Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rodents, Snakes & Insects (OSHA)
Rodents, Snakes & Insects (OSHA)
Uploaded by
Aizen Myo-o AcitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rodents, Snakes & Insects (OSHA)
Rodents, Snakes & Insects (OSHA)
Uploaded by
Aizen Myo-o AcitCopyright:
Available Formats
QUICK
CARD
TM
Rodents, Snakes
and Insects
Insects, Spiders and Ticks
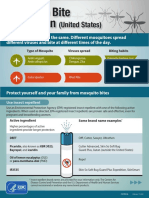
• To protect yourself from biting and stinging insects,
wear long pants, socks, and long-sleeved shirts.
• Use insect repellents that contain DEET or Picaridin.
• Treat bites and stings with over-the-counter products
that relieve pain and prevent infection.
• Avoid fire ants; their bites are painful and cause blisters.
• Severe reactions to fire ant bites (chest pain, nausea,
sweating, loss of breath, serious swelling or slurred
speech) require immediate medical treatment.
Rodents and Wild or Stray Animals
• Dead and live animals can spread diseases such as Rat
Bite Fever and Rabies.
• Avoid contact with wild or stray animals.
• Avoid contact with rats or rat-contaminated buildings.
If you can’t avoid contact, wear protective gloves and
wash your hands regularly.
• Get rid of dead animals as soon as possible.
• If bitten/scratched, get medical attention immediately.
Snakes
• Watch where you place your hands and feet when
removing debris. If possible, don’t place your fingers
under debris you are moving. Wear heavy gloves.
• If you see a snake, step back and allow it to proceed.
• Wear boots at least 10 inches high.
• Watch for snakes sunning on fallen trees, limbs or
other debris.
• A snake’s striking distance is about 1/2 the total length
of the snake.
• If bitten, note the color and shape of the snake’s head
to help with treatment.
• Keep bite victims still and calm to slow the spread of
venom in case the snake is poisonous. Seek medical
attention as soon as possible.
• Do not cut the wound or attempt to suck out the
venom. Apply first aid: lay the person down so that
the bite is below the level of the heart, and cover the
bite with a clean, dry dressing.
For more complete information:
OSHA 3265-09N-05
Occupational
Safety and Health
Administration
U.S. Department of Labor
www.osha.gov (800) 321-OSHA
You might also like
- ss580 2013Document40 pagesss580 2013Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Rodents Snakes InsectsDocument2 pagesRodents Snakes InsectsaccastNo ratings yet
- West Nile Quick CardDocument1 pageWest Nile Quick CardAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Insects, Snakes, AnimalsDocument2 pagesInsects, Snakes, Animalschaitra rNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID Training - FINALDocument30 pagesFIRST AID Training - FINALDr. Sarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- First Aid Part - 3 - 201023 - 132951Document13 pagesFirst Aid Part - 3 - 201023 - 132951VishnuNo ratings yet
- Safety PrecautionsDocument45 pagesSafety PrecautionsIvann Adriel CariagaNo ratings yet
- For Finals PEDocument6 pagesFor Finals PEAvery S. BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Stinging InsectsDocument2 pagesStinging InsectsMouradOudirNo ratings yet
- StingsDocument4 pagesStingsCM GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Accomodation Management Unit 5 - First AidDocument3 pagesAccomodation Management Unit 5 - First AidDev SuriNo ratings yet
- BCFS 8.5x11 TickSafety V1Document2 pagesBCFS 8.5x11 TickSafety V1iftikhar ahmadNo ratings yet
- safty_firstDocument8 pagessafty_firster.vishal1029No ratings yet
- Animal Bites-First Aid.Document1 pageAnimal Bites-First Aid.Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- First Aid For Insect BitesDocument18 pagesFirst Aid For Insect BitesMary Grace OgatisNo ratings yet
- Bites and Stings PPT Fix DR IsyaDocument61 pagesBites and Stings PPT Fix DR IsyamadeNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument31 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentAmeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Bites and StingsDocument8 pagesBites and StingsZechariah NicholasNo ratings yet
- First Aid For AnimalDocument15 pagesFirst Aid For AnimalIwan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- How To Protect Yourself From Mosquitoes and Ticks - The New York TimesDocument4 pagesHow To Protect Yourself From Mosquitoes and Ticks - The New York TimesStéphane VoletNo ratings yet
- Wildlife in The Workplace - VHDocument5 pagesWildlife in The Workplace - VHVeronikaNo ratings yet
- Snake Bite First AidDocument6 pagesSnake Bite First Aidmelchor bangaoilNo ratings yet
- Common Injuries and IlnnessDocument4 pagesCommon Injuries and IlnnessSLIDENo ratings yet
- Animal BitesDocument48 pagesAnimal BitesJalouis GabalfinNo ratings yet
- Bites Stings and PoisonDocument78 pagesBites Stings and PoisonkagaralNo ratings yet
- Insect Sting Prevention and Treatment - 0Document1 pageInsect Sting Prevention and Treatment - 0CM GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 30 Things You Should Have in Your Medical First Aid KitsDocument11 pages30 Things You Should Have in Your Medical First Aid KitsPrincess Villasis BaciaNo ratings yet
- First Aid EquipmentsDocument18 pagesFirst Aid EquipmentsJaiiNo ratings yet
- First Aid KitDocument15 pagesFirst Aid KitRuthNo ratings yet
- Animal Handling PDFDocument1 pageAnimal Handling PDFcityofdarwingisNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Hazards DrowningDocument28 pagesAquatic Hazards DrowningCASTRO, JANELLA T.No ratings yet
- First Aid Project MeaningDocument4 pagesFirst Aid Project Meaningjodiandennis2No ratings yet
- Animal BitesDocument18 pagesAnimal BitesNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument3 pagesBasic First AidAlexandra VelascoNo ratings yet
- First Aid - Snake BiteDocument3 pagesFirst Aid - Snake BiteNaddratul HudaNo ratings yet
- CAUSATIVE AGENT - Pediculosis (Lousiness)Document2 pagesCAUSATIVE AGENT - Pediculosis (Lousiness)Diamante MhayaleneNo ratings yet
- BitesDocument4 pagesBitesCM GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 02PE 4 - Mod4A Lesson 3 and 4 - SIR ARNOLDDocument100 pages02PE 4 - Mod4A Lesson 3 and 4 - SIR ARNOLDEleanor GelacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Sports First Aid CareDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Sports First Aid Care2023178439No ratings yet
- 1 150612160156 Lva1 App6892Document47 pages1 150612160156 Lva1 App6892Augustus CaesarNo ratings yet
- Mosquito Bite PreventionDocument2 pagesMosquito Bite PreventionGary DetmanNo ratings yet
- ESG PandemicDocument2 pagesESG PandemicMartín TapiaNo ratings yet
- P.E 12 Final LessonDocument8 pagesP.E 12 Final Lessonhanintalib21No ratings yet
- Environmental HazardsDocument19 pagesEnvironmental HazardsRasell de LunaNo ratings yet
- Snake Bites: Under SupervisionDocument4 pagesSnake Bites: Under SupervisionAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10.1 Aquatic Environmental HazardsDocument14 pagesChapter 10.1 Aquatic Environmental HazardsDiana May ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Legislative Requirements. Emergency First Aid and CPRDocument31 pagesFirst Aid Legislative Requirements. Emergency First Aid and CPRAfzaalUmairNo ratings yet
- Parent Notification of Head Lice in ClassroomDocument2 pagesParent Notification of Head Lice in ClassroomTaufa TauatainaNo ratings yet
- HSE Bulletin # 78: "Preventing Snake Bites at Work"Document1 pageHSE Bulletin # 78: "Preventing Snake Bites at Work"Syed Faisal Hassan100% (2)
- Home Kit: A Household First Aid Kit Should Include These ItemsDocument7 pagesHome Kit: A Household First Aid Kit Should Include These ItemsRonny Fardian SetiadarmaNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument35 pagesFirst AidRaja Mohan GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument48 pagesPersonal Protective Equipmentjenesis dimayugaNo ratings yet
- TIck Control MeasuresDocument1 pageTIck Control MeasuresDibya DillipNo ratings yet
- Ticks and MosquitoesDocument2 pagesTicks and MosquitoesMouradOudirNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan First AidDocument13 pagesLesson Plan First AidAlfie AyroNo ratings yet
- Bites & Stings PressDocument4 pagesBites & Stings PressNikki CoplandNo ratings yet
- SMOTW - 736 - Insect Bites and StingsDocument4 pagesSMOTW - 736 - Insect Bites and StingsCM GonzalezNo ratings yet
- E. Wounds: A Scrape, A Rug Burn, A Road Rash or A StrawberryDocument9 pagesE. Wounds: A Scrape, A Rug Burn, A Road Rash or A StrawberryKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Health CareDocument41 pagesHealth Careemanuel.ferrer.sbeNo ratings yet
- Sports First Aid KitDocument4 pagesSports First Aid KitScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- SS 506 Pt1 2004 OSH Management System SpecificationDocument19 pagesSS 506 Pt1 2004 OSH Management System SpecificationAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- SS 314 1986 Industrial Eye ProtectorDocument46 pagesSS 314 1986 Industrial Eye ProtectorAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- SS 473 Pt1 1999 Specification For Personal Eye Protectors Part 1 General RequirementsDocument62 pagesSS 473 Pt1 1999 Specification For Personal Eye Protectors Part 1 General RequirementsAizen Myo-o Acit100% (1)
- CP 91 2001 Code of Practice For Lockout ProcedureDocument20 pagesCP 91 2001 Code of Practice For Lockout ProcedureAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- SS 473 Pt2 1999 Speciification For Personal Eye Protectors Part 2 Selection, Use and MaintenanceDocument34 pagesSS 473 Pt2 1999 Speciification For Personal Eye Protectors Part 2 Selection, Use and MaintenanceAizen Myo-o Acit100% (1)
- SS 292 1984 Safety Net For Construction SiteDocument16 pagesSS 292 1984 Safety Net For Construction SiteAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- CP 62 1995 Safe Use of Tower CraneDocument17 pagesCP 62 1995 Safe Use of Tower CraneAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- CP 49 1998 Noise Control On Construction Demolition SitesDocument50 pagesCP 49 1998 Noise Control On Construction Demolition SitesAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- SS 297 1996 Steel Wire Rope For HoistingDocument40 pagesSS 297 1996 Steel Wire Rope For HoistingAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Service Life of Mobile Cranes (MOM)Document7 pagesService Life of Mobile Cranes (MOM)Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- CP 14 1996 - Code of Practice For ScaffoldsDocument98 pagesCP 14 1996 - Code of Practice For ScaffoldsAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control & Road Safety Section 5Document22 pagesTraffic Control & Road Safety Section 5Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control & Road Safety Section 1Document34 pagesTraffic Control & Road Safety Section 1Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- CP 27 1999 Code of Practice For Factory Layout - Safety, Health and WelfareDocument49 pagesCP 27 1999 Code of Practice For Factory Layout - Safety, Health and WelfareAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Commercial Diving Best Practices & It's ChallengesDocument20 pagesCommercial Diving Best Practices & It's ChallengesAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Recent Incidents Involving Diving OperationsDocument14 pagesCase Studies On Recent Incidents Involving Diving OperationsAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control & Road Safety Section 3Document50 pagesTraffic Control & Road Safety Section 3Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control & Road Safety Section 2Document14 pagesTraffic Control & Road Safety Section 2Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Personnel Lifting (Hanford Site)Document16 pagesPersonnel Lifting (Hanford Site)Aizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Building Safety Culture in DivingDocument22 pagesBuilding Safety Culture in DivingAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Aid Chem Bottling PlantsDocument13 pagesRisk Assessment Aid Chem Bottling PlantsAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice For Licensed General Waste CollectorsDocument33 pagesCode of Practice For Licensed General Waste CollectorsAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet
- 2013 WSH (Medical Examinations) (Amendment) RegDocument2 pages2013 WSH (Medical Examinations) (Amendment) RegAizen Myo-o AcitNo ratings yet