Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
ĴąŠǿŊ ŦąŊOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
ĴąŠǿŊ ŦąŊCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4: Database Management
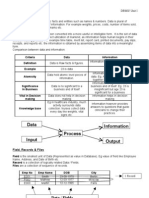
1.1 Data Management Data consists of raw facts such as employee numbers and sales figures 1.1.1 File Concepts Data are organized in a hierarchy o Bit (a binary digit) Represent the smallest piece of data a computer can process, on (1) or off (0)
o Byte A group of eight bits, called a byte, (letter, a number or a symbol)
o Field Field is typically a name, number, or combination of characters that describes an characteristic of a business object (e.g. employee no, position) or activity (e.g. sale no, sales amount)
o Record Collection of related data fields. E.g. Student number, student name
o File Collection of related records, E.g. employee file is a collection of all company employee record.
o Database Collection of integrated and related files. E.g. Student file, Exam File
1.2 The Database Approach
Chapter 4 Page 1
Traditional Approach - Separate data files are created and stored for each application program
Student_File Traditional Approach Some data may be duplicated (require extra storage space) Difficult to access data from more
Stud_I First_Na Last_Na Addre Gend Contact_N D me me ss er o S001 S002 S003 Lim Wong Lau Mei Mei Hui Hui KL Perak Femal 012e 1234567 Femal 013e 1234569 Male 0144567890
Ming Wai KL
Exam_File Stud_I First_Na D me S001 S002 S003 Lim Wong Lau Last_Na Addre Gend Subje Contact_No Grade me ss er ct Mei Mei Hui Hui KL Perak Femal 012e 1234567 Femal 013e 1234569 Male 0144567890 BM BM BM A B C
Ming Wai KL
Database Approach - Pool of related data is shared by multiple application programs
Exam_File
Stud_I First_Na Last_Na Addre Gend Contact_N Subje Grade D me me ss er o ct S001 S002 S003 Lim Wong Lau Mei Mei Hui Hui KL Perak Femal 012e 1234567 Femal 013e 1234569 Male 0144567890 BM BM BM A B C
Ming Wai KL
Common Field - to make a relationship
Exam_File Stud_ID S001
Chapter 4
Subject BM
Grade A
Database Approach Reduced data redundancy (store only once) Reduce duplicates & inconsistencies in updating Page 2
Exam_File Stud_ID S002 S003 Subject BM BM Grade B C
1.2.1 The Relational Database Model Based on the concept of two-dimensional tables, called relations. Stores data in tables that consist of rows and columns.
Each row of a table represents a data entity/ tuple Each Columns of the table represent attributes Domain - values can be placed in each column of the relational table Primary key - field or set of fields that uniquely identifies the record. E.g. Customer No.
1.3 Types of Data Files : Master file & Transaction Files Master file
o
Data file containing relatively permanent records that are generally updated periodically.
Page 3
Chapter 4
Inventory_shoe (Master File) Item_N Item_Descripti Unit_cos Unit_pric Quantit o on t e y A001 A002 Adidas New Balance RM120 RM100 RM160 RM120 10 20
Contains permanent records (remains with the
system as long as the system is in use) Updated periodically Main data
Transaction file
o
Temporary holding file that holds all changes to be made to the master file.
Inventory_shoe (Transaction File) Stock In 10 20
Item_No A001 A002
Date 12/10/2010 12/10/2010
Stock Out 5 8
to the master file (remains with the system only until the transactions are processed) Data about transactions (replace with other transactions 1.4 data for new transactions) Database Management Systems (DBMSs)
Temporary holding file holds all changes to be made
A DBMS is a set of programs that provide users with tools to add, delete, access, and analyze data stored in one location.
Common Function of DBMS 1. Data Dictionary
A repository contains data about each file in the database and each field within those files.
Chapter 4
Page 4
Uses the data dictionary to perform validation checks.
2.
File Retrieval and Maintenance
Use Query language to retrieve or select data from a database.
3.
Data Security
To specify different access privileges for different users of a DBMS. Access privileges: Actions that can be performed by specific users. To ensure that only authorized users access data at permitted times.
4. Backup and Recovery Backup - Copy the entire database into other storage media. Recovery - Restore a database when it becomes damaged or destroyed. Advantages of using DBMS 1. Reduced data redundancy
Data is organized by the DBMS and stored only once , reduce duplicate data
2.
Improved data integrity Ensures no separate files contain copies of the same piece of data. Reduce duplicates & inconsistencies in updating
3.
Better & easier access to data and information Easy to access and retrieve data from a database, using simple commands
Chapter 4
Page 5
4. Shared data
Data share over a network, by the entire organization.
Chapter 4
Page 6
You might also like
- MNS Is Training Course - Module 2Document36 pagesMNS Is Training Course - Module 2Arvin A100% (1)
- MySQLClient ServerApplicationswithVisualFoxProDocument439 pagesMySQLClient ServerApplicationswithVisualFoxProButengsDoank100% (2)
- DBMSDocument27 pagesDBMSPrateek RajpalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DatabasesDocument29 pagesIntroduction To DatabasesAmmie BioanalNo ratings yet
- HW-1 Answers DBMT KeyDocument9 pagesHW-1 Answers DBMT Keykarthikeyan RNo ratings yet
- Design Database Main Module Simplified TvetDocument238 pagesDesign Database Main Module Simplified Tvetmohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Database Management: An IntroductionDocument71 pagesDatabase Management: An IntroductionkathleenNo ratings yet
- Database BasicsDocument26 pagesDatabase BasicsnimznimuNo ratings yet
- File Systems and DatabasesDocument54 pagesFile Systems and Databasesobiwan xeonNo ratings yet
- Session 4 COMPDocument20 pagesSession 4 COMPstumaini1200usdNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Introduction To Database: Lesson 8.1: Understanding Database, Database Management SystemDocument19 pagesUnit 8: Introduction To Database: Lesson 8.1: Understanding Database, Database Management SystemScientia Online CareNo ratings yet
- Pasion, Kaye Lianne G. Relos, Yella Mae P. Santos, Monica Sophia LDocument32 pagesPasion, Kaye Lianne G. Relos, Yella Mae P. Santos, Monica Sophia LYella Mae Pariña RelosNo ratings yet
- Dbms ManualDocument22 pagesDbms ManualJaysheel ElamgodilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lecture 1Document54 pagesChapter 1 - Lecture 1Aliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- Database Management System1Document11 pagesDatabase Management System1Mohan AdariNo ratings yet
- Design of Files and Use of Auxiliary Storage DevicesDocument29 pagesDesign of Files and Use of Auxiliary Storage DevicesSidharath PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Database - 2021 T1Document33 pagesWeek 3 - Database - 2021 T1Odria ArshianaNo ratings yet
- 1.database IntroDocument28 pages1.database IntroAjiSetiajiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction: Dhanashree HuddedarDocument26 pagesUnit 1: Introduction: Dhanashree HuddedarArchit AnandNo ratings yet
- Prenentation 1Document26 pagesPrenentation 1Hasnain razaNo ratings yet
- 1-The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocument30 pages1-The Database Environment and Development Processghadafares53No ratings yet
- Unit - 8 Database and Database Management SystemDocument36 pagesUnit - 8 Database and Database Management SystemayushrauniyarguptaNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Data: Database FileDocument40 pagesHierarchy of Data: Database FileMidhun Joseph JohnNo ratings yet
- De Unit 1-Database ConceptsDocument54 pagesDe Unit 1-Database ConceptsGautam ManchandaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit IDocument30 pagesDBMS Unit IAnubhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database SystemsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Database SystemsAdultNo ratings yet
- Dbms Unit-IDocument80 pagesDbms Unit-ILaxmi Venki100% (4)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To DatabaseDocument46 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To DatabaseDibyeshNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument70 pagesDBMSGitte DnyaneshwarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - DBMS1Document37 pagesUnit 1 - DBMS1Hamodey BBMNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-16 at 10.37.30Document70 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-16 at 10.37.30Anaïs ErnestineNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument80 pagesChapter TwoOscar FrizziNo ratings yet
- 01 Undestanding DatabasesDocument13 pages01 Undestanding DatabasesMars TinNo ratings yet
- GISA Data Storage and Management Lecture5 Edited13102023Document44 pagesGISA Data Storage and Management Lecture5 Edited13102023Jecinta wNo ratings yet
- Practical File Sem 4Document40 pagesPractical File Sem 4cprateek7878No ratings yet
- Database Management System UNIT-1Document199 pagesDatabase Management System UNIT-10fficial SidharthaNo ratings yet
- 1 File Processing Systems: COMP 378 Database Systems Notes For Chapter 1 of Database System ConceptsDocument8 pages1 File Processing Systems: COMP 378 Database Systems Notes For Chapter 1 of Database System ConceptsFauzil 'AzimNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument34 pagesDatabase Management SystemsPurushothama ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ateeb Ul Haq Class XII Final Access PracticalDocument16 pagesAteeb Ul Haq Class XII Final Access PracticalAteeb ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument84 pagesDatabase Management SystemsTas MimaNo ratings yet
- The Database EnvironmentDocument37 pagesThe Database Environmentsidra_yousuf_1No ratings yet
- Module - 1-NotesDocument34 pagesModule - 1-Noteskurra trivedh sai 222010301036No ratings yet
- Week 4 Files Vs DatabasesDocument36 pagesWeek 4 Files Vs Databaseskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument52 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptsPuru RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDibyeshNo ratings yet
- Data Resource Management - 2Document33 pagesData Resource Management - 2naveetNo ratings yet
- Data & InformationDocument34 pagesData & InformationnutanmitraNo ratings yet
- Creating Database Objects TvetDocument89 pagesCreating Database Objects Tvetmohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Using Information Technology 10th Edition Williams Solutions ManualDocument44 pagesUsing Information Technology 10th Edition Williams Solutions Manuallloydkieran71epfi100% (26)
- DBMS MaterialDocument70 pagesDBMS MaterialMitesh PujaraNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Unit-I The Database Environment: Basic Concepts and Definitions: Data, Information, MetadataDocument70 pagesDatabase Management System: Unit-I The Database Environment: Basic Concepts and Definitions: Data, Information, MetadataDeekonda AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NewDocument115 pagesUnit 4 Newshabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 02Document78 pagesUnit 02Kabir SinghNo ratings yet
- Super Informatica Basics PDFDocument49 pagesSuper Informatica Basics PDFShiva CHNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Data Base Management SystemDocument36 pagesLecture On Data Base Management SystemRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- DBMS-Lecture1 (P1-C1-T1)Document17 pagesDBMS-Lecture1 (P1-C1-T1)charnegreteNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Information Technology Infrastructure: Chapter 5: Databases and Information ManagementDocument39 pagesModule 2: Information Technology Infrastructure: Chapter 5: Databases and Information ManagementSyed RazaNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems: (Revised by Jiin-Feng Chen, National Chengchi University For Classroom Use)Document40 pagesDatabase Management Systems: (Revised by Jiin-Feng Chen, National Chengchi University For Classroom Use)Aizle ApolinarNo ratings yet
- Intro To DatabaseDocument19 pagesIntro To DatabaseMrinaal MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Database and Information MangmDocument15 pagesDatabase and Information MangmjmanlbNo ratings yet
- DB2 9 for z/OS Database Administration: Certification Study GuideFrom EverandDB2 9 for z/OS Database Administration: Certification Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - BCP and DRDocument79 pagesChapter 9 - BCP and DRH Chattaraj100% (1)
- Linux Interview Questions For Experienced-1Document41 pagesLinux Interview Questions For Experienced-1seenuvasan1985No ratings yet
- Oracle To Oracle Online MigrationDocument9 pagesOracle To Oracle Online Migrationxyzabcd12No ratings yet
- SAP On DB2 Overview - UpdatedDocument48 pagesSAP On DB2 Overview - UpdatedDevender5194No ratings yet
- SQL Server Command-Line Utilities: in This ChapterDocument17 pagesSQL Server Command-Line Utilities: in This Chapternew2trackNo ratings yet
- 3BSE027630-510 en S800 I O DTM 5.3Document184 pages3BSE027630-510 en S800 I O DTM 5.3ilke HANNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics As Investigation Tool - NBR - BangladeshDocument84 pagesDigital Forensics As Investigation Tool - NBR - BangladeshChaitaly R.No ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PresentationDocument14 pagesDisaster Recovery PresentationPradito BhimoNo ratings yet
- RMAN DB RefreshDocument11 pagesRMAN DB RefreshPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wonderware West Tech Note 079 - Procedure For Backing Up Wonderware InTouch Applications - Wonderware WestDocument5 pagesWonderware West Tech Note 079 - Procedure For Backing Up Wonderware InTouch Applications - Wonderware Westlister123No ratings yet
- Competing Against SangforDocument3 pagesCompeting Against SangforLuis FernandoNo ratings yet
- Fanuc Mill 15b Programming ManualDocument571 pagesFanuc Mill 15b Programming ManualCarlos NunesNo ratings yet
- NUUO Surveillance System Manual PDFDocument134 pagesNUUO Surveillance System Manual PDFFERNANDO ANDRIOTTI VICENTINNo ratings yet
- NetBackup 7.0 Release NotesDocument122 pagesNetBackup 7.0 Release Notesrnekk2No ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Identification of Faulty SystemDocument2 pagesDiagnosis and Identification of Faulty SystemJan Icejimenez100% (1)
- Os Format TipsDocument9 pagesOs Format TipsVamsi Jayasimha KaranamNo ratings yet
- Hpe0 J57Document29 pagesHpe0 J57malikanjum718435No ratings yet
- Security Best Practices in Azure Cloud - Viktorija AlmazovaDocument31 pagesSecurity Best Practices in Azure Cloud - Viktorija Almazovagemstone lab100% (1)
- Using Sage 50 Accounting 2019Document7 pagesUsing Sage 50 Accounting 2019teresefayeNo ratings yet
- Keyscan System VII (7.0.19) User Quick Reference Guide: Table of ContentDocument8 pagesKeyscan System VII (7.0.19) User Quick Reference Guide: Table of Contentwendy vegaNo ratings yet
- Data DomainDocument11 pagesData DomainAsma RizwanNo ratings yet
- BCP and DRDocument15 pagesBCP and DRArjun R ShettyNo ratings yet
- Cyber ForensicsDocument146 pagesCyber ForensicsSahal CSNo ratings yet
- Oracle 10g Admin 1Document4 pagesOracle 10g Admin 1Syed Oneeb JafriNo ratings yet
- Backup Exec System Recovery 2010Document3 pagesBackup Exec System Recovery 2010reload8No ratings yet
- Interview Question For Oracle DBADocument111 pagesInterview Question For Oracle DBAVimlendu Kumar100% (1)
- Introduction To DruvaDocument23 pagesIntroduction To DruvaJuan OrtuviaNo ratings yet
- CloudBerry Backup For MS SQLDocument13 pagesCloudBerry Backup For MS SQLTharindu NirushanNo ratings yet