Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Accounting
Cost Accounting
Uploaded by
ravariyagautamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost Accounting
Cost Accounting
Uploaded by
ravariyagautamCopyright:
Available Formats
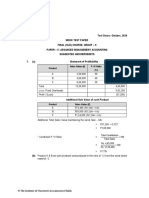
ILLUSTRATION 36
The following figures relate to Amit Ltd
Selling price per unit ₹ 40
Direct material per unit. ₹ 12
Direct labor per unit. ₹9
Other variable overheads per unit ₹7
Fixed factory overheads ₹ 3,20,000
Fixed office overheads ₹ 4,30,000
Calculate :
(1) P/V Ratio
(2) Break even sales in units and ₹
(3) Sales to earn profit of ₹ 4,50,000
(4) New break even point in ₹ and unit if total fixed overheads are increased by 15%.
SOLUTION : RS
Selling price (s) 40
Less: Variable Cost
Direct Material 12
Direct Labor 9
Variable Overheads 7 28
Contribution (c) 12
i. P/V Ratio = C *100 = 12 * 100 = 30%
S 40
ii. B.E Sales (in units) = Fixed cost = 7,50,000 = 62,500 units
Contribution per unit 12
B.E Sales (in ₹) = Fixed cost = 7,50,000 = RS.25,00,000
P/V Ratio 30%
iii. Sales Required = Fixed Cost + Desired Profit
P/V Ratio
= 7,50,000 + 4,50,000
30%
= 12,00,000 = 40,00,000
30%
iv. Present Fixed Overheads = 7,50,000
Add: 15% = 1,12,500
Revised = 8,62,500
New BEP (units) = 8,62,500 = 71,875 units
12
New BEP (RS) = 8,62,500 = RS.28,75,000
30%
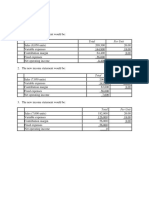
Illustration 43
A company is producing an identical product in two factories . The following are the details
in respect of both factories.
Particulars Factory X Factory Y
Selling price per unit (₹) 50 50
Variable cost per unit 40 35
(₹) 2,00,000 3,00,000
Fixed cost (₹) 40,000 30,000
Depreciation included in
above fixed cost (₹) 30,000 20,000
Sales in units 40,000 30,000
Production capacity
(units)
You are required to determine :
(1) Break even point (BEP) each factory individually.
(2) Cash break even point for each factory individually.
(3) BEP for company as a whole, assuming the present product mix is in sales ratio.
(4) Consequences on profit and BEP if product mix is changed to 2:3 and total demand
remain same.
Solution :
Particulars Factory X Factory Y
1. Break-even point: 2,00,000 3,00,000
Fixed cost 50 – 40 50 – 35
Contribution = 20,000 units =20,000 units
2. Cash Break-even Point 2,00,000 – 40,000 3,00,000 – 30,000
Fixed cost – 10 15
Depreciation =16,000 units =18,000 units
Contribution
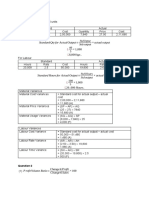
3. BEP as a whole = Complete Fixed Cost
Composite Contribution
= Rs 2,00,000 + Rs 3,00,000
10 * 3 + 15 * 2
5 5
= Rs 5,00,000 = 41,667 units
6+6
4. New Sales Mix = 50,000 * 2 = 20,000 of X
5
= 50,000 * 3 = 30,000 of Y
5
Calculation of Composite Contribution = [10 * 2] + [15*3] = 4 + 9 = RS 13
5 5
Consequence of Profit
Particulars Existing Mix New Mix
Contribution 50,000 *12 = 6,00,000 50,000*13 = 6,50,000
Less: Fixed Cost (5,00,000) (5,00,000)
Profit 1,00,000 1,50,000
Increase in Profit = Rs 1,50,000 – Rs 1,00,000 = Rs 50,000
Consequence on BEP
New BEP as a whole = Complete Fixed Cost = 5,00,000 = 38,462 units
Composite Contribution 13
So, BEP reduced by 3205 units (41,667 – 38,462).
You might also like
- IAH Ecopark & Ecopark2 Coupon - Houston Airport System PDFDocument2 pagesIAH Ecopark & Ecopark2 Coupon - Houston Airport System PDFChaitanya Karwa0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisItzi Estrella100% (4)
- Percentage of Sales MethodDocument6 pagesPercentage of Sales MethodFrancois Duvenage100% (2)
- Marginal Costing Technique: Break-Even AnalysisDocument9 pagesMarginal Costing Technique: Break-Even AnalysisAadarshNo ratings yet
- Practical Problems & Solutions Class Work Upto IL.10Document20 pagesPractical Problems & Solutions Class Work Upto IL.10Dhanishta PramodNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems - SolutionsDocument19 pagesNumerical Problems - SolutionsVishesh RohraNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing - E-Notes - Udesh Regular - Group 1Document42 pagesMarginal Costing - E-Notes - Udesh Regular - Group 1Dhiraj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Product Sales Value (') P / V Ratio (%) Contribution (') : Less: Fixed OverheadsDocument17 pagesProduct Sales Value (') P / V Ratio (%) Contribution (') : Less: Fixed OverheadsHarshawardhan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Abfm CH 8 Part 3Document6 pagesAbfm CH 8 Part 3leelavishnupriyaNo ratings yet
- 30 12 22Document8 pages30 12 22vasanthgurusamynsNo ratings yet
- Solved Prblem of Budget PDFDocument9 pagesSolved Prblem of Budget PDFSweta PandeyNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: OlutionDocument9 pagesSolved Problems: OlutionSweta PandeyNo ratings yet
- Marginal CostingDocument62 pagesMarginal CostingnehaNo ratings yet
- Differential Cost Analysis ExamplesDocument8 pagesDifferential Cost Analysis ExamplesMuhammad azeem100% (2)
- Num 2Document4 pagesNum 2nilesh nagureNo ratings yet
- Process Costing (1) 2 6Document5 pagesProcess Costing (1) 2 6epakhil01No ratings yet
- Student Solutions Chapter 8 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument7 pagesStudent Solutions Chapter 8 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisAasir NaQvi100% (1)
- Process CostingDocument6 pagesProcess Costingepakhil01No ratings yet
- RadheDocument11 pagesRadheApoorv GUPTANo ratings yet
- Relevant Costing - SolutionsDocument3 pagesRelevant Costing - SolutionsSwiss HanNo ratings yet
- F2 Past Paper - Ans05-2005Document10 pagesF2 Past Paper - Ans05-2005ArsalanACCANo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Multiple ChoiceDocument37 pagesChapter 9 - Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Multiple ChoiceBecky GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On BudgetingDocument5 pagesAssignment On BudgetingRameshNo ratings yet
- 06 Incremental AnalysisDocument11 pages06 Incremental AnalysisannarheaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5-8Document8 pagesExercise 5-8Kaye MagbirayNo ratings yet
- Name-Niraj Tawde Class - FY - MMS Roll No-55: Rohidas Patil Institute of Management StudiesDocument16 pagesName-Niraj Tawde Class - FY - MMS Roll No-55: Rohidas Patil Institute of Management StudiesmaheshNo ratings yet
- Selling Price 25 Variable Cost 12 Fixed Cost 65000 FIND Break Even Point CSRDocument6 pagesSelling Price 25 Variable Cost 12 Fixed Cost 65000 FIND Break Even Point CSRSoumya Ranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Business & Finance Chapter-7 Part-03 PDFDocument22 pagesBusiness & Finance Chapter-7 Part-03 PDFRafidul IslamNo ratings yet
- 4AC012 Answers To Week 3 Tutorial ExercisesDocument6 pages4AC012 Answers To Week 3 Tutorial ExercisesRohit Vijay PatilNo ratings yet
- Cost Management Anudeep Velagapudi PGDM6 1967Document9 pagesCost Management Anudeep Velagapudi PGDM6 1967Harsh Vardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Application of Marginal Costing TechniqueDocument7 pagesApplication of Marginal Costing TechniqueKumardeep SinghaNo ratings yet
- Assign 6 Chapter 8 Operating and Financial Leverage Cabrera 2019-2020Document12 pagesAssign 6 Chapter 8 Operating and Financial Leverage Cabrera 2019-2020mhikeedelantar100% (1)
- Marginal CostingDocument15 pagesMarginal CostingSonali MoreNo ratings yet
- 15 Marginal Costing PDFDocument14 pages15 Marginal Costing PDFSupriyoNo ratings yet
- 15 Marginal CostingDocument14 pages15 Marginal CostingHaresh KNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document16 pagesGroup 5Amelia AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Shalini Chaurasia Break Even Analysis Part 2 New Converted M.Com. Sem.-II Management AccountingDocument10 pagesShalini Chaurasia Break Even Analysis Part 2 New Converted M.Com. Sem.-II Management AccountingNetai DasNo ratings yet
- Ipcc Cost AnswerDocument13 pagesIpcc Cost AnswerHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Final PB87 Sol. MASDocument2 pagesFinal PB87 Sol. MASLJ AggabaoNo ratings yet
- CVP - GitttDocument15 pagesCVP - GitttFarid RezaNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis - Docx Final PDFDocument146 pagesCVP Analysis - Docx Final PDFDivyapratap Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 CVP ANALYSIS - GROUP 2 AE6 Strategic Business AnalysisDocument5 pagesMODULE 3 CVP ANALYSIS - GROUP 2 AE6 Strategic Business AnalysisJaime PalizardoNo ratings yet
- BEP SolutionsDocument4 pagesBEP SolutionsMahediNo ratings yet
- 3.16 ContributionDocument8 pages3.16 ContributionVishal SairamNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument5 pagesCVP AnalysisAzumi RaeNo ratings yet
- Week3 With SolutionsDocument8 pagesWeek3 With SolutionsAaliya & FaizNo ratings yet
- Fall (Winter) 2009 Examinations: Solution: (A)Document2 pagesFall (Winter) 2009 Examinations: Solution: (A)Asad RiazNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting NotesDocument6 pagesManagerial Accounting NotesMarilou GabayaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems BEP Marginal and Defferential Costing 1636367177432Document15 pagesPractice Problems BEP Marginal and Defferential Costing 1636367177432prabhuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5-1: Total Per UnitDocument18 pagesExercise 5-1: Total Per UnitSaransh Chauhan 23No ratings yet
- Chapter # 8 Exercise & Problems - AnswersDocument8 pagesChapter # 8 Exercise & Problems - AnswersZia UddinNo ratings yet
- 28 Solved PCC Cost FM Nov09Document16 pages28 Solved PCC Cost FM Nov09Karan Joshi100% (1)
- Cost June 2023-Dec2020Document100 pagesCost June 2023-Dec2020binuNo ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument11 pagesManagement AccountingMd. Showkat IslamNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisDocument26 pagesBreak Even AnalysisDr. Avijit RoychoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Acctg.7 Chapter 12 CVP R Exercises 910Document5 pagesAcctg.7 Chapter 12 CVP R Exercises 910freaann03No ratings yet
- CH 2 Cost-Volume-Profit RelationshipsDocument24 pagesCH 2 Cost-Volume-Profit RelationshipsMona ElzaherNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionHilary GaureaNo ratings yet
- MBA Advance Financial Management - ASYNCHRONUS ACTIVITYDocument9 pagesMBA Advance Financial Management - ASYNCHRONUS ACTIVITYDaniella LampteyNo ratings yet
- Units Or: 1 Which IsDocument5 pagesUnits Or: 1 Which IsTanvi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- The Cause-Effect Relationship Between Economic Growth and Stock Market Development - The Case of VietnamDocument22 pagesThe Cause-Effect Relationship Between Economic Growth and Stock Market Development - The Case of VietnamTrang Nguyễn Ngọc Hồng TrangNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1. Nature and Importance of EconomicsDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 1. Nature and Importance of EconomicsJessa BeloyNo ratings yet
- Pangasinan State University: BAC 102 - Basic MicroeconomicsDocument9 pagesPangasinan State University: BAC 102 - Basic MicroeconomicsFrancisca CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Relative Spread Strength As A Long-Term Cyclic Tool: Orex OcusDocument4 pagesRelative Spread Strength As A Long-Term Cyclic Tool: Orex OcusZoltán NagyNo ratings yet
- A Critical Analysis of APT and CAPMDocument4 pagesA Critical Analysis of APT and CAPManon_2694232370% (2)
- The Four Types of Economies Intelligent EconomistDocument6 pagesThe Four Types of Economies Intelligent EconomistEdmar OducayenNo ratings yet
- Source PlanningDocument1 pageSource Planningali.alianwarNo ratings yet
- Air India - The Virgin Airways SagaDocument5 pagesAir India - The Virgin Airways SagaShivek ChitranshNo ratings yet
- Process Costing Chapter PDFDocument50 pagesProcess Costing Chapter PDFTasfiNo ratings yet
- L5-Evaluating A Single Project - FullDocument59 pagesL5-Evaluating A Single Project - FullHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- B2B Tender PDFDocument21 pagesB2B Tender PDFAshis Kumar MuduliNo ratings yet
- A+Tale+of+Two+Moralities+ 2Document7 pagesA+Tale+of+Two+Moralities+ 2Asad Khan100% (1)
- Norway DeregulationDocument19 pagesNorway DeregulationAnonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Decision Analysis ProblemDocument2 pagesDecision Analysis ProblemGeejayFerrerPaculdo50% (2)
- Equity PrTHE EQUITY PREMIUM A Puzzleemium A PuzzleDocument17 pagesEquity PrTHE EQUITY PREMIUM A Puzzleemium A PuzzleEnrique Antonio Penson BrisindiNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy - Review of The State-of-the-ArtDocument5 pagesOffshore Wind Energy - Review of The State-of-the-ArtKerron RekhaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Services Procurement Process GuideDocument38 pagesOracle Services Procurement Process GuideKutbuddin KaraNo ratings yet
- 1 Finance-Exam-1Document22 pages1 Finance-Exam-1ashish25% (4)
- CGN Supplier Collaboration White PaperDocument7 pagesCGN Supplier Collaboration White Papershshafei8367No ratings yet
- New Product Development (NPD) and Product Life Cycle (PLC) StrategiesDocument4 pagesNew Product Development (NPD) and Product Life Cycle (PLC) StrategiesKanganFatimaNo ratings yet
- Mktg201ch 14 PPT SlidesDocument27 pagesMktg201ch 14 PPT SlidesAyush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- International Trade PDFDocument4 pagesInternational Trade PDFanto juaNo ratings yet
- Economics ScaleDocument5 pagesEconomics ScaleHepsi KonathamNo ratings yet
- Postal Stationery of Russia and Its Dependencies (1845 - 1922)Document25 pagesPostal Stationery of Russia and Its Dependencies (1845 - 1922)VDC LucienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Quantitative Demand AnalysisDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Quantitative Demand AnalysisYayandi HasnulNo ratings yet
- The Sourcing Continuum - Article by Dave WolskiDocument4 pagesThe Sourcing Continuum - Article by Dave WolskiDavid WolskiNo ratings yet
- TV Market in BangladeshDocument2 pagesTV Market in BangladeshJohn AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Technics Oil & Gas: Initiation of CoverageDocument15 pagesTechnics Oil & Gas: Initiation of Coveragecentaurus553587No ratings yet