Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Friction
Friction
Uploaded by
marillajp02Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Friction
Friction
Uploaded by
marillajp02Copyright:
Available Formats
Friction
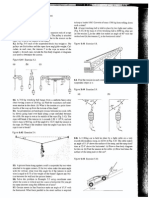
1.) The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with loose crates having a coefficient of static friction of
0.25 with the floor. If the train is initially moving at a speed of 48 km/h, in how short a distance
can the train be stopped at constant acceleration without causing the crates to slide over the
floor?
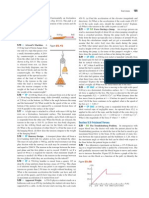
2.) A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg, including drawers and clothing, rests on the floor. (a) If
the coefficient of static friction between the bureau and the floor is 0.45, what is the magnitude
of the minimum horizontal force that a person must apply to start the bureau moving? (b) If the
drawers and clothing, with 17 kg mass, are removed before the bureau is pushed, what is the
new minimum magnitude?
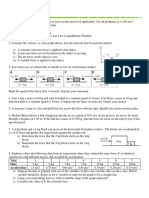
3.) A 2.5 kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force F of magnitude 6.0 N
and a vertical force P are then applied to the block (Fig. 6-17). The coefficients of friction for the
block and surface are ms=0.40 and mk=0.25. Determine the magnitude of the frictional force
acting on the block if the magnitude of P is (a) 8.0 N, (b) 10 N, and (c) 12 N.
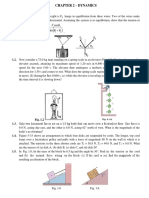
4.) A person pushes horizontally with a force of 220 N on a 55 kg crate to move it across a level
floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is 0.35. What is the
magnitude of (a) the frictional force and (b) the acceleration of the crate?
5.) A 3.5 kg block is pushed along a horizontal floor by a force of magnitude 15 N at an angle of 40
degrees with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor is
0.25. Calculate the magnitudes of (a) the frictional force on the block from the floor and (b) the
block’s acceleration.
You might also like
- Dynamics Extra Study Questions: Short AnswerDocument109 pagesDynamics Extra Study Questions: Short Answeramitdeo99No ratings yet
- GP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsDocument14 pagesGP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsUmbina Gescery100% (1)
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Document19 pagesNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargNo ratings yet
- Easy ProblemsDocument15 pagesEasy ProblemsChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentKhyzer HayyatNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tut3 1Document2 pagesTut3 1JOFFA LING JUN XIANGNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- 2018 June Test PrepquestionsDocument14 pages2018 June Test PrepquestionsSiinozuko MasentseNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheDocument7 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheRachel Du PreezNo ratings yet
- Physics 4A Chapter 5 HW ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics 4A Chapter 5 HW Problemstannguyen8No ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Laboratory No. 2 F DynamicsDocument2 pagesLaboratory No. 2 F Dynamicsjutr ruyluNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 2 - Chap - 2Document8 pagesWorksheet - 2 - Chap - 2midasasfaw100% (1)
- Compiled Structure TestDocument7 pagesCompiled Structure Testtaekim btsNo ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Dynamics 2 D Chapter Problems 2014-06-10Document25 pagesAP Phys1 Dynamics 2 D Chapter Problems 2014-06-10JabeenAhmedNo ratings yet
- JR Iit StarDocument18 pagesJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- WS5 - Work, Energy, PowerDocument3 pagesWS5 - Work, Energy, PowerYoussef Essam abdelwahabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Physics박상현No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4Winni TanNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Dynamics With Problems BoardDocument33 pagesModule 10 Dynamics With Problems Boardjose santiagoNo ratings yet
- Three Identical BallsDocument5 pagesThree Identical BallsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 ForcesDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 Forcesapi-382735450% (4)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 Fall 2022Document4 pagesAssignment - 1 Fall 2022junaidNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-3 Physics 1: Do C.DR - Serda KEC ELG Und Uz, Dr. E.U.Saka November 17, 2020Document2 pagesProblem Sheet-3 Physics 1: Do C.DR - Serda KEC ELG Und Uz, Dr. E.U.Saka November 17, 2020sanNo ratings yet
- Int Mech Practice Exam 2Document9 pagesInt Mech Practice Exam 2Kevin ApodacaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1bonbon.kentbriannNo ratings yet
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford Manisan0% (1)
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford ManisanNo ratings yet
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford ManisanNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesWork and Energy Practice QuestionsApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2.2 ForcesDocument4 pagesAssignment 2.2 Forcespanghua tanNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyDocument7 pagesChap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyTrần Hoàng Việt100% (1)
- Applications of NewtonsDocument1 pageApplications of Newtonsledesma.mj21No ratings yet
- Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument7 pagesForce & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Friction On Level SurfaceDocument2 pages5.3 Friction On Level SurfaceBenNo ratings yet
- Basic Dynamics NumericalsDocument7 pagesBasic Dynamics Numericalsashok royNo ratings yet
- All AnswersDocument22 pagesAll AnswersNadiatul JannahNo ratings yet
- 081 CH 6Document5 pages081 CH 6Harpreet BolaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet - 5chewe chewe100% (1)
- Mechanics Periodic T2W7 SolvedDocument13 pagesMechanics Periodic T2W7 SolvedigoraketaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- General Physics (Phys 1011) : Worksheet 3Document3 pagesGeneral Physics (Phys 1011) : Worksheet 3Meklit100% (1)
- Practice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Document9 pagesPractice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Hasan AlomariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Chapter 7 and 8 ProblemsDocument1 pageAssignment 2 Chapter 7 and 8 ProblemsmlondiyaseenNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash GoyalDocument2 pagesWork Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash GoyalAkash Goyal100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- Physics TestDocument5 pagesPhysics TestAnonymous FH0ak9INfUNo ratings yet
- Physics 201 Exam StudyDocument8 pagesPhysics 201 Exam StudytomvalixNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Problem Set 2016Document6 pagesTopic 2 Problem Set 2016ellie du123No ratings yet
- Cavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneDocument2 pagesCavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneMuhau ZvikomboreroNo ratings yet
- Force and Friction WorksheetDocument2 pagesForce and Friction WorksheetAdil AliNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Marilla, Jeffrey - Phsyed14Document3 pagesMarilla, Jeffrey - Phsyed14marillajp02No ratings yet
- Marilla Jeffrey - RPH - Activity 2Document2 pagesMarilla Jeffrey - RPH - Activity 2marillajp02No ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument1 pageProjectile Motionmarillajp02No ratings yet
- Marilla - Art Diary AssesmentDocument1 pageMarilla - Art Diary Assesmentmarillajp02No ratings yet
- L1 UnitsDocument1 pageL1 Unitsmarillajp02No ratings yet
- 1st INTERIM ENITV31DDocument1 page1st INTERIM ENITV31Dmarillajp02No ratings yet