Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsYear 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
Year 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
Uploaded by
2z95bjgbd8This document provides a checklist of key biology concepts and terms that students should know for their Year 9 spring semester. It includes definitions for microscope parts like the eyepiece lens and objective lens. It also defines cellular structures such as the cell membrane, chloroplasts, and ribosomes. Key biological processes are outlined, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and asexual reproduction. Other items cover topics like adaptations, enzymes, and cancer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDocument3 pagesWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Electromagnetics by Syed A NasarDocument444 pagesSolved Problems in Electromagnetics by Syed A NasarOnur Çakıroğlu78% (9)
- Science Gen EdDocument17 pagesScience Gen EdDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Science General EducDocument24 pagesScience General EducDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Science 10: Biology Unit Exam Review: Imaging TechnologyDocument12 pagesScience 10: Biology Unit Exam Review: Imaging TechnologyWilliam PittsNo ratings yet
- Bio Presentation Englsih VerDocument6 pagesBio Presentation Englsih Verchristopherjohns0321No ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviewer 1Document8 pagesGenbio Reviewer 1Franchezkka Mae Belaro100% (1)
- Biol 102 AssignmentDocument11 pagesBiol 102 AssignmentMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Organization of Cells Notes 2Document13 pagesOrganization of Cells Notes 2manarehab35No ratings yet
- Complete Topic 1 BIO IB Review ANSWERSDocument6 pagesComplete Topic 1 BIO IB Review ANSWERSLilyNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument9 pagesCells NotesJesse ChateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2 Q3 General BiologyDocument3 pagesLesson 1 and 2 Q3 General BiologyYuji HyakutakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument35 pagesChapter IOltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsKristelle Dae PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 3 The Plant CellDocument4 pagesExercise No. 3 The Plant CellMarielNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteDocument4 pagesDiagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteAdriana Santiago RoaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetgaerlanadrianneNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of Lifemunnithakur5285No ratings yet
- Beed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.Document6 pagesBeed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.GraceNo ratings yet
- Biology BookDocument51 pagesBiology BookRam NepaliNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell AnatomyDocument5 pagesModule 2 Cell Anatomy10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- 8 3+Patterns+in+NatureDocument24 pages8 3+Patterns+in+NatureSonny Hothi100% (1)
- Cell Study GuideDocument4 pagesCell Study Guidetheomokaka84No ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellCaren AdongoNo ratings yet
- Genetics - FunctionsDocument4 pagesGenetics - Functionsrhonamalupa216No ratings yet
- CH 6 BioDocument5 pagesCH 6 BioedwarddameNo ratings yet
- What Is A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesWhat Is A MicroscopeMcj TeeNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument30 pagesCell BiologyHila Jagdish bhaiNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Edible Cell ActivityDocument9 pagesScience 9 - Edible Cell ActivitySheena Mar dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDocument11 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument33 pagesBiologysiennakransiqiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2016 - 2017Document8 pagesReviewer 2016 - 2017VivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeRizwanSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument104 pagesCell BiologyADARSH RNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- 1.1:1.2 NotesDocument3 pages1.1:1.2 Notessuhailqubti33No ratings yet
- Biology 1Document5 pagesBiology 1Zeynep AkıNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument59 pagesCytologyCla Nuval100% (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument22 pagesCell BiologyFelionesNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell StructureDocument50 pagesBasic Cell StructureAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- 复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notesDocument5 pages复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notescynwuyxNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 Biology NotesDocument19 pagesYr 11 Biology Notesareebah.shahbaz1No ratings yet
- Principles of Biology: Life ..Chapter 4 .Document15 pagesPrinciples of Biology: Life ..Chapter 4 .Mohammed ShehuNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument31 pagesModule 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsConcepcion, Jemaelah P.No ratings yet
- 2cytology 70 27Document4 pages2cytology 70 27rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Guide - TeacherDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide - Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Biology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonDocument15 pagesBiology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonKalel WilsonNo ratings yet
- 4-5-Prokaryotic Cells and MembranesDocument38 pages4-5-Prokaryotic Cells and MembranesaarnavskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Document7 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument34 pagesThe Celljaco_ansaldiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell-Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined As Cells Containing Organized Nucleus and OrganellesDocument12 pagesEukaryotic Cell-Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined As Cells Containing Organized Nucleus and OrganellesgabrieleyannNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document13 pagesCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function HW AnswersDocument2 pagesCell Structure and Function HW Answersareej salimNo ratings yet
- 2022 GCSE Biology NotessefsefDocument78 pages2022 GCSE Biology NotessefsefLix FNNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Firman Pambudi: Profile SkillsDocument1 pageFirman Pambudi: Profile SkillsFirman PambudiNo ratings yet
- TOOLKIT For MPDS-August12 PDFDocument13 pagesTOOLKIT For MPDS-August12 PDFdjtj89No ratings yet
- Abe How Do You Pass The Financial Accounting ExaminationDocument2 pagesAbe How Do You Pass The Financial Accounting ExaminationSami Islam100% (1)
- SL - DMA 2233 - Lukisan CAD 2Document8 pagesSL - DMA 2233 - Lukisan CAD 2Mohamed Zulfakar Jafney ZulkfliNo ratings yet
- The Predictive Power of Students Pygmalion PerceptionsDocument23 pagesThe Predictive Power of Students Pygmalion PerceptionsErmelina BacatanNo ratings yet
- Plastisitas OtakDocument67 pagesPlastisitas OtakFtrNo ratings yet
- Yajaira I Martinez ResumeDocument2 pagesYajaira I Martinez Resumeapi-210960222No ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 10 12Document82 pagesChemistry Grade 10 12Dawson MwendaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Worksheet Polar CoordinatesDocument3 pages8.1 Worksheet Polar CoordinatesRonnieMaeMaullionNo ratings yet
- The 2C - 2I - 1R Pedagogical Approaches: Inquiry ApproachDocument11 pagesThe 2C - 2I - 1R Pedagogical Approaches: Inquiry ApproachLorefe Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Anti-Ragging Undetaking by Parents - GuardianDocument1 pageAnti-Ragging Undetaking by Parents - GuardianAmarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Action AidDocument1 pageAction AidAhmad Masoom JamshidiNo ratings yet
- Handout 2: Five-Step Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesHandout 2: Five-Step Lesson Plans_clark_oconnorNo ratings yet
- Social Networks A Learning Tool For TeamsDocument2 pagesSocial Networks A Learning Tool For TeamsLeon HaiderNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 9291Document2 pagesRepublic Act 9291ChrisEmilsonHernaezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in EntrepreneurshipDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in EntrepreneurshipSusan Ecleo100% (1)
- Shandor Professional Responsibilities For School and CommunityDocument2 pagesShandor Professional Responsibilities For School and Communityapi-640547453No ratings yet
- E1 161021009 Arief FirmansyahDocument8 pagesE1 161021009 Arief FirmansyahArief FirmnasyahNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Basic Education DepartmentDocument9 pagesCurriculum Map: Basic Education DepartmentBIT INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE TALIBONNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Hip Activities 2017Document8 pagesBrief Description of Hip Activities 2017Ranita AwangNo ratings yet
- Yeme Bozukluklarının YaygınlığıDocument7 pagesYeme Bozukluklarının YaygınlığıgülsümNo ratings yet
- Degree in Engg. High Court o P& HDocument3 pagesDegree in Engg. High Court o P& HVigneshwar Raju Prathikantam100% (2)
- Systems Engineering Manager Solutions Architect in San Jose CA Resume Michael QuanDocument3 pagesSystems Engineering Manager Solutions Architect in San Jose CA Resume Michael QuanMichaelQuanNo ratings yet
- HRMS Implementation GuideDocument362 pagesHRMS Implementation GuideDevika ChopraNo ratings yet
- Petition Letter To SKDocument2 pagesPetition Letter To SKJasmine SingletonNo ratings yet
- Plan Business Analysis Information ManagementDocument2 pagesPlan Business Analysis Information Managementsonam tiwariNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Least Mastered Competencies First QuarterDocument3 pagesGrade 6 Least Mastered Competencies First QuarterGener Taña Antonio100% (1)
- 1 - 1 Student Device Program Brochure (2022-2023)Document1 page1 - 1 Student Device Program Brochure (2022-2023)keqwlng linNo ratings yet
- Johanna Camila García: Commercial AdvisorDocument3 pagesJohanna Camila García: Commercial AdvisorKmilitha PulidoNo ratings yet
Year 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
Year 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
Uploaded by
2z95bjgbd80 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThis document provides a checklist of key biology concepts and terms that students should know for their Year 9 spring semester. It includes definitions for microscope parts like the eyepiece lens and objective lens. It also defines cellular structures such as the cell membrane, chloroplasts, and ribosomes. Key biological processes are outlined, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and asexual reproduction. Other items cover topics like adaptations, enzymes, and cancer.
Original Description:
Original Title
b5661e44dcf4749b2413d55745e880ef_20240123_161612
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a checklist of key biology concepts and terms that students should know for their Year 9 spring semester. It includes definitions for microscope parts like the eyepiece lens and objective lens. It also defines cellular structures such as the cell membrane, chloroplasts, and ribosomes. Key biological processes are outlined, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and asexual reproduction. Other items cover topics like adaptations, enzymes, and cancer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesYear 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
Year 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
Uploaded by
2z95bjgbd8This document provides a checklist of key biology concepts and terms that students should know for their Year 9 spring semester. It includes definitions for microscope parts like the eyepiece lens and objective lens. It also defines cellular structures such as the cell membrane, chloroplasts, and ribosomes. Key biological processes are outlined, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and asexual reproduction. Other items cover topics like adaptations, enzymes, and cancer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Year 9 Biology Spring 1 2024 Checklist
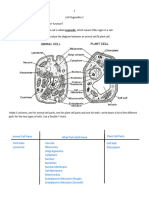
1. Eyepiece lens - The part of the microscope you look down.
2. Magnification - How much bigger something appears compared with its actual
size.
3. Objective lens - The part of the microscope that is closest to the specimen.
4. Resolution - Smallest change that can be measured by an instrument. For example,
in a microscope it is the smallest distance between two points that can be seen as
two points and not blurred into one point.
5. IAM equation – to calculate the magnification of an image, you divide the image
size by the actual size.
6. Cell (surface) membrane - It controls what goes into and out of a cell. It is often
called the cell surface membrane because eukaryotic cells contain other structures
with membranes.
7. Cell wall - A tough layer of material around some cells, which is used for protection
and support. It is stiff and made of cellulose in plants. In Bacteria it is flexible.
8. Chloroplasts - A green disc containing chlorophyll, found in plant cells. Where the
plant makes glucose, using photosynthesis.
9. Nucleus – the cellular structure that contains the DNA/chromosomes in a
eukaryotic cell (sometimes called the ‘control centre’).
10.Ribosome - Tiny sub-cellular structure that makes proteins.
11.Respiration – a series of reactions in all living cells where glucose is broken down
to release energy
12.Photosynthesis – a series of reactions that take place in the green part of plants
where carbon dioxide and water combine to form glucose and oxygen. It requires
energy from sunlight
13.Biotic factor – Living components in an ecosystem, including plants, animals,
micro-organisms
14.Abiotic factor – Non-living components in an ecosystem, such as temperature,
light and space
15.Adaptation – the features of an organism (eg plant/animal) that enable it to
survive or do a certain function
16.Variable – something that needs to be controlled during practical investigations in
order to produce valid and comparable data
17.Flagellum – a tail-like structure found on many bacteria (and sperm cells) to help
them move
18.Prokaryotic – a cell which does NOT have a nucleus (or any membrane-bound
organelles)
19.Enzyme – a biological catalyst, a molecule that speeds up reactions in living cells
20.Biuret test – the test for proteins; add potassium hydroxide and copper sulfate
solution to food. Colour changes from blue to purple if protein is present
21.Asexual reproduction – producing new organisms from one parent only; offspring
are genetically identical to the parent
22.Growth – a permanent increase in the number and/or size of cells in an organism
23.Diploid – cells with 2 sets of chromosomes (2 copies of each chromosome). In
humans, diploid number is 46
24.Metaphase – the stage in mitosis where chromosomes line up on spindle fibres
across the middle of the cell
25.Cancer – disease caused by uncontrolled cell division in the body
You might also like
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDocument3 pagesWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Electromagnetics by Syed A NasarDocument444 pagesSolved Problems in Electromagnetics by Syed A NasarOnur Çakıroğlu78% (9)
- Science Gen EdDocument17 pagesScience Gen EdDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Science General EducDocument24 pagesScience General EducDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Science 10: Biology Unit Exam Review: Imaging TechnologyDocument12 pagesScience 10: Biology Unit Exam Review: Imaging TechnologyWilliam PittsNo ratings yet
- Bio Presentation Englsih VerDocument6 pagesBio Presentation Englsih Verchristopherjohns0321No ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviewer 1Document8 pagesGenbio Reviewer 1Franchezkka Mae Belaro100% (1)
- Biol 102 AssignmentDocument11 pagesBiol 102 AssignmentMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Organization of Cells Notes 2Document13 pagesOrganization of Cells Notes 2manarehab35No ratings yet
- Complete Topic 1 BIO IB Review ANSWERSDocument6 pagesComplete Topic 1 BIO IB Review ANSWERSLilyNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument9 pagesCells NotesJesse ChateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2 Q3 General BiologyDocument3 pagesLesson 1 and 2 Q3 General BiologyYuji HyakutakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument35 pagesChapter IOltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsKristelle Dae PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 3 The Plant CellDocument4 pagesExercise No. 3 The Plant CellMarielNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteDocument4 pagesDiagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteAdriana Santiago RoaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetgaerlanadrianneNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of Lifemunnithakur5285No ratings yet
- Beed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.Document6 pagesBeed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.GraceNo ratings yet
- Biology BookDocument51 pagesBiology BookRam NepaliNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell AnatomyDocument5 pagesModule 2 Cell Anatomy10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- 8 3+Patterns+in+NatureDocument24 pages8 3+Patterns+in+NatureSonny Hothi100% (1)
- Cell Study GuideDocument4 pagesCell Study Guidetheomokaka84No ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellCaren AdongoNo ratings yet
- Genetics - FunctionsDocument4 pagesGenetics - Functionsrhonamalupa216No ratings yet
- CH 6 BioDocument5 pagesCH 6 BioedwarddameNo ratings yet
- What Is A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesWhat Is A MicroscopeMcj TeeNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument30 pagesCell BiologyHila Jagdish bhaiNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Edible Cell ActivityDocument9 pagesScience 9 - Edible Cell ActivitySheena Mar dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDocument11 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument33 pagesBiologysiennakransiqiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2016 - 2017Document8 pagesReviewer 2016 - 2017VivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeRizwanSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument104 pagesCell BiologyADARSH RNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- 1.1:1.2 NotesDocument3 pages1.1:1.2 Notessuhailqubti33No ratings yet
- Biology 1Document5 pagesBiology 1Zeynep AkıNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument59 pagesCytologyCla Nuval100% (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument22 pagesCell BiologyFelionesNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell StructureDocument50 pagesBasic Cell StructureAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- 复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notesDocument5 pages复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notescynwuyxNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 Biology NotesDocument19 pagesYr 11 Biology Notesareebah.shahbaz1No ratings yet
- Principles of Biology: Life ..Chapter 4 .Document15 pagesPrinciples of Biology: Life ..Chapter 4 .Mohammed ShehuNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument31 pagesModule 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsConcepcion, Jemaelah P.No ratings yet
- 2cytology 70 27Document4 pages2cytology 70 27rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Guide - TeacherDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide - Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Biology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonDocument15 pagesBiology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonKalel WilsonNo ratings yet
- 4-5-Prokaryotic Cells and MembranesDocument38 pages4-5-Prokaryotic Cells and MembranesaarnavskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Document7 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument34 pagesThe Celljaco_ansaldiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell-Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined As Cells Containing Organized Nucleus and OrganellesDocument12 pagesEukaryotic Cell-Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined As Cells Containing Organized Nucleus and OrganellesgabrieleyannNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document13 pagesCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function HW AnswersDocument2 pagesCell Structure and Function HW Answersareej salimNo ratings yet
- 2022 GCSE Biology NotessefsefDocument78 pages2022 GCSE Biology NotessefsefLix FNNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Firman Pambudi: Profile SkillsDocument1 pageFirman Pambudi: Profile SkillsFirman PambudiNo ratings yet
- TOOLKIT For MPDS-August12 PDFDocument13 pagesTOOLKIT For MPDS-August12 PDFdjtj89No ratings yet
- Abe How Do You Pass The Financial Accounting ExaminationDocument2 pagesAbe How Do You Pass The Financial Accounting ExaminationSami Islam100% (1)
- SL - DMA 2233 - Lukisan CAD 2Document8 pagesSL - DMA 2233 - Lukisan CAD 2Mohamed Zulfakar Jafney ZulkfliNo ratings yet
- The Predictive Power of Students Pygmalion PerceptionsDocument23 pagesThe Predictive Power of Students Pygmalion PerceptionsErmelina BacatanNo ratings yet
- Plastisitas OtakDocument67 pagesPlastisitas OtakFtrNo ratings yet
- Yajaira I Martinez ResumeDocument2 pagesYajaira I Martinez Resumeapi-210960222No ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 10 12Document82 pagesChemistry Grade 10 12Dawson MwendaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Worksheet Polar CoordinatesDocument3 pages8.1 Worksheet Polar CoordinatesRonnieMaeMaullionNo ratings yet
- The 2C - 2I - 1R Pedagogical Approaches: Inquiry ApproachDocument11 pagesThe 2C - 2I - 1R Pedagogical Approaches: Inquiry ApproachLorefe Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Anti-Ragging Undetaking by Parents - GuardianDocument1 pageAnti-Ragging Undetaking by Parents - GuardianAmarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Action AidDocument1 pageAction AidAhmad Masoom JamshidiNo ratings yet
- Handout 2: Five-Step Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesHandout 2: Five-Step Lesson Plans_clark_oconnorNo ratings yet
- Social Networks A Learning Tool For TeamsDocument2 pagesSocial Networks A Learning Tool For TeamsLeon HaiderNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 9291Document2 pagesRepublic Act 9291ChrisEmilsonHernaezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in EntrepreneurshipDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in EntrepreneurshipSusan Ecleo100% (1)
- Shandor Professional Responsibilities For School and CommunityDocument2 pagesShandor Professional Responsibilities For School and Communityapi-640547453No ratings yet
- E1 161021009 Arief FirmansyahDocument8 pagesE1 161021009 Arief FirmansyahArief FirmnasyahNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Basic Education DepartmentDocument9 pagesCurriculum Map: Basic Education DepartmentBIT INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE TALIBONNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Hip Activities 2017Document8 pagesBrief Description of Hip Activities 2017Ranita AwangNo ratings yet
- Yeme Bozukluklarının YaygınlığıDocument7 pagesYeme Bozukluklarının YaygınlığıgülsümNo ratings yet
- Degree in Engg. High Court o P& HDocument3 pagesDegree in Engg. High Court o P& HVigneshwar Raju Prathikantam100% (2)
- Systems Engineering Manager Solutions Architect in San Jose CA Resume Michael QuanDocument3 pagesSystems Engineering Manager Solutions Architect in San Jose CA Resume Michael QuanMichaelQuanNo ratings yet
- HRMS Implementation GuideDocument362 pagesHRMS Implementation GuideDevika ChopraNo ratings yet
- Petition Letter To SKDocument2 pagesPetition Letter To SKJasmine SingletonNo ratings yet
- Plan Business Analysis Information ManagementDocument2 pagesPlan Business Analysis Information Managementsonam tiwariNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Least Mastered Competencies First QuarterDocument3 pagesGrade 6 Least Mastered Competencies First QuarterGener Taña Antonio100% (1)
- 1 - 1 Student Device Program Brochure (2022-2023)Document1 page1 - 1 Student Device Program Brochure (2022-2023)keqwlng linNo ratings yet
- Johanna Camila García: Commercial AdvisorDocument3 pagesJohanna Camila García: Commercial AdvisorKmilitha PulidoNo ratings yet