Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsObgyne Finals
Obgyne Finals
Uploaded by
Adviento AngelicaThis document discusses various placental abnormalities and complications of pregnancy and childbirth. It defines different types of placental abnormalities such as bilobed placentas, placenta previa, and placental hematomas. It also describes complications related to the umbilical cord such as cord prolapse and vasoconstriction. Finally, it discusses postpartum infections and complications that can occur in the days following delivery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Anatomy Image Bank Edition 2 Updated Upto NEET PG 21Document130 pagesAnatomy Image Bank Edition 2 Updated Upto NEET PG 21Yogaabirami AbiNo ratings yet
- PLACENTADocument21 pagesPLACENTAHem Kumari80% (5)
- ETG-Australian Therapeutic Guidelines 2020 (Part 1)Document1,246 pagesETG-Australian Therapeutic Guidelines 2020 (Part 1)Omesh Prathiraja100% (1)
- Williams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Document57 pagesWilliams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Bharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument5 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Placental Disorders Flashcards - Quizlet PDFDocument11 pagesPlacental Disorders Flashcards - Quizlet PDFAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument7 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesLrak SiaNo ratings yet
- (OBa) 1.4 Plcental GRWTH and Maturation (Marinas) - PacisDocument6 pages(OBa) 1.4 Plcental GRWTH and Maturation (Marinas) - PacisClyde Yuchengco Cu-unjiengNo ratings yet
- Abnormalties in Placenta and UcDocument4 pagesAbnormalties in Placenta and UcJamaica QuetuaNo ratings yet
- LM 7 Pedia Lec NTSDocument5 pagesLM 7 Pedia Lec NTShanhananicasNo ratings yet
- Placental Abormalities (Tables)Document5 pagesPlacental Abormalities (Tables)icNo ratings yet
- Clin TG Abnormalities of The Placenta & CordDocument13 pagesClin TG Abnormalities of The Placenta & CordTami Selvi100% (2)
- Flashcards - Placenta and Fetal MembranesDocument16 pagesFlashcards - Placenta and Fetal MembranesKhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous CaputDocument5 pagesNervous CaputVellyana GustikaNo ratings yet
- 67Document57 pages67Neeruam Ellehcim Aled ZurcNo ratings yet
- Complications of Labor: PassengerDocument6 pagesComplications of Labor: PassengerR-Chian Jose Germanp100% (1)
- Placenta: Fetomaternal Organ. Fetal Part Maternal Part Transport SystemDocument21 pagesPlacenta: Fetomaternal Organ. Fetal Part Maternal Part Transport SystemAntonela CeremușNo ratings yet
- Plasenta Dan SelaputDocument18 pagesPlasenta Dan SelaputRahmi Mutia UlfaNo ratings yet
- Obstructed Labor: Basliel E. (MD)Document12 pagesObstructed Labor: Basliel E. (MD)Asteway MesfinNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument35 pagesPlacentaDrsmcsi dept of radiodiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Placenta OutlineDocument7 pagesAbnormalities of The Placenta OutlineSteve ShirmpNo ratings yet
- 4-Fetal LifeDocument11 pages4-Fetal LifeRichard ManuelNo ratings yet
- C.D Cord PresentationDocument17 pagesC.D Cord PresentationMeenatchiNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of The Placenta and CordDocument2 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and CordLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Tears: Rolf M. Embertson Cortney E. HendersonDocument1 pageCervical Tears: Rolf M. Embertson Cortney E. Hendersonomar rangelNo ratings yet
- Pedia Notes CompleteDocument27 pagesPedia Notes CompletelouvvhartNo ratings yet
- (NCM 107) 2 Embryonic and Fetal DevelopmentDocument6 pages(NCM 107) 2 Embryonic and Fetal Developmentberanabigail0No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BreastDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BreastRahmanNo ratings yet
- 109Document3 pages109Angel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Placenta PDFDocument22 pagesPlacenta PDFbookaccountNo ratings yet
- References:: Maternal and Child HealthDocument2 pagesReferences:: Maternal and Child HealthJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Face PresentationDocument4 pagesFace PresentationRose Ann HajironNo ratings yet
- CH 17 The Breast CompleteDocument36 pagesCH 17 The Breast CompleteGwen Marielle CursoNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument10 pagesPlacentaKarl Sonny UganizaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document9 pagesLec 3ibrahim.21hm32No ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 9th Edition All ChapterDocument31 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 9th Edition All Chapterbokayxasu100% (6)
- Abnormalities-Of-Placenta-And-Umbilical CordDocument53 pagesAbnormalities-Of-Placenta-And-Umbilical CordPraveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Hemangiomas of InfancyDocument20 pagesHemangiomas of InfancynissaNo ratings yet
- Midterm PPT MaternalDocument6 pagesMidterm PPT MaternalJhayneNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaDocument150 pagesFetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaKripa SusanNo ratings yet
- By - Prof. Saeed MakaremDocument27 pagesBy - Prof. Saeed MakaremIncredible DivineNo ratings yet
- Intraductal PapillomaDocument8 pagesIntraductal PapillomaNix14No ratings yet
- Bif Emb Ls 8 PlacentaDocument77 pagesBif Emb Ls 8 PlacentaJude Chisom Jnr NwaugoNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument11 pagesSpina BifidaheiyuNo ratings yet
- Implantation and PlacentaDocument52 pagesImplantation and PlacentaMs BadooNo ratings yet
- 08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes TotalDocument8 pages08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes TotalintanNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2Document6 pagesPost-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Ferlilisation, Implantation and Changes in PregnancyDocument7 pagesFerlilisation, Implantation and Changes in PregnancyLuke MatupiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy 5: Breast, Pectoral, and AxillaDocument3 pagesClinical Anatomy 5: Breast, Pectoral, and AxillaJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- 2 ApendixDocument8 pages2 Apendixمحمد عماد عليNo ratings yet
- NEJMra2308055 (1)Document8 pagesNEJMra2308055 (1)Celebfan BoyNo ratings yet
- BREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhDocument7 pagesBREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhChethranNo ratings yet
- Fronto-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele PDFDocument1 pageFronto-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele PDFtrifoniastriNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy V2Document6 pagesEctopic Pregnancy V2Aljon AgustinNo ratings yet
- TTTS NeoreviewsDocument13 pagesTTTS NeoreviewsNeha OberoiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Intrapartum Complications ReviewerDocument10 pagesNCM 109 Intrapartum Complications Reviewercrz VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Placenta - AAFPDocument22 pagesExamination of The Placenta - AAFPEi Ei MyoNo ratings yet
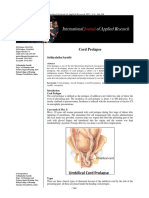
- Cord Prolapse: Sathiyalatha SarathiDocument3 pagesCord Prolapse: Sathiyalatha Sarathidiah komalaNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument5 pagesPlacenta PreviaMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Hematological SystemDocument6 pagesDiseases of The Hematological SystemAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocument10 pagesBasic Surgical InstrumentsAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics FinalsDocument1 pageObstetrics FinalsAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Self Directed LearningDocument1 pageRubric For Self Directed LearningAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Therapy Fo Respiratory Disorders (Group 9)Document26 pagesNutrition Therapy Fo Respiratory Disorders (Group 9)Adviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Surgery FinalsDocument1 pageSurgery FinalsAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cerebral Artery StrokeDocument9 pagesAnterior Cerebral Artery StrokeAlin CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- Drug Lists 1 3Document6 pagesDrug Lists 1 3Paulene Marie SicatNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray Appearances in Pneumonia and BronchiolitisDocument7 pagesChest X-Ray Appearances in Pneumonia and BronchiolitisMariani AniNo ratings yet
- Eating and Sleep-Wake Disorders Handout-1Document23 pagesEating and Sleep-Wake Disorders Handout-1Fulache, Lei Angeline B.No ratings yet
- Informative Speech OutlineDocument6 pagesInformative Speech Outlinearialis abreuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Cerebro Vascular Accident 1Document13 pagesLesson Plan On Cerebro Vascular Accident 1simonjosan67% (3)
- Urine Protein andDocument12 pagesUrine Protein andAfifah AzizNo ratings yet
- Edith Jacobson Kardex To DIscharge PlanDocument16 pagesEdith Jacobson Kardex To DIscharge PlanFranz Patrick Legria, CPAC - SNNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Abuse: Abusive Head TraumaDocument9 pagesAspects of Abuse: Abusive Head TraumaOkta Dwi Kusuma AyuNo ratings yet
- NCM 109-Cerebral PalsyDocument36 pagesNCM 109-Cerebral PalsyLeigh Ann Prosyne LozadaNo ratings yet
- Sti GonorrheaDocument6 pagesSti GonorrheaSulaiman NajirulNo ratings yet
- PacemakersDocument69 pagesPacemakersdocjeevan89100% (1)
- Dietary Therapy in Genetic EpilepsiesDocument4 pagesDietary Therapy in Genetic Epilepsiesalaahossam591No ratings yet
- 2012.01.12!02!07-48CV Mammen Chandy WebsiteDocument16 pages2012.01.12!02!07-48CV Mammen Chandy WebsitePradeep BabuNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Screening Form 0907Document2 pagesBlood Pressure Screening Form 0907Meganne Walsh100% (2)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GERD and Its ComplicationDocument25 pagesPathophysiology of GERD and Its ComplicationalmiraNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia Fact SheetDocument2 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia Fact SheetCandace MorinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJuliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- Guia-Taller Ingles - Grado Tercero PDFDocument2 pagesGuia-Taller Ingles - Grado Tercero PDFAngel Mateo100% (1)
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very NewDocument6 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very NewhusseinNo ratings yet
- Individualised Cognitive Behaviour Therapy in Patients of Substance Use Disorders: Three Case StudiesDocument5 pagesIndividualised Cognitive Behaviour Therapy in Patients of Substance Use Disorders: Three Case StudiesSupDrNo ratings yet
- Knee PainDocument2 pagesKnee PainKKNo ratings yet
- Nosocomial Infection Control - White Paper - Greg Luther - BioWarn LLCDocument10 pagesNosocomial Infection Control - White Paper - Greg Luther - BioWarn LLCGregNo ratings yet
- Human Soil-Transmitted Helminths and Lung Infections: A Guide Review For Respiratory TherapistsDocument7 pagesHuman Soil-Transmitted Helminths and Lung Infections: A Guide Review For Respiratory TherapistsParasito BioudosucNo ratings yet
- Sugar and Blood 2Document19 pagesSugar and Blood 2shaira ubaldeNo ratings yet
- 4chan Thread 252001072Document8 pages4chan Thread 252001072Gica AlecuNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Hereditary Breast and Ovarian CancerDocument43 pagesPowerPoint - Hereditary Breast and Ovarian CancerkeeNo ratings yet
Obgyne Finals
Obgyne Finals
Uploaded by
Adviento Angelica0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThis document discusses various placental abnormalities and complications of pregnancy and childbirth. It defines different types of placental abnormalities such as bilobed placentas, placenta previa, and placental hematomas. It also describes complications related to the umbilical cord such as cord prolapse and vasoconstriction. Finally, it discusses postpartum infections and complications that can occur in the days following delivery.
Original Description:
Original Title
OBGYNE-FINALS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various placental abnormalities and complications of pregnancy and childbirth. It defines different types of placental abnormalities such as bilobed placentas, placenta previa, and placental hematomas. It also describes complications related to the umbilical cord such as cord prolapse and vasoconstriction. Finally, it discusses postpartum infections and complications that can occur in the days following delivery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesObgyne Finals
Obgyne Finals
Uploaded by
Adviento AngelicaThis document discusses various placental abnormalities and complications of pregnancy and childbirth. It defines different types of placental abnormalities such as bilobed placentas, placenta previa, and placental hematomas. It also describes complications related to the umbilical cord such as cord prolapse and vasoconstriction. Finally, it discusses postpartum infections and complications that can occur in the days following delivery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
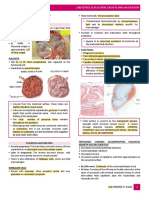
OBGYNE - form due to slowing down of maternal
blood flow leading to stasis & fibrin
1. cord inserts b/n 2 placental lobes – either
deposition
into a connecting chorionic bridge or
- -layer of fibrin diminishes O2 to villus
intervening membranes? 1:350 deliveries
- ---syncytiotrophoblast necrosis
a. Other names?
11. Types of Hematoma
2. Smaller version of bilobate placenta?
a. b/n placenta & its adjacent decidua?
- 2fold higher incidence in twin
b. b/n chorion & decidua aka
pregnancies
“subchorionic hemorrhage”?
- vascular connections of fetal origin
c. along roof of intervillous space &
- -if retained in the uterus after delivery
beneath chorionic plate? Aka
- --- HEMORRHAGE
“Breus mole”
3. All or large part of fetal membranes are
d. b/n placenta & amnion; of fetal
covered by functioning villi? -may give
vessel origin?
rise to serious hemorrhage because of
- acute events during 3rd stage labor when
associated placenta previa or accreta
cord traction ruptures a vessel near cord
4. Placenta is annular in shape?
insertion
- variant of placenta membranacea
- chronic lesions, asstd. w/ fetomaternal
- tissue atrophy in a portion of the ring, a
hemorrhage or fetal growth restriction
horseshoe shape is more common
- confused with chorioangioma
- antepartum and postpartum bleeding and
12. Calcium salts may be deposited
IUGR
throughout placenta but are most
5. Central portion of a discoidal placenta is
common on maternal surface in basal
missing?
plate
- actual hole in the placenta, more often
- Asstd. w/ nulliparity, higher
defect involves only villous tissue with
socioeconomic status & greater maternal
chorionic plate intact
serum calcium level
6. -when the chorionic plate is smaller than
- Seen in sonography
the basal plate --- placental periphery is
13. Striking enlargement of chorionic
uncovered?
villi commonly seen in severe
7. -fetal surface presents a central
erythroblastosis & fetal hydrops
depression surrounded by
- maternal diabetes, fetal congestive
- a thickened, grayish-white ring
- heart failure & maternal-fetal syphilis
- -ring is composed of a double fold of
14. Resemblance of their components
amnion and chorion, with degenerated
to the blood vessels & stroma of the
decidua and fibrin in between
chorionic villus?
8. -when the ring does not have the central
- Only BENIGN tumors of the placenta
depression with the fold of membranes?
- Well-circumscribed , rounded,
- less well defined adverse clinical
predominantly hypoechoic lesion near
outcomes
chorionic surface & protruding into
9. -deposits dense fibrinoid layer on
amnionic cavity
placental basal plate?
- > 5 cm, asstd w/ significant AV
- Blockade to normal maternal blood flow
shunting w/in placenta leading fetal
10. -small yellow white nodules w/in
anemia & hydrops
placenta are normal part of placental
aging? 15.4 most common metastatic cancers in
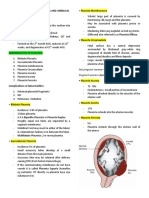
the placenta? M,L,L,Bc
16. What type of cancer can metastasize to the 28. –marked focal dilatation that develop w/in
fetus? intra-amnionic part of the umb. vein w/in its
fetal intra-abd’l portion?
17. Inflammation of the fetal membranes?
29. rare congt’l thinning of vessel wall w/
a. -leukocytes in amnionic fluid? diminished support fr Wharton jelly?
- most form at or near cord insertion into the
b. -umbilical cord? Placenta
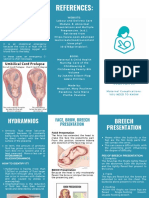
18. a condition in which the umbilical cord is asstd w/ single umb. artery, trisomy 18, fetal
inserted at or near the placental margin rather growth restriction & stillbirth
than in the center? 30. Good contractions, frequency?
31. After the expulsion of the baby and
19. insertion is normal but umbilical vessels placenta and membranes, what stage of labor?
lose their protective Wharton jelly shortly 32. How many cotyledons of the placenta?
before insertion? 33. Causes uterine contraction and peripheral
- covered only by amnion & prone to vasodilation? --> hypotension and tachy
compression, twisting & thrombosis 34. Not given to women with a history of
20. umbilical vessels spread w/ in membranes bronchial asthma?
at a distance from the placental margin, which 35. Cautiously given to women with
they reach surrounded only by a fold of amnion hypertension?
–- vessels vulnerable to compression –- fetal 36. Keeps the fundus low?
anoxia? 37. A physiologic pain experienced during
21. placental vessels overlie the cervix, lie b/n postpartum in the uterus (lower abdomen)
cervix & presenting fetal part, & supported only when the baby suckles?
by membranes? 1:5200 pregnancies 38. From expulsion of membranes up to 1 or 2
22. knobs protruding from cord surface hours post-partum, what stage?
-focal redundancies of a vessel or Wharton jelly 39. From delivery of the membrane up to 6
-w/ no clinical significance weeks post-partum?
23. active fetal movements, -high in 40. Rarely exceeds 39celsius and usually lasts
monoamnionic twins, risk of stillbirth increased <24 hours?
5-10fold, in live fetuses, increased FHR 41. What are the three complications of uterine
abnormalities but cord blood acid base values and pelvic infections?
usually normal? 42. A common cause of persisitent fever in
24. UC may be the presenting part in labor & women treated for metritis?
asstd w/ fetal malpresentation; cord prolapse or a) Begins at what day?
FHR abnormalities is an asstd labor finding? 43. A serious complication, bowel evisceration
25. focal narrowing of cord diameter that can be a morbid, surgical emergency, presents
develops in area of fetal umbilical insertion ? w/in 7-10 post-op days, high mortality risk,
26. -Found along the course of the cord; usually caused by infections?
a. epithelium –lined remnants of the allantois; 44. Uncommon severe wound infection
co-exist w/ persistently patent urachus? a) Risk factors?
b. form fr local degeneration of Wharton jelly; b) Symptoms noted until 3-5 days after
asstd w/ structural & chromosomal defects delivery
(trisomy 18 & 13 )? 45. Organs outside the uterus such as fallopian
c. found in1st tri tend to resolve completely? tube and ovary located bilaterally?
d. may portrend miscarriage & aneuploidy? 46. Intense parametrial cellulitis forming a
27. have lower perinatal morbidity & phlegmon within the leaves of the broad
mortality than those in the artery? ligament, fever persist longer than 72 hours
despite IV antimicrobial therapy, fever resolves
in 5-7 days?
47. Frequent complication in the pre-antibiotic
era, septic embolization was common, ovarian
veins may become involved?
a) Chills, occasional lower quadrant pain,
usually asymptomatic
48. An acute febrile illness w/ severe
multisystem derangement, 10-15% case-
fatality rate?
a) Caused maternal mortality
49. Post-partum incidence of mastitis?
a) Suppurative mastitis seldom appear
before the end of the 1st week
postpartum seen usually at 3rd or 4th
week, unilateral
b) Engorgement first followed by
inflammation
c) Sonography (diagnostics)
50. Immediate source of mastitis-causing
organisms is almost always caused by?
a) Resolves within 48hours
b) Dicloxacillin 500mg 4x a day
c) Erythromycin
d) Vigorous milk expression maybe be a
sufficient treatment alone
e) Continue breastfeeding
You might also like
- Anatomy Image Bank Edition 2 Updated Upto NEET PG 21Document130 pagesAnatomy Image Bank Edition 2 Updated Upto NEET PG 21Yogaabirami AbiNo ratings yet
- PLACENTADocument21 pagesPLACENTAHem Kumari80% (5)
- ETG-Australian Therapeutic Guidelines 2020 (Part 1)Document1,246 pagesETG-Australian Therapeutic Guidelines 2020 (Part 1)Omesh Prathiraja100% (1)
- Williams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Document57 pagesWilliams Obstertics, Twenty-Second Edition - Page 619 630Bharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument5 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Placental Disorders Flashcards - Quizlet PDFDocument11 pagesPlacental Disorders Flashcards - Quizlet PDFAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument7 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesLrak SiaNo ratings yet
- (OBa) 1.4 Plcental GRWTH and Maturation (Marinas) - PacisDocument6 pages(OBa) 1.4 Plcental GRWTH and Maturation (Marinas) - PacisClyde Yuchengco Cu-unjiengNo ratings yet
- Abnormalties in Placenta and UcDocument4 pagesAbnormalties in Placenta and UcJamaica QuetuaNo ratings yet
- LM 7 Pedia Lec NTSDocument5 pagesLM 7 Pedia Lec NTShanhananicasNo ratings yet
- Placental Abormalities (Tables)Document5 pagesPlacental Abormalities (Tables)icNo ratings yet
- Clin TG Abnormalities of The Placenta & CordDocument13 pagesClin TG Abnormalities of The Placenta & CordTami Selvi100% (2)
- Flashcards - Placenta and Fetal MembranesDocument16 pagesFlashcards - Placenta and Fetal MembranesKhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous CaputDocument5 pagesNervous CaputVellyana GustikaNo ratings yet
- 67Document57 pages67Neeruam Ellehcim Aled ZurcNo ratings yet
- Complications of Labor: PassengerDocument6 pagesComplications of Labor: PassengerR-Chian Jose Germanp100% (1)
- Placenta: Fetomaternal Organ. Fetal Part Maternal Part Transport SystemDocument21 pagesPlacenta: Fetomaternal Organ. Fetal Part Maternal Part Transport SystemAntonela CeremușNo ratings yet
- Plasenta Dan SelaputDocument18 pagesPlasenta Dan SelaputRahmi Mutia UlfaNo ratings yet
- Obstructed Labor: Basliel E. (MD)Document12 pagesObstructed Labor: Basliel E. (MD)Asteway MesfinNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument35 pagesPlacentaDrsmcsi dept of radiodiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Placenta OutlineDocument7 pagesAbnormalities of The Placenta OutlineSteve ShirmpNo ratings yet
- 4-Fetal LifeDocument11 pages4-Fetal LifeRichard ManuelNo ratings yet
- C.D Cord PresentationDocument17 pagesC.D Cord PresentationMeenatchiNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of The Placenta and CordDocument2 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and CordLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Tears: Rolf M. Embertson Cortney E. HendersonDocument1 pageCervical Tears: Rolf M. Embertson Cortney E. Hendersonomar rangelNo ratings yet
- Pedia Notes CompleteDocument27 pagesPedia Notes CompletelouvvhartNo ratings yet
- (NCM 107) 2 Embryonic and Fetal DevelopmentDocument6 pages(NCM 107) 2 Embryonic and Fetal Developmentberanabigail0No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BreastDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BreastRahmanNo ratings yet
- 109Document3 pages109Angel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Placenta PDFDocument22 pagesPlacenta PDFbookaccountNo ratings yet
- References:: Maternal and Child HealthDocument2 pagesReferences:: Maternal and Child HealthJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Face PresentationDocument4 pagesFace PresentationRose Ann HajironNo ratings yet
- CH 17 The Breast CompleteDocument36 pagesCH 17 The Breast CompleteGwen Marielle CursoNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument10 pagesPlacentaKarl Sonny UganizaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document9 pagesLec 3ibrahim.21hm32No ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 9th Edition All ChapterDocument31 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 9th Edition All Chapterbokayxasu100% (6)
- Abnormalities-Of-Placenta-And-Umbilical CordDocument53 pagesAbnormalities-Of-Placenta-And-Umbilical CordPraveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Hemangiomas of InfancyDocument20 pagesHemangiomas of InfancynissaNo ratings yet
- Midterm PPT MaternalDocument6 pagesMidterm PPT MaternalJhayneNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaDocument150 pagesFetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaKripa SusanNo ratings yet
- By - Prof. Saeed MakaremDocument27 pagesBy - Prof. Saeed MakaremIncredible DivineNo ratings yet
- Intraductal PapillomaDocument8 pagesIntraductal PapillomaNix14No ratings yet
- Bif Emb Ls 8 PlacentaDocument77 pagesBif Emb Ls 8 PlacentaJude Chisom Jnr NwaugoNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument11 pagesSpina BifidaheiyuNo ratings yet
- Implantation and PlacentaDocument52 pagesImplantation and PlacentaMs BadooNo ratings yet
- 08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes TotalDocument8 pages08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes TotalintanNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2Document6 pagesPost-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Ferlilisation, Implantation and Changes in PregnancyDocument7 pagesFerlilisation, Implantation and Changes in PregnancyLuke MatupiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy 5: Breast, Pectoral, and AxillaDocument3 pagesClinical Anatomy 5: Breast, Pectoral, and AxillaJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- 2 ApendixDocument8 pages2 Apendixمحمد عماد عليNo ratings yet
- NEJMra2308055 (1)Document8 pagesNEJMra2308055 (1)Celebfan BoyNo ratings yet
- BREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhDocument7 pagesBREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhChethranNo ratings yet
- Fronto-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele PDFDocument1 pageFronto-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele PDFtrifoniastriNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy V2Document6 pagesEctopic Pregnancy V2Aljon AgustinNo ratings yet
- TTTS NeoreviewsDocument13 pagesTTTS NeoreviewsNeha OberoiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Intrapartum Complications ReviewerDocument10 pagesNCM 109 Intrapartum Complications Reviewercrz VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Placenta - AAFPDocument22 pagesExamination of The Placenta - AAFPEi Ei MyoNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse: Sathiyalatha SarathiDocument3 pagesCord Prolapse: Sathiyalatha Sarathidiah komalaNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument5 pagesPlacenta PreviaMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Hematological SystemDocument6 pagesDiseases of The Hematological SystemAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocument10 pagesBasic Surgical InstrumentsAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics FinalsDocument1 pageObstetrics FinalsAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Self Directed LearningDocument1 pageRubric For Self Directed LearningAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Therapy Fo Respiratory Disorders (Group 9)Document26 pagesNutrition Therapy Fo Respiratory Disorders (Group 9)Adviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Surgery FinalsDocument1 pageSurgery FinalsAdviento AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cerebral Artery StrokeDocument9 pagesAnterior Cerebral Artery StrokeAlin CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- Drug Lists 1 3Document6 pagesDrug Lists 1 3Paulene Marie SicatNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray Appearances in Pneumonia and BronchiolitisDocument7 pagesChest X-Ray Appearances in Pneumonia and BronchiolitisMariani AniNo ratings yet
- Eating and Sleep-Wake Disorders Handout-1Document23 pagesEating and Sleep-Wake Disorders Handout-1Fulache, Lei Angeline B.No ratings yet
- Informative Speech OutlineDocument6 pagesInformative Speech Outlinearialis abreuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Cerebro Vascular Accident 1Document13 pagesLesson Plan On Cerebro Vascular Accident 1simonjosan67% (3)
- Urine Protein andDocument12 pagesUrine Protein andAfifah AzizNo ratings yet
- Edith Jacobson Kardex To DIscharge PlanDocument16 pagesEdith Jacobson Kardex To DIscharge PlanFranz Patrick Legria, CPAC - SNNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Abuse: Abusive Head TraumaDocument9 pagesAspects of Abuse: Abusive Head TraumaOkta Dwi Kusuma AyuNo ratings yet
- NCM 109-Cerebral PalsyDocument36 pagesNCM 109-Cerebral PalsyLeigh Ann Prosyne LozadaNo ratings yet
- Sti GonorrheaDocument6 pagesSti GonorrheaSulaiman NajirulNo ratings yet
- PacemakersDocument69 pagesPacemakersdocjeevan89100% (1)
- Dietary Therapy in Genetic EpilepsiesDocument4 pagesDietary Therapy in Genetic Epilepsiesalaahossam591No ratings yet
- 2012.01.12!02!07-48CV Mammen Chandy WebsiteDocument16 pages2012.01.12!02!07-48CV Mammen Chandy WebsitePradeep BabuNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Screening Form 0907Document2 pagesBlood Pressure Screening Form 0907Meganne Walsh100% (2)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GERD and Its ComplicationDocument25 pagesPathophysiology of GERD and Its ComplicationalmiraNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia Fact SheetDocument2 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia Fact SheetCandace MorinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJuliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- Guia-Taller Ingles - Grado Tercero PDFDocument2 pagesGuia-Taller Ingles - Grado Tercero PDFAngel Mateo100% (1)
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very NewDocument6 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very NewhusseinNo ratings yet
- Individualised Cognitive Behaviour Therapy in Patients of Substance Use Disorders: Three Case StudiesDocument5 pagesIndividualised Cognitive Behaviour Therapy in Patients of Substance Use Disorders: Three Case StudiesSupDrNo ratings yet
- Knee PainDocument2 pagesKnee PainKKNo ratings yet
- Nosocomial Infection Control - White Paper - Greg Luther - BioWarn LLCDocument10 pagesNosocomial Infection Control - White Paper - Greg Luther - BioWarn LLCGregNo ratings yet
- Human Soil-Transmitted Helminths and Lung Infections: A Guide Review For Respiratory TherapistsDocument7 pagesHuman Soil-Transmitted Helminths and Lung Infections: A Guide Review For Respiratory TherapistsParasito BioudosucNo ratings yet
- Sugar and Blood 2Document19 pagesSugar and Blood 2shaira ubaldeNo ratings yet
- 4chan Thread 252001072Document8 pages4chan Thread 252001072Gica AlecuNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Hereditary Breast and Ovarian CancerDocument43 pagesPowerPoint - Hereditary Breast and Ovarian CancerkeeNo ratings yet