Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsBus Acc. 10
Bus Acc. 10
Uploaded by
sab1) Accounting is a tool used to measure the financial position of businesses and other entities. It involves recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions.
2) There are three main types of business entities: sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Sole proprietorships have a single owner, partnerships have multiple owners who share profits and losses, and corporations are legally separate from their owners.
3) Entrepreneurship plays a significant role in a country's economy by encouraging competition, helping the economic recovery process, and facilitating monetary flow. The government supports entrepreneurship through agencies that register and regulate different types of businesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- English Translation of A Birth Certificate From Honduras PDFDocument1 pageEnglish Translation of A Birth Certificate From Honduras PDFDulce m vazquez67% (6)
- John Deere 4055 4255 4455 4555 4755 4955 Shopmanual Sec WatDocument20 pagesJohn Deere 4055 4255 4455 4555 4755 4955 Shopmanual Sec Watdoris97% (32)
- IGCSE Business Studies Revision NotesDocument11 pagesIGCSE Business Studies Revision NotesWambui Kahende100% (3)
- American Girl Presentaton Team-6Document9 pagesAmerican Girl Presentaton Team-6Ashish Kaushal RanjanNo ratings yet
- Bin Card Format ExcelDocument6 pagesBin Card Format Excellsatchithananthan100% (3)
- FF 2021 A+ Student Notes Unit 3 Business Management FINALDocument77 pagesFF 2021 A+ Student Notes Unit 3 Business Management FINALhenwytran1No ratings yet
- Entrep - 1st Mid QTRDocument9 pagesEntrep - 1st Mid QTRGrace Anne CacayanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Intro To EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - Intro To EntrepreneurshipAldrin VerganoNo ratings yet
- Building Your Knowledge Things You Have To Do To Start Your Business 1Document8 pagesBuilding Your Knowledge Things You Have To Do To Start Your Business 1Velpandian ManiNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 01: PPT by DglanoyDocument12 pagesEntrepreneurship 01: PPT by DglanoyJust HelpingNo ratings yet
- Business AS NotesDocument114 pagesBusiness AS NotesMohamedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business NotesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business Notesmusfiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentCzarina Espiritu BagsitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentCzarina Espiritu BagsitNo ratings yet
- ENTREPDocument11 pagesENTREPChristian SubaldoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Undertake"Document7 pagesEntrepreneurship: Undertake"KIMLARAANDREA MARIANONo ratings yet
- BUSFIN - MidDocument6 pagesBUSFIN - MidCanceran CarolynNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting and BusinessDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Accounting and BusinessJames Matthew BedayoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Unit 4Document14 pagesEntrepreneurship Unit 4renzbiala123No ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument12 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPAnne Gwynneth RadaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Economic IssuesDocument25 pagesContemporary Economic IssuesjustineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To FinanceDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Financenurfatimah473No ratings yet
- Entrep 4Document3 pagesEntrep 4Jeanne Grazielle PogataNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Forms of BusinessDocument35 pagesTopic 1 - Forms of Businessrikitiksev27No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Week 1 Session 1 Expectations: Skills Needed To Start Your Own BusinessDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurship Week 1 Session 1 Expectations: Skills Needed To Start Your Own BusinessRachel BandiolaNo ratings yet
- B&M Ebook 1st ED17-20 PDFDocument4 pagesB&M Ebook 1st ED17-20 PDFCarlos Sergio Robles MejíaNo ratings yet
- Ent51112 PrelimsDocument15 pagesEnt51112 PrelimsPrecious GregorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2@2016 4MEngDocument12 pagesChapter 2@2016 4MEngyiheyis mulatuNo ratings yet
- FinMan Reviewe Chapter 4to6Document14 pagesFinMan Reviewe Chapter 4to6Jannah May BolanoNo ratings yet
- Concise Notes Three Topics 64461088d391cDocument18 pagesConcise Notes Three Topics 64461088d391cShehzar Ali100% (1)
- The Dynamic Business Environment-1Document47 pagesThe Dynamic Business Environment-1Avneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Igse Accounting: by Ms Tara EsaDocument89 pagesIgse Accounting: by Ms Tara EsaDIllaNo ratings yet
- Part1 ReviewDocument22 pagesPart1 ReviewNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial MindDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurial MindShenielyn Bartolome NapolitanoNo ratings yet
- Business - Section 4 - Jaime TarlieDocument11 pagesBusiness - Section 4 - Jaime Tarliejaime.tarlieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Danica SuperalesNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Katz - ESB - 6e - Chap001 - PPTDocument13 pagesWeek 1-Katz - ESB - 6e - Chap001 - PPTHind AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz - Financial ManagementDocument4 pagesQuick Quiz - Financial ManagementJanine Lenie PadronesNo ratings yet
- Business OwnershipDocument3 pagesBusiness OwnershipJeenal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 InterDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Intermuhamed ademNo ratings yet
- Organization Management Module 15Document12 pagesOrganization Management Module 15Michelle AJCNNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Katz ESB 6e Chap001Document13 pagesWeek 1-Katz ESB 6e Chap001cristianaNo ratings yet
- Abakkus All Cap PMS - PPT - Jan 24Document24 pagesAbakkus All Cap PMS - PPT - Jan 24lalitNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument60 pagesChapter FourKebrie GezahegnNo ratings yet
- Business OwnershipDocument3 pagesBusiness Ownershipzaara.kauserxNo ratings yet
- Besor Y1t1Document23 pagesBesor Y1t1tenderjuicyiyyyNo ratings yet
- Organizational Plan ReviewerDocument3 pagesOrganizational Plan ReviewerJohnric ArtilloNo ratings yet
- Applied Entrepreneurship Reviewer 1Document12 pagesApplied Entrepreneurship Reviewer 1Multifandom GirlNo ratings yet
- 2011-0021 37 Enterpreneurship PDFDocument22 pages2011-0021 37 Enterpreneurship PDFswankyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesModule 1 Entrepreneurshipheart.sopeaNo ratings yet
- FBM Module 1Document19 pagesFBM Module 1Sassy BitchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - MODES OF ENTERING INTERNATIONAL BUSINESSDocument11 pagesChapter 5 - MODES OF ENTERING INTERNATIONAL BUSINESSAngelica CeleridadNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Bisnis Chapter 6Document24 pagesPengantar Bisnis Chapter 6Raiyan Raju ManwaniNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document18 pagesCH 2ዘንገና ቲዩብNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Types of Business OrganizationsDocument1 pageWeek 4 Types of Business OrganizationsThrolin ThundershieldNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE 3.5.1 and 3.52 - Classification of Businesses and Small Firms - Miss PatelDocument24 pagesCIE IGCSE 3.5.1 and 3.52 - Classification of Businesses and Small Firms - Miss PatelJingyao HanNo ratings yet
- Arch Firms TypesDocument51 pagesArch Firms Typesldelosreyes122No ratings yet
- 20 To 22 - GE05 - FECGBL - G.company Administration & Finance (25%) - by MD - Monowar Hossain FCMA, CPA, FCS, ACADocument12 pages20 To 22 - GE05 - FECGBL - G.company Administration & Finance (25%) - by MD - Monowar Hossain FCMA, CPA, FCS, ACAadnan.shajonNo ratings yet
- Nature and Forms of Business OrganizationsDocument19 pagesNature and Forms of Business OrganizationsJL ToralNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 ReviewDocument5 pagesFabm 1 ReviewIya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Org and MGT, Q1, W4Document9 pagesOrg and MGT, Q1, W4Raquel MCborondiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - : Modes of Entering International BusinessDocument52 pagesChapter 5 - : Modes of Entering International BusinessRheo DemetrialNo ratings yet
- Forming A Business. TKDocument42 pagesForming A Business. TKUmut baran ÖzNo ratings yet
- Home Based Business Ideas: Business Ideas You Can Do With Little Or No MoneyFrom EverandHome Based Business Ideas: Business Ideas You Can Do With Little Or No MoneyNo ratings yet
- Countryfocus KazakhstanDocument10 pagesCountryfocus KazakhstanDouglas FunkNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 PortfolioDocument11 pagesBab 4 PortfolioWan SazarenaNo ratings yet
- 1264 SNAP PID ModuleDocument7 pages1264 SNAP PID ModuleAlexander Charry GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 3 Nov 2020Document1 pageSteel Design 3 Nov 2020IaamIiaann100% (1)
- Abu Dhabi With Dubai Bonanza 445 1 1 2390 FTPL-BI-1439Document15 pagesAbu Dhabi With Dubai Bonanza 445 1 1 2390 FTPL-BI-1439Navnitlal ShahNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of BD With Comments N Case Laws by Latifur RahmanDocument275 pagesThe Constitution of BD With Comments N Case Laws by Latifur RahmanMd Ahsan-Ul- Kabir100% (1)
- 5.3. 402020-01391-08-PI-SPC-0002 Rev0 PDFDocument136 pages5.3. 402020-01391-08-PI-SPC-0002 Rev0 PDFsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Application For ECFMG Certification - InstructionsDocument2 pagesApplication For ECFMG Certification - InstructionszidaneNo ratings yet
- Knorish Sales Funnels-1Document16 pagesKnorish Sales Funnels-1rajesh mouliNo ratings yet
- PCUPDocument6 pagesPCUPBonn PustaNo ratings yet
- GDXDocument30 pagesGDXsatishjsrNo ratings yet
- THE IKEA APPROACH - ViralDocument2 pagesTHE IKEA APPROACH - ViralfredrickyadavNo ratings yet
- Wartung Assyst Plus 204 enDocument32 pagesWartung Assyst Plus 204 enKent Wai100% (1)
- Chapter N Shear CenterDocument6 pagesChapter N Shear CenterDem Austria EspinoNo ratings yet
- 1-5 Highway ProgrammingDocument12 pages1-5 Highway ProgrammingBeau NorNo ratings yet
- Company Profile CLS-SDocument12 pagesCompany Profile CLS-SwagihNo ratings yet
- TLEICT9 Module (Week 1) PDFDocument5 pagesTLEICT9 Module (Week 1) PDFAN GelNo ratings yet
- BEng (Hons) Software Engineering - 12 Months (Top-Up Degree) - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKDocument19 pagesBEng (Hons) Software Engineering - 12 Months (Top-Up Degree) - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKLSBRNo ratings yet
- Duolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerDocument7 pagesDuolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerMaria AgnesNo ratings yet
- Amie Syllabus Sec B MiningDocument19 pagesAmie Syllabus Sec B MiningSangeet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Survey of Road DataDocument23 pagesSurvey of Road DataMuddasar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Welcome Brochure 2020-2021Document25 pagesWelcome Brochure 2020-2021George IashviliNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in MetalsDocument5 pagesCorrosion in MetalsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Query & BIDocument14 pagesPower Query & BIzubair muhammad0% (2)
- Mindset MattersDocument19 pagesMindset Mattersracer100% (2)
- Hungary Amends Trademark Act - LexologyDocument2 pagesHungary Amends Trademark Act - LexologyHoward TsaiNo ratings yet
Bus Acc. 10
Bus Acc. 10
Uploaded by
sab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pages1) Accounting is a tool used to measure the financial position of businesses and other entities. It involves recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions.
2) There are three main types of business entities: sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Sole proprietorships have a single owner, partnerships have multiple owners who share profits and losses, and corporations are legally separate from their owners.
3) Entrepreneurship plays a significant role in a country's economy by encouraging competition, helping the economic recovery process, and facilitating monetary flow. The government supports entrepreneurship through agencies that register and regulate different types of businesses.
Original Description:
Original Title
BUS_ACC._10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Accounting is a tool used to measure the financial position of businesses and other entities. It involves recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions.
2) There are three main types of business entities: sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Sole proprietorships have a single owner, partnerships have multiple owners who share profits and losses, and corporations are legally separate from their owners.
3) Entrepreneurship plays a significant role in a country's economy by encouraging competition, helping the economic recovery process, and facilitating monetary flow. The government supports entrepreneurship through agencies that register and regulate different types of businesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesBus Acc. 10
Bus Acc. 10
Uploaded by
sab1) Accounting is a tool used to measure the financial position of businesses and other entities. It involves recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions.
2) There are three main types of business entities: sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Sole proprietorships have a single owner, partnerships have multiple owners who share profits and losses, and corporations are legally separate from their owners.
3) Entrepreneurship plays a significant role in a country's economy by encouraging competition, helping the economic recovery process, and facilitating monetary flow. The government supports entrepreneurship through agencies that register and regulate different types of businesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
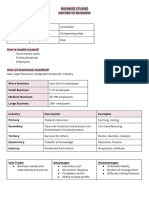
Business Accounting QUARTER 3 | S.Y.
2023-2024
☆ Opening and Managing self-owned
Lesson 1: Entrepreneurship business
⤷ Businesses that are being
☆ It is a process of actions of an managed by others for the benefit
entrepreneur who is always in search of of the owners do not fall within the
something new to exploit new ideas into sphere of entrepreneurship.
gainful opportunities by accepting the risk
and uncertainty of the enterprise (De
Guzman, 2018) TYPES OF BUSINESS: Forms of
★ It is a science of converting ideas into Ownership
business (Abad, 2009)
Sole Proprietorship (Reg. w/ DTI)
Business vs Entrepreneurship
★ The simplest and easiest business to
● Businesses focus more on providing
organize.
products or services for the purpose of
☆ Controlled and owned by an
making profit (not wealth-creating
individual/entrepreneur
venture)
★ The owner is the sole responsible of all the
● Entrepreneurship on the contrary
liabilities of the business
focuses on generating new value, and
☆ The sole proprietors are considered single
this value could be social, emotional,
taxpayers.
aesthetic, and/or financial.
★ Single ownership
☆ No sharing of profit and loss
Salient Features of Entrepreneurship
★ One man’s capital
☆ Art of Correct Practices
☆ Unlimited Liability
⤷ There is constant change which
★ Less legal formalities
denotes movements and
☆ One man control
innovation.
☆ Wealth-Creating Venture
Partnership (Reg. w/ SEC)
⤷ Entrepreneurship is operating within
★ It is owned by two or more persons who
the concept of wealth creation
contribute resources into the entity
rather than profit generation.
☆ Partners divide the the profits of the
☆ Provides Valuable Goods and Services
business among themselves
⤷ The entrepreneur defines value
★ They have mutual agreement on how the
from the perspective of the buyers
decisions will be made and on how future
and not only from his/her own
partners will be admitted and how
because what is valuable to the
arguments will be resolved.
entrepreneur may not be of any
☆ Partnerships can be general or limited
value to the customers.
Page 1 Grade 10 | Semester 1 | Quarter 3 | Business Accounting Good Luck !
Corporation (Reg. w/ SEC) How significant is Entrepreneurship in the
★ It has a distinct legal personality separate economy of the country?
from its owners. ☆ It encourages competitiveness and
☆ Private corporations may have a minimum thereby challenges entrepreneurs to keep
of five members with at least one member improving their products and services.
which is a natural born Filipino and a ★ It helps find an entrepreneurial niche in the
citizen of the country. world market.
★ It is owned and established under the ☆ It helps hasten the economic recovery
Corporation Code of the Philippines and process of the Philippines during financial
regulated by the SEC. turmoil or crackdown.
☆ The minimum paid-up capital required of ★ It facilitates the smooth flow of money in
corporations in the Philippines is PHP the local market.
5,000.00. ☆ It assists the national government in its
★ Types of Corporation desire to have favorable economic ratings
⤷ Stock Corporation in the world market.
⤷ Non-stock Corporation
Cooperative (Reg. w/ CDA)
Types of Business according to the
★ A cooperative is a business organization Nature of Activities
owned by a group of individuals and is
operated for their mutual benefit. ● Service Business - this provides intangible
☆ The persons making up the group are goods or services to customers.
called members. ☆ ex: accounting firms, law firms
★ Cooperatives may be incorporated or ○ Merchandising Business - usually generate
unincorporated profit by providing markup price on their
goods available for sale.
RA no. 9501 - An Act to promote Entrepreneurship by - sell tangible products; buy and sell
Strengthening Development and Assistance Programs - buys finished or almost finished
to Micro, Small and Medium Scale Enterprises goods from their supplier then
resells them to customers
SEC. 3. Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) as ☆ ex: bookstores, clothing stores,
Beneficiaries. —
department stores, grocery
MSMEs shall be defined as any business activity or
● Manufacturing Business - manufacturers
enterprise engaged in industry, agribusiness and/or or producers
services, whether single proprietorship, cooperative,
- buy materials, convert them into
partnership or corporation whose total assets, inclusive
products, and then sell the
of those arising from loans but exclusive of the land on
products to other companies or to
which the particular business entity’s office, plant and
equipment are situated, must have value falling under the final customers
the following categories: ☆ ex: URC, Susie’s Cuisine, San
Miguel Corp, furniture businesses,
Micro : not more than ₱3,000,000 shoe makers, potteries
Small : ₱3,000,001 - ₱15,000,000 ○ Agriculture and Mining Companies - these
Medium : ₱15,000,001 - ₱100,000,000 companies are engaged in producing or
exploration of raw or natural materials
such as plants.
Page 2 Grade 10 | Semester 1 | Quarter 3 | Business Accounting Good Luck !
● Hybrid Business - multinational businesses
are companies that may be classified in
more than one type of business
☆ ex: restaurants, salons
☆ Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) -
business and name registration
★ Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) -
business tax
☆ Securities and Exchange Commission
(SEC) - registration and supervision of
corporations and securities
★ Cooperative Development Authority
(CDA) - register all types of cooperatives
Page 3 Grade 10 | Semester 1 | Quarter 3 | Business Accounting Good Luck !
★ Accounting is a tool to measure the
Lesson 2: Accounting financial position of any entity involved in
The American Institution of Certified Public economic activity. Accounting is an aid to
Accountants (AICPA) defines accounting as.. management. It is a system that keeps
⤷ The art of recording, classifying, and record of financial events and analyzes
summarizing in a significant manner and them for presenting reports of the financial
in terms of money, transactions and results and position of an economic entity.
events which are, in part at least of
financial character, and interpreting the
USERS OF ACCOUNTING INFO
result thereof.
● Board of Directors
Accounting - a service to business/organizations. ○ Owners & Managers
● Employees
○ Business Partners & Stake-holders
● Creditors/Lenders
○ Government Agencies
Financial Financial Info Non-financial / invalid
★ Monetary value
Gasoline of delivery vehicle Purchase Request
⤷ Tangible
⤷ Intangible Electric consumption Savings of the workers
Example: Supermarket
☆ Tangible - cash/check/products Payment for the Kitchen Salary of the workers
★ Intangible - services of the supplies
employees/right to use space
AC units of the business
Functions of Accounting in Business
★ Accounting is a discipline, well-equipped
with techniques and methods through
which all types of transactions measurable
in terms of money or money’s worth can
be recorded, classified and summarized in
a proper and systematic way.
☆ Accounting helps present and explain
income, expenditure, profit-loss and
asset-liabilities of a particular period and
helps the management and investors to
be provided with necessary information
and statements.
Page 4 Grade 10 | Semester 1 | Quarter 3 | Business Accounting Good Luck !
06. Accounting Period
Lesson 3: GAAP
★ This principle entails a business to
The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles complete the whole accounting
➔ According to De Guzman, 2018, GAAP is a process over a specific time period.
framework and guidelines of the 07. Conservatism
accounting profession. Its purpose is to ★ The principle of conservatism gives
standard accounting concepts, principles guidance on how to record
and procedures. uncertain events and estimates.
The principle of conservatism
states that one should always
11 PRINCIPLES
consider any error on the most
01. Business Entity conservative side of any
★ A business is considered a separate transaction.
entity from the owner(s) and 08. Consistency
should be treated separately. ★ This principle states that
02. Going Concern companies should use the same
★ It assumes that an entity will accounting treatment for similar
continue to operate independently. events and transactions overtime.
03. Monetary Unit 09. Materiality Concept
★ The business financial transactions ★ This materiality concept, also called
recorded and reported should be in the materiality constraint, states
the monetary unit, such as that financial information is
Philippine peso, US dollar, Canadian material to the financial statements
dollar, etc. Thus, any non-financial if it would change the opinion or
or non-monetary information that view of a reasonable person.
cannot be measured in a monetary 10. Objectivity
unit is not recorded in the ★ This principle states that
accounting books, but instead, a accounting information and
memorandum will be used. financial reporting should be
04. Historical Cost independent and supported with
★ All business resources acquired unbiased evidence. This means
should be valued and recorded that accounting information must
based on the actual cash be based on research and facts,
equivalent or original cost of not merely a preparer's opinion.
acquisition, not the prevailing 11. Revenue Recognition Principle
market value or future value. ★ This states that revenue should be
05. Matching Concept recognized and recorded when it is
★ This principle requires that revenue realized or realizable and when it is
recorded, in a given accounting earned.
period, should be an equivalent
expense recorded, in order to show
the true profit of the business.
Page 5 Grade 10 | Semester 1 | Quarter 3 | Business Accounting Good Luck !
You might also like
- English Translation of A Birth Certificate From Honduras PDFDocument1 pageEnglish Translation of A Birth Certificate From Honduras PDFDulce m vazquez67% (6)
- John Deere 4055 4255 4455 4555 4755 4955 Shopmanual Sec WatDocument20 pagesJohn Deere 4055 4255 4455 4555 4755 4955 Shopmanual Sec Watdoris97% (32)
- IGCSE Business Studies Revision NotesDocument11 pagesIGCSE Business Studies Revision NotesWambui Kahende100% (3)
- American Girl Presentaton Team-6Document9 pagesAmerican Girl Presentaton Team-6Ashish Kaushal RanjanNo ratings yet
- Bin Card Format ExcelDocument6 pagesBin Card Format Excellsatchithananthan100% (3)
- FF 2021 A+ Student Notes Unit 3 Business Management FINALDocument77 pagesFF 2021 A+ Student Notes Unit 3 Business Management FINALhenwytran1No ratings yet
- Entrep - 1st Mid QTRDocument9 pagesEntrep - 1st Mid QTRGrace Anne CacayanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Intro To EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - Intro To EntrepreneurshipAldrin VerganoNo ratings yet
- Building Your Knowledge Things You Have To Do To Start Your Business 1Document8 pagesBuilding Your Knowledge Things You Have To Do To Start Your Business 1Velpandian ManiNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 01: PPT by DglanoyDocument12 pagesEntrepreneurship 01: PPT by DglanoyJust HelpingNo ratings yet
- Business AS NotesDocument114 pagesBusiness AS NotesMohamedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business NotesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business Notesmusfiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentCzarina Espiritu BagsitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business and Investment EnvironmentCzarina Espiritu BagsitNo ratings yet
- ENTREPDocument11 pagesENTREPChristian SubaldoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Undertake"Document7 pagesEntrepreneurship: Undertake"KIMLARAANDREA MARIANONo ratings yet
- BUSFIN - MidDocument6 pagesBUSFIN - MidCanceran CarolynNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting and BusinessDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Accounting and BusinessJames Matthew BedayoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Unit 4Document14 pagesEntrepreneurship Unit 4renzbiala123No ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument12 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPAnne Gwynneth RadaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Economic IssuesDocument25 pagesContemporary Economic IssuesjustineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To FinanceDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Financenurfatimah473No ratings yet
- Entrep 4Document3 pagesEntrep 4Jeanne Grazielle PogataNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Forms of BusinessDocument35 pagesTopic 1 - Forms of Businessrikitiksev27No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Week 1 Session 1 Expectations: Skills Needed To Start Your Own BusinessDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurship Week 1 Session 1 Expectations: Skills Needed To Start Your Own BusinessRachel BandiolaNo ratings yet
- B&M Ebook 1st ED17-20 PDFDocument4 pagesB&M Ebook 1st ED17-20 PDFCarlos Sergio Robles MejíaNo ratings yet
- Ent51112 PrelimsDocument15 pagesEnt51112 PrelimsPrecious GregorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2@2016 4MEngDocument12 pagesChapter 2@2016 4MEngyiheyis mulatuNo ratings yet
- FinMan Reviewe Chapter 4to6Document14 pagesFinMan Reviewe Chapter 4to6Jannah May BolanoNo ratings yet
- Concise Notes Three Topics 64461088d391cDocument18 pagesConcise Notes Three Topics 64461088d391cShehzar Ali100% (1)
- The Dynamic Business Environment-1Document47 pagesThe Dynamic Business Environment-1Avneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Igse Accounting: by Ms Tara EsaDocument89 pagesIgse Accounting: by Ms Tara EsaDIllaNo ratings yet
- Part1 ReviewDocument22 pagesPart1 ReviewNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial MindDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurial MindShenielyn Bartolome NapolitanoNo ratings yet
- Business - Section 4 - Jaime TarlieDocument11 pagesBusiness - Section 4 - Jaime Tarliejaime.tarlieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Danica SuperalesNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Katz - ESB - 6e - Chap001 - PPTDocument13 pagesWeek 1-Katz - ESB - 6e - Chap001 - PPTHind AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz - Financial ManagementDocument4 pagesQuick Quiz - Financial ManagementJanine Lenie PadronesNo ratings yet
- Business OwnershipDocument3 pagesBusiness OwnershipJeenal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 InterDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Intermuhamed ademNo ratings yet
- Organization Management Module 15Document12 pagesOrganization Management Module 15Michelle AJCNNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Katz ESB 6e Chap001Document13 pagesWeek 1-Katz ESB 6e Chap001cristianaNo ratings yet
- Abakkus All Cap PMS - PPT - Jan 24Document24 pagesAbakkus All Cap PMS - PPT - Jan 24lalitNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument60 pagesChapter FourKebrie GezahegnNo ratings yet
- Business OwnershipDocument3 pagesBusiness Ownershipzaara.kauserxNo ratings yet
- Besor Y1t1Document23 pagesBesor Y1t1tenderjuicyiyyyNo ratings yet
- Organizational Plan ReviewerDocument3 pagesOrganizational Plan ReviewerJohnric ArtilloNo ratings yet
- Applied Entrepreneurship Reviewer 1Document12 pagesApplied Entrepreneurship Reviewer 1Multifandom GirlNo ratings yet
- 2011-0021 37 Enterpreneurship PDFDocument22 pages2011-0021 37 Enterpreneurship PDFswankyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesModule 1 Entrepreneurshipheart.sopeaNo ratings yet
- FBM Module 1Document19 pagesFBM Module 1Sassy BitchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - MODES OF ENTERING INTERNATIONAL BUSINESSDocument11 pagesChapter 5 - MODES OF ENTERING INTERNATIONAL BUSINESSAngelica CeleridadNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Bisnis Chapter 6Document24 pagesPengantar Bisnis Chapter 6Raiyan Raju ManwaniNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document18 pagesCH 2ዘንገና ቲዩብNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Types of Business OrganizationsDocument1 pageWeek 4 Types of Business OrganizationsThrolin ThundershieldNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE 3.5.1 and 3.52 - Classification of Businesses and Small Firms - Miss PatelDocument24 pagesCIE IGCSE 3.5.1 and 3.52 - Classification of Businesses and Small Firms - Miss PatelJingyao HanNo ratings yet
- Arch Firms TypesDocument51 pagesArch Firms Typesldelosreyes122No ratings yet
- 20 To 22 - GE05 - FECGBL - G.company Administration & Finance (25%) - by MD - Monowar Hossain FCMA, CPA, FCS, ACADocument12 pages20 To 22 - GE05 - FECGBL - G.company Administration & Finance (25%) - by MD - Monowar Hossain FCMA, CPA, FCS, ACAadnan.shajonNo ratings yet
- Nature and Forms of Business OrganizationsDocument19 pagesNature and Forms of Business OrganizationsJL ToralNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 ReviewDocument5 pagesFabm 1 ReviewIya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Org and MGT, Q1, W4Document9 pagesOrg and MGT, Q1, W4Raquel MCborondiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - : Modes of Entering International BusinessDocument52 pagesChapter 5 - : Modes of Entering International BusinessRheo DemetrialNo ratings yet
- Forming A Business. TKDocument42 pagesForming A Business. TKUmut baran ÖzNo ratings yet
- Home Based Business Ideas: Business Ideas You Can Do With Little Or No MoneyFrom EverandHome Based Business Ideas: Business Ideas You Can Do With Little Or No MoneyNo ratings yet
- Countryfocus KazakhstanDocument10 pagesCountryfocus KazakhstanDouglas FunkNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 PortfolioDocument11 pagesBab 4 PortfolioWan SazarenaNo ratings yet
- 1264 SNAP PID ModuleDocument7 pages1264 SNAP PID ModuleAlexander Charry GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 3 Nov 2020Document1 pageSteel Design 3 Nov 2020IaamIiaann100% (1)
- Abu Dhabi With Dubai Bonanza 445 1 1 2390 FTPL-BI-1439Document15 pagesAbu Dhabi With Dubai Bonanza 445 1 1 2390 FTPL-BI-1439Navnitlal ShahNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of BD With Comments N Case Laws by Latifur RahmanDocument275 pagesThe Constitution of BD With Comments N Case Laws by Latifur RahmanMd Ahsan-Ul- Kabir100% (1)
- 5.3. 402020-01391-08-PI-SPC-0002 Rev0 PDFDocument136 pages5.3. 402020-01391-08-PI-SPC-0002 Rev0 PDFsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Application For ECFMG Certification - InstructionsDocument2 pagesApplication For ECFMG Certification - InstructionszidaneNo ratings yet
- Knorish Sales Funnels-1Document16 pagesKnorish Sales Funnels-1rajesh mouliNo ratings yet
- PCUPDocument6 pagesPCUPBonn PustaNo ratings yet
- GDXDocument30 pagesGDXsatishjsrNo ratings yet
- THE IKEA APPROACH - ViralDocument2 pagesTHE IKEA APPROACH - ViralfredrickyadavNo ratings yet
- Wartung Assyst Plus 204 enDocument32 pagesWartung Assyst Plus 204 enKent Wai100% (1)
- Chapter N Shear CenterDocument6 pagesChapter N Shear CenterDem Austria EspinoNo ratings yet
- 1-5 Highway ProgrammingDocument12 pages1-5 Highway ProgrammingBeau NorNo ratings yet
- Company Profile CLS-SDocument12 pagesCompany Profile CLS-SwagihNo ratings yet
- TLEICT9 Module (Week 1) PDFDocument5 pagesTLEICT9 Module (Week 1) PDFAN GelNo ratings yet
- BEng (Hons) Software Engineering - 12 Months (Top-Up Degree) - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKDocument19 pagesBEng (Hons) Software Engineering - 12 Months (Top-Up Degree) - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKLSBRNo ratings yet
- Duolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerDocument7 pagesDuolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerMaria AgnesNo ratings yet
- Amie Syllabus Sec B MiningDocument19 pagesAmie Syllabus Sec B MiningSangeet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Survey of Road DataDocument23 pagesSurvey of Road DataMuddasar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Welcome Brochure 2020-2021Document25 pagesWelcome Brochure 2020-2021George IashviliNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in MetalsDocument5 pagesCorrosion in MetalsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Query & BIDocument14 pagesPower Query & BIzubair muhammad0% (2)
- Mindset MattersDocument19 pagesMindset Mattersracer100% (2)
- Hungary Amends Trademark Act - LexologyDocument2 pagesHungary Amends Trademark Act - LexologyHoward TsaiNo ratings yet