Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ex.1 Conc and Analysis
Ex.1 Conc and Analysis
Uploaded by
Ghabriel Javier SembranoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ex.1 Conc and Analysis
Ex.1 Conc and Analysis
Uploaded by
Ghabriel Javier SembranoCopyright:
Available Formats
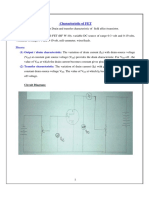
Analysis:
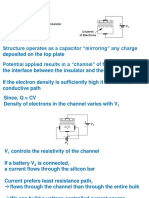
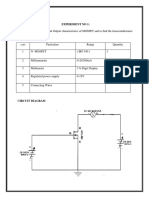
In the experiment, the gate-source voltage (V GS) varied from 0 to -6 volts, and the drain-
source voltage (VDS) ranged from 0 to 8 volts. When setting the gate-source and drain-source
voltage to 0 V, the drain current (I D) was 0 mA. Increasing the gate-source voltage (V GS) showed
a consistent 0 mA current through the drain (I D). This absence of current indicates that the
transistor is in the cut-off region, non-conductive under these voltage conditions. The
observation of ID yielding 0 mA when the gate-source voltage is -1 to -6 volts is caused by the
characteristics of the MPF-102 Transistor, where a negative gate-source voltage generates a
depletion region in the channel, limits the flow of current. When the gate-source voltage (V GS) is
set to 0V and the drain-source voltage (V DS) ranged from 1 to 8 volts, the transistor conducts.
This shift from cut-off to active conduction was verified with a digital multimeter, indicating
current flow between the drain and source terminals at 0V gate-source voltage. The MPF-102
Transistor graph demonstrates a direct and proportional relationship between the drain-source
voltage (VDS) and the drain current (ID). As the drain-source voltage increased from 1 V to 8 V, I D
yields a consistent increase. The initial step up from 0V to 2V caused an increase in the drain
current (ID) from 0 mA to 7.52 mA, demonstrating the transistor’s sensitivity to voltage changes.
This pattern continues with subsequent increases in drain-source voltage (V DS), with current
values reaching 8.2 mA at 3 V and eventually peaking at 10.9 mA at 8 V.
Conclusion:
In summary, the experiment with the MPF-102 Transistor reveals that the device operates
in the cut-off region, exhibiting non-conductivity when the gate-source voltage (V GS) is set to -1
to -6 volts. Conversely, when the gate-source voltage is set to 0 V and the drain-source voltage
(VDS) increases from 1 to 8 volts, the transistor transitions to active conduction. The observed
direct and proportional relationship between drain-source voltage (V DS) and drain current (ID)
indicates the transistor's sensitivity to voltage changes, with increasing VDS resulting in a
consistent rise in drain current (ID).
You might also like
- Characteristics of FETDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of FETYogesh Kumar100% (1)
- MOSFETSDocument102 pagesMOSFETSVedant WaliaNo ratings yet
- Plot Characteristics of FETDocument4 pagesPlot Characteristics of FETTapobroto Chatterjee100% (2)
- Experiment-3:: Cadence Virtuoso 6.1.7 - 64bDocument9 pagesExperiment-3:: Cadence Virtuoso 6.1.7 - 64bSrujan MulkaNo ratings yet
- Analysis 1Document1 pageAnalysis 1Ghabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Field Effect TransistorDocument16 pagesUnit - Vi Field Effect TransistorBhavaniPrasadNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of FET: Object: Apparatus UsedDocument5 pagesCharacteristic of FET: Object: Apparatus UsedYedla Santosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument3 pagesField Effect TransistorssumitNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument3 pagesField Effect TransistorsHemant SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Notes 1Document9 pagesMosfet Notes 1Anil SaiNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Physical Operation (Cont'd) MOSFET Current/Voltage CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesMOSFET Physical Operation (Cont'd) MOSFET Current/Voltage CharacteristicsSuleman KhanNo ratings yet
- CH 63 PDFDocument26 pagesCH 63 PDFJawad Ul Hassan ShahNo ratings yet
- JFET CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesJFET CharacteristicsKRSTNo ratings yet
- Electronic ProjectsDocument1 pageElectronic ProjectsSanthosh SanNo ratings yet
- IV. Field Effect Transistor CompleteDocument42 pagesIV. Field Effect Transistor Completegarlic breadNo ratings yet
- Mos Transistor Theory: Unit - 1 Chapter - 2Document34 pagesMos Transistor Theory: Unit - 1 Chapter - 2Nava KrishnanNo ratings yet
- ECE 251 - Lecture 02 PDFDocument7 pagesECE 251 - Lecture 02 PDFwhatthefu100% (1)
- 6.field Effect Transistor Characteristics: To Study About Drain and Transfer Characteristics of FETDocument5 pages6.field Effect Transistor Characteristics: To Study About Drain and Transfer Characteristics of FETTarannum KhatunNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor TransistorsDocument39 pagesMetal Oxide Semiconductor TransistorsK MukundNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - JFET - NSESP 2021Document16 pagesGroup 1 - JFET - NSESP 2021Sisilia Anabina TariganNo ratings yet
- 368463600-JFET-Summary - PPT 20240314 132059 0000Document91 pages368463600-JFET-Summary - PPT 20240314 132059 0000Yanis SlimaniNo ratings yet
- P E Lab FinalDocument63 pagesP E Lab FinalARVIND100% (1)
- HandyDocument2 pagesHandyKaranpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Field Effect Transistor JfetDocument21 pagesUnit 3 Field Effect Transistor Jfetrakesh hudedNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor NotesDocument21 pagesField Effect Transistor NotessaraswatnidhiNo ratings yet
- Bee IiiDocument68 pagesBee IiiTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Characteristics (ECE126: Laboratory 1)Document13 pagesMOSFET Characteristics (ECE126: Laboratory 1)Klinn Cabresos100% (1)
- Experiment 3: N-Channel Jfet Characteristics: ED Sem IiiDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: N-Channel Jfet Characteristics: ED Sem IiiDipankar PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Lab Report FinalDocument5 pagesVlsi Lab Report FinalvenkiNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)Document5 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)sgmdhussainNo ratings yet
- Transistor MatchingDocument2 pagesTransistor MatchingAndonio GondeNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)Document3 pagesCharacteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)HCKERNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) EditDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) Editruhiyahnazihah_15106No ratings yet
- 10 Mosfet+CharacteristicsDocument5 pages10 Mosfet+CharacteristicsKarthikKumarNo ratings yet
- Mos Transistor TheoryDocument144 pagesMos Transistor TheorymailtolokiNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument4 pagesField Effect TransistorsdwaswaNo ratings yet
- 7 JFET CharacteristicsDocument22 pages7 JFET CharacteristicsAnsar AnsarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Mos DeviceDocument28 pagesElectrical Properties of Mos Devicemayamohan7250% (1)
- Basic Electrical Properties of MosDocument10 pagesBasic Electrical Properties of Mosmayamohan725No ratings yet
- Both Bjts and Fets, Are Equally Important and Each Offers Distinct Advantages and Has Unique Areas of Application.)Document19 pagesBoth Bjts and Fets, Are Equally Important and Each Offers Distinct Advantages and Has Unique Areas of Application.)Maxwell LumorNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument40 pagesField Effect TransistorsRatanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of P-N Junction Diodehybe07jiminNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:: Date: AIM: To Obtain Transfer Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (FET) TheoryDocument2 pagesExperiment No:: Date: AIM: To Obtain Transfer Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (FET) TheoryDharmistha VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- JFET CharactersticsDocument7 pagesJFET CharactersticsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Unit I - FETDocument19 pagesUnit I - FETJadhav BhagavatNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Device StructureDocument15 pagesMosfet: Device StructureNoorullah ShariffNo ratings yet
- This Is Your Presentation TitleDocument18 pagesThis Is Your Presentation TitleSwaroop BijuNo ratings yet
- Mosfet CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesMosfet CharacteristicsAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- Transistor Curve TracerDocument39 pagesTransistor Curve TracerGayan ShashiNo ratings yet
- V. Mosfet PDFDocument33 pagesV. Mosfet PDFleeminho_janxiNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Huda Mohammed Stage 3Document11 pagesMosfet: Huda Mohammed Stage 3الزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 JFET Theory and ApplicationsDocument28 pagesChapter 4 JFET Theory and ApplicationsPadmavathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FinalDocument15 pagesChapter 2 FinalPandimadevi SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- JFET Characteristics PDFDocument9 pagesJFET Characteristics PDFSougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- HW1Document2 pagesHW1priyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument75 pagesAEC Lab Manualphalanetra100% (1)
- Transistor Curve TracerDocument26 pagesTransistor Curve TracerpecceriniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document120 pagesLecture Note 1LinhHoàngTrươngNo ratings yet
- 2S AY2324 ScheduleDocument1 page2S AY2324 ScheduleGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Other Sample ProblesDocument4 pagesOther Sample ProblesGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- EDA SummaryDocument13 pagesEDA SummaryGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6 Delta Wye Circuit 1Document15 pagesTOPIC 6 Delta Wye Circuit 1Ghabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document1 pageHomework 3Ghabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet