNo ratings yet
- Questions On This Quiz Are Based On Information From .: Earth Science: SeasonsDocument2 pagesQuestions On This Quiz Are Based On Information From .: Earth Science: SeasonschristalNo ratings yet
- Top Law Firm in Dubai, UAE - RAALCDocument20 pagesTop Law Firm in Dubai, UAE - RAALCraalc uaeNo ratings yet
- RubricsDocument2 pagesRubricsJohannes B. MirafuentesNo ratings yet
- 20 Century Cases Where No Finding of Gross Immorality Was MadeDocument6 pages20 Century Cases Where No Finding of Gross Immorality Was MadeLeonel OcanaNo ratings yet
- Pyton Ls DynaDocument9 pagesPyton Ls DynaNandaNo ratings yet
- Superior Court of California County of Santa Clara Civil DivisionDocument30 pagesSuperior Court of California County of Santa Clara Civil DivisionMitchNo ratings yet
- CHEMFISH Fluorinated CompoundsDocument11 pagesCHEMFISH Fluorinated Compoundssunny StevenNo ratings yet
- Ajax Asynchronous Javascript + XML: "A Fundamental Shift in What'S Possible On The Web"Document60 pagesAjax Asynchronous Javascript + XML: "A Fundamental Shift in What'S Possible On The Web"lucasNo ratings yet
- The Early History of Manganese and The Recognition of ItsDocument23 pagesThe Early History of Manganese and The Recognition of ItsPlutus PHNo ratings yet
- BMW IcebreakersDocument2 pagesBMW IcebreakersdunamisbzNo ratings yet
- CH 19-Def Volumetrica de Solucionario de GroverDocument36 pagesCH 19-Def Volumetrica de Solucionario de Grover1rubena1No ratings yet
- Department of AgricultureDocument3 pagesDepartment of AgricultureSheila May LantoNo ratings yet
- Love Song For A VampireDocument1 pageLove Song For A VampireVivianamorteccinaNo ratings yet
- Group Poject CONTRACT ESTIMATION BaruDocument21 pagesGroup Poject CONTRACT ESTIMATION BarualnzNo ratings yet
- Eric Moses Et AlDocument7 pagesEric Moses Et AlEmily BabayNo ratings yet
- Rate Anaylsis LouversDocument1 pageRate Anaylsis LouversSyed Tasveer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Study On Organic Modification of Aluminum Powder Coating - Sun2017Document10 pagesStudy On Organic Modification of Aluminum Powder Coating - Sun2017Eugene PaiNo ratings yet
- VollyballDocument4 pagesVollyballCristina LataganNo ratings yet
- Akash Karia - Anti-Procrastination For Writers - The Writer's Guide To Stop Procrastinating, Start Writing and Create A Daily Writing Ritual-AkashKaria - Com (2014) PDFDocument99 pagesAkash Karia - Anti-Procrastination For Writers - The Writer's Guide To Stop Procrastinating, Start Writing and Create A Daily Writing Ritual-AkashKaria - Com (2014) PDFNeman AshrafNo ratings yet
- RKSV Securities India Private Limited Registered Corporate AddressDocument2 pagesRKSV Securities India Private Limited Registered Corporate AddressAjarihant OrthoNo ratings yet
- Coats Tire ChangerDocument32 pagesCoats Tire ChangergomooneyNo ratings yet
- BF Necromancer Supplement r11Document13 pagesBF Necromancer Supplement r11Michael KirchnerNo ratings yet
- Role of Agnikarma in Pain ManagementDocument9 pagesRole of Agnikarma in Pain ManagementPoonam KailoriaNo ratings yet
- Resultados de Búsqueda: Artículos Académicos para Vocal Function Exercises Stemple PDFDocument3 pagesResultados de Búsqueda: Artículos Académicos para Vocal Function Exercises Stemple PDFleandro__scribdNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TheoDocument6 pagesModule 2 TheoMichlee Joy Paguila LagocNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nieghbors On Japan Student NotebookDocument9 pagesInfluence of Nieghbors On Japan Student Notebookapi-233464494No ratings yet
- Live Outside The BoxDocument2 pagesLive Outside The BoxKrishnaKumarDeepNo ratings yet
- It8078 Web Design and ManagementDocument27 pagesIt8078 Web Design and ManagementsanjayNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Benefits of HoneyDocument8 pagesMedicinal Benefits of HoneyTauseef AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cini Manual PDF FreeDocument536 pagesCini Manual PDF FreeJaeIlLee100% (1)