Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8.edc 17 9 Aug 2016
8.edc 17 9 Aug 2016
Uploaded by
iqbal husseinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8.edc 17 9 Aug 2016
8.edc 17 9 Aug 2016
Uploaded by
iqbal husseinCopyright:
Available Formats
EDC 17
(D08 Common Rail Engine)
Training Academy
MAN Trucks India Pvt. Ltd.
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 1 of 34
June 2016
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This material is exclusively intended for training purposes.
Reproduction, duplication, distribution, editing translation, microfilming and storage and/or processing in
electronic systems including databases and online services are not allowed without the written approval of
MAN Trucks India.
Products, aggregates or services listed may be trademarks, service marks or trade names of MAN Trucks
India. All rights are reserved. MAN® is registered trademark of MAN Truck & Bus in Germany and other
countries including India.
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 2 of 34
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
General
In recent years, legislators and customers alike have increasingly demanded better environmental
credentials, improved fuel consumption, more constant speeds for PTO operation as well as reduced
exhaust and noise emissions from diesel engines. This trend will continue in the future.
The Common Rail injection system meets all the requirements placed on a modern internal combustion
engine. In conjunction with electronically controlled gearshift systems, anti-lock braking systems, anti-spin
regulators and systems for controlling the running gear and brakes etc., this system increases vehicle
economy, improves driving comfort and takes some of the burden off the driver and the environment.
Structure and mode of function
Good mixture formation is the precondition for efficient combustion. The injection system plays a central
role in this. The correct quantity of fuel must be injected at the right time and with a high pressure. The
common rail system is a trend-setting high-pressure injection system, which involves the separation of
pressurisation and injection. The fuel for the individual cylinders comes from a shared accumulator which is
constantly kept at high pressure. The accumulator is pressurised by a high pressure pump. This pressure
can be changed to suit the relevant operating conditions. Each cylinder is equipped with an injector which is
controlled by a solenoid valve. The injected fuel quantity is determined by the discharge cross-section of the
injector, the opening time of the solenoid and the accumulator pressure. A system pressure of up to 2500
bar can be reached.
Separation of the pressurisation and injection functions allows a better injection characteristic and,
therefore, improves combustion development. Any injection pressure within the characteristic map can be
selected. Multipoint injection, i.e. with pre- and post-injection, is possible. The fuel quantities, start of
injection, pre-injection and post-injection are controlled by extremely fast solenoid valves. Another
advantage of common rail systems is that they can be fitted to existing engines without having to modify the
cylinder head.
Schematic Diagram of EDC
1 Quantity-controlled high pressure
pump
2 High-pressure accumulator (rail)
3 Pressure-limiting valve
4 Rail pressure sensor
5 Injectors
6 Control unit EDC17
7 Further sensors and actuators
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 3 of 34
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
A435 control unit EDC17
Description-
(A) Plug connector A, 58-pin
(B) Connector not used
(C) Plug connector C, 96-pin
(D) Injector connector, 16-pin
The main tasks of the EDC17 control unit are to control the injection quantity, regulate the point of injection
and activate the starter. The optimal injection quantity and point of injection are calculated to ensure
optimum combustion in all engine operating states.
The control unit evaluates the sensor signals and then calculates the actuation signals for the injectors.
The control unit (software/hardware) is designed for a maximum of eight cylinders.
The control unit software contains the following function groups:
– Fuel quantity setpoint generation, fuel dosing
– Fuel pressure control with high pressure pump
– Fuel pressure deactivation (limp-home function)
– Idling control
– Maximum-speed governor, smoke and torque limiting
– Adaptive individual cylinder torque control (smooth running control)
– Cylinder cutoff
– Exhaust gas recirculation
– Air system/exhaust gas aftertreatment
– Exhaust gas temperature and exhaust gas management
– Charging pressure governing system (wastegate control)
– Signal detection and calculation of operating variables
– Diagnosis and monitoring functions
– OBD functionality
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 4 of 34
Pin assignment of plug connector A
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 5 of 34
Pin assignment of plug connector B
This plug connector is empty during use as control unit EDC17. No pins are connected.
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 6 of 34
Pin assignment of plug connector C
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 7 of 34
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 8 of 34
Pin assignment of plug connector D
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 9 of 34
CP3.3 High Pressure Pump
Description
The tasks of the high pressure pump are to generate the high pressure
required for injection and to supply an adequate quantity of fuel in all
operating states. The high pressure pump is driven by the engine and is
mounted on D08 series engines in the same position as a conventional
injection pump.
The fuel is forced from a pre-supply pump to the fuel filter system (KSC)
via fuel lines and then into the high pressure pump "suction chamber" via
the proportional valve. The pre-supply pump is flange-mounted on the
high pressure pump. The proportional valve (MProp) is mounted on the
suction side of the high pressure pump.
The proportional valve is an actuator for controlling the fuel pressure in the
high-pressure accumulator (rail).
The CP3 high pressure pump is a radial piston pump with 3 cylinders.
Y332 proportional fuel valve
Description
The proportional fuel valve is an actuator for controlling the
fuel pressure in the high-pressure accumulator (rail).
The proportional fuel valve is located on the low-pressure
side (input side) of the high pressure pump and is bolted to
the CP3 high pressure pump housing.
The proportional fuel valve is controlled using a PWM output
(pulse width modulated signal):
Duty factor 100%: proportional valve closed (zero fuel
quantity delivery)
Duty factor 0%: proportional valve open (maximum
delivery)
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 10 of 34
The control circuit consists of a rail pressure sensor, control unit EDC17 and proportional fuel valve.
Note on terminology: The proportional fuel valve can also be designated "proportional valve" or "MProp".
Both terms are permitted. MProp is the German abbreviation for (fuel) quantity proportional valve.
Pin Assignment
High-pressure accumulator (rail)
Description
The name "Common Rail" is derived from the
design and function of the high-pressure
accumulator. The fuel is injected into the
individual cylinders via this common accumulator
which is also a fuel distributor or distributor rail.
Here the fuel is constantly under high pressure
and only needs to be extracted at the right time.
The rail has the following tasks:
Storing the fuel
Preventing pressure fluctuations
The rail is a pipe made from forged steel. The
diameter and length of this pipe vary depending
on the engine. To prevent pressure fluctuations,
the largest possible volume must be aimed for,
i.e. pipe as long as possible and pipe diameter
as large as possible. However, a small volume is better for fast starting of the engine. Therefore, the volume
has to be configured as precisely as possible to suit the engine in question.
The pressure-limiting valve and the rail pressure sensor are also mounted on the rail.
Pressure-limiting valve
Description
The pressure-limiting valve is mounted on the high-pressure accumulator (rail) and
functions as a pressure relief valve with pressure limiting. The pressure-limiting valve
limits the pressure in the rail. If the pressure is too high, it uncovers a drain hole. At
normal operating pressure, a spring pushes a piston tight into the valve seat so that the
rail remains closed. Only once the maximum system pressure is exceeded is a piston
pressed against a spring by the pressure in the rail.
The pressure-limiting valve consists of two pistons. If the rail pressure is too high (at
approx. 2200 bar), the first piston moves and permanently uncovers part of a cross-
section so that the fuel can flow out of the rail. The rail pressure is then kept constant at
around 700 to 800 bar. The engine continues running and the vehicle can be driven to the nearest MAN
service outlet at reduced full-load quantity.
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 11 of 34
The pressure-limiting valve does not close again until the engine has been stopped and the rail pressure
has fallen below 50 bar – i.e. once it has opened, the 2nd stage remains open for as long as the engine is
running.
If the pressure-limiting valve does not open quickly enough, it is forced open. To force open the pressure
limiting valve, the proportional fuel valve is opened by interrupting the power supply and the extraction of
fuel via the injectors is blocked. The rail pressure rises rapidly until the pressure-limiting valve opening
pressure is reached. If forcing open the valve does not have the desired effect, e.g. due to jamming of the
pressure-limiting valve, the engine is stopped.
Note: The control unit EDC17 monitors how long the pressure-limiting valve is open. Fault SPN 4386
appears after a period of 360 minutes. The number of openings of the pressure-limiting valve is also
monitored. Once the pressure-limiting valve has opened 100 times, the fault SPN 4381 is set. These faults
cannot be deleted in the usual way, but only via the MAN-cats® function "Reset acquired values for
pressure-limiting valve".
The acquired values must also be reset via MAN-cats® following replacement of the pressure-limiting valve.
The tightening torque of exactly 100 Nm must be observed!
B487 rail pressure sensor
Description
The rail pressure sensor monitors the fuel pressure in the high-pressure
accumulator (rail). The aim is to ensure a specified pressure for the operating
point concerned in the high-pressure accumulator (rail). The rail pressure
sensor is mounted on the rail.
Pin Assignment
Y341 injector cylinder 1
Description
The following description based on the example of injector cylinder 1 (Y341) also applies for all other
injectors installed:
Y342 injector, cylinder 2
Y343 injector, cylinder 3
Y344 injector, cylinder 4
Y345 injector, cylinder 5
Y346 injector, cylinder 6
The injector is used to inject fuel into the combustion chamber. The EDC17 control unit specifies the
injection period (injector coil actuation period for pre-injection, main injection and possible post-injection) as
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 12 of 34
well as the time of the injection and activates an extremely fast solenoid valve in the injector. The solenoid
valve armature opens or closes the control chamber outlet restrictor. If the outlet restrictor is open, the
pressure in the control chamber falls and the nozzle needle opens. If the outlet restrictor is closed, the
pressure in the control chamber rises and the nozzle needle is closed. The opening behaviour of the nozzle
needle (opening and closing speed) is therefore determined by the inlet and outlet restrictor in the injector
control chamber.
The injector leakage quantity (leakage via outlet restrictor and nozzle needle) is returned to the tank via the
return line (leakage line). The exact injection quantity is determined by the outlet cross-section of the
nozzle, the solenoid valve opening duration and the rail pressure.
B488 speed increment sensor (Crankshaft)
Description
This speed sensor on the flywheel is used to measure (calculate) the crank
angle of the crankshaft. This information is vital for ensuring the injectors for the
individual cylinders are actuated at the correct time.
The pulse-generating wheel is designed as an increment wheel. This speed
sensor is therefore referred to as a speed increment sensor. The increment
wheel is part of the flywheel and has 60 –2 = 58 holes (6x5 mm) spaced at 6°
intervals. Two of the bores are missing in order to form a gap. The purpose of
the gap is to determine the 360° crank angle of the engine (one crankshaft
revolution) and it is assigned to a defined crankshaft position of cylinder 1. The engine can also start with
speed increment sensor only or with speed segment sensor only.
In the case of operation with speed increment sensor only, test injections are carried out at gas flow TDC
and ignition TDC as the EDC without speed segment sensor first has to locate the correct ignition TDC.
Once the control unit detects a speed reaction (ignition), it has found the correct TDC. The engine then
starts and runs as with both speed sensors.
The speed increment sensor consists of a permanent magnet and a coil with a large number of windings.
The magnet "touches" the rotating component to be detected – in this case the increment wheel mounted
on the crankshaft – with its magnetic field. The current flow is amplified whenever a hole moves past the
sensor. The current flow is weaker in the gaps in-between. This gives rise to an inductive voltage in the
sensor coil. This voltage is evaluated by the control unit. The gap between the sensor and the increment
wheel is approx. 1 mm.
Pin Assignment
B489 speed segment sensor (Camshaft)
Description
The camshaft controls the engine intake and exhaust valves. It rotates at half
the speed of the crankshaft. Its position determines whether a piston is in the
compression stroke or the exhaust stroke whilst it moves towards TDC. This
information cannot be obtained based on the crankshaft position during starting.
However, when driving, the information generated by the speed increment
sensor on the crankshaft is sufficient for determining the engine state.
Therefore, if the speed sensor on the camshaft fails during driving, the control
unit is still aware of the engine state. The pulse-generating wheel is designed as
a segment wheel and is driven by the camshaft. This speed sensor is therefore
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 13 of 34
referred to as a speed segment sensor. The segment wheel is also referred to as a phase wheel. It has one
phase mark per cylinder (e.g. 6 marks in the case of 6-cylinder engines or 4 marks in the case of 4-cylinder
engines) and a synchronisation mark. The phase mark is a tooth on the phase wheel. The phase marks are
evenly distributed around the phase wheel. The synchronisation mark is an additional mark on the phase
wheel right behind one of the phase marks. Its purpose is to determine the engine angle position within
720° crank angle.
If the speed segment sensor fails, the control unit will initially not be able to detect the ignition TDC during
the next start. As a result, the ignition TDC from cylinder 1 is always selected first in this case. If this
assumption is correct, the engine switches on and runs as normal. If it is incorrect, the engine will not start
and a new start attempt will need to be carried out. Statistically speaking, every second start attempt will
thus be successful.
The speed segment sensor has the same design and function as the speed increment sensor for acquiring
the crankshaft speed.
Pin Assignment
B104 oil pressure sensor
Description
The oil pressure sensor protects the engine. It monitors the oil pressure. The
pressure measuring range is from 0 bar (0.5 V) to 6 bar (4.5 V).
Pin assignment
B623 charging pressure/temperature sensor
Description
The charging pressure sensor measures the absolute charging pressure. The
sensor element and an electronic control unit (for signal amplification and
temperature compensation) are integrated on a silicon chip. The active surface
of the silicon chip is exposed to a reference vacuum. The intake manifold
pressure is forwarded via a discharge stub to the rear of the diaphragm which is
resistant to the measuring medium.
The charging pressure sensor is also equipped with a temperature sensor.
Together with the charge air temperature sensor (B123), its purpose is to monitor
EGR. The charging pressure sensor is fitted upstream of the EGR inlet line whilst
the charge air temperature sensor is fitted downstream of the inlet line. The
different temperatures of the two sensors enable the plausibility of the EGR rate
to be checked.
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 14 of 34
Pin Assignment
Measured value
B124 coolant temperature sensor
Description
The temperature sensor supplies the control unit with information about the coolant
temperature. The control unit calls up various engine characteristic maps,
depending on the coolant temperature.
Pin Assignment
Measured value
B561 exhaust gas temperature sensor upstream of SCR.
Description
The temperature sensor monitors the exhaust gas temperature upstream of
the selective catalytic converter.
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 15 of 34
Pin Assignment
Measured value
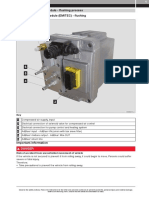
A808 AdBlue supply module (Dosing Unit)
Description
The MAN AdBlue® system is an exhaust gas aftertreatment
system for commercial vehicles fitted with an SCR catalytic
converter (reduction catalytic converter). This reduces nitrogen
oxides by up to 85% and particulates by up to 40%. A 32.5%
urea/water mix (AdBlue) is fed into the exhaust gas stream
upstream of the SCR catalytic converter.
The MAN AdBlue® system with Emitec NoNOx supply module
works with compressed air support.
The compressed air ensures optimum atomisation when feeding
the AdBlue into the exhaust gas stream.
Pin Assignment X2
Pin assignment of
plug connector X1
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 16 of 34
Y437 coolant solenoid valve (Magnetic Valve AdBlue) - Optional
AdBlue has high water content and is therefore at great risk of freezing.
It freezes at temperatures below -11°C. As a result, the system must be
heated. Initially, all internal and external lines, the supply module
(internally, via a filter) and the tank are heated. The internal heaters are
electrical; engine coolant is used for heating the tank and the external
lines. A pipe coil is installed in the AdBlue tank and heated coolant from
the engine circuit circulates through it. The valve switches the heating
circuit on or off as required, thus regulating the heating circuit of the
AdBlue tank.
Note: In bus/coach circuit diagrams, this component is also referred to as "Y511 AdBlue tank heating
valve".
Pin Assignment
B628 AdBlue Level and Temperature combination sensor
Description
The sensor monitors the fill level, temperature and AdBlue quality in the AdBlue
tank.
The fill level is determined using floats via reed contacts to which a defined
resistance value is allocated.
An NTC thermistor is used to determine the temperature.
The AdBlue quality is determined on the basis of the ultrasonic transit time method
(i.e. by means of acoustic waves).
The values are prepared in evaluation electronics and communicated via the CAN
bus.
Pin assignment
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 17 of 34
B994 NOx sensor II OBD
Description
The NOx sensor II OBD measures the nitrogen oxide
concentration and the oxygen content in the exhaust gas stream
downstream of the SCR catalytic converter, i.e. at the end of the
exhaust stream, after all catalytic converters.
The operating principle of the NOx sensor is based on the
decomposition of nitrogen oxide by means of a catalytically active
electrode. The measurement of the oxygen produced here is
familiar from the linear lambda probe. The layout of the multi-layer
zirconium dioxide sensor ceramic (ZrO2) contains two chambers: In the first chamber, the oxygen
contained in the exhaust gas is reduced or increased to a constant partial pressure of several 10
ppm by applying a pump current. The necessary current is proportional to the air ratio reciprocal
value. In the second chamber, the NOx reduction takes place at the measuring electrode. The
current required for keeping the electrode area free of oxygen is proportional to the nitrogen oxide
concentration and forms the measured signal.
Note- on assembly: The NOx sensor must only be fitted using the assembly paste WEICON Anti-
Seize High-Tech, MAN item number 09.16012-0133. The use of other assembly materials can
result in incorrect measurements
Pin Assignment
Cluster AdBlue Connector. X4 (8 pin)
Pin1 – Check lamp AdBlue.
Pin2 – AdBlue Selection Switch
Pin3 – CAN_L signal
Pin4 – CAN_H signal
Pin5 / 6 / 7 / 8 = NC – Not
connected.
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 18 of 34
A1154 electronic relay for flame-start system
Description
The control of the flame-start system was changed with the introduction of Euro
6. The EDC control unit now actuates the system via the LIN data bus by
means of an electronic relay.
Pin Assignment plug connector A
Pin Assignment Plug Connector B
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 19 of 34
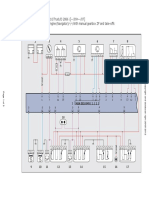
PTM STEP 4 Pin Assignments
PTM A1124 pin assignments
Connector Pin In/Out Wire no. Designation Function
1 I 31000 KL31_1 Ground
VS 3 I 60044 KL15 Power Supply Terminal 15 ( Through Fuse- F1027) 24V
5 I 60027 KL30_1 Direct Supply (Through Fuse- F1026) 24V
7 O 60089 RedWarnLampHSout Red Warning Lamp
A
15 O 60090 YellowWarnLampHSout Yellow Warning Lamp
33 O 17101 Flame-start Ind Yellow Indication Lamp
4 I/O 185 diagCAN_H CAN High signal (Diagnosis) X200
5 I/O 159 M_CAN_H CAN High signal (Engine)
10 I 60146 accPedal2in Accelerator pedal 2 input
11 O 31017 ambientTempGNDout Outside (Ambient) temperature Ground
16 I/O 186 diagCAN_L CAN Low signal (Diagnosis) X200
B 17 I/O 160 M_CAN_L CAN Low signal (Engine)
20 I 16500 C3roadSpeedIn C3 road speed signal input
32 I 60007 clutchSwitchClosedStateIn Clutch switch closed state input
36 I 31016 MDB_HGB_GNDout MDB / HGB Ground (Engine Speed range/ Max. road speed Limiter)
37 O 43301 engineBrakeHSout Engine brake high side output
45 I 60145 accPedal1in Accelerator pedal 1 input
1 I 60147 ambientTempIn Outdoor (Ambient) temperature sensor input
7 I 60587 extEngineControlSetPlusIn Request external engine control set plus input (Start switch)
9 I 60528 cruiseControlSetMinusIn Cruise control set minus input
10 I 43310 engineBrakeReqIn Engine brake request input
17 I 50300 engineStartKl50reqIn Engine start KL50 request input
19 I 60588 extEngineControlSetMinusIn Request external engine control set minus input (Stop switch)
20 I 68528 parkingBrakeStateIn Parking brake state input
23 I 60525 intermediateSpdCtrl1reqIn Intermediate speed control 1 request input
C 26 I 60523 HGBreqIn HGB request input ( HGB max. speed limit )
27 I 16116 coolantLevelIn Coolant level input
32 I 60504 cruiseControlReqIn Cruise control request input
34 I 60006 brakeSwitchStateIn Brake switch state input
35 I 60526 intermediateSpdCtrl2reqIn Intermediate speed control 2 request input
37 I 60524 MDBreqIn MDB request input ( MDB engine speed range )
45 I 60527 cruiseControlSetPlusIn Cruise control set plus input
47 I 60641 intermediateSpdCtrl3reqIn Intermediate speed control 3 request input
48 I 60144 transNeutralStateIn Transmission state neutral input
MDB – Engine speed range
HGB – Maximum road speed limiter
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 20 of 34
DIAGNOSIS with MAN-cats® II
General
Most control units that can be tested using MAN-cats® are connected with diagnostic socket X200 pin 3/4
via a communication line. The diagnostic system stimulates a specific control unit via the communication
line. The control unit responds and transmits the faults stored in its diagnostic memory via the
communication line in digital code.
"KWP-on-CAN" control units such as TBM and ECAS2 do not have a communication line. Control units with
KWP-on-CAN diagnosis are stimulated by the vehicle management computer/Power Train Manager
communication line.
Diagnostic socket HD-OBD (X200)
The SPN diagnostic codes can be downloaded from the diagnostic memory of various control units using
MAN-cats® (connection to diagnostic socket X200). The results are displayed on the MAN-cats® display.
The 16-pin diagnostic socket HD-OBD according to ISO 15031-3 replaces the former 12-pin MAN
diagnostic socket.
In future, this OBD standardisation will, for the first time, provide a uniform diagnostic system for the
exhaustrelevant components of almost all vehicles worldwide.
Pin Assignment.
Fault storage
The system constantly inspects itself. A signal range check (area check) is run for this purpose. During this
check, the system polls all signals to determine that they are present and plausible. Polling is performed in
a specific time pattern (specified by the software). The control unit itself is also checked continuously during
the entire program run time. The first check always takes place when the ignition is switched on (checksum
test). If faults occur during operation, these faults are saved to the diagnostic memory and a message
appears on the driver's display.
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 21 of 34
The following occurs in the event of a fault entry:
Diagnostic memory entry identification (SPN)
Fault type identification (FMI)
Fault priority assignment
Fault frequency detection
Detection of framework conditions (two environmental conditions) when the fault was categorised.
Sporadic faults are recorded by a self-healing counter after they have disappeared for the first time. This
means that a specific frequency number is set and this number is decremented by 1 each time the vehicle
is started. If the fault stops occurring and the counter reaches the value zero, the corresponding fault block
is deleted and any subsequent fault blocks processed.
The following actions are initiated automatically depending on the evaluation of a fault that has
occurred:
Changeover to a suitable default function to permit continued driving, although with some
restrictions. This allows the vehicle to be driven to the nearest MAN service workshop.
Immediate engine stop if required for safety reasons.
As soon as a fault occurs, a fault block is stored in the diagnostic memory or an already existing fault is
updated. In addition, this fault block is sent via CAN bus to the OBDU (on-board diagnostic unit), which is
part of the central on-board computer, via the vehicle management computer.
This message contains the following information:
Fault detection = SPN (suspect parameter number)
Environmental condition 1 = SPN1 with accompanying measured value
Environmental condition 2 = SPN2 with accompanying measured value
Fault type (cause) = FMI (failure mode identification)
Fault priority = PRIO (priority)
Each individual fault is therefore assigned a priority because the faults diagnosed and stored by the control
unit can involve different risks.
Fault Display via. Blink Code
Fault display:
The electronic control unit has self-diagnostic capabilities for all outputs and various inputs. The error at the inputs, outputs and
internal faults are detected, analyzed and stored in diagnostic memory of PTM - ECU.
These errors are displayed in the instrument cluster in the form of Blink Codes.
To display the fault codes
Step 1 - switch “ON” the ignition of vehicle. In case of “Engine Trouble” lamp will glow continuously.
Step 2 - press the accelerator pedal for 3 times up to kick-down position, then indication lamp on cluster (engine shut off) starts
blinking.
Step 3 - count this blinks to identify the SPN – Suspect Parameter Number /DTC- Diagnostic Trouble Code.
Blink Code reading.
The start of a fault code is initiated with the Engine Shut off Indicator in instrument panel.
After a specified time pause, the red warning lamp flashes the first number. The value of the number determines how often the
warning lamp flashes to output a number. This is followed by a specified time pause and then the next number is flashed, etc. (Blink
codes are 3 / 4 digits)
Once a complete fault code has been flashed, the steps 2 & 3 shall be repeated.
If another DTC is available in error memory, next code will start flashing.
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 22 of 34
e.g.-
As it is possible to have fault codes that contain the number zero, a separate figure exists for this. The number zero is output by
flashing three times with fast time period duration.
SPN - Diagnosis code Description
Below is a list of the diagnostic codes, or in the event of an error in the display of the instrumentation MAN-cats ® II computer
screen. In the below table diagnosis code description, summary, diagnosis status, priority, system response, cause &
troubleshooting information is given.
SPN - Suspect Parameter Number - Fault
FMI - Failure Mode Identification – Error
FMI (Failure Mode Identification) status indicators
FMI 0 fault not specified
FMI 1 too high
FMI 2 too low
FMI 3 implausible
FMI 4 no signal available
FMI 5 short-circuit to ground
FMI 6 short-circuit to +UBat
FMI 7 short-circuit
FMI 8 signal faulty
FMI 9 device fault
FMI 10 interruption
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 23 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Plausibility with environment pressure 102 2 3
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Too high 102 2 1
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Too low 102 4 2
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Plausibility with simulation 102 4 8
Coolant Temperature: Too high 110 2 1
Coolant Temperature: Too low 110 4 2
Battery Voltage: Too high 168 4 1
Battery Voltage: Too low 168 4 2
Battery Voltage: Short circuit to battery (internal sensing) 168 4 6
Battery Voltage: Short circuit to ground (internal sensing) 168 4 5
Environment Temperature: Too high 171 4 1
Environment Temperature: Too low 171 4 2
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Plausibility with simulation 173 4 3
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Too high 173 5 1
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Too low 173 4 2
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Difference in temperature is too big 173 5 8
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Difference in temperature is too small 173 5 9
Engine CAN: Error-Passive 609 2 8
Engine CAN: Bus-Off 609 2 4
Injector 1: No load 651 2 10
Injector 1: Short circuit 651 2 7
Injector 1: Short circuit high side to low side 651 2 9
Injector 2: No load 652 2 10
Injector 2: Short circuit 652 2 7
Injector 2: Short circuit high side to low side 652 2 9
Injector 3: No load 653 2 10
Injector 3: Short circuit 653 2 7
Injector 3: Short circuit high side to low side 653 2 9
Injector 4: No load 654 2 10
Injector 4: Short circuit 654 2 7
Injector 4: Short circuit high side to low side 654 2 9
Injector 5: No load 655 2 10
Injector 5: Short circuit 655 2 7
Injector 5: Short circuit high side to low side 655 2 9
Injector 6: No load 656 2 10
Injector 6: Short circuit 656 2 7
Injector 6: Short circuit high side to low side 656 2 9
Sensor Supply Monitor 3 1079 2 8
Sensor Supply Monitor 1 1080 2 8
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Too high 1131 4 1
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Too low 1131 4 2
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Plausibility with other temperature sensor 1131 4 8
CAN-Message Aux Inf: AdBlue tank level defect 1761 4 3
CAN-Message Aux Inf: AdBlue tank level invalid 1761 4 8
Overspeed detection 3009 2 1
Main Relay: Stick 3014 2 3
CAN-Message PTM1: Data length error 3016 2 8
CAN-Message PTM1: Time out 3016 2 4
CAN-Message PTM1: Bank switch off signal invalid 3017 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: Engine brake state invalid 3018 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: Overspeed request invalid 3019 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: High idle parameter selection invalid 3020 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: Power train state invalid 3021 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: Ramp switch off request invalid 3022 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: Intermediate speed controller set point invalid 3023 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: High idle set point invalid 3024 5 8
CAN-Message PTM1: High idle set point too low 3024 5 2
CAN-Message PTM1: Driver demand torque invalid 3025 5 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Data length error 3027 2 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Time out 3027 2 4
CAN-Message PTM2: Maximum engine rotational acceleration invalid 3028 4 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Mode request invalid 3029 5 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Low idle parameter selection invalid 3030 4 4
CAN-Message PTM2: Low idle set point invalid 3030 4 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Low idle set point out of range 3030 4 1
CAN-Message PTM2: Engine stop request invalid 3031 5 2
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 24 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
CAN-Message PTM2: Input shaft speed invalid 3032 5 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Limiting torque invalid 3033 5 8
CAN-Message PTM2: Limiting torque out of range 3034 5 8
CAN-Message PTM3: Data length error 3035 2 8
CAN-Message PTM3: Time out 3035 2 4
CAN-Message PTM3: Accelerator pedal position invalid 3036 4 8
CAN-Message PTM3: Retarder oil temperature invalid 3037 4 8
CAN-Message PTM3: Intermediate speed controller feedback factor invalid 3038 5 8
CAN-Message PTM3: Vehicle distance/operating hours invalid 3039 5 8
CAN-Message PTM3: Vehicle stop state invalid 3040 5 8
CAN-Message Aux Inf: AdBlue tank temperature defect 3043 4 3
CAN-Message Aux Inf: AdBlue tank temperature invalid 3043 4 8
Environment Pressure: Pressure implausible 3046 4 3
Environment Pressure: Signal error 3046 4 4
Environment Pressure: Loose contact 3046 4 11
Environment Pressure: Short circuit to battery or open load 3046 4 6
Environment Pressure: Short circuit to ground 3046 4 5
CAN-Message TCO1: Time out 3047 4 4
CAN-Message Time Date: Time out 3048 4 4
CAN-Message TPC: Data length error 3049 2 8
CAN-Message TPC: Time out 3049 2 4
CAN-Message Eng Temp: Time out 3050 4 4
CAN-Message AMB: Time out 3051 4 4
CAN-Message AuxStsZBR1: Time out 3052 3 4
CAN-Message CRI1: Time out 3053 4 4
Immobiliser system: Wrong key 3076 2 8
Immobiliser system: No key 3077 2 3
ECU Monitoring: Rail pressure implausible 3083 1 3
Rail Pressure Sensor: Positive offset too high 3083 1 1
Rail Pressure Sensor: Negative offset too low 3083 1 2
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Pressure implausible 3088 5 3
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Loose contact 3088 2 11
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Open load or short circuit to battery 3088 2 6
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Short circuit (to ground) 3088 2 5
Coolant Temperature: Temperature implausible 3091 5 3
Coolant Temperature: Signal error 3091 5 4
Coolant Temperature: Loose contact 3091 5 11
Coolant Temperature: Short circuit to battery 3091 5 6
Coolant Temperature: Short circuit to ground 3091 5 5
Coolant Temperature: Open load 3091 5 10
Rail Pressure Sensor: Open load or short cut to battery 3099 1 6
Rail Pressure Sensor: Short circuit (to ground) 3099 1 5
AdBlue Tank Level: Warning Level 1 3456 5 2
AdBlue Tank Level: Warning Level 2 3457 2 2
AdBlue Tank Level: Warning Level 3 3457 2 2
AdBlue Tank Level: Warning Level 4 3457 2 2
OBD-CAN: Error-Passive 3673 4 8
OBD-CAN: Bus-Off 3673 4 4
Master/Slave-CAN: Error-Passive 3674 2 8
Master/Slave-CAN: Bus-Off 3674 2 4
EDC Internal Temperature 1: Open load or short circuit to battery 3735 4 6
EDC Internal Temperature 1: Short circuit (to ground) 3735 4 5
Metering Unit: Over temperature 3747 1 1
Metering Unit: Lowside power stage short circuit to battery 3747 1 6
Metering Unit: Lowside power stage short circuit to ground 3747 1 5
Metering Unit: Loose contact 3748 1 4
Metering Unit: Open load 3748 1 10
Metering Unit: Highside power stage short circuit to battery 3748 1 6
Metering Unit: Highside power stage short circuit to ground 3748 1 5
Metering Unit: Internal current sensing voltage too high 3748 1 1
Metering Unit: Internal current sensing voltage too low 3748 1 2
Starter: Highside power stage short circuit to battery 3751 2 6
Starter: Highside power stage short circuit to ground 3751 2 5
Starter: Open load 3751 2 10
Starter: Over temperature 3751 2 9
Starter: Lowside power stage short circuit to battery 3751 2 1
Starter: Lowside power stage short circuit to ground 3751 2 2
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 25 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
Camshaft Speed: Signal disturbance 3752 2 8
Camshaft Speed: No Signal 3752 2 4
Camshaft Speed: Offset error 3752 2 1
Camshaft Speed: Short circuit to battery 3752 2 6
Camshaft Speed: Short circuit (to ground) 3752 2 5
Camshaft Speed: Open load 3752 2 10
Crankshaft Speed: Signal disturbance 3753 2 8
Crankshaft Speed: No signal 3753 2 4
Crankshaft Speed: Short circuit to battery 3753 2 6
Crankshaft Speed: Short circuit (to ground) 3753 2 5
Crankshaft Speed: Open load 3753 2 10
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Rail pressure too low 3775 1 2
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Rail pressure too high 3775 1 1
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Rail pressure too high (second stage) 3775 1 9
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Positive governor deviation 3776 2 1
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Negative governor deviation at zero delivery 3777 1 1
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Negative governor deviation at zero delivery (second stage) 3777 1 9
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Setpoint value of metering unit in overrun too high 3778 1 1
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Check of the volume flow balance 3779 1 1
Rail Pressure Governor (MeUn-Mode): Check of the volume flow at low idle 3780 1 1
Pressure Relief Valve: Valve open 3781 1 1
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Implausible 3792 4 3
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Loose contact 3792 5 11
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Open load or short circuit to battery 3792 5 10
Temperature OxiCat Upstream: Short circuit (to ground) 3792 5 5
MI Lamp: Open load 3798 4 10
MI Lamp: Over temperature 3798 4 1
MI Lamp: Short cut to battery 3798 4 6
MI Lamp: Short cut to ground 3798 4 5
Compressed Air Valve: Open load 3802 2 10
Compressed Air Valve: Over temperature 3802 2 9
Compressed Air Valve: Short circuit to battery 3802 2 6
Compressed Air Valve: Short circuit to ground 3802 2 5
Starter: Maximum starting time exceeded 3813 2 8
Aftertreatment-CAN: Error-Passive 3819 5 8
Aftertreatment-CAN: Bus-Off 3819 5 4
Can-Message TCO1: Vehicle speed error 3821 4 4
CAN-Message ATI1: Time out 3822 4 4
Misfire Detection: Multiple cylinders 3823 5 3
Misfire Detection: Cylinder 1 in firing order 3824 5 3
Misfire Detection: Cylinder 2 in firing order 3825 5 3
Misfire Detection: Cylinder 3 in firing order 3826 5 3
Misfire Detection: Cylinder 4 in firing order 3827 5 3
Misfire Detection: Cylinder 5 in firing order 3828 5 3
Misfire Detection: Cylinder 6 in firing order 3829 5 3
CAN-Message ATO1: Time out 3830 4 4
Coolant Temperature: Plausibility after engine start 3843 4 8
Coolant Temperature: Plausibility after high load operation 3843 4 3
Environment Temperature: Plausibility with boost temperature 3845 4 3
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Implausible 3847 4 3
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Signal error 3847 5 4
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Loose contact 3847 5 11
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Short circuit to battery 3847 5 6
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Short circuit (to ground) 3847 5 5
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Open load 3847 5 10
Environment Temperature: Temperature implausible 3848 4 3
Environment Temperature: Loose contact 3848 4 11
Environment Temperature: Short circuit to battery 3848 4 6
Environment Temperature: Short circuit to ground 3848 4 5
Environment Temperature: Open load 3848 4 10
EDC Internal Temperature 2: Open load or short circuit to battery 3854 4 6
EDC Internal Temperature 2: Short circuit (to ground) 3854 4 5
ECU Monitoring: Energizing time during overrun too high 3863 1 1
Boost Temperature: Plausibility with boost pressure 3868 4 3
EDC Internal Temperature 2: Too high 3871 4 1
EDC Internal Temperature 2: Too low 3871 4 2
EDC Internal Temperature 1: Too high 3872 4 1
EDC Internal Temperature 1: Too low 3872 4 2
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 26 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Open load 3919 4 10
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Short circuit 3919 4 7
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx invalid 3920 4 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx-signal too high 3920 4 7
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx-signal too low 3920 4 10
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Lambda-signal too high 3921 4 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Lambda-signal too high 3921 4 1
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Lambda-signal too low 3921 4 2
Rail Pressure Sensor: Too many pressure jumps 3926 1 11
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Plausibility with environment pressure 3942 4 3
Boost Temperature (High Pressure): Cooling error 3946 2 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: O2-signal too high 3972 4 1
NOx-Sensor Downstream: O2-signal too low 3972 4 2
Intake Air System: First fresh air temperature sensor at cold start implausible 4033 4 3
Intake Air System: Second fresh air temperature sensor at cold start implausible 4034 4 3
Intake Air System: Third fresh air temperature sensor at cold start implausible 4035 4 3
Intake Air System: Fourth fresh air temperature sensor at cold start implausible 4036 4 3
Intake Air System: Fifth fresh air temperature sensor at cold start implausible 4037 4 3
Intake Air System: More than one fresh air temperature sensor at cold start implausible 4038 4 3
Actuator Supply: Group 1 short circuit to battery 4039 2 6
Actuator Supply: Group 1 short circuit to ground 4039 2 5
Actuator Supply: Group 2 short circuit to battery 4040 2 6
Actuator Supply: Group 2 short circuit to ground 4040 2 5
Actuator Supply: Group 3 short circuit to battery 4041 1 6
Actuator Supply: Group 3 short circuit to ground 4041 1 5
Coolant Temperature: Plausibility with other temperature sensor 4045 4 3
EDC internal: Communication with Cj945 4049 2 9
High power reduction without failure (eg hot temperature,...) 4057 5 1
CAN-Message Aux Inf: Time out 4058 4 4
CAN-Message DSI1: Time out 4059 4 8
CAN-Message DSI2: Time out 4060 4 8
CAN-Message EDC4: Boost temperature invalid 4061 4 8
CAN-Message ERC1: Time out 4062 4 8
CAN-Message EngRetCfg: BAM time out 4065 4 8
CAN-Message: EngRetCfg: Paket time out 4066 4 8
Flame Start System: No response from eRelais 4067 3 9
LIN-Message ERRes1: Time out 4067 3 8
LIN-Message ERRes2: Time out 4067 3 8
LIN-Message ERRes3: Time out 4067 3 8
OBD: Torque limiter active 4069 7 1
EDC internal: Communication error with Cy146[1] 4070 5 8
EDC internal: Communication error with Cy146[2] 4071 5 8
EDC internal: Communication error with Cy146[3] 4072 5 8
EDC internal: Communication error with Cy317 4073 5 8
EDC internal: Communication error with Cy320 4074 5 8
Power stages: Battery voltage too high 4075 4 1
Power stages: Battery voltage too low 4075 4 2
CAN-Message DSI1: Urea dosing quantity defect 4076 4 3
CAN-Message DSI1: Urea dosing quantity invalid 4076 4 8
CAN-Message DSI2: Urea temperature defect 4077 4 3
CAN-Message DSI2: Urea temperature invalid 4077 4 8
CAN-Message DSI1: Urea doser state invalid 4078 4 8
CAN-Message ACK: Time out 4079 2 8
EEPROM: Erase Error 4085 4 8
EEPROM: Read Error 4086 4 8
EEPROM: Write Error 4087 4 8
ECU Monitoring: Injection cut off 4089 2 10
Two Mass Fly Wheel: In resonance point 4090 4 10
Exhaust Temperature: Temperature 1 too high 4091 4 10
Exhaust Temperature: Temperature 1 too low 4091 4 5
Exhaust Temperature: Temperature 6 too high 4096 4 10
Exhaust Temperature: Temperature 6 too low 4096 4 5
Camshaft Speed: Sensor mount error 4097 2 8
Exhaust Gas System: Plausibility of more exhaust-gas temperature 4205 4 3
Exhaust Gas System: Plausibility of first exhaust-gas temperature 4210 4 3
Exhaust Gas System: Plausibility of sixth exhaust-gas temperature 4215 4 3
Exhaust Gas System: Model based plausiblity check of first exhaust-gas temperature 4221 4 3
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 27 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
Exhaust Gas System: Model based plausiblity check of sixth exhaust-gas temperature 4226 4 3
Engine Idle Speed Controller: Engine speed too high during low idle 4228 4 1
Engine Idle Speed Controller: Engine speed too low during low idle 4228 4 2
Injection System: Booster capacitor exceeded 4229 4 2
Injection System: Fuel quantity is above the limit of high pressure pump 4230 4 2
Injection System: Count of injection is above system limit 4231 4 2
Injection System: Number of injection is above limit of CPU 4232 4 2
Injection unit: Start not successful 4233 4 9
Injection Valve: Rail pressure too low, no injection 4234 2 2
LIN-Bus: Blocked bus 4235 3 4
LIN-Bus: Master absent 4235 3 4
Injection Bank 1: Short circuit 4237 2 7
Injection Bank 1: Short circuit to ground 4237 2 5
Injection Bank 2: Short circuit 4238 2 7
Injection Bank 2: Short circuit to ground 4238 2 5
Injection Power stage: Chip error 4239 5 9
Injector 1: Faulty programming of injector adjustment values 4240 4 9
Injector 2: Faulty programming of injector adjustment values 4241 4 9
Injector 3: Faulty programming of injector adjustment values 4242 4 9
Injector 4: Faulty programming of injector adjustment values 4243 4 9
Injector 5: Faulty programming of injector adjustment values 4244 4 9
Injector 6: Faulty programming of injector adjustment values 4245 4 9
Injector 1: Pattern Error 4250 2 8
Injector 2: Pattern Error 4251 2 8
Injector 3: Pattern Error 4252 2 8
Injector 4: Pattern Error 4253 2 8
Injector 5: Pattern Error 4254 2 8
Injector 6: Pattern Error 4255 2 8
ECU Monitoring: A/D-Converter error 4264 2 3
ECU Monitoring: A/D-Converter retiometry correction out of range 4266 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Internal communication error 4267 5 8
Injection Power stage: SPI timeout 4268 5 4
ECU Monitoring: SPI-Bus interrupted 4268 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Multiple ROM errors 4269 5 9
ECU Monitoring: Internal communication error 4270 5 4
ECU Monitoring: Error during shut off test 4271 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Error setting MM response time 4272 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Error in SPI communication 4273 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Undervoltage during shut off test 4274 5 2
ECU Monitoring: Overvoltage during shut off test 4274 5 1
ECU Monitoring: Shut off test error 4275 5 9
ECU Monitoring: Task error 4276 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Error during positive test 4277 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Time monitoring error of shut off test 4278 5 8
ECU Monitoring: Engine speed error 4281 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Energizing time implausible 4282 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Start of energizing implausible 4283 2 3
ECU Monitoring: Zero fuel learning values implausible 4284 2 3
ECU Monitoring: Post injection 2 efficiency implausible 4285 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Post injection 2 shut off implausible 4286 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Post injection 3 efficiency implausible 4287 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Quantity wave correction implausible 4288 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Actual engine torque too high 4290 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Torque reduction in lead path active 4291 2 1
ECU Monitoring: Torque reduction in lead path active 4292 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Torque reduction in set path active 4293 2 8
x 4294 2 1
x 4294 2 2
Main Relay: Early opening 4295 2 9
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Heater implausible 4296 4 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Lambda implausible 4297 4 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx implausible 4298 4 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Power supply error 4304 4 8
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Dynamic check 4306 4 8
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Feedback error 4307 4 8
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Heating not in range 4308 4 8
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx adaption too high 4309 4 1
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx adaption too low 4309 4 2
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 28 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
ECU Monitoring: No communication to power stages 4319 2 8
ECU Monitoring: Power stage shut off during under voltage not successful 4320 2 2
ECU Monitoring: Power stage shut off during overvoltage not successful 4320 2 1
Potential Long Term error 4321 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4322 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4323 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4324 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4325 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4326 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4327 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4328 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4329 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4330 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4331 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4332 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4333 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4334 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4335 4 8
Potential Long Term error 4336 4 8
ECU Monitoring: Power stage shut off not successful 4337 2 8
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Heater open load 4341 4 10
NOx-Sensor Upstream: Heater open load 4342 4 10
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Lambda open load 4343 4 10
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx open load 4344 4 10
NOx-Sensor Upstream: NOx open load 4345 4 10
CAN-Message AT1IGC1: Time out 4365 4 8
CAN-Message AT1IGC2: Time out 4366 4 8
Application Check: Engine efficiency maps not correct 4372 4 3
CAN-Message AT1OGC2: Time out 4374 4 8
CAN-Message AT1OGC1: Time out 4377 4 8
CAN-Message AT1OGC1: NH3 correction invalid 4380 4 8
Pressure Relief Valve: Valve opened to often 4381 4 1
Pressure Relief Valve: Force open performing pressure increase 4382 2 1
Pressure Relief Valve: Force open performing pressure shocks 4383 2 1
Pressure Relief Valve: Valve opening ensured 4384 2 9
Pressure Relief Valve: Pressure outside tolerance with open valve 4385 2 9
Pressure Relief Valve: Valve opened to long 4386 4 1
CAN-Message AT1IGC1: NH3 correction invalid 4387 4 8
CAN-Message AT1OGC2: NO2 correction invalid 4388 4 8
CAN-Message AT1IGC2: NO2 correction invalid 4389 4 8
Rail Pressure Governor: Battery voltage too low 4390 5 2
Rail Pressure Governor (CPC-Mode): Pressure valve setpoint too high 4391 2 3
Rail Pressure Governor (CPC-Mode): Rail pressure too low 4392 2 2
Rail Pressure Governor (CPC-Mode): Rail pressure too high 4392 2 1
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Positive governor deviation 4393 2 1
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Positive governor deviation combined with the set value of the 4394 2 1
pressure control valve
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Negative governor deviation combined with the set value of 4395 2 1
the pressure control valve
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Rail pressure too low 4396 2 2
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Rail pressure too high 4396 2 1
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Negative governor deviation combined with the set value of 4397 2 1
the pressure control valve (second stage)
Rail Pressure Governor (PCV-Mode): Rail pressure too high (second stage) 4398 2 1
Rail pressure governor: Rail pressure too high in limp home mode 4399 2 1
AdBlue System: Defreezing of the dosing system failed 4400 4 9
AdBlue System: Defreezing of dosing system failed due to heater error 4400 4 8
AdBlue System: Dosing system report a system error 4401 4 9
AdBlue System: Dosing system report a system error during dosing 4401 4 8
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Heater short circuit 4403 4 7
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Lambda short circuit 4405 4 7
NOx-Sensor Downstream: NOx short circuit 4406 4 7
Sensor Supply Monitor 2 4409 3 8
Sensor Supply 12V: Supply voltage too high 4410 2 6
Sensor Supply 12V: Supply voltage too low 4410 2 5
Internal Supply 12V: Supply voltage too high 4411 2 1
Internal Supply 12V: Supply voltage too low 4411 2 2
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 29 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
Small Signal Stage Monitor 3 4414 2 8
Small Signal Stage Monitor 4 4415 2 8
Service Lamp: Open load 4416 4 10
Service Lamp: Over temperature 4416 4 1
Service Lamp: Short circuit to battery 4416 4 6
Service Lamp: Short circuit to ground 4416 4 5
ECU Reset: Reset class 0 detected 4419 2 9
ECU Reset: Reset class 1 detected 4420 5 9
ECU Reset: Reset class 2 detected 4421 5 9
CAN-Message AT1OGC1: NOx gain correction invalid 4422 4 3
CAN-Message AT1OGC1: NOx offset correction invalid 4422 4 8
CAN-Message AT1OGC2: Pressure correction invalid 4428 4 8
Temperature Particle Filter Downstream: Differences in temperature too high 4429 4 3
CAN-Message AT1OGC2: O2 pressure correction invalid 4433 4 8
CAN-Message AT1IGC1: NOx gain correction invalid 4436 4 3
CAN-Message AT1IGC1: NOx offset correction invalid 4436 4 8
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Implausible 4437 4 3
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Loose contact 4437 4 11
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Open load or short circuit to battery 4437 4 10
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Short circuit (to ground) 4437 4 5
Temperature SCRCat Upstream: Implausible 4438 4 3
Temperature SCRCat Upstream: Loose contact 4438 4 11
Temperature SCRCat Upstream: Open load or short circuit to battery 4438 4 10
Temperature SCRCat Upstream: Short circuit (to ground) 4438 4 5
AdBlue Heating System: Open load 4439 4 10
AdBlue Heating System: Power stage over temperature 4439 4 1
AdBlue Heating System: Short circuit to battery 4439 4 6
AdBlue Heating System: Short circuit to ground 4439 4 5
CAN-Message TCO1: Vehicle speed defect 4441 4 8
CAN-Message AT1IGC2: Pressure correction invalid 4442 4 8
CAN-Message AT1IGC2: O2 pressure correction invalid 4443 4 8
CAN-Message ThrVlv: Time out 4444 5 8
CAN-Message PGNRQGlb: Time out 4445 4 8
CAN-Message PGNRQ: Time out 4446 4 8
Sensor Supply Monitor 1 4447 2 8
Sensor Supply Monitor 2 4448 2 8
Sensor Supply Monitor 3 4449 1 8
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 1 too high 4450 2 1
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 1 too low 4450 2 2
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 2 too high 4451 2 1
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 2 too low 4451 2 2
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 3 too high 4452 2 1
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 3 too low 4452 2 2
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 4 too high 4453 2 1
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 4 too low 4453 2 2
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 5 too high 4454 2 1
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 5 too low 4454 2 2
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 6 too high 4455 2 1
Injection System: Zero fuel learning cylinder 6 too low 4455 2 2
Boost Pressure Monitoring: Boost pressure too high 4460 2 1
AdBlue System: NOx-Emission over limit 1 4462 4 8
AdBlue System: NOx-Emission over limit 2 4463 4 8
AdBlue System: Urea consumption too high 4464 4 1
AdBlue System: Urea consumption too low 4464 2 2
Boost Pressure Controller: Severe pressure deviation 4466 2 8
Urea heater valve error 4467 5 8
Urea temp too high 4467 4 1
Urea temp too low 4467 4 2
NOx-Emission too high after AdBlue refilling 4469 5 1
Vehicle Speed: Invalid 4470 4 3
Flame Start System: No burning flame 4475 3 4
Flame Start System: Glow plug driver defect 4475 3 8
Flame Start System: Glow plug open load 4475 3 10
Flame Start System: Glow plug driver overheat 4475 3 9
Flame Start System: Glow plug short circuit to battery 4475 3 6
Flame Start System: Glow plug short circuit to ground 4475 3 5
Flame Start System: Glow plug current implausible high 4475 3 1
Flame Start System: Glow plug current implausible low 4475 3 2
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 30 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
Flame Start System: Solenoid valve driver defect 4477 3 9
Flame Start System: Solenoid valve open load 4477 3 10
Flame Start System: Solenoid valve driver overheat 4477 3 1
Flame Start System: Solenoid valve short circuit to battery 4477 3 6
Flame Start System: Solenoid valve short circuit to ground 4477 3 5
CAN-Message AuxStat1: Light test state invalid 4478 3 8
Camshaft Speed: SPC error 4492 2 8
Crankshaft Speed: SPC error 4492 2 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Plausibility with lambda sensor 4527 4 3
NOx-Sensor Downstream: Plausibility with NOx-Sensor upstream 4527 4 8
Rail Pressure Governor: Pressure reduction after engine stopped not possible 4533 2 4
AdBlue System: Adaption at maximum 4534 4 1
AdBlue System: Urea concentration too low 4535 0 1
AdBlue System: Urea temperature not in range 4535 4 3
AdBlue System: Urea concentration too low (warning limit) 4535 2 2
Inducement System: Warning (AdBlue quality) 4535 2 1
NOx-Sensor Upstream: Lambda short circuit 4536 4 7
Inducement System: Warning (Dosing interruption) 4547 2 2
Inducement System: Warning (AdBlue consumption) 4547 2 1
Inducement System: Warning (EGR error) 4548 2 1
Inducement System: Warning (Monitoring error) 4548 2 4
Particle Filter: Service Regeneration needed 4549 2 1
AdBlue System: Urea consumption too low (warning) 4551 5 1
Thermoelement 1: Device Error 4556 5 9
Thermoelement 1: Open Load 4556 5 10
Thermoelement 1: Short circuit to battery 4556 5 6
Thermoelement 1: Short circuit to ground 4556 5 5
CAN-Message EgTFrm1: Temperature 1 invalid 4556 5 8
CAN-Message EgTFrm1: Time out 4559 5 8
CAN-Message EgTFrm2: PCB Error 4560 5 8
Thermoelementcontrolunit: Cold junction open load 4560 5 10
Thermoelementcontrolunit: Cold junction plausibility 4560 5 3
Thermoelementcontrolunit: Cold junction short circuit 4560 5 7
Thermoelementcontrolunit: Device error 4560 5 9
Thermoelement 4: Device Error 4561 5 9
Thermoelement 4: Open Load 4561 5 10
Thermoelement 4: Short circuit to battery 4561 5 6
Thermoelement 4: Short circuit to ground 4561 5 5
CAN-Message EgTFrm2: Temperature 4 invalid 4561 5 8
CAN-Message EgTFrm2: Time out 4562 5 8
Anti-Tampering System: Creep mode active 4565 4 1
Anti-Tampering System: Creep mode override 4566 4 1
Anti-Tampering System: Creep mode power stage error 4566 4 8
Anti-Tampering System: Activation time out 4566 4 4
ECU Monitoring: Starter release plausibility 4567 2 3
Smooth Running Control: Cylinder 1 in fire sequence out of range 4571 2 1
Smooth Running Control: Cylinder 2 in fire sequence out of range 4572 2 1
Smooth Running Control: Cylinder 3 in fire sequence out of range 4573 2 1
Smooth Running Control: Cylinder 4 in fire sequence out of range 4574 2 1
Smooth Running Control: Cylinder 5 in fire sequence out of range 4575 2 1
Smooth Running Control: Cylinder 6 in fire sequence out of range 4576 2 1
Tuning Protection 4587 2 8
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: SCRCat not present 4588 4 8
Vehicle Speed Limiter: Open load 4589 4 10
Vehicle Speed Limiter: Over temperature 4589 4 1
Vehicle Speed Limiter: Short circuit to battery 4589 4 6
Vehicle Speed Limiter: Short circuit to ground 4589 4 5
CAN-Message AMB: Environment temperature invalid 4590 0 1
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Over boost 4591 5 1
Boost Pressure (High Pressure): Under boost 4591 5 2
Boost Pressure (Low Pressure): Over boost 4592 5 1
Boost Pressure (Low Pressure): Under boost 4592 5 2
Environment Temperature: Plausibility with air mass sensor temperature 4593 4 1
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Too high 4594 4 1
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Too low 4594 4 2
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Temperature decreasing too fast 4594 4 8
Temperature SCRCat Downstream: Differences in temperature too low 4594 4 9
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 31 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
CAN-Message DPFC1: Time out 4595 5 4
CAN-Message PTM4: Regeneration inhibition invalid 4595 4 3
CAN-Message PTM4: Regeneration request invalid 4595 4 8
CAN-Message PTM4: Data length error 4596 4 8
CAN-Message PTM4: Time out 4596 4 4
CAN-Message PTM4: Urea tank level validity information invalid 4596 4 3
CAN Message CRI1: Urea concentration invalid 4597 4 3
CAN Message CRI1: Urea tank temperature invalid 4598 4 8
AdBlue System: Urea consumption too low 4600 4 2
Temperature Thermoelement 1: Temperature too high 4601 5 1
Temperature Thermoelement 1: Temperature too low 4601 5 2
Thermoelementcontrolunit Temperature: Too high 4604 5 1
Thermoelementcontrolunit Temperature: Too low 4604 5 2
Thermoelementcontrolunit Power Supply: Too high 4605 5 1
Thermoelementcontrolunit Power Supply: Too low 4605 5 2
Temperature Thermoelement 4: Temperature too high 4606 5 1
Temperature Thermoelement 4: Temperature too low 4606 5 2
Rail Pressure Limiting: Irreversible shut-off 4609 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Rail pressure over limit 4610 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Rail pressure not plausible 4611 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Maximum rail pressure limiting count reached 4612 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Maximum rail pressure limiting time reached 4613 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Reversible shut-off 4614 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Torque Limit 4615 4 8
Rail Pressure Limiting: Rail pressure over limit 4616 4 8
OxiCat: Oxidation catalyst defect 4617 5 8
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5004 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5004 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5006 0 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5006 0 7
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5006 0 10
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5014 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5014 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5014 0 10
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5016 0 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5017 0 7
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5021 0 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5022 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5022 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5022 0 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5035 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5035 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5036 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5036 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5037 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5037 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5038 0 6
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5039 0 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5040 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5040 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5042 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5042 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5555 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5555 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5555 0 10
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5556 0 10
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5557 0 3
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5557 0 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5558 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5558 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5559 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5559 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5560 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5560 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5561 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5561 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5562 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5562 0 1
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 32 of 34
Description SPN Prio FMI
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5563 0 2
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5563 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5564 0 3
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 5565 0 3
CAN-Message DM1DCU: Time out BAM to packet 5600 4 9
CAN-Message DM1DCU: Byte length error 5601 4 9
CAN-Message DM1DCU: Time out packet to packet 5602 4 9
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8046 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8047 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8048 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8049 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8050 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8051 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8052 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8053 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8054 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8055 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8056 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8057 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8058 0 1
Array of Diagnostic Fault check for SPN and FMI matching of DM1DCU message 8059 0 1
CAN-Message DM1DCU: Time out 8060 4 4
CAN-Message DM1DCU: Unknown SPN 8064 4 1
Injection Bank 1: Time out 8109 4 1
Injection Bank 2: Time out 8110 4 1
ECU Monitoring: Energizing time during overrun and over heat protection too high 8111 4 1
Inducement System: Power reduction (EGR error) 8121 0 2
Inducement System: Creep mode (EGR error) 8122 0 2
Inducement System: Power reduction (Dosing interruption) 8124 0 2
Inducement System: Creep mode (Dosing interruption) 8125 0 2
Inducement System: Creep Mode (AdBlue tank empty) 8127 0 2
Inducement System: Power reduction (AdBlue consumption) 8128 0 2
Inducement System: Creep mode (AdBlue consumption) 8129 0 2
Inducement System: Power reduction (AdBlue quality) 8131 0 2
Inducement System: Creep mode (AdBlue quality) 8132 0 2
Inducement System: Power reduction (Monitoring error) 8134 0 2
Inducement System: Creep mode (Monitoring error) 8135 0 4
PTM EM STEP- IV SPN List
S.No SPN Description
1 168 Battery voltage Signal
2 5546 Speed signal responsible for Speed limit
3 5547 Speed limit is not possible
4 5548 Engine start without a start command
5 5552 Actual engine torque Signal
6 5557 Channel 1 accelerator pedal error signal
7 5558 Channel 2 accelerator pedal error signal
8 5560 Barometric Pressure CAN-Signal
9 5570 Clutch travel sensor signal
10 5576 Engine Coolant Temperature CAN-Signal
11 5577 Engine Oil Pressure CAN signal
12 5578 Engine Speed CAN signal
13 5581 Engine brake output Signal
14 5600 CAN signal Nominal Friction Torque Percent
15 5614 CAN signal Engine Percent Load at Current Speed
16 5615 Exhaust back pressure sensor ground Signal
17 5616 Exhaust back pressure sensor power supply signal
18 5617 Exhaust back pressure sensor signal
19 5627 CAN signal Engine Torque Reference (Engine Configuration)
20 5640 CAN signal Acknowledge start command
21 5643 CAN signal emergency request
MTI-Training Academy EDC 17 Common Rail Page 33 of 34
S.No SPN Description
22 5644 CAN signal null sets requirements for motor brake
23 5645 CAN signal start request
24 5647 Voltage terminal 15 signal
25 5651 CAN signal EDR-limiting torque
26 5672 Transmission Neutral Switch
27 5681 Diagnosis CAN bus off
28 5682 Engine CAN bus off
29 5685 Accelerator pedal signal
30 5713 Internal Error Of ECU
31 5715 Internal Error Of ECU
32 5717 Internal Error Of ECU
33 5718 Internal Error Of ECU
34 5719 Internal Error Of ECU
35 5720 Internal Error Of ECU
36 5721 Internal Error Of ECU
37 5724 Internal Error Of ECU
38 5725 Internal Error Of ECU
39 5726 Internal Error Of ECU
40 5727 Internal Error Of ECU
41 5728 Internal Error Of ECU
42 5729 Internal Error Of ECU
43 5730 Internal Error Of ECU
44 5731 Internal Error Of ECU
45 5733 Internal Error Of ECU
46 5734 Internal Error Of ECU
47 5736 Internal Error Of ECU
48 5737 Internal Error Of ECU
49 5738 Internal Error Of ECU
50 5739 Internal Error Of ECU
51 5740 Internal Error Of ECU
52 5741 Internal Error Of ECU
53 5743 Internal Error Of ECU
54 5764 terminal 50 Signal
55 5766 Demolition of M-CAN signal
56 5768 Absolute clutch travel
57 5769 Failure of cruise control functionality
58 5771 Internal Error Of ECU
59 5772 Internal Error Of ECU
60 5775 Coolant level Signal
61 5776 Coolant temperature Signal
62 5777 Coolant temperature Signal
63 5778 Digital Input of clutch
64 5779 Frequency / PWM Signal Input
65 5872 CAN Signal
66 5842 Line fault at the output red warning lamp on pin A7
67 5549 Immobiliser 1 other pairing
68 5556 Ambient Temperature Sensor
69 5674 Signal "Current Gear" cannot be calculated
70 5680 Signal "transmission Actual Gear Ratio" cannot be calculated
71 5704 Current purely virtual gear ratio
MTI-Training Academy VES- EDC 17 Page 34 of 34
You might also like
- Parts Manual - SHG 190 - 2011 ModelDocument357 pagesParts Manual - SHG 190 - 2011 Modeliqbal hussein100% (4)
- Daf Ix Ecsdc5 BlockdiagramDocument28 pagesDaf Ix Ecsdc5 BlockdiagramMircea Gilca100% (1)
- DAF Truck 16 Pole Diagnostic Pinout Diagram @Document3 pagesDAF Truck 16 Pole Diagnostic Pinout Diagram @Anonymous YAb02J100% (1)
- VIC + Compteur DAFDocument106 pagesVIC + Compteur DAFmaxime le sann100% (2)
- EBS3.1 Repair GuideDocument40 pagesEBS3.1 Repair GuidealeksandrNo ratings yet
- Neoplan CityLiner Spare Parts Catalog-2Document220 pagesNeoplan CityLiner Spare Parts Catalog-2CRAC100% (2)
- Ecas For Trucks 8150100273 PDFDocument113 pagesEcas For Trucks 8150100273 PDFMircea Gilca83% (6)
- MAN Injectie Electronica EDC M S 6 4 PDFDocument63 pagesMAN Injectie Electronica EDC M S 6 4 PDFarmin100% (1)
- ECU System and DEC SystemDocument30 pagesECU System and DEC SystemHariNo ratings yet
- Wabco Atc CanDocument36 pagesWabco Atc CanCostel Caraman100% (1)
- Daf Ix BBM BlockdiagramDocument46 pagesDaf Ix BBM BlockdiagramMircea Gilca100% (2)
- SPN FMI Fault Region Fault Reaction Fault Description Remedy Ecas Can2 DTC ListDocument6 pagesSPN FMI Fault Region Fault Reaction Fault Description Remedy Ecas Can2 DTC Listxaime166100% (1)
- MAN TGA FFR Component List PDFDocument5 pagesMAN TGA FFR Component List PDFAlexander GryshcheniukNo ratings yet
- CAN Connection, VIC-3 Electronic Unit (D358)Document3 pagesCAN Connection, VIC-3 Electronic Unit (D358)Vincent Price100% (1)
- ZF Est 48Document98 pagesZF Est 48Андрій ЯвнийNo ratings yet
- CDCDCDocument61 pagesCDCDCAndrijana Majo100% (1)
- T66 2 Ecam 81995985292 EngDocument104 pagesT66 2 Ecam 81995985292 EngGonçalo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Document2 pagesFault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Стефан Тасиќ100% (1)
- Location, EBS-3 ECU (D376)Document1 pageLocation, EBS-3 ECU (D376)Daniel PricopNo ratings yet
- 01A-3 Power Supply After Contact XLRTEH4300G038443Document5 pages01A-3 Power Supply After Contact XLRTEH4300G038443НиколайNo ratings yet
- P Dmci (D965) : Ower Supply and Earth of Electronic UnitDocument136 pagesP Dmci (D965) : Ower Supply and Earth of Electronic UnitBranko Andric100% (1)
- Bova Lexio EBS WiringDocument44 pagesBova Lexio EBS WiringVMGroup 2008No ratings yet
- Coduri Man TGXDocument31 pagesCoduri Man TGXMocanu LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- DW13294103Document72 pagesDW13294103p_jankoNo ratings yet
- 07E-1 TraXon XLRAEM4100G211062Document1 page07E-1 TraXon XLRAEM4100G211062Dtl DiagNo ratings yet
- XF105 System and Component Information Als-S: D M STDocument42 pagesXF105 System and Component Information Als-S: D M STAnd DronNo ratings yet
- A808 AdBlue Supply Module - Flushing Process - EngDocument5 pagesA808 AdBlue Supply Module - Flushing Process - EngGonçalo PereiraNo ratings yet
- EST-42 GearboxDocument64 pagesEST-42 GearboxVilneda77% (13)
- ABS 6 System PDFDocument46 pagesABS 6 System PDFVincent Price100% (1)
- Driving With EuroTronicDocument18 pagesDriving With EuroTronicBroCactus100% (2)
- MANWIS - XSLT - Body Acelerator PedalDocument6 pagesMANWIS - XSLT - Body Acelerator PedalaliNo ratings yet
- Ecas - Optiride PDFDocument71 pagesEcas - Optiride PDFDinu Gabriel100% (2)
- Ix Astronic Lite BlockdiagramDocument26 pagesIx Astronic Lite BlockdiagramBranko Andric100% (1)
- Daf Ix Est41 BlockdiagramDocument20 pagesDaf Ix Est41 BlockdiagramMircea Gilca100% (1)
- Daf Sectiondiagram Ecs-Dc3 Cf65 A0442Document3 pagesDaf Sectiondiagram Ecs-Dc3 Cf65 A0442Mircea GilcaNo ratings yet
- MAN TGX KondicionerDocument2 pagesMAN TGX KondicionerPetar Nikolaev100% (1)
- 03G-1 Pci Xlrteh4300g033850Document5 pages03G-1 Pci Xlrteh4300g033850Daniel PricopNo ratings yet
- T-18 Descrierea Sistemului EDC7Document271 pagesT-18 Descrierea Sistemului EDC7Andrei State100% (1)
- Daf Ix Achea BlockdiagramDocument46 pagesDaf Ix Achea BlockdiagramMircea GilcaNo ratings yet
- FFR Test Step ListDocument26 pagesFFR Test Step Listumar chNo ratings yet
- Truck/MAN/TG-A/310/Truck/D 2866 / ( - /99 - /07) VDO/FFR Vehicle-Engine (Navigator) /-/-/with Manual Gearbox ZF and Take-OffsDocument5 pagesTruck/MAN/TG-A/310/Truck/D 2866 / ( - /99 - /07) VDO/FFR Vehicle-Engine (Navigator) /-/-/with Manual Gearbox ZF and Take-OffsRomica CiorneiNo ratings yet
- MAN K100 Electrical System TGS-TGXDocument236 pagesMAN K100 Electrical System TGS-TGXrijas rijas100% (2)
- Daf Ix Atc BlockdiagramDocument24 pagesDaf Ix Atc BlockdiagramMircea Gilca100% (1)
- KIBES® Body and Chassis Control: Multiplex System For Commercial VehiclesDocument20 pagesKIBES® Body and Chassis Control: Multiplex System For Commercial VehiclesGyörgy BáriNo ratings yet
- System Manual Alarm System: DW032656 English Printed in The NetherlandsDocument112 pagesSystem Manual Alarm System: DW032656 English Printed in The NetherlandsP GlNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes: STO U AndriivDocument19 pagesFault Codes: STO U AndriivAtochkavNo ratings yet
- MAN TGA FFR Component ListDocument5 pagesMAN TGA FFR Component Listronitmanoj100% (2)
- MAN TG A FFR Code ListDocument14 pagesMAN TG A FFR Code ListOumarba Kamanda100% (2)
- Central On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302Document55 pagesCentral On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302esam Philipe100% (1)
- Fault Codes: Diesel (Engine Control - DMCI Delphi - KOEO (Engine Off) )Document3 pagesFault Codes: Diesel (Engine Control - DMCI Delphi - KOEO (Engine Off) )Aleksandar Nikolovski0% (1)
- Kerax ITC 1998 ENDocument114 pagesKerax ITC 1998 ENKevine KhaledNo ratings yet
- MAN-Trouble Codes - FFR - 32 A 3527Document28 pagesMAN-Trouble Codes - FFR - 32 A 3527Gastao100% (1)
- Complete Program Denoxtronic Diesel Systems: For The Testing and Repair ofDocument8 pagesComplete Program Denoxtronic Diesel Systems: For The Testing and Repair ofAlessandro SambugaroNo ratings yet
- Ix Ebs BlockdiagramDocument32 pagesIx Ebs BlockdiagramBranko AndricNo ratings yet
- MAN PTM CONTROL UNIT Service Information-3Document22 pagesMAN PTM CONTROL UNIT Service Information-3Oroszi GáborNo ratings yet
- Electrical SystemDocument2 pagesElectrical Systemdaniel_jorge_10100% (1)
- Frame Engine: EMS - Engine Management SystemDocument1 pageFrame Engine: EMS - Engine Management SystemAbner Souza100% (1)
- Daf EupDocument144 pagesDaf EupDenis Shihskoff100% (1)
- EBS 5 Student BookletDocument44 pagesEBS 5 Student BookletAriel100% (1)
- Group 13E Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemDocument57 pagesGroup 13E Electronically Controlled Fuel Systemandleralfonso7308No ratings yet
- 164 TWSM0814R 4M5 enDocument71 pages164 TWSM0814R 4M5 enClaudio Rene Silva HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ac Tech Mch Drives Installation Operation ManualDocument91 pagesAc Tech Mch Drives Installation Operation Manualiqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- Bhutan QM Rem PG1Document1 pageBhutan QM Rem PG1iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- 684 MK1 Technical Training Rev - 01Document96 pages684 MK1 Technical Training Rev - 01iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management of Fast Moving Spares Parts of Veh Eqpt Plants A Practical Approach For Field Workshops Base Workshops of Border Roads Organisation Ijariie13344Document36 pagesInventory Management of Fast Moving Spares Parts of Veh Eqpt Plants A Practical Approach For Field Workshops Base Workshops of Border Roads Organisation Ijariie13344iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 06-01-2023 15.03Document1 pageCamScanner 06-01-2023 15.03iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- 03-20-2022 13-14-33Document5 pages03-20-2022 13-14-33iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- QUOT - 1477569 RigsarDocument1 pageQUOT - 1477569 Rigsariqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Layout Plan Opt 5Document1 pageElectrical Layout Plan Opt 5iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- FLAMCO-HP500 Installation DrawingDocument1 pageFLAMCO-HP500 Installation Drawingiqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- MT1.0 - Permanant - Foundation Drawing - (Skid) - INLINE BIN - 01 - Sheet 1 Off 2Document1 pageMT1.0 - Permanant - Foundation Drawing - (Skid) - INLINE BIN - 01 - Sheet 1 Off 2iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- Cable Track Sizing Final Sheet 15.07.23Document6 pagesCable Track Sizing Final Sheet 15.07.23iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- Resume Contents - Rev 1Document14 pagesResume Contents - Rev 1Yeshi UchihaNo ratings yet
- Enrique Granados: Danza Espanola No.2 (Oriental)Document7 pagesEnrique Granados: Danza Espanola No.2 (Oriental)JuanSubelsaNo ratings yet
- Fault AnalysisDocument68 pagesFault AnalysismohamadeisaNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things: Jordi Salazar, Santiago SilvestreDocument31 pagesInternet of Things: Jordi Salazar, Santiago SilvestreMaicol CoaguilaNo ratings yet
- Effective Delivery of Synchronous and Asynchronous Teaching Reflection SynchronousDocument2 pagesEffective Delivery of Synchronous and Asynchronous Teaching Reflection SynchronousE Noicale GadibeNo ratings yet
- 345Document2 pages345MiguelLalanguiNo ratings yet
- Kobiawa's Degree ProjectDocument70 pagesKobiawa's Degree ProjectNana AmaNo ratings yet
- White Flag of The Dead Free Audiobooks Online: Link in Page 4 To Listen or Download BookDocument4 pagesWhite Flag of The Dead Free Audiobooks Online: Link in Page 4 To Listen or Download BookBonRobertNo ratings yet
- Flow Control ValveDocument5 pagesFlow Control Valvezakaria100% (1)
- Concepts (PPT) - Data PreprocessingDocument19 pagesConcepts (PPT) - Data Preprocessingmtemp7489No ratings yet
- Tps 54312Document27 pagesTps 54312Dino NecciNo ratings yet
- Film Sound Production Project BriefDocument3 pagesFilm Sound Production Project BriefREYNOLD ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Power Off Reset Reason BackupDocument4 pagesPower Off Reset Reason BackupSit CtvNo ratings yet
- How To Reset Password Quick Guide: Hikvision Technical Support TeamDocument15 pagesHow To Reset Password Quick Guide: Hikvision Technical Support TeamShailendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Management and Tecnology Harishchandra Post Graduate CollegeDocument16 pagesFaculty of Management and Tecnology Harishchandra Post Graduate Collegeaniket chauhanNo ratings yet
- Penawaran Harga OverHoul Nissan RD 10Document3 pagesPenawaran Harga OverHoul Nissan RD 10rian borlandNo ratings yet
- Effect of Water Injection On Reservoir Performance ofDocument18 pagesEffect of Water Injection On Reservoir Performance ofKacha SmitNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 FM LeetDocument5 pagesAssignment-3 FM LeetŔÄHÙŁ ÇHÓÜĐHÃŔŸNo ratings yet
- Anggi Ginanjar Supriatna: Kec - Pacet Kab - Bandung 40385 West Java, Indonesia EmailDocument10 pagesAnggi Ginanjar Supriatna: Kec - Pacet Kab - Bandung 40385 West Java, Indonesia EmailRandy NetofaNo ratings yet
- Crouzet Millenium - Mascable Programming CableDocument2 pagesCrouzet Millenium - Mascable Programming CableFeras AdvertisementsNo ratings yet
- Configuration For CA-7 - IBM DocumentationDocument7 pagesConfiguration For CA-7 - IBM DocumentationFedericopolidoro Polidoro NicolettiNo ratings yet
- SAN Congestion! Understanding, Troubleshooting, Mitigating in A Cisco FabricDocument174 pagesSAN Congestion! Understanding, Troubleshooting, Mitigating in A Cisco FabricPavan NavNo ratings yet
- TLE4997E2: Programmable Linear Hall SensorDocument34 pagesTLE4997E2: Programmable Linear Hall SensortanmaysutariaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Factor Corrector Using ArduinoDocument77 pagesAutomatic Power Factor Corrector Using ArduinoVinay kumarNo ratings yet
- Gerhardt Vapodest 30sDocument40 pagesGerhardt Vapodest 30sAnonymous YwFJrk0yC100% (3)
- Shashank Eumind ProjectDocument3 pagesShashank Eumind Projectapi-536196914No ratings yet
- Sri Krishna Arts and Science Computer Technology: Course Coordinator Dr. V. S. Anita Sofia Prof. & HeadDocument78 pagesSri Krishna Arts and Science Computer Technology: Course Coordinator Dr. V. S. Anita Sofia Prof. & HeadAnita Sofia VNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes QAS 200VdDocument118 pagesManual de Partes QAS 200VdLeandro ToledoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Int Unit1 Follow-upEmailDocument3 pagesPre-Int Unit1 Follow-upEmailJennifer Leal PavaNo ratings yet
- Belimo Sensors Master-Format En-UsDocument7 pagesBelimo Sensors Master-Format En-UsRexell CusipagNo ratings yet