Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WS C2 U4 Eng Ans
WS C2 U4 Eng Ans
Uploaded by
yanaaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- River Training Structures - GroynesDocument17 pagesRiver Training Structures - GroynesShabana Khan67% (3)
- Floods and DroughtsDocument15 pagesFloods and DroughtsVaani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 26043514chapter Five - River Training and Flood ControlDocument26 pagesLecturenote - 26043514chapter Five - River Training and Flood ControlAnu PathakNo ratings yet
- NWP0 REPL1 Concepts 0 and 0 MethodsDocument27 pagesNWP0 REPL1 Concepts 0 and 0 MethodsGEF Curso online HEC-HMSNo ratings yet
- Uwater Resource EnvironmentrDocument27 pagesUwater Resource EnvironmentrNguyen Van KienNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 River Training WorksDocument28 pagesChapter-4 River Training WorksAbdulbasit Aba BiyaNo ratings yet
- Peter Robins PaperDocument7 pagesPeter Robins PaperArief Danial RahmanNo ratings yet
- River Engineering and Stream Restoration: P. Julien S. IkedaDocument37 pagesRiver Engineering and Stream Restoration: P. Julien S. IkedaDa VeNo ratings yet
- Flood Control-Technical Standards and Guidelines For Planning and DesignDocument144 pagesFlood Control-Technical Standards and Guidelines For Planning and Designacumen architects and planners ltdNo ratings yet
- Irrigation (Flood Control)Document5 pagesIrrigation (Flood Control)Vergel De TorresNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Reservoir Sediment Routing by Flushing, Replenishing, and Bypassing Sediments in Japanese River BasinsDocument8 pagesIntegrated Management of Reservoir Sediment Routing by Flushing, Replenishing, and Bypassing Sediments in Japanese River BasinsPedroNo ratings yet
- CBP 13369Document65 pagesCBP 13369jagath2005ukNo ratings yet
- Design Presentation Flood Control StructuresDocument17 pagesDesign Presentation Flood Control StructuresNowell PenoniaNo ratings yet
- Title of Case Study:: Oroklini Wetland Restoration in CyprusDocument4 pagesTitle of Case Study:: Oroklini Wetland Restoration in CyprusCHALLA MOUNICANo ratings yet
- WWF Valuing RiversDocument35 pagesWWF Valuing RiversCherry Rose MontojoNo ratings yet
- Public Consultation: On The River Basin Management Plan FOR IRELAND (2018-2021)Document104 pagesPublic Consultation: On The River Basin Management Plan FOR IRELAND (2018-2021)mao sanmiguelNo ratings yet
- HydroDocument26 pagesHydroAhmad BilaalNo ratings yet
- Open Drains and Channels DesignDocument29 pagesOpen Drains and Channels DesignNizar SeraNo ratings yet
- Draft Policy On Sediment Mgmt-June2017Document23 pagesDraft Policy On Sediment Mgmt-June20171sumit9876No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Stormwater Treatment ElementsDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Stormwater Treatment ElementsZhang Han XiangownnoobzNo ratings yet
- What Is River Restoration Final PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Is River Restoration Final PDFArsalan MakhdoomiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sediment Management in Hydropower Projects CWC 2018Document16 pagesGuidelines For Sediment Management in Hydropower Projects CWC 2018ManojNo ratings yet
- 12 - Russo - Channel Maintenance and Coastal Restoration in LouisianaDocument14 pages12 - Russo - Channel Maintenance and Coastal Restoration in LouisianaChun Wai SooNo ratings yet
- Water Resources and EngineeringDocument14 pagesWater Resources and EngineeringEunice Joy Tabucanon VillegasNo ratings yet
- Water Sensitive Urban Design - A Stormwater Management PerspectiveDocument44 pagesWater Sensitive Urban Design - A Stormwater Management PerspectiveNor Hidayah Mohd RazaliNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic StructureDocument11 pagesHydraulic StructureSuman HazamNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Flood Retention BasinsDocument17 pagesSustainable Flood Retention BasinsPiotr GrabowieckiNo ratings yet
- IX DrainageDocument2 pagesIX DrainageShalini ThakurNo ratings yet
- Wsud Tech Guidelines PDFDocument351 pagesWsud Tech Guidelines PDFTravis SmithNo ratings yet
- WS C2 U5 Eng AnsDocument7 pagesWS C2 U5 Eng AnsyanaaNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline Flood ControlDocument6 pagesTopic Outline Flood ControlCathy AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Hydrolink 2018 3Document32 pagesHydrolink 2018 3Kheler SernaqueNo ratings yet
- River Training Works: 3.1 ObjectivesDocument14 pagesRiver Training Works: 3.1 Objectivestesh100% (3)
- Factsheet River enDocument3 pagesFactsheet River enPetra DelgadoNo ratings yet
- DrainageDesignGuide PDFDocument795 pagesDrainageDesignGuide PDFEric ChanNo ratings yet
- Restoration Planning & DesignDocument8 pagesRestoration Planning & DesignAquiles Berrocal RodriguezNo ratings yet
- River Landscapes in The UK - Answer SheetDocument5 pagesRiver Landscapes in The UK - Answer SheetKarlina MikekNo ratings yet
- Irrigation and Drainage DevelopmentDocument31 pagesIrrigation and Drainage Developmentebagalan2022No ratings yet
- Water Resources System Modeling: River Basin Planning and ManagementDocument22 pagesWater Resources System Modeling: River Basin Planning and ManagementRas MekonnenNo ratings yet
- IWRM Report Submitted by Alemu Tezera Hung Quach and Thuy BuiDocument17 pagesIWRM Report Submitted by Alemu Tezera Hung Quach and Thuy Buiismail abibNo ratings yet
- Guideline 02Document70 pagesGuideline 02resti sucilestariNo ratings yet
- JFM Fevnfm TKDocument25 pagesJFM Fevnfm TKHanaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyXendra AqeylaaNo ratings yet
- MoM International Workshop On Coastal Reservoir, 26-27 October 2020Document27 pagesMoM International Workshop On Coastal Reservoir, 26-27 October 2020Yasruddin MtNo ratings yet
- 01river Engineering 13-14Document14 pages01river Engineering 13-14arsathNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Management 002Document112 pagesWater Resource Management 002Kumaran ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- WRE Course OutlineDocument2 pagesWRE Course OutlineJustine Anthony SalazarNo ratings yet
- Territorial Cohesion and Water Management in EuropeDocument82 pagesTerritorial Cohesion and Water Management in Europepedro_arsenioNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: WRPM and System ConceptDocument44 pagesChapter-2: WRPM and System Conceptkidus sileshNo ratings yet
- CH 12 River Training and Bank Protection PDFDocument15 pagesCH 12 River Training and Bank Protection PDFKreen132100% (1)
- Lucrare BadalutaDocument4 pagesLucrare BadalutanistoraliNo ratings yet
- Synopsis TemplateDocument5 pagesSynopsis TemplatePrashant MallickNo ratings yet
- Ocean - Chile. COP24Document17 pagesOcean - Chile. COP24Eduardo Silva BesaNo ratings yet
- Keeping Rivers Alive PDFDocument40 pagesKeeping Rivers Alive PDFmv.No ratings yet
- River Frontdevelopment 140322040936 Phpapp02Document35 pagesRiver Frontdevelopment 140322040936 Phpapp02Ar Jivan ShindeNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability Analysis PDFDocument23 pagesVulnerability Analysis PDFAlbina LaraNo ratings yet
- ReportfinalDocument98 pagesReportfinalMae DalangpanNo ratings yet
- River Training and Flood Control: Chapter FiveDocument26 pagesRiver Training and Flood Control: Chapter FiveHassan Abib BasalNo ratings yet
- River Conservation and ManagementFrom EverandRiver Conservation and ManagementPhilip BoonNo ratings yet
- Management of Marine Protected Areas: A Network PerspectiveFrom EverandManagement of Marine Protected Areas: A Network PerspectivePaul D. GoriupNo ratings yet
- COMP2501 - Assignment - 1 - Questions - RMD 2Document7 pagesCOMP2501 - Assignment - 1 - Questions - RMD 2yanaaNo ratings yet
- WS C2 U6 Eng AnsDocument7 pagesWS C2 U6 Eng AnsyanaaNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Coordination in Humans: ExerciseDocument9 pagesCH 16 Coordination in Humans: ExerciseyanaaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyyanaaNo ratings yet
- Math Factorization of Polynomials Ex. Suggested AnswerDocument22 pagesMath Factorization of Polynomials Ex. Suggested AnsweryanaaNo ratings yet
- Answers: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesAnswers: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyyanaaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Money Creation by Topic Past Paper Marking SchemeDocument3 pagesCh. 9 Money Creation by Topic Past Paper Marking SchemeyanaaNo ratings yet
- Biology CH.41Document56 pagesBiology CH.41yanaaNo ratings yet
- Aristo Biology Mock Exam 2020Document58 pagesAristo Biology Mock Exam 2020yanaaNo ratings yet
- Aristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersDocument9 pagesAristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersyanaaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Development Act of 2020Document369 pagesWater Resources Development Act of 2020Brian MastNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Geo Lesson 7Document18 pagesClass 8 Geo Lesson 78C-Ahmed Musawwir - Dj067No ratings yet
- STATUS OF DESIGN IN CANALS DIVISION, IDRB - Details of Work For Which Additional Details Sought From Field OfficesDocument1 pageSTATUS OF DESIGN IN CANALS DIVISION, IDRB - Details of Work For Which Additional Details Sought From Field OfficesnidhisasidharanNo ratings yet
- 1-India Relief Features - 1-16Document16 pages1-India Relief Features - 1-16saijitesh.gNo ratings yet
- GFD Water Rescue ManualDocument42 pagesGFD Water Rescue Manualtaufik_maulana87No ratings yet
- Assignment 01: Irrigation EngineeringDocument10 pagesAssignment 01: Irrigation EngineeringMoudud Ul Islam AwanNo ratings yet
- TD-39 Using HEC-RAS For Dam Break StudiesDocument74 pagesTD-39 Using HEC-RAS For Dam Break StudiesMarcele ColferaiNo ratings yet
- Godavari Water Dispute Tribunal AwardDocument221 pagesGodavari Water Dispute Tribunal AwardSampath Bulusu100% (1)
- Bundh BreedingDocument3 pagesBundh BreedingNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- South Centrral California Coast Steelhead Threats Assessment SummaryDocument87 pagesSouth Centrral California Coast Steelhead Threats Assessment SummaryGreenspace, The Cambria Land TrustNo ratings yet
- Te Kahui Kaupeka Conservation Park PDFDocument3 pagesTe Kahui Kaupeka Conservation Park PDFeaglebrdNo ratings yet
- Physiography of Flowing Water: OutlineDocument12 pagesPhysiography of Flowing Water: OutlineHasaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Bigarella 1973Document68 pagesBigarella 1973Leandro FernandesNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Analysis For The Proposed BridgeDocument8 pagesHydrological Analysis For The Proposed BridgeRoshan khadkaNo ratings yet
- Is 6966 1989 (PART 1) Hydraulics Design of Barrages and WeirsDocument12 pagesIs 6966 1989 (PART 1) Hydraulics Design of Barrages and Weirsarvind.singhNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources of BiharDocument1 pageNatural Resources of BiharManaal KhanamNo ratings yet
- Study of Hydropower Plants of Himachal PradeshDocument65 pagesStudy of Hydropower Plants of Himachal PradeshBhavesh KaushalNo ratings yet
- With Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western MountainsDocument3 pagesWith Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western Mountainshajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- Hoover DamDocument22 pagesHoover DamJERRY PAUL VARGHESENo ratings yet
- Design Aspects: 6.0 GeneralDocument22 pagesDesign Aspects: 6.0 GeneralshamsuNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 27Document2 pagesCase Study No. 27Felix De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Work Program For Excavation For DamDocument1 pageWork Program For Excavation For DamBernie QuepNo ratings yet
- Project RAC River Awareness and CleanlinessDocument8 pagesProject RAC River Awareness and CleanlinessKyla Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- Introducing Large Rivers Gupta Avijit Full ChapterDocument67 pagesIntroducing Large Rivers Gupta Avijit Full Chaptersharon.woods690100% (5)
- Lecture 7 - Landforms, Mountains and PlateausDocument14 pagesLecture 7 - Landforms, Mountains and Plateauskeshav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Agno River Science FinalDocument7 pagesAgno River Science FinalAureigh Kian MatiasNo ratings yet
- HEC HMS ThesisDocument13 pagesHEC HMS ThesisMaulik M RafaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Energy DissipationDocument40 pagesChapter Two: Energy Dissipationashenafi negusNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering Ce-432 LDocument18 pagesIrrigation Engineering Ce-432 LAhmed FiazNo ratings yet
- Jandora Riha EmbankmentdambreachDocument169 pagesJandora Riha EmbankmentdambreachZanele MbathaNo ratings yet
WS C2 U4 Eng Ans
WS C2 U4 Eng Ans
Uploaded by
yanaaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WS C2 U4 Eng Ans
WS C2 U4 Eng Ans
Uploaded by
yanaaCopyright:
Available Formats
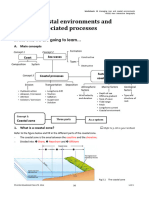
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
Unit 4 Management of river basins
In this unit, we are going to learn…
A. Main concepts
Concept 1
Channelisation
Hard strategies Bank protection
Dam and reservoir
Concept 4
Concept 2 Land use zoning
Effectiveness
River Afforestation of measures
Soft strategies
management Flood warning system
Managed retreat or do nothing
Concept 3 Education and training
Other measures
Legislation and monitoring
Concept 1:
Hard strategies of
river management Definition Types Functions
provided by rivers
1. What is river management? Refer to p. 52 in your textbook
− River management adopts a comprehensive and integrated approach to tackle river problems. It
serves three main purposes:
Reduce flooding and pollution problems
Maintain the stability of river channels
Preserve ecosystems of river basins
2. What are the hard strategies of river management? Refer to p. 52-54 in your textbook
− Hard strategies are traditional engineering measures that aim to resist the energy of running water.
− They involve building artificial structures to change the shape of the river channel.
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 29 Unit 4
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
a. Channelisation
What is it? An engineering measure to straighten, deepen and widen a river channel
What are its − To control the velocity and discharge of the river
functions? − To reduce the risk of flooding
Refer to Fig.4.1 and answer the questions.
1. Give evidence to support that the river is
channelised.
The rive channel is straight in shape / Little
vegetation found on the river banks / the river banks
are paved with concrete which means human
modifications have been taken
Fig.4.1 A channelised river
2. What are the changes in the following characteristics of the river after channelisation?
Channel depth Increase / Decrease Sinuosity Higher / Lower
Channel width Increase / Decrease River velocity Increase / Decrease
Channel gradient Increase / Decrease Bankfull discharge Increase / Decrease
3. Explain why channelisation can reduce the risk of flooding with reference to the changes above.
River velocity has increased so that excess floodwater can be discharged away rapidly
Bankfull discharge has increased which means the maximum capacity of the river has increased
b. River bank protection
What is it? − Building of artificial structures such as dykes, ripraps, gabions and groynes
along the river banks
− Below are two examples:
Gabion: Metal cages filled with rocks
Riprap: Large rocks piled up along the
river banks
What are its − To disperse energy of flowing water and reduce erosion of river banks
functions? − To raise the river banks and increase the water-holding capacity of a river
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 30 Unit 4
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
Refer to Fig.4.2 and answer the questions.
1. Identify the type of bank protection in Fig.4.2.
Groynes
2. What kind of materials is it usually made of?
Stones / Concrete
3. What is its function? Fig.4.2 A bank protection measure
To lower river velocity by extending from the banks /
hence to protect the banks from erosion
c. Dam and reservoir
What is it? − Dams are built across a river to control the amount of discharge
− Reservoirs are built behind the dams for storing water
What are its Dam construction is usually a multi-purpose scheme that brings many benefits:
functions? Regulates river flow and prevents flooding
Reservoir stores water for irrigation and other uses
Provides hydroelectricity
Improves navigation in rivers
Refer to Fig.4.3 and answer the questions.
1. Identify the project shown in the photo.
Three Gorges Project
2. In which course of the Chang Jiang is it built?
Middle course
3. Name two main objectives of the project. Fig.4.3 A project along the Chang Jiang
Flood control / Provide hydroelectricity
4. Many government officials support the project. Why?
The project can reduce the risk of flooding in downstream areas, protecting the life and property of
millions of people / The supply of hydroelectricity reduces the dependence on coal / reduces CO2
emission / provides water use in dry seasons
5. Suggest some disadvantages of the project.
Needs huge investment / Extensive areas of forests and valleys are flooded / Loss of important
historical and cultural heritages / Millions of people have to be relocated / Damming of the river
reduces the supply of nutrient-rich sediment to downstream areas
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 31 Unit 4
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
Concept 2:
Soft strategies of
river management Definition Types Functions
provided by rivers
1. What are the soft strategies of river management? Refer to p. 54-56 in your textbook
− Soft strategies are works with the nature to reduce the impact of erosion, instead of preventing it.
− Their construction and maintenance are usually (more / less) expensive than hard strategies.
Identify the soft strategies shown in the figures below. Answer the questions as well.
a. Type of strategy: Land use zoning
Risk of flooding (increases / b. How does it work?
decreases) away from the river − Assess the risk of flooding on different parts of the floodplain
channel − Assign appropriate land uses to reduce the impact of flooding
− The closer to the river banks, the (higher / lower) the risk of
flooding, and density of development should be (lower /
higher)
− What development is the best at the river bank?
Farming Wetland park Housing development
a. Type of strategy: Afforestation
b. How does it work?
− Vegetation protects the river banks from erosion
− It also promotes infiltration and reduces surface runoff
a. Type of strategy: Flood warning system
b. How does it work?
− Advise people to carry out immediate strategies to reduce the
impacts of imminent floods
− e.g. placing sand bags, evacuating to shelters
a. Type of strategy: Managed retreat or do nothing
b. How does it work?
− Adopted in places with low economic value or no significant
risks to people
− Allows the river to flood naturally
− Sometimes it is called managed flooding
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 32 Unit 4
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
Concept 3:
Other measures of
river management Types Functions
provided by rivers
1. What are the other strategies of river management? Refer to p. 56 in your textbook
Purpose Example
a. Education and − To raise the awareness of − Information leaflets to update the
training stakeholders and the public of public and the stakeholders about
river management practices and government policies and
environmental conservation corresponding responsibilities
(Fig.4.4)
− Organise training programmes and
seminars for farmers and business
sectors on river-friendly farming
methods and pollution-reduction
technologies
b. Legislation and − To protect river ecosystem − Country Parks Ordinance
monitoring − To reduce pollution − Set up water quality monitoring
stations
1. Guess the reasons for the government to
implement the programme.
Many village houses do not have proper
sewerage collection and treatment
facilities
Growing population living in village
houses
Protect streams and rivers from pollution
2. Under the programme, what responsibilities do
village house owners have?
Carry out the sewer connection from
Sewage from village house their houses to the terminal connection
point
Terminal connection point Bear the future maintenance costs
To sewage
Public sewer
treatment works
Fig.4.4 A brief outline of the programme
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 33 Unit 4
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
Concept 4:
Effectiveness of
different measures Benefits vs. Costs
1. How effective are these management methods? Refer to p. 57 in your textbook
The table below summarises the various methods in river management. Give ONE benefit and ONE cost for
each method.
Which river problem
Benefit Cost
does it tackle?
Channelisation
Flooding
Refer to textbook p.57
A. Hard for the answers.
Bank protection
engineering Flooding
strategies
Dams and reservoirs
Flooding
Land use zoning
Flooding
Afforestation Soil erosion /
B. Soft Flooding
engineering
strategies Flood warning system
Flooding
Managed retreat or do
nothing Flooding
Education and training Water pollution
and ecosystem
disturbance
C. Other
measures Water pollution
Legislation
and ecosystem
disturbance
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 34 Unit 4
Worksheets: C2 Managing river and coastal environments
HKDSE New Interactive Geography
Extension Flooding problem in Hong Kong
According to the Drainage Services Department, only 11 flooding black spots remained in Hong Kong in
2014 (Table A). The two major black spots are located in Yuen Long and Tai Po (Table B).
Hong Kong Island 3 Location District
Kowloon 1 Shek Wu Wai Yuen Long
New Territories 7 Ting Kok Road Tai Po
Source: DSD Source: DSD
Table A Distribution of flooding black spots in Table B Two major flooding black spots in Hong Kong in 2014
Hong Kong in 2014
1. In which part of Hong Kong are most flooding black spots located?
New Territories
2. Browse the website of the Drainage Services Department
(http://www.dsd.gov.hk/EN/Flood_Prevention/index.html) and fill in the following information.
Cause of flooding Short-term measure Long-term measure
Shek Wu Wai Low-lying area / Drainage Regular desilting of channel Drainage
channels do not have enough / Drainage improvement improvement works
capacity works
Ting Kok Road Low-lying area / Depletion of Carry out desilting of Drainage
flood storage due to channel when necessary / improvement works
landfilling / Blockage of inlets Installation of grills at the
and outlets of embedded inlet of the pipes /
pipes by tree trunks, rubbish Removal of substructure at
and construction materials the outlet of the pipes
3. a. Wan Chai is a minor flooding black spot in Hong Kong Island. Why does flooding occur there?
Extensive concrete-paved areas result in rapid surface runoff when there is heavy rain / Low-lying
relief / It is an old urban area that the storm water drainage system was built long time ago of
lower protection standard
b. Browse the website and compare the mitigation measures carried out in Wan Chai. Are they
different from those above? Why?
Different measures are carried out in Wan Chai / There are no river channels in Wan Chai /
Rainwater is only removed via the storm water drainage system / However, upgrading of the
system is difficult and takes time due to high development density
© Aristo Educational Press LTD. 2014 35 Unit 4
You might also like
- River Training Structures - GroynesDocument17 pagesRiver Training Structures - GroynesShabana Khan67% (3)
- Floods and DroughtsDocument15 pagesFloods and DroughtsVaani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 26043514chapter Five - River Training and Flood ControlDocument26 pagesLecturenote - 26043514chapter Five - River Training and Flood ControlAnu PathakNo ratings yet
- NWP0 REPL1 Concepts 0 and 0 MethodsDocument27 pagesNWP0 REPL1 Concepts 0 and 0 MethodsGEF Curso online HEC-HMSNo ratings yet
- Uwater Resource EnvironmentrDocument27 pagesUwater Resource EnvironmentrNguyen Van KienNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 River Training WorksDocument28 pagesChapter-4 River Training WorksAbdulbasit Aba BiyaNo ratings yet
- Peter Robins PaperDocument7 pagesPeter Robins PaperArief Danial RahmanNo ratings yet
- River Engineering and Stream Restoration: P. Julien S. IkedaDocument37 pagesRiver Engineering and Stream Restoration: P. Julien S. IkedaDa VeNo ratings yet
- Flood Control-Technical Standards and Guidelines For Planning and DesignDocument144 pagesFlood Control-Technical Standards and Guidelines For Planning and Designacumen architects and planners ltdNo ratings yet
- Irrigation (Flood Control)Document5 pagesIrrigation (Flood Control)Vergel De TorresNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Reservoir Sediment Routing by Flushing, Replenishing, and Bypassing Sediments in Japanese River BasinsDocument8 pagesIntegrated Management of Reservoir Sediment Routing by Flushing, Replenishing, and Bypassing Sediments in Japanese River BasinsPedroNo ratings yet
- CBP 13369Document65 pagesCBP 13369jagath2005ukNo ratings yet
- Design Presentation Flood Control StructuresDocument17 pagesDesign Presentation Flood Control StructuresNowell PenoniaNo ratings yet
- Title of Case Study:: Oroklini Wetland Restoration in CyprusDocument4 pagesTitle of Case Study:: Oroklini Wetland Restoration in CyprusCHALLA MOUNICANo ratings yet
- WWF Valuing RiversDocument35 pagesWWF Valuing RiversCherry Rose MontojoNo ratings yet
- Public Consultation: On The River Basin Management Plan FOR IRELAND (2018-2021)Document104 pagesPublic Consultation: On The River Basin Management Plan FOR IRELAND (2018-2021)mao sanmiguelNo ratings yet
- HydroDocument26 pagesHydroAhmad BilaalNo ratings yet
- Open Drains and Channels DesignDocument29 pagesOpen Drains and Channels DesignNizar SeraNo ratings yet
- Draft Policy On Sediment Mgmt-June2017Document23 pagesDraft Policy On Sediment Mgmt-June20171sumit9876No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Stormwater Treatment ElementsDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Stormwater Treatment ElementsZhang Han XiangownnoobzNo ratings yet
- What Is River Restoration Final PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Is River Restoration Final PDFArsalan MakhdoomiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sediment Management in Hydropower Projects CWC 2018Document16 pagesGuidelines For Sediment Management in Hydropower Projects CWC 2018ManojNo ratings yet
- 12 - Russo - Channel Maintenance and Coastal Restoration in LouisianaDocument14 pages12 - Russo - Channel Maintenance and Coastal Restoration in LouisianaChun Wai SooNo ratings yet
- Water Resources and EngineeringDocument14 pagesWater Resources and EngineeringEunice Joy Tabucanon VillegasNo ratings yet
- Water Sensitive Urban Design - A Stormwater Management PerspectiveDocument44 pagesWater Sensitive Urban Design - A Stormwater Management PerspectiveNor Hidayah Mohd RazaliNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic StructureDocument11 pagesHydraulic StructureSuman HazamNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Flood Retention BasinsDocument17 pagesSustainable Flood Retention BasinsPiotr GrabowieckiNo ratings yet
- IX DrainageDocument2 pagesIX DrainageShalini ThakurNo ratings yet
- Wsud Tech Guidelines PDFDocument351 pagesWsud Tech Guidelines PDFTravis SmithNo ratings yet
- WS C2 U5 Eng AnsDocument7 pagesWS C2 U5 Eng AnsyanaaNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline Flood ControlDocument6 pagesTopic Outline Flood ControlCathy AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Hydrolink 2018 3Document32 pagesHydrolink 2018 3Kheler SernaqueNo ratings yet
- River Training Works: 3.1 ObjectivesDocument14 pagesRiver Training Works: 3.1 Objectivestesh100% (3)
- Factsheet River enDocument3 pagesFactsheet River enPetra DelgadoNo ratings yet
- DrainageDesignGuide PDFDocument795 pagesDrainageDesignGuide PDFEric ChanNo ratings yet
- Restoration Planning & DesignDocument8 pagesRestoration Planning & DesignAquiles Berrocal RodriguezNo ratings yet
- River Landscapes in The UK - Answer SheetDocument5 pagesRiver Landscapes in The UK - Answer SheetKarlina MikekNo ratings yet
- Irrigation and Drainage DevelopmentDocument31 pagesIrrigation and Drainage Developmentebagalan2022No ratings yet
- Water Resources System Modeling: River Basin Planning and ManagementDocument22 pagesWater Resources System Modeling: River Basin Planning and ManagementRas MekonnenNo ratings yet
- IWRM Report Submitted by Alemu Tezera Hung Quach and Thuy BuiDocument17 pagesIWRM Report Submitted by Alemu Tezera Hung Quach and Thuy Buiismail abibNo ratings yet
- Guideline 02Document70 pagesGuideline 02resti sucilestariNo ratings yet
- JFM Fevnfm TKDocument25 pagesJFM Fevnfm TKHanaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyXendra AqeylaaNo ratings yet
- MoM International Workshop On Coastal Reservoir, 26-27 October 2020Document27 pagesMoM International Workshop On Coastal Reservoir, 26-27 October 2020Yasruddin MtNo ratings yet
- 01river Engineering 13-14Document14 pages01river Engineering 13-14arsathNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Management 002Document112 pagesWater Resource Management 002Kumaran ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- WRE Course OutlineDocument2 pagesWRE Course OutlineJustine Anthony SalazarNo ratings yet
- Territorial Cohesion and Water Management in EuropeDocument82 pagesTerritorial Cohesion and Water Management in Europepedro_arsenioNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: WRPM and System ConceptDocument44 pagesChapter-2: WRPM and System Conceptkidus sileshNo ratings yet
- CH 12 River Training and Bank Protection PDFDocument15 pagesCH 12 River Training and Bank Protection PDFKreen132100% (1)
- Lucrare BadalutaDocument4 pagesLucrare BadalutanistoraliNo ratings yet
- Synopsis TemplateDocument5 pagesSynopsis TemplatePrashant MallickNo ratings yet
- Ocean - Chile. COP24Document17 pagesOcean - Chile. COP24Eduardo Silva BesaNo ratings yet
- Keeping Rivers Alive PDFDocument40 pagesKeeping Rivers Alive PDFmv.No ratings yet
- River Frontdevelopment 140322040936 Phpapp02Document35 pagesRiver Frontdevelopment 140322040936 Phpapp02Ar Jivan ShindeNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability Analysis PDFDocument23 pagesVulnerability Analysis PDFAlbina LaraNo ratings yet
- ReportfinalDocument98 pagesReportfinalMae DalangpanNo ratings yet
- River Training and Flood Control: Chapter FiveDocument26 pagesRiver Training and Flood Control: Chapter FiveHassan Abib BasalNo ratings yet
- River Conservation and ManagementFrom EverandRiver Conservation and ManagementPhilip BoonNo ratings yet
- Management of Marine Protected Areas: A Network PerspectiveFrom EverandManagement of Marine Protected Areas: A Network PerspectivePaul D. GoriupNo ratings yet
- COMP2501 - Assignment - 1 - Questions - RMD 2Document7 pagesCOMP2501 - Assignment - 1 - Questions - RMD 2yanaaNo ratings yet
- WS C2 U6 Eng AnsDocument7 pagesWS C2 U6 Eng AnsyanaaNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Coordination in Humans: ExerciseDocument9 pagesCH 16 Coordination in Humans: ExerciseyanaaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyyanaaNo ratings yet
- Math Factorization of Polynomials Ex. Suggested AnswerDocument22 pagesMath Factorization of Polynomials Ex. Suggested AnsweryanaaNo ratings yet
- Answers: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesAnswers: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyyanaaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Money Creation by Topic Past Paper Marking SchemeDocument3 pagesCh. 9 Money Creation by Topic Past Paper Marking SchemeyanaaNo ratings yet
- Biology CH.41Document56 pagesBiology CH.41yanaaNo ratings yet
- Aristo Biology Mock Exam 2020Document58 pagesAristo Biology Mock Exam 2020yanaaNo ratings yet
- Aristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersDocument9 pagesAristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersyanaaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Development Act of 2020Document369 pagesWater Resources Development Act of 2020Brian MastNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Geo Lesson 7Document18 pagesClass 8 Geo Lesson 78C-Ahmed Musawwir - Dj067No ratings yet
- STATUS OF DESIGN IN CANALS DIVISION, IDRB - Details of Work For Which Additional Details Sought From Field OfficesDocument1 pageSTATUS OF DESIGN IN CANALS DIVISION, IDRB - Details of Work For Which Additional Details Sought From Field OfficesnidhisasidharanNo ratings yet
- 1-India Relief Features - 1-16Document16 pages1-India Relief Features - 1-16saijitesh.gNo ratings yet
- GFD Water Rescue ManualDocument42 pagesGFD Water Rescue Manualtaufik_maulana87No ratings yet
- Assignment 01: Irrigation EngineeringDocument10 pagesAssignment 01: Irrigation EngineeringMoudud Ul Islam AwanNo ratings yet
- TD-39 Using HEC-RAS For Dam Break StudiesDocument74 pagesTD-39 Using HEC-RAS For Dam Break StudiesMarcele ColferaiNo ratings yet
- Godavari Water Dispute Tribunal AwardDocument221 pagesGodavari Water Dispute Tribunal AwardSampath Bulusu100% (1)
- Bundh BreedingDocument3 pagesBundh BreedingNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- South Centrral California Coast Steelhead Threats Assessment SummaryDocument87 pagesSouth Centrral California Coast Steelhead Threats Assessment SummaryGreenspace, The Cambria Land TrustNo ratings yet
- Te Kahui Kaupeka Conservation Park PDFDocument3 pagesTe Kahui Kaupeka Conservation Park PDFeaglebrdNo ratings yet
- Physiography of Flowing Water: OutlineDocument12 pagesPhysiography of Flowing Water: OutlineHasaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Bigarella 1973Document68 pagesBigarella 1973Leandro FernandesNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Analysis For The Proposed BridgeDocument8 pagesHydrological Analysis For The Proposed BridgeRoshan khadkaNo ratings yet
- Is 6966 1989 (PART 1) Hydraulics Design of Barrages and WeirsDocument12 pagesIs 6966 1989 (PART 1) Hydraulics Design of Barrages and Weirsarvind.singhNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources of BiharDocument1 pageNatural Resources of BiharManaal KhanamNo ratings yet
- Study of Hydropower Plants of Himachal PradeshDocument65 pagesStudy of Hydropower Plants of Himachal PradeshBhavesh KaushalNo ratings yet
- With Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western MountainsDocument3 pagesWith Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western Mountainshajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- Hoover DamDocument22 pagesHoover DamJERRY PAUL VARGHESENo ratings yet
- Design Aspects: 6.0 GeneralDocument22 pagesDesign Aspects: 6.0 GeneralshamsuNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 27Document2 pagesCase Study No. 27Felix De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Work Program For Excavation For DamDocument1 pageWork Program For Excavation For DamBernie QuepNo ratings yet
- Project RAC River Awareness and CleanlinessDocument8 pagesProject RAC River Awareness and CleanlinessKyla Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- Introducing Large Rivers Gupta Avijit Full ChapterDocument67 pagesIntroducing Large Rivers Gupta Avijit Full Chaptersharon.woods690100% (5)
- Lecture 7 - Landforms, Mountains and PlateausDocument14 pagesLecture 7 - Landforms, Mountains and Plateauskeshav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Agno River Science FinalDocument7 pagesAgno River Science FinalAureigh Kian MatiasNo ratings yet
- HEC HMS ThesisDocument13 pagesHEC HMS ThesisMaulik M RafaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Energy DissipationDocument40 pagesChapter Two: Energy Dissipationashenafi negusNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering Ce-432 LDocument18 pagesIrrigation Engineering Ce-432 LAhmed FiazNo ratings yet
- Jandora Riha EmbankmentdambreachDocument169 pagesJandora Riha EmbankmentdambreachZanele MbathaNo ratings yet