Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contracts Reviewer 2
Contracts Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Christine Mae AltarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Contracts FLOW ChartDocument6 pagesContracts FLOW Chartbooda262695% (22)
- Creative Encounter With God in Worship - A Critical Reflection On Howard ThurmanDocument12 pagesCreative Encounter With God in Worship - A Critical Reflection On Howard ThurmanRev. Alcenir Oliveira, MDiv, MBA, BBA & BPANo ratings yet
- 2.22 NASPA 2019 Program Book EPB PDFDocument182 pages2.22 NASPA 2019 Program Book EPB PDFMarques Redd100% (1)
- The Power of Acceptance PDFDocument13 pagesThe Power of Acceptance PDFmanas999100% (12)
- lt2 EthicsDocument10 pageslt2 Ethicsapi-445796097No ratings yet
- Impact of Training Programs Towards Employees Performance of DILGDocument42 pagesImpact of Training Programs Towards Employees Performance of DILGRexanCamposNo ratings yet
- Contracts Flow ChartDocument6 pagesContracts Flow Chartcarlspackler983100% (5)
- LABOR LAW Reviewer POQUIZDocument16 pagesLABOR LAW Reviewer POQUIZmegzycutes387183% (6)
- Chart - Kinds of ContractsDocument1 pageChart - Kinds of ContractsGONZALES, JULIE ANN, S.No ratings yet
- Lecture 14 (2022)Document16 pagesLecture 14 (2022)CHRISTIA ALYSSA MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- Contract ActDocument91 pagesContract ActAakash_Shah_702No ratings yet
- Contracts Outline 2020Document17 pagesContracts Outline 2020Savana DegroatNo ratings yet
- Culled Primarily From The Lectures of Atty. Kenneth Glenn L. ManuelDocument45 pagesCulled Primarily From The Lectures of Atty. Kenneth Glenn L. Manueldarkbliss MNo ratings yet
- Notes in ContractsDocument5 pagesNotes in ContractsSehyuk LimNo ratings yet
- LAW ON SALES - SummaryDocument3 pagesLAW ON SALES - SummaryAUBREY MAE MANALONo ratings yet
- Law On Contracts Notes 1Document5 pagesLaw On Contracts Notes 1Rose Marie Lacsamana BarreteNo ratings yet
- Family LawDocument33 pagesFamily Lawmokoenadinny99No ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act, 1872Document59 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872Neeranjali NairNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act, 1872Document70 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872migpatel7970No ratings yet
- 2.0 Law On Credit Transactions 2.1 Pledge, Real Mortgage and Chattel Mortgage 2.1.1 Nature and RequisitesDocument5 pages2.0 Law On Credit Transactions 2.1 Pledge, Real Mortgage and Chattel Mortgage 2.1.1 Nature and RequisitesChristine Mae Fernandez MataNo ratings yet
- Notes in Contracts-VillaDocument6 pagesNotes in Contracts-VillaAmor VillaNo ratings yet
- SalesDocument13 pagesSalesJenny Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- L-201 Final Review Session Sun. 12 BU-109 (Tentative)Document7 pagesL-201 Final Review Session Sun. 12 BU-109 (Tentative)rlidell01No ratings yet
- Gasser Final NotesDocument12 pagesGasser Final NotesVGANo ratings yet
- Free Consent: Coercion, Undue Influence, Fraud & Misrepresentation (CUFM)Document48 pagesFree Consent: Coercion, Undue Influence, Fraud & Misrepresentation (CUFM)MUHMMAD ARSALAN 13728No ratings yet
- CONTRACTS ProvisionsDocument2 pagesCONTRACTS ProvisionskhaiNo ratings yet
- Equity ExamNotesDocument44 pagesEquity ExamNotesusherthNo ratings yet
- Contract ActDocument98 pagesContract ActAnkur Dubey67% (3)
- Contract Law - Consideration SC3Document26 pagesContract Law - Consideration SC3Ganesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ca51011 - Law On Obligations and Contracts: Article 1156 of The Civil Code of The PhilippinesDocument47 pagesCa51011 - Law On Obligations and Contracts: Article 1156 of The Civil Code of The Philippinesyvonne salasNo ratings yet
- RFBT ReviewersDocument13 pagesRFBT ReviewersRose MarieNo ratings yet
- Law PaperDocument194 pagesLaw PaperTessaNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract Sa 9 1 21Document40 pagesLaw of Contract Sa 9 1 21Aparna JRNo ratings yet
- Law of Agency - Part IDocument13 pagesLaw of Agency - Part ITabi D.No ratings yet
- Legal Questions and Answers (End-Term)Document22 pagesLegal Questions and Answers (End-Term)sayanchakrabortymba2022No ratings yet
- 12 Agency Nov 4Document5 pages12 Agency Nov 4Chezka Bianca TorresNo ratings yet
- Defective ContractsDocument3 pagesDefective ContractsAngge D.No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1Trúc BùiNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract ActDocument8 pagesIndian Contract ActManish SinghNo ratings yet
- CPT Mercantile Law Revision Notes YMKPNBH3Document48 pagesCPT Mercantile Law Revision Notes YMKPNBH3mahesh bawgeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Promissory EstoppelDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Promissory EstoppelAdam 'Fez' Ferris100% (3)
- Contract ActDocument38 pagesContract Actsneh sumanNo ratings yet
- Civil Law Review 2 Notes (Atty. Carla E. Santamaria-Sena)Document90 pagesCivil Law Review 2 Notes (Atty. Carla E. Santamaria-Sena)Daverick PacumioNo ratings yet
- Obligations Part 1Document11 pagesObligations Part 1DanicaNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Contract Vs Contract of MarriageDocument7 pagesOrdinary Contract Vs Contract of MarriageVenNo ratings yet
- ConsiderationDocument54 pagesConsiderationBrandon WongNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument4 pagesContractsElle BadussyNo ratings yet
- Presented by Neha Bansal Ankita Tyagi Gurpreet Kaur Veni RathiDocument12 pagesPresented by Neha Bansal Ankita Tyagi Gurpreet Kaur Veni RathiRishikesh KaushikNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Kruti BhattNo ratings yet
- Contracts Complete Outline Chapter 3: Liability in The Absence of Bargained-For-ExchangeDocument24 pagesContracts Complete Outline Chapter 3: Liability in The Absence of Bargained-For-ExchangeJohnny Emm100% (2)
- Corporate & Other Laws: Ca-InterDocument15 pagesCorporate & Other Laws: Ca-IntersonuNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument21 pagesLaw On ContractsHannah SyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture ThreeDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture Threesimangalisokhoza37No ratings yet
- Part 13 - Video LectureDocument10 pagesPart 13 - Video LectureApril ToledoNo ratings yet
- Dentistry 162 - : 1.1 - ObligationsDocument4 pagesDentistry 162 - : 1.1 - ObligationsGeeNo ratings yet
- BUSINESSS LAW FINAL 4sepDocument196 pagesBUSINESSS LAW FINAL 4sepHARSHIT SAXENANo ratings yet
- Comparison of Islamic and English ContractDocument27 pagesComparison of Islamic and English ContractAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contract Mind MapsDocument8 pagesThe Law of Contract Mind MapsSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- 5 Object of The ContractDocument4 pages5 Object of The ContractBankowski PhotographyNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerErika DiangNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument13 pagesCONTRACTSykckjzfzsmNo ratings yet
- Course: Legal Technici: An English Lesson 10Document32 pagesCourse: Legal Technici: An English Lesson 10Joselyn Pamela Cutipa CohailaNo ratings yet
- 3 General Principles of Contract ActDocument43 pages3 General Principles of Contract ActSamit DasNo ratings yet
- Contract Law - Consideration SCDocument29 pagesContract Law - Consideration SCreena0610 gNo ratings yet
- Bigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawFrom EverandBigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawNo ratings yet
- Generation CHRIST Assembly PDFDocument15 pagesGeneration CHRIST Assembly PDFSTEVE JHONSON LepasanaNo ratings yet
- αὐτάρκης in Stoicism and Phil 4.11Document20 pagesαὐτάρκης in Stoicism and Phil 4.11Alexander BurgaNo ratings yet
- Fase 4 - Hacia Una Solución de Conflictos AmbientalesDocument4 pagesFase 4 - Hacia Una Solución de Conflictos AmbientalesLina Maria SilvaNo ratings yet
- USNORTHCOM FaithfulPatriotDocument33 pagesUSNORTHCOM FaithfulPatriotnelson duringNo ratings yet
- Pasport Form DDNI06330312GO0330Document0 pagesPasport Form DDNI06330312GO0330Awdhesh Singh BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Examen PCE Ingles 2022 Resuelto Escuela PCEDocument6 pagesExamen PCE Ingles 2022 Resuelto Escuela PCECésar PHNo ratings yet
- 03 - Prerequisites of Collective BargainingDocument8 pages03 - Prerequisites of Collective BargainingGayatri Dhawan100% (1)
- Yamuna Biodiversity ParkDocument5 pagesYamuna Biodiversity ParkPriyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Sumbitted To: Submitted By:: Even Lamps OF AdvocacyDocument6 pagesSumbitted To: Submitted By:: Even Lamps OF Advocacyudita goelNo ratings yet
- 4th 2 9 20201Document5 pages4th 2 9 20201Viner Hernan SantosNo ratings yet
- Abraham Lincoln OUTLINEDocument3 pagesAbraham Lincoln OUTLINEWilder Jose BCNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Prelim Transes - MoralityDocument6 pagesBioethics Prelim Transes - MoralityAleah JayaganNo ratings yet
- Buason Vs PanuyasDocument5 pagesBuason Vs PanuyasVeepee PanzoNo ratings yet
- IncelsDocument42 pagesIncelsjosebardamuNo ratings yet
- Audit Rules 1Document125 pagesAudit Rules 1Shikha AroraNo ratings yet
- Copyright Jeopardy 1Document55 pagesCopyright Jeopardy 1api-446508079No ratings yet
- Company ProfileDocument19 pagesCompany ProfileDiana CitraNo ratings yet
- Temporary Employment CommentsDocument4 pagesTemporary Employment CommentsCzar Ian AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Transactional LeadershipDocument5 pagesTransactional Leadershipal-obinay shereenNo ratings yet
- AFFIDAVITDocument1 pageAFFIDAVITpot420_aivanNo ratings yet
- Iberia 2012 CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY ReportDocument126 pagesIberia 2012 CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY ReportCSRMedia NetworkNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics IA RFDDocument53 pagesCode of Ethics IA RFDbautista bautistaNo ratings yet
- CIVPRO - Case Compilation No. 2Document95 pagesCIVPRO - Case Compilation No. 2Darla GreyNo ratings yet
- Constructions of Motherhood in Euripides' Medea: John GivenDocument15 pagesConstructions of Motherhood in Euripides' Medea: John GivenJosé María RissoNo ratings yet
- CASE 1: Joanne JoannaDocument4 pagesCASE 1: Joanne JoannaMiruna CiteaNo ratings yet
Contracts Reviewer 2
Contracts Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Christine Mae AltarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Contracts Reviewer 2
Contracts Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Christine Mae AltarCopyright:
Available Formats
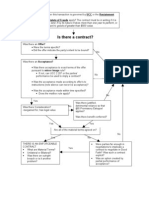
Law on Obligations and Contracts – Contracts
Contracts – meeting of the minds; agreement; covenant – binding oneself.
▪ Legal meaning – In meeting basically promising to give or perform a service except certain
agreements: special law that need written contract unless no binding happened. E.g.:
a. Sales in 300k - Land
b. Register (bounds in terms of contract) – Vehicles
Why’s important?
Note:
A contract has the force of the law of contract.
Interpretation – If there’s a doubt - if there’s
Elements of the Contracts: no room of misinterpretation always knows
Example To Remember: the context of the contract.
▪ Subject Matter – object of the contract E.g. What’s the intention of a refund of
(Employment) contract.
▪ Consideration – reason why you’re entering
Reminder: Judge can enforce the law of
the contract (Salary) contract and rescinded the contract.
(What) Object except:
▪ Outside of Commerce of Men – (the word commerce synonym for the word “kalakalan” which
makes the object be sold). Commercial Transaction.
Therefore, things and services out of commerce of men are inexistent and void from the
beginning in terms of contracts. E.g. Public Roads, Life, and Parts of the Body esp. Internal
organs.
▪ In transmissible of rights – Rights that cannot be transferred. E.g. Future Things & Personal Rights
etc.
▪ Impossible object / service – will never happen or never exist.
▪ Contrary to Law, Moral, Public Order, Public Policy, and Good Customs.
▪ Determinate – identifiable (Quantitative) without the need of new contract.
(Why) Cause or Consideration – according to ACT. 1350 GENERAL RULES
Exceptions:
▪ Gratuitous – Personal reasons, liberality, the kindness of
beneficence. E.g. Donation and Scholarship A. Age
▪ Remuneratory or Remunerative – Service with an B. Diminished Mental
Capability / Demented
exchange of reward. Always in medium of money and
C. Deaf & Mute – Illiterate (No
numerical value. E.g. Employment Sign language)
▪ Onerous – Burden (parties are reciprocally obligated to D. Intoxicated State
each other) E.g. Insurance (Life & Health),
Employment, and Travel Insurance
(Who) Consent – If there’s an acceptance, there’s an agreement of minds. Only the problem if it’s
Valid or Invalid.
Legally Insane – not knowing the right or wrong. Lucid Interval – Legal term for period of sanity.
❖ Grounds of Vitiated / Defected Consent (Voidable)
Ratification – giving formal consent /
A. Error or Mistake
making it officially valid.
B. Force or Violence
C. Intimidation or Threat
Novation – creating new agreement
D. Undue influence – (Undue means ‘di nararapat)
to replace the old one and agreed by
E. Fraud or Deceit
both parties.
Prescription Period – refers to the length of time within
which a party is allowed to bring forth a legal action or claim. It is a right in a certain amount of time. E.g.
Warranty.
Rescissible Voidable Unenforceable Void & Inexistent
Factors Contract Contract Contract Contract
OBJECT Yes Yes Yes
CAUSE Yes Yes Yes Not all are
CONSENT Yes Yes, but vitiated Yes, but by one present.
without or in excess
of authority
Fraud No No No
Mistake No At least one is No No
Force No present. No No
Threat No No No
Undue No No No
intimidation
CAN BE RATIFIED Yes Yes Yes No
If rescinded or Contract is valid Contract is valid, Remains Has no validity
voided, when is from the beginning but once voided, unenforceable from from the start.
the validity of the and loses effect it becomes void the start, unless
contract and when only from the from the start. ratified and then it
does contract lose point when it was becomes a valid
effect? rescinded. contract.
Obligations before Obligations All obligations are No obligations
Effect on rescission remain remain until dormant unless arise because
obligtions demandable. voided, then all ratified, and then there is no
obligations becomes contract.
performed can be demandable.
undone because
NO obligations
SHOULD have
arisen.
You might also like
- Contracts FLOW ChartDocument6 pagesContracts FLOW Chartbooda262695% (22)
- Creative Encounter With God in Worship - A Critical Reflection On Howard ThurmanDocument12 pagesCreative Encounter With God in Worship - A Critical Reflection On Howard ThurmanRev. Alcenir Oliveira, MDiv, MBA, BBA & BPANo ratings yet
- 2.22 NASPA 2019 Program Book EPB PDFDocument182 pages2.22 NASPA 2019 Program Book EPB PDFMarques Redd100% (1)
- The Power of Acceptance PDFDocument13 pagesThe Power of Acceptance PDFmanas999100% (12)
- lt2 EthicsDocument10 pageslt2 Ethicsapi-445796097No ratings yet
- Impact of Training Programs Towards Employees Performance of DILGDocument42 pagesImpact of Training Programs Towards Employees Performance of DILGRexanCamposNo ratings yet
- Contracts Flow ChartDocument6 pagesContracts Flow Chartcarlspackler983100% (5)
- LABOR LAW Reviewer POQUIZDocument16 pagesLABOR LAW Reviewer POQUIZmegzycutes387183% (6)
- Chart - Kinds of ContractsDocument1 pageChart - Kinds of ContractsGONZALES, JULIE ANN, S.No ratings yet
- Lecture 14 (2022)Document16 pagesLecture 14 (2022)CHRISTIA ALYSSA MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- Contract ActDocument91 pagesContract ActAakash_Shah_702No ratings yet
- Contracts Outline 2020Document17 pagesContracts Outline 2020Savana DegroatNo ratings yet
- Culled Primarily From The Lectures of Atty. Kenneth Glenn L. ManuelDocument45 pagesCulled Primarily From The Lectures of Atty. Kenneth Glenn L. Manueldarkbliss MNo ratings yet
- Notes in ContractsDocument5 pagesNotes in ContractsSehyuk LimNo ratings yet
- LAW ON SALES - SummaryDocument3 pagesLAW ON SALES - SummaryAUBREY MAE MANALONo ratings yet
- Law On Contracts Notes 1Document5 pagesLaw On Contracts Notes 1Rose Marie Lacsamana BarreteNo ratings yet
- Family LawDocument33 pagesFamily Lawmokoenadinny99No ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act, 1872Document59 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872Neeranjali NairNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act, 1872Document70 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872migpatel7970No ratings yet
- 2.0 Law On Credit Transactions 2.1 Pledge, Real Mortgage and Chattel Mortgage 2.1.1 Nature and RequisitesDocument5 pages2.0 Law On Credit Transactions 2.1 Pledge, Real Mortgage and Chattel Mortgage 2.1.1 Nature and RequisitesChristine Mae Fernandez MataNo ratings yet
- Notes in Contracts-VillaDocument6 pagesNotes in Contracts-VillaAmor VillaNo ratings yet
- SalesDocument13 pagesSalesJenny Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- L-201 Final Review Session Sun. 12 BU-109 (Tentative)Document7 pagesL-201 Final Review Session Sun. 12 BU-109 (Tentative)rlidell01No ratings yet
- Gasser Final NotesDocument12 pagesGasser Final NotesVGANo ratings yet
- Free Consent: Coercion, Undue Influence, Fraud & Misrepresentation (CUFM)Document48 pagesFree Consent: Coercion, Undue Influence, Fraud & Misrepresentation (CUFM)MUHMMAD ARSALAN 13728No ratings yet
- CONTRACTS ProvisionsDocument2 pagesCONTRACTS ProvisionskhaiNo ratings yet
- Equity ExamNotesDocument44 pagesEquity ExamNotesusherthNo ratings yet
- Contract ActDocument98 pagesContract ActAnkur Dubey67% (3)
- Contract Law - Consideration SC3Document26 pagesContract Law - Consideration SC3Ganesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ca51011 - Law On Obligations and Contracts: Article 1156 of The Civil Code of The PhilippinesDocument47 pagesCa51011 - Law On Obligations and Contracts: Article 1156 of The Civil Code of The Philippinesyvonne salasNo ratings yet
- RFBT ReviewersDocument13 pagesRFBT ReviewersRose MarieNo ratings yet
- Law PaperDocument194 pagesLaw PaperTessaNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract Sa 9 1 21Document40 pagesLaw of Contract Sa 9 1 21Aparna JRNo ratings yet
- Law of Agency - Part IDocument13 pagesLaw of Agency - Part ITabi D.No ratings yet
- Legal Questions and Answers (End-Term)Document22 pagesLegal Questions and Answers (End-Term)sayanchakrabortymba2022No ratings yet
- 12 Agency Nov 4Document5 pages12 Agency Nov 4Chezka Bianca TorresNo ratings yet
- Defective ContractsDocument3 pagesDefective ContractsAngge D.No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1Trúc BùiNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract ActDocument8 pagesIndian Contract ActManish SinghNo ratings yet
- CPT Mercantile Law Revision Notes YMKPNBH3Document48 pagesCPT Mercantile Law Revision Notes YMKPNBH3mahesh bawgeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Promissory EstoppelDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Promissory EstoppelAdam 'Fez' Ferris100% (3)
- Contract ActDocument38 pagesContract Actsneh sumanNo ratings yet
- Civil Law Review 2 Notes (Atty. Carla E. Santamaria-Sena)Document90 pagesCivil Law Review 2 Notes (Atty. Carla E. Santamaria-Sena)Daverick PacumioNo ratings yet
- Obligations Part 1Document11 pagesObligations Part 1DanicaNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Contract Vs Contract of MarriageDocument7 pagesOrdinary Contract Vs Contract of MarriageVenNo ratings yet
- ConsiderationDocument54 pagesConsiderationBrandon WongNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument4 pagesContractsElle BadussyNo ratings yet
- Presented by Neha Bansal Ankita Tyagi Gurpreet Kaur Veni RathiDocument12 pagesPresented by Neha Bansal Ankita Tyagi Gurpreet Kaur Veni RathiRishikesh KaushikNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Kruti BhattNo ratings yet
- Contracts Complete Outline Chapter 3: Liability in The Absence of Bargained-For-ExchangeDocument24 pagesContracts Complete Outline Chapter 3: Liability in The Absence of Bargained-For-ExchangeJohnny Emm100% (2)
- Corporate & Other Laws: Ca-InterDocument15 pagesCorporate & Other Laws: Ca-IntersonuNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument21 pagesLaw On ContractsHannah SyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture ThreeDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture Threesimangalisokhoza37No ratings yet
- Part 13 - Video LectureDocument10 pagesPart 13 - Video LectureApril ToledoNo ratings yet
- Dentistry 162 - : 1.1 - ObligationsDocument4 pagesDentistry 162 - : 1.1 - ObligationsGeeNo ratings yet
- BUSINESSS LAW FINAL 4sepDocument196 pagesBUSINESSS LAW FINAL 4sepHARSHIT SAXENANo ratings yet
- Comparison of Islamic and English ContractDocument27 pagesComparison of Islamic and English ContractAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contract Mind MapsDocument8 pagesThe Law of Contract Mind MapsSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- 5 Object of The ContractDocument4 pages5 Object of The ContractBankowski PhotographyNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerErika DiangNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument13 pagesCONTRACTSykckjzfzsmNo ratings yet
- Course: Legal Technici: An English Lesson 10Document32 pagesCourse: Legal Technici: An English Lesson 10Joselyn Pamela Cutipa CohailaNo ratings yet
- 3 General Principles of Contract ActDocument43 pages3 General Principles of Contract ActSamit DasNo ratings yet
- Contract Law - Consideration SCDocument29 pagesContract Law - Consideration SCreena0610 gNo ratings yet
- Bigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawFrom EverandBigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawNo ratings yet
- Generation CHRIST Assembly PDFDocument15 pagesGeneration CHRIST Assembly PDFSTEVE JHONSON LepasanaNo ratings yet
- αὐτάρκης in Stoicism and Phil 4.11Document20 pagesαὐτάρκης in Stoicism and Phil 4.11Alexander BurgaNo ratings yet
- Fase 4 - Hacia Una Solución de Conflictos AmbientalesDocument4 pagesFase 4 - Hacia Una Solución de Conflictos AmbientalesLina Maria SilvaNo ratings yet
- USNORTHCOM FaithfulPatriotDocument33 pagesUSNORTHCOM FaithfulPatriotnelson duringNo ratings yet
- Pasport Form DDNI06330312GO0330Document0 pagesPasport Form DDNI06330312GO0330Awdhesh Singh BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Examen PCE Ingles 2022 Resuelto Escuela PCEDocument6 pagesExamen PCE Ingles 2022 Resuelto Escuela PCECésar PHNo ratings yet
- 03 - Prerequisites of Collective BargainingDocument8 pages03 - Prerequisites of Collective BargainingGayatri Dhawan100% (1)
- Yamuna Biodiversity ParkDocument5 pagesYamuna Biodiversity ParkPriyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Sumbitted To: Submitted By:: Even Lamps OF AdvocacyDocument6 pagesSumbitted To: Submitted By:: Even Lamps OF Advocacyudita goelNo ratings yet
- 4th 2 9 20201Document5 pages4th 2 9 20201Viner Hernan SantosNo ratings yet
- Abraham Lincoln OUTLINEDocument3 pagesAbraham Lincoln OUTLINEWilder Jose BCNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Prelim Transes - MoralityDocument6 pagesBioethics Prelim Transes - MoralityAleah JayaganNo ratings yet
- Buason Vs PanuyasDocument5 pagesBuason Vs PanuyasVeepee PanzoNo ratings yet
- IncelsDocument42 pagesIncelsjosebardamuNo ratings yet
- Audit Rules 1Document125 pagesAudit Rules 1Shikha AroraNo ratings yet
- Copyright Jeopardy 1Document55 pagesCopyright Jeopardy 1api-446508079No ratings yet
- Company ProfileDocument19 pagesCompany ProfileDiana CitraNo ratings yet
- Temporary Employment CommentsDocument4 pagesTemporary Employment CommentsCzar Ian AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Transactional LeadershipDocument5 pagesTransactional Leadershipal-obinay shereenNo ratings yet
- AFFIDAVITDocument1 pageAFFIDAVITpot420_aivanNo ratings yet
- Iberia 2012 CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY ReportDocument126 pagesIberia 2012 CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY ReportCSRMedia NetworkNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics IA RFDDocument53 pagesCode of Ethics IA RFDbautista bautistaNo ratings yet
- CIVPRO - Case Compilation No. 2Document95 pagesCIVPRO - Case Compilation No. 2Darla GreyNo ratings yet
- Constructions of Motherhood in Euripides' Medea: John GivenDocument15 pagesConstructions of Motherhood in Euripides' Medea: John GivenJosé María RissoNo ratings yet
- CASE 1: Joanne JoannaDocument4 pagesCASE 1: Joanne JoannaMiruna CiteaNo ratings yet