Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EM4 Practical Electric Circuitry
EM4 Practical Electric Circuitry
Uploaded by
Nathan TvascorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EM4 Practical Electric Circuitry
EM4 Practical Electric Circuitry
Uploaded by
Nathan TvascorCopyright:
Available Formats
1
PRACTICAL ELECTRIC
CIRCUITRY
USES OF ELECTRICITY
Electricity is used in
Lighting
Machines
Security
Communication
Heating
COST OF ELECTRICITY
Cost of electricity = cost per unit X no of units
No of units = time in hours X power in kilowatts. [ 1 unit is equal to 1 kilowatt-hour.(kWh)]
Example.
If BPC sells electricity at P0.55 per unit, calculate the cost of using two 100 W bulbs for ten
hours.
No of units = 2 x 100W x 10 hrs
= 2 x 0.1 kW x 10 hrs
= 2 kWh
Cost = 20 kWh x P0.55
= P1.10
DANGERS OF ELECTRICITY
(a) Damaged Insulation
An electric shock can occur if a current flows from the electric circuit through a
person’s body to the Earth. This can happen when someone touches the exposed part
of the wire carrying current (live wire).
(b) Overheating Of Cables
When current increases through a conductor, the amount of heat energy lost due to the
resistance of the wire increases. This can lead to explosion, fire or the cables
overheating.
(c) Damp Conditions
Water can conduct electricity. When the body is wet, the resistance of the body
decreases hence more current can flow through the body. One can get a shock if s/he
operates an appliance with wet hands since water can conduct electricity.
(d) Overloading A Socket
When a socket is overloaded with many appliances, the current from the mains
increases which will lead to increased heat produced by cables. This can cause the
insulating material to melt or cause an explosion or fire.
Practical Electrical Circuitry leemok productions 2011©
2
SAFE USE OF ELECTRICITY
Fuses
This is a safety device made from tin coated-copper wire. It has a low melting point such that
it melts and breaks the circuit when current through it exceeds a certain value called the fuse
rating. This could be due to short circuits or overheating of cables. A fuse ensures that the
current carrying capacity of the wire is not exceeded.
To calculate the fuse rating one has to know the power rating of the device. For example, a
3kW 240V electric fire needs a current of about
Therefore a 13A fuse is recommended.
Fuses and switches are always connected to the live wire so as to isolate the appliance from
the current source when the appliance is not in use or in case of a short circuit.
Earthing
Appliances that are made of metal on the outer case must be earthed as a safety precaution.
This connects the body of the appliance to the ground. When the device is faulty or the ‘live’
wire breaks and touches the metal case, the earth wire will channel the charge to the ground
to prevent any electric shocks.
Double Insulation
Appliances that are made from non-metal outer case are usually double-insulated using a
tough, stiff non-conducting material. This prevents electric current to flow to the user in case
there is a fault. Devices that are double insulated carry the sign below.
3 Pin Mains Plug
Earth wire (green or/and yellow). This is connected to the earth pin.
Live wire (brown). This is connected to the live pin. It carries live current to the circuit.
Neutral wire (blue). This is connected to the neutral pin. It is earthed at the power station.
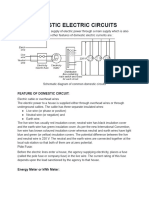
RING MAIN CIRCUIT
Practical Electrical Circuitry leemok productions 2011©
3
Practical Electrical Circuitry leemok productions 2011©
You might also like
- Bgcse Sda 4Document210 pagesBgcse Sda 4Nathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- SPDI Feb 2023 Final Mock QuestionaireDocument15 pagesSPDI Feb 2023 Final Mock QuestionaireJustin Fernandez0% (1)
- Calculation For SpliceDocument15 pagesCalculation For SpliceSandeep Singh0% (1)
- Fe MasterDocument67 pagesFe Masterapi-279749816No ratings yet
- Practical ElectricityDocument48 pagesPractical ElectricityLinaNo ratings yet
- Phy Unit 19 Model Answers - UploadDocument4 pagesPhy Unit 19 Model Answers - UploadNazib UchchhasNo ratings yet
- Safety in Electrical SystemsDocument18 pagesSafety in Electrical Systemsasteway gonfaNo ratings yet
- c19 Practical Electricity CompressedDocument11 pagesc19 Practical Electricity CompressedSherazNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document9 pagesElectricity 1okguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Electricity in The HomeDocument6 pagesFact Sheet Electricity in The HomeivanNo ratings yet
- Electricity in The HomeDocument10 pagesElectricity in The HomeHomok NokiNo ratings yet
- Igcse 21 MainselectricityDocument53 pagesIgcse 21 MainselectricityHany ElGezawy100% (2)
- Domestic Electric CircuitsDocument5 pagesDomestic Electric CircuitsGowshikaNo ratings yet
- Domestic Electric CircuitDocument4 pagesDomestic Electric Circuitdjdevils143No ratings yet
- IGCSE 21 MainsElectricityDocument53 pagesIGCSE 21 MainsElectricityShakeel MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Module 24 SAHITA Electrical InstallationDocument16 pagesModule 24 SAHITA Electrical InstallationLungisaniNo ratings yet
- Beee PPT LN 5Document25 pagesBeee PPT LN 5Omprakash GNo ratings yet
- Dangers of ElectricityDocument2 pagesDangers of ElectricityFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance: Unit of Resistance - Ohm ( )Document7 pagesElectrical Resistance: Unit of Resistance - Ohm ( )Sumit ShankarNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument47 pagesElectrical SafetyNo Hope100% (1)
- 420 Electronics Hardware XDocument121 pages420 Electronics Hardware Xmukesh092008No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety With Temporary Electrical InstallationDocument39 pagesElectrical Safety With Temporary Electrical InstallationBharath Cj100% (1)
- Lab ManualDocument96 pagesLab ManualASWANI RAJAN50% (2)
- 8.6 & 8.7 Fuse & Earth Wire, SafetyDocument12 pages8.6 & 8.7 Fuse & Earth Wire, SafetyAtunn Ismail100% (1)
- Practical ElectricityDocument18 pagesPractical ElectricityJamaica RamosNo ratings yet
- Danger of ElectricityDocument6 pagesDanger of ElectricitySensei J-daiNo ratings yet
- 6 IGCSE-Mains ElectricityDocument57 pages6 IGCSE-Mains ElectricityHoracio FerrándizNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy FinalDocument43 pagesElectrical Energy FinalMarjorette BuyuccanNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument28 pagesElectrical SafetyAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- General Electrical SafetyDocument8 pagesGeneral Electrical SafetyemegdadNo ratings yet
- Safety Electrical ApplicationDocument58 pagesSafety Electrical ApplicationakelariveraNo ratings yet
- Direct Current: Cells and Batteries Supply Electric Current Which Always Flows This Is CalledDocument42 pagesDirect Current: Cells and Batteries Supply Electric Current Which Always Flows This Is CalledMokYikLamNo ratings yet
- Electric PowerDocument36 pagesElectric PowerfruqaiyahamzaNo ratings yet
- Fire & Explosion Hazard From Electricity1Document20 pagesFire & Explosion Hazard From Electricity1pbontyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 21 MainsElectricityDocument55 pagesIGCSE 21 MainsElectricitysalmanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Awareness TrainingDocument52 pagesElectrical Safety Awareness Trainingbouarbi walidNo ratings yet
- NEW 4.2 Electronics (S) %Document49 pagesNEW 4.2 Electronics (S) %Anisha BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Physicy Test XDocument12 pagesPhysicy Test XMerimaNo ratings yet
- Power DistributionDocument46 pagesPower DistributionAdrian CamasosaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Electrical SafetyDocument39 pagesBasic Principles of Electrical SafetynamhtsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Hazards: How Do You Respond To Electrical Incidents (Electrocution) ?Document4 pagesElectrical Hazards: How Do You Respond To Electrical Incidents (Electrocution) ?roythomascNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Safe Electricity ApplicationDocument14 pagesLesson 9 Safe Electricity ApplicationRonnie AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8Document5 pagesElectrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8John Mark PrestozaNo ratings yet
- 3-Pin Plug: Based On The International Colour CodeDocument4 pages3-Pin Plug: Based On The International Colour CodesitiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Past PaperDocument14 pagesElectrical Past PaperdiciiuniverseNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety AwarenessDocument7 pagesElectrical Safety AwarenessCarlos FabillarNo ratings yet
- Ground Fault ProtectionDocument11 pagesGround Fault ProtectionJuan Espinoza100% (1)
- 8 - Phy - ElectricityDocument6 pages8 - Phy - Electricityunknownabcd1860No ratings yet
- HPS Terminal Automation Brochure 02-09-10 Rev4 EopDocument2 pagesHPS Terminal Automation Brochure 02-09-10 Rev4 EopapisituNo ratings yet
- Amta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical SafetyDocument67 pagesAmta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical Safetydunlut pelemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Wiring System and DistributionDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Wiring System and DistributionMohamad Syahmi100% (1)
- G9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityDocument4 pagesG9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- Ee Safety Eeab 3323Document85 pagesEe Safety Eeab 3323XMplify LinkNo ratings yet
- Electrical HazardsDocument56 pagesElectrical HazardsZainorin AliNo ratings yet
- T.C. Forensic - JAPANESE REPORTS ON ELECTRICAL FIRE CAUSES - Abstract 15Document3 pagesT.C. Forensic - JAPANESE REPORTS ON ELECTRICAL FIRE CAUSES - Abstract 15ecordova1No ratings yet
- Electrical Hazards ConstructionDocument77 pagesElectrical Hazards Constructiondh25881No ratings yet
- Chap 1 .Ppt. 2012Document68 pagesChap 1 .Ppt. 2012Philimond SegieNo ratings yet
- New Electrical Safety PresentDocument148 pagesNew Electrical Safety PresentSHIJAD SRAJUNo ratings yet
- Deshaunie SullivanDocument17 pagesDeshaunie SullivanK KgfdfNo ratings yet
- Transient Overvoltage ProtectionDocument41 pagesTransient Overvoltage Protectionshadi22No ratings yet
- MAins ElectricityDocument26 pagesMAins ElectricityKhobz On topNo ratings yet
- PneumaticsDocument16 pagesPneumaticsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument26 pagesMetalsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument32 pagesGearsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument12 pagesElectronicsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- Bgcse Sda p1Document238 pagesBgcse Sda p1Nathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- EM1 MagnetismDocument7 pagesEM1 MagnetismNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- 2008 p3 - 102814Document7 pages2008 p3 - 102814Nathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- 0654 Transpiration QuestionsDocument9 pages0654 Transpiration QuestionsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- EM7 Thermionic EmissionDocument3 pagesEM7 Thermionic EmissionNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- EM2 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesEM2 ElectrostaticsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- Middle School Stemscopedia Life Science Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument5 pagesMiddle School Stemscopedia Life Science Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- 2016 p3 - 103558Document8 pages2016 p3 - 103558Nathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- 8.thermal Expansion of Matter - SdaDocument7 pages8.thermal Expansion of Matter - SdaNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- 2009 p3 - 102935Document6 pages2009 p3 - 102935Nathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- MEM311 Manual 09192014Document77 pagesMEM311 Manual 09192014Sam Yang SunNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator: Service ManualDocument49 pagesRefrigerator: Service ManualSugavanan ThangavelNo ratings yet
- Hot Dip Galvanizing ProcessDocument13 pagesHot Dip Galvanizing ProcessNatarajan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor Plan: Existing Fcu-01 1-SCD 600X600 MM, NECK 150X150 MM 30 L/S Per EachDocument1 pageGround Floor Plan: Existing Fcu-01 1-SCD 600X600 MM, NECK 150X150 MM 30 L/S Per Eachmhmedgomaa74No ratings yet
- DoR Pavement Design GuidelinesDocument60 pagesDoR Pavement Design GuidelinesSabin Bajracharya83% (6)
- Report Injection MouldingDocument11 pagesReport Injection MouldingJilly ArasuNo ratings yet
- Building Constraction 2Document22 pagesBuilding Constraction 2Abdala M KreemNo ratings yet
- ENGGBOQABSTRACTREPORT NewDocument1,274 pagesENGGBOQABSTRACTREPORT NewUTTAL RAYNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Versiline Cui 56990Document4 pagesBrochure - Versiline Cui 56990Azar SKNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document27 pagesLecture 3Dhiraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH3030 5.8.2020Document14 pagesCH3030 5.8.2020Ram Lakhan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 2990Document21 pagesAstm D 2990mahamad AziNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentLowell SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Plastic Wastes in Concrete: A ReviewDocument13 pagesUtilization of Plastic Wastes in Concrete: A ReviewDebjani BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Tem No. Group Item Code (If Any)Document21 pagesTem No. Group Item Code (If Any)M/S RS ENTERPRISENo ratings yet
- Murray Roberts (Willy Cocquyt PR Eng 860106) Calculation Sheet Input SheetDocument23 pagesMurray Roberts (Willy Cocquyt PR Eng 860106) Calculation Sheet Input SheetMbalekelwa MpembeNo ratings yet
- CLT Presentation 25.11.20 PDFDocument125 pagesCLT Presentation 25.11.20 PDFdjordjevic19762991No ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument8 pagesChecklistVenkatumeshNo ratings yet
- 0714 Nitrogen PDFDocument2 pages0714 Nitrogen PDFSuresh PelluruNo ratings yet
- Anual Estimate 19-20 (17-18 SSR)Document16 pagesAnual Estimate 19-20 (17-18 SSR)k v rajeshNo ratings yet
- ACI 318 Anchoring To ConcreteDocument2 pagesACI 318 Anchoring To ConcreteYoanNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Glass HandoutDocument81 pagesAspects of Glass HandoutBonnie Lowe100% (1)
- Steel Framing ReferenciaDocument15 pagesSteel Framing ReferenciaConrado AlveoNo ratings yet
- Samsung Refrigerator: Service Center & RepairDocument15 pagesSamsung Refrigerator: Service Center & Repairthanuja valurothuNo ratings yet
- Bharath Creative AluminiumDocument3 pagesBharath Creative AluminiumSubodh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Study of Elastic-Plastic Fracture Toughness Determination: Journal of Materials Science October 1993Document6 pagesStudy of Elastic-Plastic Fracture Toughness Determination: Journal of Materials Science October 1993viverefeliceNo ratings yet
- WSS Welding Handbook 2013 Full LowresDocument552 pagesWSS Welding Handbook 2013 Full LowresdadaNo ratings yet