Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WPT Xi Centre Che Neet 10-12-23
WPT Xi Centre Che Neet 10-12-23
Uploaded by
Deena chemistCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ARP5015BDocument16 pagesARP5015BBertoliNo ratings yet
- Reaction IntermediatesDocument7 pagesReaction Intermediatespinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- WPT Rasi Xi Che Iit Jee 04-03-24Document3 pagesWPT Rasi Xi Che Iit Jee 04-03-24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Xi CH#04Document4 pagesXi CH#04papukhan67zkqNo ratings yet
- Day-2 Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesDay-2 Chemical BondingpriyanshuNo ratings yet
- CPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDocument5 pagesCPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- SET Periodic - Property CPP (1) (1) (1Document3 pagesSET Periodic - Property CPP (1) (1) (1ishman singh bediNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Tutorial - 1Document4 pagesChemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Tutorial - 1shauryaNo ratings yet
- Neet 11Document4 pagesNeet 11snehakar3011No ratings yet
- STS Cashprize Test Chemistry 2023Document3 pagesSTS Cashprize Test Chemistry 2023Saim ShahNo ratings yet
- Rasi WPT Xi Che Neet 01-1-1-24Document3 pagesRasi WPT Xi Che Neet 01-1-1-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Neet Sample 1Document24 pagesNeet Sample 1iamniteshgargNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample Paper Model-1Document36 pagesNEET Sample Paper Model-1Shyamala GopinathNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsDocument7 pagesExercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsNavita Rajgaria0% (1)
- 9 Chemistry Chemical BondingDocument3 pages9 Chemistry Chemical BondingHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chemistry With AnswerDocument11 pagesMCQ Chemistry With Answerrudra1234749384No ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry D.P.P. - V: CH C C 2 & Hybridisation Is SPDocument4 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry D.P.P. - V: CH C C 2 & Hybridisation Is SPRanveermd SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Cy Section-A Multiple Choice Questins (MCQ) Q.1-Q.10 Carry One Mark EachDocument6 pagesChemistry-Cy Section-A Multiple Choice Questins (MCQ) Q.1-Q.10 Carry One Mark EachParul kandolaNo ratings yet
- WPT LT Neet Che 17-12-23Document4 pagesWPT LT Neet Che 17-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam 11th CHM MEDI-CAPSDocument4 pagesAnnual Exam 11th CHM MEDI-CAPSVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- Objectives: CH - OHDocument18 pagesObjectives: CH - OHHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Dec. 2017 Chemical Sciences Paper With SolutionDocument42 pagesDec. 2017 Chemical Sciences Paper With SolutionSoumya Ganguly50% (2)
- 1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalDocument7 pages1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalShudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDocument13 pagesSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 22nd May 2024Document6 pagesChemistry 22nd May 2024Ayush GhatakNo ratings yet
- Model QP 3Document4 pagesModel QP 3Swarnabha BiswasNo ratings yet
- Du Chemistry Entrace Questions For PG 2016 PaperDocument9 pagesDu Chemistry Entrace Questions For PG 2016 PaperKERALA SEARCHSNo ratings yet
- CH 3 XiDocument3 pagesCH 3 XiKhurram AwanNo ratings yet
- D & F Block QueDocument9 pagesD & F Block QueMahesh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Vsepr TheoryDocument2 pagesSheet 2 Vsepr Theorykrishna17673No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding DTS-4Document2 pagesChemical Bonding DTS-4nervoussolomon3No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Full Chapter Practice Sheet Solution - Chemical BondingDocument83 pagesChemical Bonding - Full Chapter Practice Sheet Solution - Chemical BondingIndian WeebNo ratings yet
- P-Block DTS-3Document2 pagesP-Block DTS-3Rudra guptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding DTS-1Document2 pagesChemical Bonding DTS-1nervoussolomon3No ratings yet
- LT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Document2 pagesLT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC - I (2019) Overseas: Section - A (Marks 17)Document1 pageChemistry HSSC - I (2019) Overseas: Section - A (Marks 17)Qasim Nazir100% (1)
- Set of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument6 pagesSet of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry50% (4)
- CHEMICAL BONDING AssignmentDocument4 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING AssignmentSoham NagNo ratings yet
- E1 PPT PDFDocument103 pagesE1 PPT PDFNammaacademyNo ratings yet
- Dec 2016 Chemistry PaperDocument24 pagesDec 2016 Chemistry PaperDaniella MendoncaNo ratings yet
- Q.paper Aiims 2021Document190 pagesQ.paper Aiims 2021anandramNo ratings yet
- IOC - IRP - Home Test-1 (Without Answer) - SendDocument8 pagesIOC - IRP - Home Test-1 (Without Answer) - SendNicholas BourbakiNo ratings yet
- Grand Btest-Chemistry (Mains) Paper 2Document9 pagesGrand Btest-Chemistry (Mains) Paper 2SouradipNo ratings yet
- 11 Chem F.TDocument4 pages11 Chem F.TTanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Csir Net Chemical Science 2012 DecemberDocument26 pagesCsir Net Chemical Science 2012 Decembersahuchem123No ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry 1st Year Chapter 6 FullDocument3 pages1 Chemistry 1st Year Chapter 6 Fullmahar zafarNo ratings yet
- Test Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesTest Chemical Bondingdevansh dewanNo ratings yet
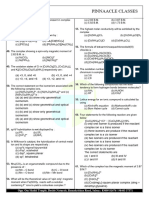
- Pisr Paper 1st Year 1-6Document3 pagesPisr Paper 1st Year 1-6SingularityNo ratings yet
- 2780iit Jee Chemistry Question Paers 2005Document5 pages2780iit Jee Chemistry Question Paers 2005Suraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Quiz 01072015Document4 pagesChemical Bonding - Quiz 01072015Shan RudraNo ratings yet
- Revised Chemistry Paper-IDocument4 pagesRevised Chemistry Paper-Iuzairabbasi96098No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry MCQsDocument56 pages12th Chemistry MCQsmuhammadsufian8888No ratings yet
- Che Neet 1Document4 pagesChe Neet 1pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Chemical Bonding QnsDocument5 pagesUnit2 Chemical Bonding QnsArunsethupatNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements - 7Document1 pageP Block Elements - 7Prudhvi YelisettiNo ratings yet
- I Preparatory I PU Chemistry QPDocument3 pagesI Preparatory I PU Chemistry QPadityahegde1122No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Book Back 1 Mark Questions em 217340Document18 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Book Back 1 Mark Questions em 217340kgadhithya2006No ratings yet
- Term-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDocument6 pagesTerm-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDarshan NayakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Class: 12 Topic: Chemical Bonding DPD. NO.: 09Document2 pagesChemistry: Class: 12 Topic: Chemical Bonding DPD. NO.: 09DeepNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1Document6 pages12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1HpNo ratings yet
- CRP & CLUNY XII NEET CHE 24-06-24Document7 pagesCRP & CLUNY XII NEET CHE 24-06-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit Key 07-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit Key 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 10-12-23Document3 pagesWPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 10-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit 07-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Xi Rasi Che Neet Key 2-12-23Document2 pagesWPT Xi Rasi Che Neet Key 2-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xii DPT Bot 29.03.24Document6 pagesXii DPT Bot 29.03.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT RPT Jee Phy 18.02.24Document4 pagesLT RPT Jee Phy 18.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 33 Centre Rasi Iit Jee Che Key 09-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 33 Centre Rasi Iit Jee Che Key 09-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Neet Key 07-12-23Document8 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Neet Key 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Revision Schedule 23-24Document22 pagesRevision Schedule 23-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT Jee DPT 15.02.24Document3 pagesLT Jee DPT 15.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 45 KeyDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry 45 KeyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT DPT 15 Jee 21.02.2024 KeyDocument1 pageLT DPT 15 Jee 21.02.2024 KeyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi ND Phy Iit CPT 19.02.24Document4 pagesXi ND Phy Iit CPT 19.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT DPT Jee Key 22.02.24Document1 pageLT DPT Jee Key 22.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Rasi WPT Xi Che Iit Key 01-1-1-24Document2 pagesRasi WPT Xi Che Iit Key 01-1-1-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT CRP Xi Che Neet Key 18-02-24Document6 pagesWPT CRP Xi Che Neet Key 18-02-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi Rasi Phy Iit WPT 19.02.24 KeyDocument1 pageXi Rasi Phy Iit WPT 19.02.24 KeyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi ND CPT ZoologyDocument4 pagesXi ND CPT ZoologyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Coordination WSDocument3 pagesCoordination WSDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Document2 pagesLT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Dptchem & Zoo01.2024Document2 pagesDptchem & Zoo01.2024Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Iit JeeDocument2 pagesWPT Iit JeeDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 21-11-23Document4 pagesWPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 21-11-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Jee GrandDocument16 pagesJee GrandDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- CPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDocument5 pagesCPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- X ND WPT Che 1 17-10-22Document1 pageX ND WPT Che 1 17-10-22Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi Rasi Neet Che WPT QP 22.01.2024Document3 pagesXi Rasi Neet Che WPT QP 22.01.2024Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- F BlockDocument10 pagesF BlockDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi CRP Neet Che WPT QP 31.12.2023Document3 pagesXi CRP Neet Che WPT QP 31.12.2023Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Efectos de La Mezcla de Lecitina PGPRDocument8 pagesEfectos de La Mezcla de Lecitina PGPRGina JibajaNo ratings yet
- Sceecs 2016 7509295Document6 pagesSceecs 2016 7509295Hoàng Nam PhạmNo ratings yet
- Suntek HC 801ADocument54 pagesSuntek HC 801AapocalipcNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigo 1Document7 pagesInverse Trigo 1aryansharmabjym121No ratings yet
- AS 102725 LaserDisplacementSensor GC 600R84 GB AS 1079-2Document28 pagesAS 102725 LaserDisplacementSensor GC 600R84 GB AS 1079-2PraveenNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Aug 02, 2023Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Aug 02, 2023Shubh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Flange Management Rev 1 160216081830Document31 pagesFlange Management Rev 1 160216081830Ali100% (1)
- YS 11 Laboratory Activity # 1Document3 pagesYS 11 Laboratory Activity # 1HECTOR ARANTE TANNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis and Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles From TulsiDocument10 pagesBiosynthesis and Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles From TulsiRabeea NasirNo ratings yet
- A Novel Physics Node For Nakamura Crystallization KineticsDocument6 pagesA Novel Physics Node For Nakamura Crystallization KineticsHiba MhiriNo ratings yet
- Instrument Engineers Handbook PDFDocument7 pagesInstrument Engineers Handbook PDFSterling GordianNo ratings yet
- Threading Inserts: Now in To Conquer ISO S MaterialsDocument32 pagesThreading Inserts: Now in To Conquer ISO S MaterialsAchmad Arifudin HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Problem39 10Document1 pageProblem39 10IENCSNo ratings yet
- 0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDocument2 pages0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDiep NguyenNo ratings yet
- R: T E T G O: AYS HE Ikonal Reatment of Eometric PticsDocument15 pagesR: T E T G O: AYS HE Ikonal Reatment of Eometric PticsRajiv ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 03a. Alternating Current (128-153)Document27 pages03a. Alternating Current (128-153)Mupli RajeshNo ratings yet
- Terminal Signal Connected To Test Condition Voltage (V) Inspection ItemDocument15 pagesTerminal Signal Connected To Test Condition Voltage (V) Inspection ItemyanivyehezkelNo ratings yet
- Building An Electrolytic Capacitor: Applications Q CXV Q C VDocument5 pagesBuilding An Electrolytic Capacitor: Applications Q CXV Q C VMatheus SilvestriniNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Chemistry: Liceo de BuenavistaDocument4 pagesSolved Problems Chemistry: Liceo de BuenavistaFatima VeneracionNo ratings yet
- Datasheet STP3NB100 Mosfet N IndigoDocument6 pagesDatasheet STP3NB100 Mosfet N Indigopepemex3No ratings yet
- Fe282 PDFDocument33 pagesFe282 PDFdhmbasNo ratings yet
- Distillation: Enthalpy Concentration Methods (HX) Diagram or Ponchon Savarit MethodDocument9 pagesDistillation: Enthalpy Concentration Methods (HX) Diagram or Ponchon Savarit MethodRose Dane Escobedo DiestaNo ratings yet
- Manual 7VK512Document132 pagesManual 7VK512Leonardo Ortiz PastranaNo ratings yet
- GeneralData Forozan NewDocument1 pageGeneralData Forozan NewRos Neftegaz TransitNo ratings yet
- Test 7 SMKCH Ques&AnsDocument8 pagesTest 7 SMKCH Ques&AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsDocument36 pagesObjectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsOriLokisNo ratings yet
- Ana College of Engineering and Management Studies: Power QualityDocument59 pagesAna College of Engineering and Management Studies: Power Qualityprabhu kirpaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Buoyancy and Floatation - Tutorial SolutionDocument20 pages4 - Buoyancy and Floatation - Tutorial SolutionbakrichodNo ratings yet
- K Delphi BCM GW K Platform: Non-CANDocument2 pagesK Delphi BCM GW K Platform: Non-CANmaxonNo ratings yet
WPT Xi Centre Che Neet 10-12-23
WPT Xi Centre Che Neet 10-12-23
Uploaded by
Deena chemistOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WPT Xi Centre Che Neet 10-12-23
WPT Xi Centre Che Neet 10-12-23
Uploaded by
Deena chemistCopyright:
Available Formats
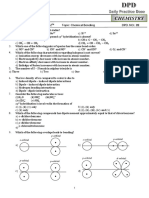
PINNAACLE CLASSES
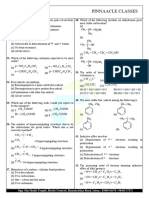
31. The species that does not contain peroxide ion is (a) Exhibit oxidation state of +4 only
PbO 2 H O
(b) 2 2 (c)
SrO2 (d)
(b) Exhibit oxidation state of +2 and +4
(a) (c) Form M–2 and M4+ ions
BaO 2 (d) Form M2+ and M4+ ions
32. Which of the following oxides is neutral 40. CO2 in water behaves as :
CO SnO2 SiO 2
(a) (b) (c) (d) (a) Weak dibasic acid H2CO3
ZnO (b) Weak monobasic acid HO – CO2H
(c) Weak diacid base CO(OH)2
33. The C–X bond energy order and thermal stability (d) Weak monoacid base HO – CO2H
for carbon tetra-halides is :
(a) CF4> CCl4> CBr4> CI4 (b) CCl4> CBr4>
CI4> CF4 41. The oxide which is not a reducing agent is :
(c) CI4> CBr4> CCl4 > CF4 (d) None of these (a) CO2 (b) NO2 (c) SO2 (d)
CIO2
34. Which statement is correct with respect to the
property of the elements with increase in atomic 42. When steam is passed through red hot coke :
number in the carbon family ? (a) CO2 and H2 are obtained (b) CO and N2
(a) Their metallic character decreases are formed
(b) The stability of +2 oxidation state increases (c) CO and H2 are obtained (d) Petrol gas is
(c) Their ionisation energy increases
(d) Their atomic size decreases obtained
35. ''Inorganic benzene'' and ''benzene'' can be 43. Coal gas is a mixture of :
distinguished by - (a) CO and H2
(a) The reaction with HCl (b) H2, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons,
(b) The reaction with ROH CO, CO2, N2 and O2
(c) The stability of the benzene in water
(c) Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons
(d) All of the above
(d) CO, CO2 and CH4
36. Graphite is a soft solid lubricant extremely difficult
to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour 44. Inductive effect involves :
is that graphite.
(a) Is a non-crystalline substance. (a) Delocalisation of -electrons
(b) Is an allotropic form of diamond (b) Partial displacement of -electrons
(c) Has molecules of variable molecular masses (c) Delocalisation of -electrons
like polymers (d) Displacement of lone pair electrons.
(d) Has carbon atoms arranged in large plates of
rings of strongly bound carbon atoms with weak
interplate bonds. 45. Select correct statement about I effect?
(a) I effect transfers electrons from one carbon
37. The stability of dihalides of Si, Ge, Sn and Pb
increases steadily in the sequence: atom to another.
(b) I effect is the polarisation of bond
(a) GeX2< SiX2< SnX2< PbX2
electrons.
(b) SiX2< GeX2< PbX2< SnX2
(c) I effect creates net charge in the molecule.
(c) SiX2< GeX2< SnX2< PbX2
(d) I effect is distance independent.
(d) PbX2< SnX2< GeX2< SiX2
46. Decreasing –I effect of given groups is :
38. CO forms a volatile compound with :
(a) Nickel (b) Copper (c) Sodium (d)
(i) –CN (ii) – NO2
Aluminium
(iii) –NH2 (iv) –F
39. Elements of group 14 : (a) iii > ii > i > iv (b) ii > iii > iv > i
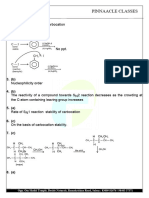
Opp. Om Shakti Temple, Beside Naturals, Ramakrishna Road, Salem : 83009 81676 / 98403 37371
PINNAACLE CLASSES
(c) iii > ii > iv > i (d) ii > i > iv > iii (c) –OH (d) –F
47. Which of the following is the strongest – group : 54. Hyperconjugation is.
(a) σ −π conjugation.
(a) – (CH3)3 (b) – (b) Noticed due to delocalization of σ and π
bonds.
(c) – (CH3)2 (d) – F (c) No bond resonance.
(d) All the above.
48. Resonance is delocalisation of :
55. The number of hyperconjugating structures shown
(a) electrons (b) electrons by the carbocations are given below. Which one is
not correctly matched?
(c) electrons (d) None +
CH 3 −C −CH 3
|
49. Resonance involves :
(a) CH 3 - 9 hyperconjugating structures
(a) Delocalization of -electrons along a +
conjugated system. (b) CH 3 −C H −CH 3 − 8 hyperconjugating
(b) Delocalization of lone pair along a structures
conjugated system. +
(c) Delocalization of negative charge along a (c) CH 3 −C H 2 - 3 hyperconjugating structures
conjugated system. +
(d) All are correct. (d) C H 3 - No hyperconjugating structures
50. During delocalization, which statement is 56. Inductive effect involves
(a) Displacement of σ − electrons resulting in
(a) Net charge remains same polarization
(b) Number of paired electrons remain same (b) Displacement of π− electrons resulting in
(c) Number of unpaired electrons remain same polarization
(d) Energy of resonating structures always
(c) Delocalisation of σ − electrons
remains same
(d) Delocalisation of π − electrons.
51. Which of the following species can not show
57. The increasing order of electron donating inductive
resonance? effect of alkyl group is.
(a)
−H <−CH 3 <−C 2 H 5 <−C3 H 7
(b)
−H >−CH 3 >−C 2 H 5 >−C3 H 7
(a) (b)
(c)
−H <−C 2 H 5 <−CH 3 <−C3 H 7
−H >−C 2 H 5 >−CH 3 >−C3 H 7
(c) (d)
(d)
52. Which of the following group show +M effect?
58. Inductive effect of which atom or group is taken as
(a) –CN (b) –O–NO zero to compare inductive effect of other atoms?
(a) Hydrogen (b) Chlorine
(c) –CCl3 (d) –CHO
(c) Carbon (d) Oxygen
53. Which of the following group show –M and –I effect
59. In which of the following species hyperconjugation
?
is possible?
(a) –NO2 (b) –NH2
Opp. Om Shakti Temple, Beside Naturals, Ramakrishna Road, Salem : 83009 81676 / 98403 37371
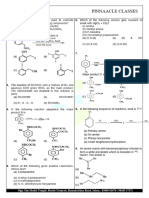
PINNAACLE CLASSES
−
(a) CH 3 −C H 2
(b)
C 6 H 5 −CH 3
(c)
CH 2 =CH 2
CH 3
|
CH 3 − C − CH=CH 2
|
CH 3
(d)
60. Maximum – I effect is exerted by the group
−C 6 H 5 (b) −OCH 3 (c) −Cl (d)
−NO 2
(a)
Opp. Om Shakti Temple, Beside Naturals, Ramakrishna Road, Salem : 83009 81676 / 98403 37371
You might also like
- ARP5015BDocument16 pagesARP5015BBertoliNo ratings yet
- Reaction IntermediatesDocument7 pagesReaction Intermediatespinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- WPT Rasi Xi Che Iit Jee 04-03-24Document3 pagesWPT Rasi Xi Che Iit Jee 04-03-24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Xi CH#04Document4 pagesXi CH#04papukhan67zkqNo ratings yet
- Day-2 Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesDay-2 Chemical BondingpriyanshuNo ratings yet
- CPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDocument5 pagesCPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- SET Periodic - Property CPP (1) (1) (1Document3 pagesSET Periodic - Property CPP (1) (1) (1ishman singh bediNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Tutorial - 1Document4 pagesChemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Tutorial - 1shauryaNo ratings yet
- Neet 11Document4 pagesNeet 11snehakar3011No ratings yet
- STS Cashprize Test Chemistry 2023Document3 pagesSTS Cashprize Test Chemistry 2023Saim ShahNo ratings yet
- Rasi WPT Xi Che Neet 01-1-1-24Document3 pagesRasi WPT Xi Che Neet 01-1-1-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Neet Sample 1Document24 pagesNeet Sample 1iamniteshgargNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample Paper Model-1Document36 pagesNEET Sample Paper Model-1Shyamala GopinathNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsDocument7 pagesExercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsNavita Rajgaria0% (1)
- 9 Chemistry Chemical BondingDocument3 pages9 Chemistry Chemical BondingHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chemistry With AnswerDocument11 pagesMCQ Chemistry With Answerrudra1234749384No ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry D.P.P. - V: CH C C 2 & Hybridisation Is SPDocument4 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry D.P.P. - V: CH C C 2 & Hybridisation Is SPRanveermd SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Cy Section-A Multiple Choice Questins (MCQ) Q.1-Q.10 Carry One Mark EachDocument6 pagesChemistry-Cy Section-A Multiple Choice Questins (MCQ) Q.1-Q.10 Carry One Mark EachParul kandolaNo ratings yet
- WPT LT Neet Che 17-12-23Document4 pagesWPT LT Neet Che 17-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam 11th CHM MEDI-CAPSDocument4 pagesAnnual Exam 11th CHM MEDI-CAPSVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- Objectives: CH - OHDocument18 pagesObjectives: CH - OHHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Dec. 2017 Chemical Sciences Paper With SolutionDocument42 pagesDec. 2017 Chemical Sciences Paper With SolutionSoumya Ganguly50% (2)
- 1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalDocument7 pages1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalShudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDocument13 pagesSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 22nd May 2024Document6 pagesChemistry 22nd May 2024Ayush GhatakNo ratings yet
- Model QP 3Document4 pagesModel QP 3Swarnabha BiswasNo ratings yet
- Du Chemistry Entrace Questions For PG 2016 PaperDocument9 pagesDu Chemistry Entrace Questions For PG 2016 PaperKERALA SEARCHSNo ratings yet
- CH 3 XiDocument3 pagesCH 3 XiKhurram AwanNo ratings yet
- D & F Block QueDocument9 pagesD & F Block QueMahesh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Vsepr TheoryDocument2 pagesSheet 2 Vsepr Theorykrishna17673No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding DTS-4Document2 pagesChemical Bonding DTS-4nervoussolomon3No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Full Chapter Practice Sheet Solution - Chemical BondingDocument83 pagesChemical Bonding - Full Chapter Practice Sheet Solution - Chemical BondingIndian WeebNo ratings yet
- P-Block DTS-3Document2 pagesP-Block DTS-3Rudra guptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding DTS-1Document2 pagesChemical Bonding DTS-1nervoussolomon3No ratings yet
- LT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Document2 pagesLT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC - I (2019) Overseas: Section - A (Marks 17)Document1 pageChemistry HSSC - I (2019) Overseas: Section - A (Marks 17)Qasim Nazir100% (1)
- Set of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument6 pagesSet of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry50% (4)
- CHEMICAL BONDING AssignmentDocument4 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING AssignmentSoham NagNo ratings yet
- E1 PPT PDFDocument103 pagesE1 PPT PDFNammaacademyNo ratings yet
- Dec 2016 Chemistry PaperDocument24 pagesDec 2016 Chemistry PaperDaniella MendoncaNo ratings yet
- Q.paper Aiims 2021Document190 pagesQ.paper Aiims 2021anandramNo ratings yet
- IOC - IRP - Home Test-1 (Without Answer) - SendDocument8 pagesIOC - IRP - Home Test-1 (Without Answer) - SendNicholas BourbakiNo ratings yet
- Grand Btest-Chemistry (Mains) Paper 2Document9 pagesGrand Btest-Chemistry (Mains) Paper 2SouradipNo ratings yet
- 11 Chem F.TDocument4 pages11 Chem F.TTanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Csir Net Chemical Science 2012 DecemberDocument26 pagesCsir Net Chemical Science 2012 Decembersahuchem123No ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry 1st Year Chapter 6 FullDocument3 pages1 Chemistry 1st Year Chapter 6 Fullmahar zafarNo ratings yet
- Test Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesTest Chemical Bondingdevansh dewanNo ratings yet
- Pisr Paper 1st Year 1-6Document3 pagesPisr Paper 1st Year 1-6SingularityNo ratings yet
- 2780iit Jee Chemistry Question Paers 2005Document5 pages2780iit Jee Chemistry Question Paers 2005Suraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Quiz 01072015Document4 pagesChemical Bonding - Quiz 01072015Shan RudraNo ratings yet
- Revised Chemistry Paper-IDocument4 pagesRevised Chemistry Paper-Iuzairabbasi96098No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry MCQsDocument56 pages12th Chemistry MCQsmuhammadsufian8888No ratings yet
- Che Neet 1Document4 pagesChe Neet 1pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Chemical Bonding QnsDocument5 pagesUnit2 Chemical Bonding QnsArunsethupatNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements - 7Document1 pageP Block Elements - 7Prudhvi YelisettiNo ratings yet
- I Preparatory I PU Chemistry QPDocument3 pagesI Preparatory I PU Chemistry QPadityahegde1122No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Book Back 1 Mark Questions em 217340Document18 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Book Back 1 Mark Questions em 217340kgadhithya2006No ratings yet
- Term-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDocument6 pagesTerm-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDarshan NayakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Class: 12 Topic: Chemical Bonding DPD. NO.: 09Document2 pagesChemistry: Class: 12 Topic: Chemical Bonding DPD. NO.: 09DeepNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1Document6 pages12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1HpNo ratings yet
- CRP & CLUNY XII NEET CHE 24-06-24Document7 pagesCRP & CLUNY XII NEET CHE 24-06-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit Key 07-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit Key 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 10-12-23Document3 pagesWPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 10-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit 07-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Xi Rasi Che Neet Key 2-12-23Document2 pagesWPT Xi Rasi Che Neet Key 2-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xii DPT Bot 29.03.24Document6 pagesXii DPT Bot 29.03.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT RPT Jee Phy 18.02.24Document4 pagesLT RPT Jee Phy 18.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 33 Centre Rasi Iit Jee Che Key 09-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 33 Centre Rasi Iit Jee Che Key 09-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Neet Key 07-12-23Document8 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Neet Key 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Revision Schedule 23-24Document22 pagesRevision Schedule 23-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT Jee DPT 15.02.24Document3 pagesLT Jee DPT 15.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 45 KeyDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry 45 KeyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT DPT 15 Jee 21.02.2024 KeyDocument1 pageLT DPT 15 Jee 21.02.2024 KeyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi ND Phy Iit CPT 19.02.24Document4 pagesXi ND Phy Iit CPT 19.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT DPT Jee Key 22.02.24Document1 pageLT DPT Jee Key 22.02.24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Rasi WPT Xi Che Iit Key 01-1-1-24Document2 pagesRasi WPT Xi Che Iit Key 01-1-1-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT CRP Xi Che Neet Key 18-02-24Document6 pagesWPT CRP Xi Che Neet Key 18-02-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi Rasi Phy Iit WPT 19.02.24 KeyDocument1 pageXi Rasi Phy Iit WPT 19.02.24 KeyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi ND CPT ZoologyDocument4 pagesXi ND CPT ZoologyDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Coordination WSDocument3 pagesCoordination WSDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- LT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Document2 pagesLT RPT2 Jee Che 18-02-24Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Dptchem & Zoo01.2024Document2 pagesDptchem & Zoo01.2024Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Iit JeeDocument2 pagesWPT Iit JeeDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- WPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 21-11-23Document4 pagesWPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 21-11-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Jee GrandDocument16 pagesJee GrandDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- CPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDocument5 pagesCPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- X ND WPT Che 1 17-10-22Document1 pageX ND WPT Che 1 17-10-22Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi Rasi Neet Che WPT QP 22.01.2024Document3 pagesXi Rasi Neet Che WPT QP 22.01.2024Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- F BlockDocument10 pagesF BlockDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Xi CRP Neet Che WPT QP 31.12.2023Document3 pagesXi CRP Neet Che WPT QP 31.12.2023Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Efectos de La Mezcla de Lecitina PGPRDocument8 pagesEfectos de La Mezcla de Lecitina PGPRGina JibajaNo ratings yet
- Sceecs 2016 7509295Document6 pagesSceecs 2016 7509295Hoàng Nam PhạmNo ratings yet
- Suntek HC 801ADocument54 pagesSuntek HC 801AapocalipcNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigo 1Document7 pagesInverse Trigo 1aryansharmabjym121No ratings yet
- AS 102725 LaserDisplacementSensor GC 600R84 GB AS 1079-2Document28 pagesAS 102725 LaserDisplacementSensor GC 600R84 GB AS 1079-2PraveenNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Aug 02, 2023Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Aug 02, 2023Shubh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Flange Management Rev 1 160216081830Document31 pagesFlange Management Rev 1 160216081830Ali100% (1)
- YS 11 Laboratory Activity # 1Document3 pagesYS 11 Laboratory Activity # 1HECTOR ARANTE TANNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis and Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles From TulsiDocument10 pagesBiosynthesis and Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles From TulsiRabeea NasirNo ratings yet
- A Novel Physics Node For Nakamura Crystallization KineticsDocument6 pagesA Novel Physics Node For Nakamura Crystallization KineticsHiba MhiriNo ratings yet
- Instrument Engineers Handbook PDFDocument7 pagesInstrument Engineers Handbook PDFSterling GordianNo ratings yet
- Threading Inserts: Now in To Conquer ISO S MaterialsDocument32 pagesThreading Inserts: Now in To Conquer ISO S MaterialsAchmad Arifudin HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Problem39 10Document1 pageProblem39 10IENCSNo ratings yet
- 0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDocument2 pages0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDiep NguyenNo ratings yet
- R: T E T G O: AYS HE Ikonal Reatment of Eometric PticsDocument15 pagesR: T E T G O: AYS HE Ikonal Reatment of Eometric PticsRajiv ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 03a. Alternating Current (128-153)Document27 pages03a. Alternating Current (128-153)Mupli RajeshNo ratings yet
- Terminal Signal Connected To Test Condition Voltage (V) Inspection ItemDocument15 pagesTerminal Signal Connected To Test Condition Voltage (V) Inspection ItemyanivyehezkelNo ratings yet
- Building An Electrolytic Capacitor: Applications Q CXV Q C VDocument5 pagesBuilding An Electrolytic Capacitor: Applications Q CXV Q C VMatheus SilvestriniNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Chemistry: Liceo de BuenavistaDocument4 pagesSolved Problems Chemistry: Liceo de BuenavistaFatima VeneracionNo ratings yet
- Datasheet STP3NB100 Mosfet N IndigoDocument6 pagesDatasheet STP3NB100 Mosfet N Indigopepemex3No ratings yet
- Fe282 PDFDocument33 pagesFe282 PDFdhmbasNo ratings yet
- Distillation: Enthalpy Concentration Methods (HX) Diagram or Ponchon Savarit MethodDocument9 pagesDistillation: Enthalpy Concentration Methods (HX) Diagram or Ponchon Savarit MethodRose Dane Escobedo DiestaNo ratings yet
- Manual 7VK512Document132 pagesManual 7VK512Leonardo Ortiz PastranaNo ratings yet
- GeneralData Forozan NewDocument1 pageGeneralData Forozan NewRos Neftegaz TransitNo ratings yet
- Test 7 SMKCH Ques&AnsDocument8 pagesTest 7 SMKCH Ques&AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsDocument36 pagesObjectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsOriLokisNo ratings yet
- Ana College of Engineering and Management Studies: Power QualityDocument59 pagesAna College of Engineering and Management Studies: Power Qualityprabhu kirpaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Buoyancy and Floatation - Tutorial SolutionDocument20 pages4 - Buoyancy and Floatation - Tutorial SolutionbakrichodNo ratings yet
- K Delphi BCM GW K Platform: Non-CANDocument2 pagesK Delphi BCM GW K Platform: Non-CANmaxonNo ratings yet