Professional Documents
Culture Documents
toPH UP - Social Science
toPH UP - Social Science
Uploaded by
Andre BenuyoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
toPH UP - Social Science
toPH UP - Social Science
Uploaded by
Andre BenuyoCopyright:
Available Formats
ToPH UP BENUYO
ToPH UP Social Science
P
Prepared by: Andre Gabriel Benuyo
U
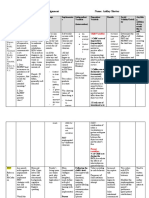
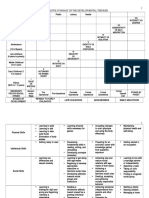
Age Freud Stage Crisis Virtue Important events Notes Miscellaneous
(years) & Key question
H
0-1.5 Oral Infancy Trust vs. Hope Feeding/Comfort Total dependence Mother’s voice, familiar faces,
P
Mistrust stranger anxiety
Is my world safe Attachment behaviors
To
At birth: brain 10% of adult
volume
1.5-3 Anal Toddler Autonomy vs. Will Toilet training/Dressing Active, explorative Issue of control (toilet training)
YO
Shame
Can I do things by myself or Clear evidence of Attachment theory (survival by
need I always rely on emotions maintaining proximity, sensitivity,
others? responsiveness)
U
Transitional objects
EN
Magical thinking
Imaginary companion
B
3-6 Phallic Preschool Age Initiative vs. Purpose Exploration/Play Remarkable physical Oedipal complex (resolved by
Guilt and emotional growth identification)
P Am I good or bad?
Rapid language Superego formation (outcome of
U
development identification)
Body parts/injury Triangulated relationship
H
awareness
Gender role
P
At 5: brain at 90% of adult volume
To
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
At 7: anatomic structures and
myelination almost complete
P
6-12 Latency School Age Industry vs. Competence School/Activities Entry into the Ascribed vs. Achieved status
U
Inferiority community
How can I be good? Absolute morality (consolidating
H
Remarkable growth values for superego formation)
(physical, cognitive,
P
moral, social) At 11: brain volume as adult
To
New roles
Same sex groupings
become polarized
YO
Biological changes
(puberty, interest in
opposite sex)
U
12-21 Adolescence Identity vs. Fidelity Social relationships/Identity Between onset of Earlier onset associated with
EN
Role Diffusion sexual maturation and higher rates of anxiety,
I. Early adolescence (10-13) Who am I and where am I attaining adult status depression, behavior problems
● State of arousal and going?
B
heightened sexual interest Gray matter growth Sexually-mature body,
● Need for privacy spurt just before sexually-active brain, immature
puberty, myelination neurobehavioral system for
II.
●
Middle adolescence (14-17)
Sexual desires intensified
P continues self-control
U
● Brief intense relationships Last connections to be Delayed prefrontal cortex
● Please the object of love established: maturation cause inability to
● Obsession on loyalty to peers ● Prefrontal cortex inhibit pleasurable experiences
H
● Identity, own profile (executive), limbic (not reach adult size until early
& cerebellum 20s)
P
III. Late adolescence (18-21) (emotional)
To
● Greater mastery and ● Prefrontal cortex,
experience VTA & nucleus
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
● More mature, more accumbens
discriminate relationships (dopamine,
P
● Friends by shared interests, midbrain reward
U
temperament reciprocity (less system)
by group identity)
Environment and
H
culture produce
behaviors and
P
meanings
To
21-40 Early Adult Intimacy vs. Love Intimate relationships Intimacy as capacity to Assumption of major social roles
Isolation give and to receive
Am I loved and wanted? Exploring options
Peak biological
YO
development
40-65 Middle Age Generativity Care Work and parenthood Create or nurture things
vs. Stagnation that will outlast them
U
Will I provide something or
real value?
EN
65+ Old Age/Senescence Wisdom vs. Wisdom Reflection on life Full circle with joy
Despair
B
Have I lived a full life? Retirement
Economic security,
P dealing with losses
U
H
P
To
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
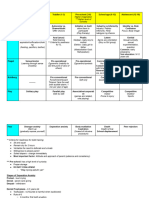
Frameworks Theories Notes Miscellaneous
P
Psychodynamic 1. Ego psychology (Freud) Unconscious mind (early life experiences, Past is prologue, child is the father of
● Tripartite Theory (id, ego, superego) templates, critical periods) man, neurons that wire together fire
U
● Psychosexual Stages together
○ Oral - dependency, aggression,
H
breastfeeding Attachment Theory
○ Anal - self-control ● Secure
P
○ Phallic - oedipal & electra complexes, ○ Low anxiety, low avoidance
triangulated relationships, conscience, ○ Responsive caregiver
To
identification, superego development ○ Strange Situation
○ Latency - unconscious latency, mastery of Experiment
the environment ● Avoidant
○ Genital - forming connections ○ Low anxiety, high avoidance
YO
● Defense mechanisms (ego) ○ Non-threatening but
unresponsive caregiver
2. Object relations theory ● Anxious/Preoccupied
● Early life relationships are internalized ○ High anxiety, low avoidance
U
(unconscious template) ○ Clingy, expects to be
abandoned, please others
EN
3. Self psychology (Kohut) ● Fearful/Disorganized
● Sense of self is developed through how others ○ High anxiety, high avoidance
reflect oneself ○ Mixed responses
B
○ Mirroring - understand
○ Idealizing - emulate
○ Twinship - relate
P
4. Attachment theory (Bowlby, Ainsworth)
U
● Patterns of attachment in early life (template)
Cognitive Aaron Beck Core beliefs/Schemata Early experience -> Core beliefs ->
H
● The way people feel and and behave are - Established system of looking at self, Unhelpful rules (dysfunctional
influenced by conscious, present-based thinking others, and the world (accumulation of assumptions) -> Triggers (critical
P
processes and contents (here and now life experiences) incidents) -> Problem activated
To
thoughts)
● Not situations per se that affect a person, but Intermediate beliefs Maintenance cycle of problem
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
how one cognitively processes it - Rules and expectations that a person - Situations at work, thoughts,
● Thoughts, emotions, bodily sensations, behavior uses to navigate life (arises from core emotions, body reactions,
P
influence one another beliefs/schemata) behaviors, results, consequences
U
Common Cognitive Distortions (unhelpful automatic Automatic thoughts
thoughts) - fortune telling, minimizing, catastrophizing, - Unhelpful, immediate at the conscious
H
self-blaming, mind reading, mental filtering, should and level
must, labeling
P
Behavioral Linked usually with cognitive theory Antecedent - setting vs triggering events Discounts the fact that people have their
To
Behavior - target vs. replacement behavior own will and discernment
Conditioning (antecedent -> behavior -> consequence) Consequence - access vs avoid/escape
Not anchor on mental processing, whether conscious or
YO
unconscious
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov) - learning is a product of
associating stimulus and response
U
Operant Conditioning (Skinner) - consequences can be
EN
altered to serve as reinforcement and punishment
Shaping - behaviors are habituated by repetition and
B
building up
Vicarious learning and modeling - behaviors can be
P
learned by observation (rewarded, role models)
U
Neurodevelopmental Executive functions - managing oneself
and one’s resources to achieve a goal
(mental control & self-regulation), by
H
frontal cortices of brain
Theory of Cognitive Development (Piaget) Teenage brain - executive functions
P
take longer to develop (very intelligent,
To
poor impulse control), overdrive of
Sensorimotor 0-2 Infancy & Mastery of movements, sensory stimulation,
limbic system
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
● Prefrontal cortex - immature,
Toddler symbolic representation, concept formation
prone to high-risk behavior
P
Pre-operational 2-7 Preschool Magical thinking, intuition-based thought, ● Amygdala - more impulsive
U
egocentricity, logic not yet established ● Parietal lobe - not process
information effectively
Concrete Operational 7-11 School Logic formed, conservation, classification, ● Ventral striatum - more excited
H
decentration, reversibility, seriation, sociocentricity by reward than consequence
(other people’s perspectives) ● Hippocampus - tremendous
P
learning curve
Formal Operational 11-above Higher order reasoning, abstraction, reasoning
To
Adolescence (inductive & deductive) Mentalization - understand one’s own
and others’ mental states, being in
another’s mind, basis for empathy
YO
Mindfulness - fully present at the
moment, aware of thoughts, feelings,
actions
U
Psychosocial Psychological function and development always occur Function and development are not seen to Maladaptive tendency - syntonic, too
in relation to social and environmental context be intrinsically driven but directed toward much good
EN
adaptation to the external environment Malignant tendency - dystonic, too
Theory of Psychosocial Development (Erikson) much bad
- See Trans 1 table
B
Sensory Withdrawal
Ecological Systems Theory (Bronfenbrenner)
maladjustment
● Microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem,
P
macrosystem, chronosystem Shameless Compulsion
U
willfulness
Ruthlessness Inhibition
H
Narrow virtuosity Inertia
P
Fanaticism Repudiation
To
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
Promiscuity Exclusivity
P
Over-extension Rejectivity
U
Presumption Disdain
H
P
Humanistic/Existential People are by nature drawn to purpose, meaning, and Development and functioning are not Morality - person’s perception and
self-fulfillment incidental & not passive, but from desire for reasoning of right and wrong affecting
To
goodness and growth emotionality and motivating behavior
Hierarchy of Needs (Maslow)
- Physiological, safety, belonging & love, esteem, Stages of Moral Development (Kohlberg)
self-actualization
YO
Pre-conventional (3-7)
Logotherapy (Frankl)
Beneficial for oneself
- People by nature find meaning in their life
situations, even in the most adverse experiences
U
Obedience/ Infancy Punishment
Punishment
Wellbeing Theory (Seligman)
EN
- Positive psychology (wellness orientation) Self-interest Preschool Rewards/
- PERMA Model (Positive emotions, engagement, Benefit
relationships, meaning, achievements) (ego-
B
centrism)
Conventional (8-13)
P Correct by society
U
Conformity/ School Good
Interpersonal boy/good
Accord girl
H
For
P
approval
To
Authority/ Law and
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
ToPH UP BENUYO
Social Order order
P
Societal
U
standards
Post-conventional (Adulthood)
H
Principles & Ethics, Differ from person to
person
P
Social Teens Understand
To
Contract reasons
behind rules
(utilitarian)
YO
Universal Adulthood Values
Principles transcend
mutual
U
benefit
EN
–end–
B
P
U
H
P
To
ToPH UP Social Science (BENUYO)
You might also like
- The Dark ManDocument2 pagesThe Dark ManHyemi Mimi100% (1)
- Worksheetsfrom 101 Trauma Informed InterventionsDocument7 pagesWorksheetsfrom 101 Trauma Informed InterventionsFaran100% (6)
- Blood Sorcery Rites of Damnation Spell Casting SummaryDocument3 pagesBlood Sorcery Rites of Damnation Spell Casting SummaryZiggurathNo ratings yet
- 09 Pediatrics PLE 2019 RatioDocument66 pages09 Pediatrics PLE 2019 RatioMei Bejerano - Roldan100% (1)
- Psychodynamic Theories: Comparative MatrixDocument2 pagesPsychodynamic Theories: Comparative MatrixErdanx SanchezNo ratings yet
- Gateway-B1 SB Unit7Document28 pagesGateway-B1 SB Unit7anisalera1507No ratings yet
- Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (Gpius 2) Scale Items & InstructionsDocument2 pagesGeneralized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (Gpius 2) Scale Items & InstructionsShariqa100% (1)
- Physical, Cognitive, and Psychosocial CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesPhysical, Cognitive, and Psychosocial CharacteristicsmamarilyvongwynethNo ratings yet
- PDF Comparison of Freud Erikson Piaget Kohlberg Theories Developmental PhenomenaDocument3 pagesPDF Comparison of Freud Erikson Piaget Kohlberg Theories Developmental PhenomenaJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Ncm105 TheoriesDocument2 pagesNcm105 TheoriesVeyNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Composite 2019 Revision Document - Questions - For Printing (Document93 pagesLife Sciences Composite 2019 Revision Document - Questions - For Printing (mmathapelosekina985No ratings yet
- Complete Citation of Reference Used (With Pages)Document2 pagesComplete Citation of Reference Used (With Pages)Charissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Brand Scorecard+Taylor New NNDocument20 pagesBrand Scorecard+Taylor New NNjianxinaNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology of SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesPsychopathology of SchizophreniaJoshoua MalanaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psych March 9 24Document20 pagesDevelopmental Psych March 9 24rose virayNo ratings yet
- Physical Cogniti Ve Langua Ge Social/ Emotion Al Moral: Yea RsDocument8 pagesPhysical Cogniti Ve Langua Ge Social/ Emotion Al Moral: Yea RsVanTaneoNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development StagesDocument8 pagesGrowth and Development StagesRic Russel PamaNo ratings yet
- S02 T02 PSY1 AttachmentDocument3 pagesS02 T02 PSY1 AttachmentJen Beatrice DiazNo ratings yet
- Sex Development-Sexuality-Gender Perfomativity Within A Holistic ContextDocument15 pagesSex Development-Sexuality-Gender Perfomativity Within A Holistic ContextPatienceNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology of SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesPsychopathology of SchizophreniaYashmine CastrenceNo ratings yet
- Viii. Psychopathology of Schizophrenia: Trust vs. Mistrust (Infant) Oral Stage (0 - 1-Year-Old)Document4 pagesViii. Psychopathology of Schizophrenia: Trust vs. Mistrust (Infant) Oral Stage (0 - 1-Year-Old)Anonymous TpI3Lk50No ratings yet
- Module 2 Developing The Whole PersonDocument59 pagesModule 2 Developing The Whole PersonJoemar MaganteNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DevelopmentDocument15 pagesCognitive DevelopmentAryan TomarNo ratings yet
- Emoji-Feeling-StripsDocument8 pagesEmoji-Feeling-StripsElfridaNo ratings yet
- Art of Parenting BGDDocument8 pagesArt of Parenting BGDkundansudNo ratings yet
- Childhood Development TheoriesDocument1 pageChildhood Development TheoriesAbdelrahman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Musical Expression, Mind MapDocument1 pageMusical Expression, Mind MapScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Understands World Through: Senses & Actions Language & Symbols Mental Images Logic, Categories Hypotheticals, Scientific ReasoningDocument2 pagesUnderstands World Through: Senses & Actions Language & Symbols Mental Images Logic, Categories Hypotheticals, Scientific ReasoningMeg LiebNo ratings yet
- Developmental MilestonesDocument4 pagesDevelopmental Milestonesschxzerrydawn100% (3)
- Pedia Normal NotesDocument12 pagesPedia Normal NotesMaria TagubaNo ratings yet
- Royal: The Pentagon Review Specialist, IncDocument31 pagesRoyal: The Pentagon Review Specialist, IncClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- TALK MilestonesDocument10 pagesTALK MilestonesDEAN MIKO BULLONo ratings yet
- Communication Milestones - Expected Skills: 3 MonthsDocument10 pagesCommunication Milestones - Expected Skills: 3 MonthsYana GuarinoNo ratings yet
- An Effective Manager Will Always Hire The Smartest Person AvailableDocument21 pagesAn Effective Manager Will Always Hire The Smartest Person AvailableArun RaiNo ratings yet
- Neuro AssessmentDocument3 pagesNeuro AssessmentTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Growth and Development TableDocument7 pagesPediatric Growth and Development TableNaynah Belldandy BalcosNo ratings yet
- Developmental StagesDocument3 pagesDevelopmental StagesdoryscumbeNo ratings yet
- المراجعة النهائية - لغة إنجليزية - تانية ثانوى ترم اول 2022Document65 pagesالمراجعة النهائية - لغة إنجليزية - تانية ثانوى ترم اول 2022Shereen MagdyNo ratings yet
- Developmental MilestonesDocument2 pagesDevelopmental MilestonesMonisha RaviNo ratings yet
- SW C2 EDUCATION - Adolescents in The 21st Century. Generation Clash TW SW ColorDocument4 pagesSW C2 EDUCATION - Adolescents in The 21st Century. Generation Clash TW SW ColorPascual Cano VicenteNo ratings yet
- Cnl-518-Rs-T8bereavementacrossthelifespan Melissa-AguirreDocument3 pagesCnl-518-Rs-T8bereavementacrossthelifespan Melissa-Aguirreapi-385824900No ratings yet
- Age Gross Motor Fine Motor Adaptive Personal/Social Speech and Language Cognitive Emotional SourceDocument13 pagesAge Gross Motor Fine Motor Adaptive Personal/Social Speech and Language Cognitive Emotional SourceHanniel Jufet GolosindaNo ratings yet
- Human RightsDocument2 pagesHuman RightsAlazne OrfilaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Growth and Development TableDocument6 pagesPediatric Growth and Development Tablemichael angelo leonardoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Individual TASK - Table of Psychosocial Theories and TherapyDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Individual TASK - Table of Psychosocial Theories and TherapyAndrew Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Child SP ExampleDocument6 pagesChild SP ExamplelourdesNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Prelim and Finals ReviewerDocument32 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Prelim and Finals ReviewerJewel Mae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Preview: Teacher EvaluationDocument3 pagesPreview: Teacher EvaluationJoel LogboNo ratings yet
- EQ 360 Client Sample Report Emotional Intelligence EQ IDocument51 pagesEQ 360 Client Sample Report Emotional Intelligence EQ IDamien RibonNo ratings yet
- Adobe RX Week 2Document1 pageAdobe RX Week 2Elaiza Flor ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Developmental Theories and Other Relevant TheoriesDocument9 pagesUnit 3: Developmental Theories and Other Relevant TheoriesHemera BacarezaNo ratings yet
- PMT Internship Synthesis TableDocument19 pagesPMT Internship Synthesis Tableapi-519066299No ratings yet
- Comparative Summary of The Developmental Theories 1Document3 pagesComparative Summary of The Developmental Theories 1Teyn AnnNo ratings yet
- Johanna Hedva - in Defence of DepersonsDocument59 pagesJohanna Hedva - in Defence of DepersonsNina HoechtlNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis Theory: Psychodynamic Theories of PersonalityDocument13 pagesPsychoanalysis Theory: Psychodynamic Theories of PersonalityAngel BolecheNo ratings yet
- Global ThinkerDocument31 pagesGlobal Thinkerarun4719No ratings yet
- PTSD Tables For AssessmentDocument7 pagesPTSD Tables For AssessmentOdalis VelezNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones: Age Motor Speech Vision and Hearing SocialDocument6 pagesDevelopmental Milestones: Age Motor Speech Vision and Hearing SocialAdnan RezaNo ratings yet
- Pedia NormalDocument5 pagesPedia NormaltacpalseedNo ratings yet
- Your Lines of IntelligenceDocument1 pageYour Lines of IntelligencefdalamaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Growth & DevelopmentDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Growth & DevelopmentDIZZA MAE BATURIANONo ratings yet
- Psychopathology of Alcohol-Induced Psychosis: EtiologyDocument3 pagesPsychopathology of Alcohol-Induced Psychosis: EtiologySharlaine CabanayanNo ratings yet
- Forms PensionersDocument15 pagesForms PensionersAnimesh DasNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and Health Aspects of Voice and Speech ProfessionsDocument34 pagesOccupational Safety and Health Aspects of Voice and Speech ProfessionskaaanyuNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryRosida IdaNo ratings yet
- Biophilic Design: ARC407 DissertationDocument4 pagesBiophilic Design: ARC407 DissertationAaryan JainNo ratings yet
- Geography P1 May-June 2023 EngDocument20 pagesGeography P1 May-June 2023 Engtanielliagreen0No ratings yet
- MAD Practical 6Document15 pagesMAD Practical 6DIVYESH PATELNo ratings yet
- BDM SF 3 6LPA 2ndlisDocument20 pagesBDM SF 3 6LPA 2ndlisAvi VatsaNo ratings yet
- The Little Magazine RamRamDocument5 pagesThe Little Magazine RamRamJasdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 8 (September) (AutoRecovered) 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan 8 (September) (AutoRecovered) 1Rutchie AbantoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanPutra AginaNo ratings yet
- Gershwin George Rhapsody in Blue For Sax Quartet 64734Document113 pagesGershwin George Rhapsody in Blue For Sax Quartet 64734Jessica HowardNo ratings yet
- Simatic S7 Mpi Direct DriverDocument50 pagesSimatic S7 Mpi Direct Drivernilton_bertoldoNo ratings yet
- GEO01 - CO1.2 - Introduction To Earth Science (Geology)Document14 pagesGEO01 - CO1.2 - Introduction To Earth Science (Geology)Ghia PalarcaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Organizational Behavior: de Castro, Donna Amor Decretales, Thea Marie Estimo, Adrian Maca-Alin, SaharaDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Organizational Behavior: de Castro, Donna Amor Decretales, Thea Marie Estimo, Adrian Maca-Alin, SaharaAnna Marie RevisadoNo ratings yet
- Manual Tecnico Jblgo PDFDocument2 pagesManual Tecnico Jblgo PDFMarcosDanielSoaresNo ratings yet
- Kepler Problem - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument4 pagesKepler Problem - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFrizal123No ratings yet
- Report 1Document9 pagesReport 135074Md Arafat Khan100% (1)
- CyberbullyingDocument8 pagesCyberbullyingapi-433558817No ratings yet
- 1.2 FMCC221 - Introduction To International Businesss - Part 1Document19 pages1.2 FMCC221 - Introduction To International Businesss - Part 1Bernie D. TeguenosNo ratings yet
- AQU4518R4 DatasheetDocument2 pagesAQU4518R4 Datasheetcostin.bantoiuNo ratings yet
- Final Simple Research (BS CRIM. 1-ALPHA)Document5 pagesFinal Simple Research (BS CRIM. 1-ALPHA)Julius VeluntaNo ratings yet
- Law Enforcement Agency Indentifiers Crosswalk, 2012Document23 pagesLaw Enforcement Agency Indentifiers Crosswalk, 2012Samuel KaminNo ratings yet
- The Material Culture of The Postsocialist CityDocument15 pagesThe Material Culture of The Postsocialist Cityjsgt1980No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Task 3 - Reader Guru Adventure! - Evaluation Quiz - Revisión Del IntentoDocument7 pagesUnit 1 - Task 3 - Reader Guru Adventure! - Evaluation Quiz - Revisión Del IntentoNelson AbrilNo ratings yet
- Name:-Muhammad Shabbir Roll No. 508194950Document11 pagesName:-Muhammad Shabbir Roll No. 508194950Muhammad ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Prolog Programs Are A Collection of FactsDocument23 pagesProlog Programs Are A Collection of FactsAbni booNo ratings yet
- English in Common 2b Split Student Book With Activebook and Workbook Volume 2 Part 2Document26 pagesEnglish in Common 2b Split Student Book With Activebook and Workbook Volume 2 Part 2Pancho NohalesNo ratings yet