Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation of Toxoplasm
Presentation of Toxoplasm
Uploaded by
o6131040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesToxoplasma gondii is an intracellular parasite that can infect many warm-blooded animals including humans. It causes the disease toxoplasmosis, which has varying clinical manifestations depending on a person's immune status. Toxoplasmosis is transmitted through ingesting undercooked meat or cat feces and has a life cycle involving cats. In those with weak immune systems, it can cause severe diseases like encephalitis or pneumonia. Congenital toxoplasmosis from infection during pregnancy poses risks for infants like neurological or eye complications. Diagnosis involves serological tests to detect antibodies or molecular tests to find the parasite's DNA in samples.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentToxoplasma gondii is an intracellular parasite that can infect many warm-blooded animals including humans. It causes the disease toxoplasmosis, which has varying clinical manifestations depending on a person's immune status. Toxoplasmosis is transmitted through ingesting undercooked meat or cat feces and has a life cycle involving cats. In those with weak immune systems, it can cause severe diseases like encephalitis or pneumonia. Congenital toxoplasmosis from infection during pregnancy poses risks for infants like neurological or eye complications. Diagnosis involves serological tests to detect antibodies or molecular tests to find the parasite's DNA in samples.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesPresentation of Toxoplasm
Presentation of Toxoplasm
Uploaded by
o613104Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular parasite that can infect many warm-blooded animals including humans. It causes the disease toxoplasmosis, which has varying clinical manifestations depending on a person's immune status. Toxoplasmosis is transmitted through ingesting undercooked meat or cat feces and has a life cycle involving cats. In those with weak immune systems, it can cause severe diseases like encephalitis or pneumonia. Congenital toxoplasmosis from infection during pregnancy poses risks for infants like neurological or eye complications. Diagnosis involves serological tests to detect antibodies or molecular tests to find the parasite's DNA in samples.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
:Toxoplasma
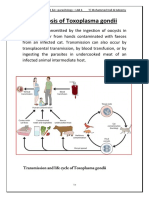
Is gondii is an intracellular parasite that infects a wide range of warm-
blooded animals, including humans. It is the causative agent of
toxoplasmosis, a disease that can have varying clinical manifestations
depending on the immune status of the individual. Here is some
information on transmission, life cycle, pathogenesis, clinical features, and
diagnosis of Toxoplasma:
توكسوبالزما غوندي هو طفيل داخل الخاليا يصيب مجموعة واسعة توكسوبالزما
غوندي هو طفيل داخل الخاليا يصيب مجموعة واسعة من الحيوانات ذات الدم
وهو مرض، وهو العامل المسبب لمرض التوكسوبالزموز. بما في ذلك البشر،الدافئ
يمكن أن يظهر بأعرا العاملs.
- In immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS or
undergoing organ transplantation, Toxoplasma can cause severe disease,
including encephalitis, pneumonia, and disseminated infection.
- Congenital toxoplasmosis can lead to severe neurological and ocular
complications in infants if the mother becomes infected during pregnancy.
4-Diagnosis
To diagnose toxoplasmosis, several methods can be employed:
- Serological tests: Detect antibodies (IgG and IgM) against Toxoplasma in
the blood. IgM antibodies indicate recent infection, while IgG antibodies
indicate past exposure or chronic infection.
- Molecular tests: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can detect Toxoplasma
DNA in various clinical specimens, such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or
amniotic fluid.
- Histopathology: Examination of tissue samples (biopsy or autopsy) can
reveal the presence of Toxoplasma organisms or cysts
You might also like
- Toxoplasma GondiDocument15 pagesToxoplasma GondiAnonymous PiGbPxkHNo ratings yet
- ToxoplasmosisDocument38 pagesToxoplasmosistummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Toxoplasma GondiiDocument6 pagesToxoplasma GondiiSyawal HariadiNo ratings yet
- RB - Petersen. Toxoplasmosis, UpToDate, 2019Document12 pagesRB - Petersen. Toxoplasmosis, UpToDate, 2019GuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Torch: Jessica Santoso Moderator: Dr. Maimun ZA, M.Kes, SP - PKDocument79 pagesTorch: Jessica Santoso Moderator: Dr. Maimun ZA, M.Kes, SP - PKTommy KristantoNo ratings yet
- ToxoplasmaDocument32 pagesToxoplasmaDaxNo ratings yet
- Tokso (Neuro)Document38 pagesTokso (Neuro)ninda karisaNo ratings yet
- 1) Peripheral BloodDocument21 pages1) Peripheral BloodRundNo ratings yet
- Spirochetes 2023Document42 pagesSpirochetes 2023Ahmed khanNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Gondii.Document21 pagesToxoplasma Gondii.Sean MaguireNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis: Acute Systemic DiseaseDocument13 pagesToxoplasmosis: Acute Systemic DiseaseClaudia NovitayantiNo ratings yet
- WWW Ncbi NLM Nih GovDocument4 pagesWWW Ncbi NLM Nih GovhilmayuniarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Last Moment RevisionDocument16 pagesMicrobiology Last Moment RevisionDeepak MainiNo ratings yet
- ToxoplasmosisDocument12 pagesToxoplasmosisaltabeb hasoon100% (2)
- Chronic Active Toxoplasmosis PDFDocument15 pagesChronic Active Toxoplasmosis PDFHugo AzzolinaNo ratings yet
- Jiu 189Document9 pagesJiu 189barreirosanchez984No ratings yet
- Infection in Pregnancy ' JESDocument59 pagesInfection in Pregnancy ' JESmember12dNo ratings yet
- Infecciones Parasitarias SNC SN 2019Document11 pagesInfecciones Parasitarias SNC SN 2019RENZO ALEJANDRO ACUÑA FLORESNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Gondii: by Group 6 Stella Fresky Wisdayanti Batara (K011171806) Andi Ravida Rahma (K011171807)Document13 pagesToxoplasma Gondii: by Group 6 Stella Fresky Wisdayanti Batara (K011171806) Andi Ravida Rahma (K011171807)FenniEffendyMcGallaghanNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis: C H A P T E R 2 - 9 - 1 0Document10 pagesToxoplasmosis: C H A P T E R 2 - 9 - 1 0Muhammad Afiq HusinNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Gondii QuestionsDocument10 pagesToxoplasma Gondii QuestionsHussien SabryNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis, Diagnostic and Management of ToxoplasmosisDocument7 pagesPathogenesis, Diagnostic and Management of ToxoplasmosisSadam_fasterNo ratings yet
- Review MuñozDocument17 pagesReview MuñozVic PastorNo ratings yet
- ID-Micro L9 (Atypical Bacteria)Document20 pagesID-Micro L9 (Atypical Bacteria)Oraco1No ratings yet
- Protozoal Infections 29 April 2013Document87 pagesProtozoal Infections 29 April 2013Nive KojNo ratings yet
- Topic: "Picoronoviruses. Coxsackie. ECHO. Laboratory Diagnostics"Document26 pagesTopic: "Picoronoviruses. Coxsackie. ECHO. Laboratory Diagnostics"deekshit dcNo ratings yet
- SPIROCHETES (Treponema, Borrelia and Leptospira)Document4 pagesSPIROCHETES (Treponema, Borrelia and Leptospira)Muneer Al-DahbaliNo ratings yet
- طفيليات عملي الحكمة المعمل6صيدلةDocument4 pagesطفيليات عملي الحكمة المعمل6صيدلةMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- HistoplasmosisDocument13 pagesHistoplasmosisMohammed Yousif mzoriNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis and LaishmaniosisDocument49 pagesToxoplasmosis and LaishmaniosisTarikNo ratings yet
- Anti-Toxoplasma Gondii Antibodies in Patients With Chronic Heart FailureDocument4 pagesAnti-Toxoplasma Gondii Antibodies in Patients With Chronic Heart Failurerais123No ratings yet
- Para Handout - Coccidia - ToxoplasmaDocument15 pagesPara Handout - Coccidia - ToxoplasmaDerick SemNo ratings yet
- Protozoa, Sorozoa, Toxoplasma Gondii, DR Nageeb Aljunidi, 2024Document61 pagesProtozoa, Sorozoa, Toxoplasma Gondii, DR Nageeb Aljunidi, 2024المصمم ابو محمدNo ratings yet
- Senin 20 Oktober 2014 - Parasit 1 - Parasitologi - Toxoplasma - 12Document32 pagesSenin 20 Oktober 2014 - Parasit 1 - Parasitologi - Toxoplasma - 12Zahra AstriantaniNo ratings yet
- Plabable 2020 Infectious Disease BDRDocument69 pagesPlabable 2020 Infectious Disease BDRDr. Saqib RazaNo ratings yet
- ApicomplexaDocument51 pagesApicomplexaruthNo ratings yet
- Parasitology International: ReviewDocument7 pagesParasitology International: ReviewAhmad PradhanaNo ratings yet
- ToxoplasmosisDocument0 pagesToxoplasmosisAhmad Badrul AminNo ratings yet
- Neglected Parasitic Infections in The United States: ToxoplasmosisDocument6 pagesNeglected Parasitic Infections in The United States: ToxoplasmosispamepomeNo ratings yet
- Lec. 8.toxoplasmosis .Document19 pagesLec. 8.toxoplasmosis .Ahmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Artikel B.inggris Kel.10Document2 pagesArtikel B.inggris Kel.10Sheilla CkdNo ratings yet
- Fungal Lung DiseasesDocument28 pagesFungal Lung Diseasessultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Irina Magdalena Dumitru Ovidius University R NromaniaDocument24 pagesIrina Magdalena Dumitru Ovidius University R NromaniaUtarirnNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiaDocument40 pagesToxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiadhaineyNo ratings yet
- ToxoplasmosisDocument38 pagesToxoplasmosisemmaNo ratings yet
- Bagian Mikrobiologi FK Universitas Tanjungpura 2013Document49 pagesBagian Mikrobiologi FK Universitas Tanjungpura 2013ChandraNo ratings yet
- Mycoplasma Is An Overlooked Lyme Co-Infection: Got A Question?Document26 pagesMycoplasma Is An Overlooked Lyme Co-Infection: Got A Question?Anamaria BaloghNo ratings yet
- Yersinis SPP & Pasturella SPP - Jkt..2023Document45 pagesYersinis SPP & Pasturella SPP - Jkt..2023alicerugaibula123No ratings yet
- 4-Trypanosoma 240530 235411Document13 pages4-Trypanosoma 240530 235411Aya AyotaNo ratings yet
- IDS QuizDocument163 pagesIDS Quizd99452727No ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: IdcasesDocument8 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: IdcasesDaniel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases and Immunity: Set By: Mrs. Emebet Mohammed Mr. Solomon Taddesse Dr. Amir AlelignDocument32 pagesInfectious Diseases and Immunity: Set By: Mrs. Emebet Mohammed Mr. Solomon Taddesse Dr. Amir AlelignTsegaye YalewNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseaseDocument151 pagesInfectious Diseasebolt boltNo ratings yet
- Chapter13 PATHOGENESIS AND HOST DEFENSE MECHANISMDocument6 pagesChapter13 PATHOGENESIS AND HOST DEFENSE MECHANISMJeah Mae MacabitasNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma TropmedDocument27 pagesToxoplasma TropmedDickyNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. Source: Wikimedia Commons Author: Ladyofhats (2010)Document3 pagesLife Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. Source: Wikimedia Commons Author: Ladyofhats (2010)Friets KatuukNo ratings yet
- 18 Staphylococci, Streptococci, Meningococci, GonococciDocument72 pages18 Staphylococci, Streptococci, Meningococci, GonococciManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Toxocaroza Larvara Grava Prezentare de CazDocument6 pagesToxocaroza Larvara Grava Prezentare de CazMadaMadutsaNo ratings yet
- Cats and Toxoplasma: A Comprehensive Guide to Feline ToxoplasmosisFrom EverandCats and Toxoplasma: A Comprehensive Guide to Feline ToxoplasmosisNo ratings yet
- The Infection Game Supplement: new infections, retroviruses and pandemicsFrom EverandThe Infection Game Supplement: new infections, retroviruses and pandemicsNo ratings yet