Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis 1
Analysis 1
Uploaded by
Ghabriel Javier SembranoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis 1
Analysis 1
Uploaded by
Ghabriel Javier SembranoCopyright:
Available Formats
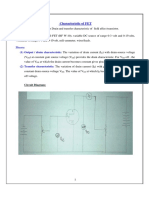
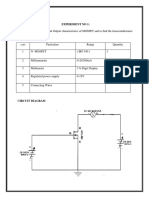
In the experiment, the gate-source voltage (VGS) varied from 0 to -6 volts, and the drain-source
voltage (VDS) ranged from 0 to 8 volts. When setting the gate-source and drain-source voltage to
0 V, the drain current (ID) was 0 mA. Increasing the gate-source voltage (VGS) showed a
consistent 0 mA current through the drain (ID). This absence of current indicates that the
transistor is in the cut-off region, non-conductive under these voltage conditions. The
observation of ID yielding 0 mA when the gate-source voltage is -1 to -6 volts is caused by the
characteristics of the MPF-102 Transistor, where a negative gate-source voltage generates a
depletion region in the channel, limits the flow of current. When the gate-source voltage (V GS) is
set to 0V and the drain-source voltage (VDS) ranges from 1 to 8 volts, the transistor conducts.
This shift from cut-off to active conduction was verified with a digital multimeter, indicating
current flow between the drain and source terminals at 0V gate-source voltage.
The JFET n-Channel Characteristics Chart, shown in Figure 64, reveals a direct and proportional
relationship between the applied drain-source voltage (Vds) and the resulting drain current (Id).
As Vds is gradually increased from 1V to 8V, Id shows a consistent and noticeable increase. This
behavior is consistent with the expected characteristics of a JFET. The initial step up in Vds from
1V to 2V causes an increase in Id from 6.42mA to 7.52mA, demonstrating the device's
sensitivity to voltage changes. This pattern continues with subsequent increases in Vds, with
current values reaching 8.2mA at 3V, 9.44mA at 5V, 9.95mA at 6V, 10.44mA at 7V, and
eventually peaking at 10.9mA at 8V. This observed pattern represents the JFET's response to
variations in the external applied voltage, providing useful information for circuit designers and
engineers. The analysis emphasizes the importance of understanding and controlling Vds in order
to regulate the JFET's operating characteristics, as well as its utility in electronic circuits
requiring precise current control.
You might also like
- Plot Characteristics of FETDocument4 pagesPlot Characteristics of FETTapobroto Chatterjee100% (2)
- Characteristics of FETDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of FETYogesh Kumar100% (1)
- Measuring Mosfet Curve Tracer PDFDocument11 pagesMeasuring Mosfet Curve Tracer PDFEugene Chew100% (2)
- Ex.1 Conc and AnalysisDocument1 pageEx.1 Conc and AnalysisGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- 6.field Effect Transistor Characteristics: To Study About Drain and Transfer Characteristics of FETDocument5 pages6.field Effect Transistor Characteristics: To Study About Drain and Transfer Characteristics of FETTarannum KhatunNo ratings yet
- 7 JFET CharacteristicsDocument22 pages7 JFET CharacteristicsAnsar AnsarNo ratings yet
- IV. Field Effect Transistor CompleteDocument42 pagesIV. Field Effect Transistor Completegarlic breadNo ratings yet
- P E Lab FinalDocument63 pagesP E Lab FinalARVIND100% (1)
- ECD LAB # 05 (1)Document4 pagesECD LAB # 05 (1)tariqshanza33No ratings yet
- Characteristic of FET: Object: Apparatus UsedDocument5 pagesCharacteristic of FET: Object: Apparatus UsedYedla Santosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.Document56 pagesExperiment No.vishugoldy100% (1)
- Characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)Document3 pagesCharacteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)HCKERNo ratings yet
- Manual Jfet and MosfetDocument8 pagesManual Jfet and MosfetSubhadip MaityNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Lab Report FinalDocument5 pagesVlsi Lab Report FinalvenkiNo ratings yet
- Osciladores Ingles 1Document6 pagesOsciladores Ingles 1Edwin Mauricio ArizaNo ratings yet
- Department OF Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment OF Electronics and Communication EngineeringRishi Raj KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesMosfet CharacteristicsAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- JFET Characteristics PDFDocument9 pagesJFET Characteristics PDFSougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Huda Mohammed Stage 3Document11 pagesMosfet: Huda Mohammed Stage 3الزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor: V R V Const IDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor: V R V Const Iindhu.csNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Field Effect TransistorDocument16 pagesUnit - Vi Field Effect TransistorBhavaniPrasadNo ratings yet
- Bee IiiDocument68 pagesBee IiiTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- EE301-Fall 2016: Laboratory #6: MOS TRANSISTORSDocument3 pagesEE301-Fall 2016: Laboratory #6: MOS TRANSISTORSOrhunNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Taslima Rahman MiliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: N-Channel Jfet Characteristics: ED Sem IiiDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: N-Channel Jfet Characteristics: ED Sem IiiDipankar PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsManikandan P Engineering EEE100% (1)
- Experiment No:: Date: AIM: To Obtain Transfer Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (FET) TheoryDocument2 pagesExperiment No:: Date: AIM: To Obtain Transfer Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (FET) TheoryDharmistha VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument75 pagesAEC Lab Manualphalanetra100% (1)
- FET TransistorsDocument19 pagesFET TransistorsOmer BallakNo ratings yet
- Depletion Mode MOSFETDocument10 pagesDepletion Mode MOSFETkeyboard2014No ratings yet
- JFET CharactersticsDocument7 pagesJFET CharactersticsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 10 Mosfet+CharacteristicsDocument5 pages10 Mosfet+CharacteristicsKarthikKumarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualDocument77 pagesElectronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualpdnkiranNo ratings yet
- Expt 13 - JFET-CharaceristicsDocument8 pagesExpt 13 - JFET-CharaceristicssamarthNo ratings yet
- ECE 251 - Lecture 02 PDFDocument7 pagesECE 251 - Lecture 02 PDFwhatthefu100% (1)
- Group 1 - JFET - NSESP 2021Document16 pagesGroup 1 - JFET - NSESP 2021Sisilia Anabina TariganNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument4 pagesMOSFETAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Electronic ProjectsDocument1 pageElectronic ProjectsSanthosh SanNo ratings yet
- Pee Exp-5Document7 pagesPee Exp-5ThunderBird GamerNo ratings yet
- 1.a.characteristics of MOSFETDocument8 pages1.a.characteristics of MOSFETSamudrala SrikarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2 (Fet)Document4 pagesExperiment No 2 (Fet)Jaideep Singh100% (1)
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument40 pagesField Effect TransistorsRatanNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document2 pagesLab 6mohhassonaNo ratings yet
- SUMSEM2023-24 BECE101L TH VL2023240700125 2024-06-12 Reference-Material-IIDocument23 pagesSUMSEM2023-24 BECE101L TH VL2023240700125 2024-06-12 Reference-Material-IIarbaz4923No ratings yet
- Regulation - 2018 Basic Electronics-18ELN14Document12 pagesRegulation - 2018 Basic Electronics-18ELN14Fairoz FairozNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Field Effect Transistor JfetDocument21 pagesUnit 3 Field Effect Transistor Jfetrakesh hudedNo ratings yet
- HandyDocument2 pagesHandyKaranpal SinghNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Transistor OperationDocument4 pagesMOSFET Transistor Operationarowona.hamidNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument22 pagesElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabDocument9 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabHussain HadiNo ratings yet
- 1 To 5 ManualDocument30 pages1 To 5 ManualRoshan DodiyaNo ratings yet
- Fet As VCRDocument6 pagesFet As VCRRicha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Circuit - FET Ampop Gain Control 06Document6 pagesCircuit - FET Ampop Gain Control 06Dhuvi LuvioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Field Effect Transistors: A. Introduction To FetsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Field Effect Transistors: A. Introduction To FetsBmanNo ratings yet
- Regulation - 2018: Basic Electronics-18ELN14Document12 pagesRegulation - 2018: Basic Electronics-18ELN14DaisyQueenNo ratings yet
- Fet Characteristics: ObjectDocument5 pagesFet Characteristics: ObjectpankajmadhuNo ratings yet
- 4200 Pulsed-IV ApplicationsGuideDocument75 pages4200 Pulsed-IV ApplicationsGuideStefan-Marian IordacheNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 2S AY2324 ScheduleDocument1 page2S AY2324 ScheduleGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- EDA SummaryDocument13 pagesEDA SummaryGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Ex.1 Conc and AnalysisDocument1 pageEx.1 Conc and AnalysisGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Other Sample ProblesDocument4 pagesOther Sample ProblesGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6 Delta Wye Circuit 1Document15 pagesTOPIC 6 Delta Wye Circuit 1Ghabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document1 pageHomework 3Ghabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet