Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MG Ca and P
MG Ca and P
Uploaded by
Julianne Roselle Pontillas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document provides information on photometric tests for measuring magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus levels in serum or plasma. It describes the principles, reagents, specimens, wavelengths, and reference ranges for each test. The magnesium test uses xylidyl blue to form a purple complex with magnesium ions. The calcium test uses arsenazo III to form a blue complex with calcium ions. The phosphorus test uses a colorimetric method with phosphomolybdic acid. The document also lists some clinical significance and interfering substances for each test.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mg-Ca-and-P
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on photometric tests for measuring magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus levels in serum or plasma. It describes the principles, reagents, specimens, wavelengths, and reference ranges for each test. The magnesium test uses xylidyl blue to form a purple complex with magnesium ions. The calcium test uses arsenazo III to form a blue complex with calcium ions. The phosphorus test uses a colorimetric method with phosphomolybdic acid. The document also lists some clinical significance and interfering substances for each test.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMG Ca and P
MG Ca and P
Uploaded by
Julianne Roselle PontillasThis document provides information on photometric tests for measuring magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus levels in serum or plasma. It describes the principles, reagents, specimens, wavelengths, and reference ranges for each test. The magnesium test uses xylidyl blue to form a purple complex with magnesium ions. The calcium test uses arsenazo III to form a blue complex with calcium ions. The phosphorus test uses a colorimetric method with phosphomolybdic acid. The document also lists some clinical significance and interfering substances for each test.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
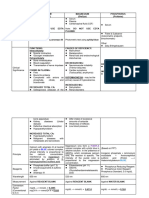
MAGNESIUM CALCIUM PHOSPHORUS
Fiske&Subbarow Method, 5 Minute Test
METHOD Photometric test using xylidyl blue Photometric test using arsenazo III Micro Method, Colorimetric,
binochromatic
Magnesium ions form a purple colored complex with Calcium with arsenazo III at neutral pH yields a blue
xylidyl blue in alkaline solution. In presence of gedta, colored complex whose intensity is directly
PRINCIPLE which complex calcium ions, the reaction is specific. proportional to the calcium concentration.
The intensity of the purple colored complex is directly Interference by magnesium is removed by addition of
proportional to the magnesium concentration. 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid.
ETHANOLAMINE—pH 11 = 750 mmol/L PHOSPHATE BUFFER-ph 7.5 = 50 mmol/L Phosphorus Reducing Reagent
REAGENTS GEDTA-60 umol/L 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid = 5 mmol/L Phosphorus Color Reagent
XYLIDYL BLUE-110 umol/L Arsenazo III = 120 umol/L Phosphorus Standard
CHROMOGEN XYLIDYL BLUE ARSENAZO III PHOSPHOMOLYBDIC ACID
Serum, heparin plasma, or urine (NO EDTA
SPECIMEN Serum,plasma, csf, urine (no edta plasma) Serum
PLASMA)
520 nm, 500-550 nm (increase of absorbance)
WAVELENGTH 650 nm, 630-670 nm 600 nm
628 nm, 575-650 nm (decrease of absorbance)
OPTICAL PATH 1 cm 1 cm
TEMPERATURE 20-25C/37C 20-25C/37C
MEASUREMENT Against reagent blank Against reagent blank Against reagent/water blank
CONVERSION 0.2495 (mg/d- mmol/L)
0.4114 (mg/dl-mmol/L) 0.324 (mg/dL-mmol/L)
FACTOR 0.025 (mg/24h-mmol/24h
INTERFERING
Ascorbic acid, bilirubin, lipemia, magnesium,
SUBSTANCES Ascorbic acid, bilirubin, lipemia, calcium, hemoglobin
hemoglobin
SERUM: SERUM/PLASMA:
NEONATES: 1.2-2.6 mg/dl 8.6-10.3 mg/dL SERUM:
REFERENCE
CHILDREN: 1.5-2.3 mg/dl URINE: Adult: 2.5-4.5 mg/dL
RANGE
WOMEN: 1.8-2.6 mg/dl Women: <250 mg/24h Infant and Children: 3.5-6.5 mg/dL
MEN: 1.8-2.6 mg/dl Men: <300 mg/24h
HYPOMAGNESEMIA:
HYPOCALCEMIA:
neuromuscular irritability (tremor, seizures)
osteoporosis
cardia symptoms (tachycardia, arrythmia) LOW:
dialysis patients
CLINICAL HYPERMAGNESEMIA: rickets
defective intestinal absorption
SIGNIFICANCE dehydration
hypoparathyroidism
renal disorders HIGH:
HYPERCALCEMIA:
excessive intake of antacids Severe nephritis
hyperparathyroidism
ASSOCIATED WITH:
malignant diseases with metastases and sarcoidosis
Weakness of reflexes and low blood pressure
Strontium salts in medicine may lead to strongly
NOTES:
increased calcium levels.
You might also like
- NCLEX LabValues CheatSheetDocument2 pagesNCLEX LabValues CheatSheetOlrac Agairdam100% (1)
- Ca-Mg-P (Tabulated)Document3 pagesCa-Mg-P (Tabulated)maja.amora.swuNo ratings yet
- Luid and Electrolyte Balance: M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM UniversityDocument30 pagesLuid and Electrolyte Balance: M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM UniversityCarmen MolinaNo ratings yet
- Uric AcidDocument2 pagesUric AcidAmmar MostafaNo ratings yet
- Hypon at R em Ia: ST Epw Ise Appr Oach T o Diagn Osis: Ser U M Sodiu M 135 M M Ol/ LDocument1 pageHypon at R em Ia: ST Epw Ise Appr Oach T o Diagn Osis: Ser U M Sodiu M 135 M M Ol/ LMaría José GalvisNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Metabolisme BawaanDocument19 pagesKelainan Metabolisme BawaannurmultazamNo ratings yet
- ToxicDocument12 pagesToxicAaron Jed Tan PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Midterms CC2 - Tabled Pckge InsertsDocument11 pagesMidterms CC2 - Tabled Pckge InsertsrallaysaNo ratings yet
- New Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument45 pagesNew Inborn Error of Metabolismmannan mangal100% (1)
- ELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Document3 pagesELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Alondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- ENZYMES AML LPS Package InsertDocument5 pagesENZYMES AML LPS Package InsertCindy Mae A. PogoyNo ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan IpdDocument26 pagesKegawatdaruratan IpdSuci Nurul AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Compiled High Yield Questions and Recalls For Board ExamDocument48 pagesCompiled High Yield Questions and Recalls For Board Examqnx6696m7fNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument34 pagesANEMIAAkashNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes LecDocument4 pagesElectrolytes LecMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument40 pagesHyponatremiaarchana p sNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NDocument41 pagesDisorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NBharath Kumar PamulapatiNo ratings yet
- KIDNEY DISEASES and LIVER DISEASES CHARTDocument16 pagesKIDNEY DISEASES and LIVER DISEASES CHARThira khatriNo ratings yet
- Con MGMT of CKD - Dubem & CollinsDocument42 pagesCon MGMT of CKD - Dubem & CollinscollinsmagNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea: Atan Baas SinuhajiDocument41 pagesDiarrhoea: Atan Baas SinuhajicarinasheliapNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in Pregnancy-1Document29 pagesAnaemia in Pregnancy-1Anuja RajurkarNo ratings yet
- Uric Acid SLR INSERTDocument1 pageUric Acid SLR INSERTventasmedicarescNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Laboratorium Rumah Sakit Umum Sari Mutiara Lubuk PakamDocument1 pageLaboratorium Rumah Sakit Umum Sari Mutiara Lubuk PakamIgor SimalangoNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- NAHCO3Document2 pagesNAHCO3Krizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Hypophosphat Emia: Presented By: Ramirez, Nichole Robles, Hannah Saquilayan, Kristine Siazon, ColeenDocument37 pagesHypophosphat Emia: Presented By: Ramirez, Nichole Robles, Hannah Saquilayan, Kristine Siazon, ColeenKyle De Sagun OtedaNo ratings yet
- AHS NephrologyDocument58 pagesAHS NephrologyMonika StephyNo ratings yet
- Heaptic EncephalopathyDocument16 pagesHeaptic Encephalopathydk.clinicalresearchNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledPaul GasparNo ratings yet
- Fluitest Urea: BiolyzerDocument4 pagesFluitest Urea: BiolyzerLhiyvind PaoNo ratings yet
- AlpDocument4 pagesAlpGregorio De Las CasasNo ratings yet
- Mtap Clinical MicrosDocument52 pagesMtap Clinical MicrosHillary BautistaNo ratings yet
- Yashwanth Hypothroidism.Document14 pagesYashwanth Hypothroidism.Yashwanth N BNo ratings yet
- Tests For Glucose 1 - Benedict'S Test: Cus04 (Cupric Sulfide) + Reducing Substance HeatDocument17 pagesTests For Glucose 1 - Benedict'S Test: Cus04 (Cupric Sulfide) + Reducing Substance HeatLyka PapaNo ratings yet
- Ge Acute NusindoDocument69 pagesGe Acute NusindoShiaNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Name: T.V.Satyanarayana Date: 27/09/2008 Address: CHINNAMIRAM Sex: M Age:42 Ref. Doctor: Dr. V.Venkata Rao Garu - RMPDocument14 pagesPatient'S Name: T.V.Satyanarayana Date: 27/09/2008 Address: CHINNAMIRAM Sex: M Age:42 Ref. Doctor: Dr. V.Venkata Rao Garu - RMPSARVANIDIAGNOSTICS &X-RAYNo ratings yet
- Ua 440 - 576 XL-1000 - Xsys0042 - 72 - FDocument4 pagesUa 440 - 576 XL-1000 - Xsys0042 - 72 - FNonameNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bambang Tridjaja - Hyponatremia Endocrin ApproachDocument42 pagesDr. Bambang Tridjaja - Hyponatremia Endocrin ApproachayushintamahaputriNo ratings yet
- EZYMESDocument3 pagesEZYMESEZRA LESINONo ratings yet
- Bilirubin (Total and Direct)Document1 pageBilirubin (Total and Direct)Risqon Anjahiranda AdiputraNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument6 pagesGlaucomaGiormaru CuntapayNo ratings yet
- Leia Knight 1 PDFDocument3 pagesLeia Knight 1 PDFAnonymous enET0WdPNo ratings yet
- Theresa To PrintDocument6 pagesTheresa To PrintmtarriolaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: Test Results Normal ValuesDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Report: Test Results Normal ValuesMark Laurence Cruz PascuaNo ratings yet
- List of Tests Ordered: Test Name StatusDocument4 pagesList of Tests Ordered: Test Name StatuslakshayNo ratings yet
- Yazz AmilasaDocument2 pagesYazz AmilasaFlorence ToroNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes & Acid-Base BalanceDocument108 pagesFluids and Electrolytes & Acid-Base BalanceAYTONA, JAMAICA F.No ratings yet
- Nama: Alamat: Umur: Diagnosa:: CatatanDocument1 pageNama: Alamat: Umur: Diagnosa:: CatatanPU Trii ChandraNo ratings yet
- Ashirwad (Chikki)Document11 pagesAshirwad (Chikki)Ashirwad DadeiaNo ratings yet
- GBSDocument35 pagesGBSJanine CabreraNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageHypocalcemia Testing AlgorithmAnonymous HdHd7ePNo ratings yet
- At 87212Document2 pagesAt 87212NurhisyamNo ratings yet
- Blood: Nikita Sebastian 1 Year Post Graduate Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics JSSDCHDocument94 pagesBlood: Nikita Sebastian 1 Year Post Graduate Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics JSSDCHNikita SebastianNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rsisa JilidDocument16 pagesLaporan Rsisa JilidGinaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base DisordersDocument66 pagesAcid Base DisordersIvan HensonNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lab V2Document14 pagesPhysiology Lab V2Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Hyper Calc Emi ADocument31 pagesHyper Calc Emi AFatima SajidNo ratings yet
- Salty-Testing Skin, Chronic Respiratory Problems, Lung Infections, Poor Growth/weight Loss, Meconium IleusDocument8 pagesSalty-Testing Skin, Chronic Respiratory Problems, Lung Infections, Poor Growth/weight Loss, Meconium IleusOrhan AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Chemical Ideas Section 11 AnswersDocument2 pagesChemical Ideas Section 11 AnswersvkrmmahalNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - X Golden Sample Paper - 2021-22Document72 pagesSCIENCE - X Golden Sample Paper - 2021-22krish patelNo ratings yet
- Possible Health Benefits of ApplesDocument11 pagesPossible Health Benefits of ApplesEirojram MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Pages de Esab Hanbook-3Document1 pagePages de Esab Hanbook-3Amin ThabetNo ratings yet
- Optical Emission Spectrometric Analysis of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys by The Argon Atmosphere, Point-to-Plane, Unipolar Self-Initiating Capacitor DischargeDocument11 pagesOptical Emission Spectrometric Analysis of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys by The Argon Atmosphere, Point-to-Plane, Unipolar Self-Initiating Capacitor DischargeTrần Huy NamNo ratings yet
- Zinc Oxide and Salicylic Acid PasteDocument1 pageZinc Oxide and Salicylic Acid PasteKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- SPIP26 Decision Guide Antacid Suspensions-4Document2 pagesSPIP26 Decision Guide Antacid Suspensions-4ZachNo ratings yet
- Caldo Asparagina PseudomonasDocument2 pagesCaldo Asparagina PseudomonasMSc Penélope MeloNo ratings yet
- Magnesium EbookDocument19 pagesMagnesium Ebooksale18100% (9)
- Protein Determination by The Lowry MethodDocument1 pageProtein Determination by The Lowry MethodTenzin TashiNo ratings yet
- White Paper Zinc Citrate - A Highly Bioavailable Zinc SourceDocument10 pagesWhite Paper Zinc Citrate - A Highly Bioavailable Zinc SourceVic Veeraj GoyaramNo ratings yet
- Ard 2480 TDDocument2 pagesArd 2480 TDRajajeevan AtputharajahNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Alloys: A Technical Seminar OnDocument7 pagesAluminium Alloys: A Technical Seminar Onlucky jhaNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument238 pagesEngineering ChemistryYashNo ratings yet
- 904 Media - Japan - English - 0624Document17 pages904 Media - Japan - English - 0624Jason WuNo ratings yet
- Peanuts As Functional Food: A ReviewDocument28 pagesPeanuts As Functional Food: A ReviewLPATI12No ratings yet
- Chlorine Dioxide, Method 10126, 02-2009, 9th EdDocument8 pagesChlorine Dioxide, Method 10126, 02-2009, 9th EdRajeshkumar ElangoNo ratings yet
- International Gcse Combined Science 9204 Chemistry Extension Question Paper 1 Nov20Document32 pagesInternational Gcse Combined Science 9204 Chemistry Extension Question Paper 1 Nov20Brandon LeeNo ratings yet
- Black Beauty AbrasiveDocument10 pagesBlack Beauty AbrasiveJesus De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Copper Post LabDocument3 pagesChemistry of Copper Post LabFerid HacizadeNo ratings yet
- Types of Knowledge: Mrs. KayDocument13 pagesTypes of Knowledge: Mrs. KaySahir Khan100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22ZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- Water Reuse Strategies: Steel Industry Case StudiesDocument15 pagesWater Reuse Strategies: Steel Industry Case StudiesMashaelNo ratings yet
- Aluminium AlloyDocument14 pagesAluminium AlloyDanu MamlukatNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1c ChemistryDocument11 pagesExercise 1c Chemistryapi-533545229No ratings yet
- Titration Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesTitration Questions and Answersngah lidwineNo ratings yet
- Bonding Basics IonicDocument2 pagesBonding Basics Ionicwosli3No ratings yet
- Mineral Nutrients of Palaiya Sadam PDFDocument2 pagesMineral Nutrients of Palaiya Sadam PDFraja singamNo ratings yet
- Ti 1000 0206 - enDocument2 pagesTi 1000 0206 - enJamil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Black Magic SFT: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet Black Magic SFT: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company123456ccNo ratings yet