Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Hygiene and Aseptic Technique
Hand Hygiene and Aseptic Technique
Uploaded by
imadhassanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hand Hygiene and Aseptic Technique
Hand Hygiene and Aseptic Technique
Uploaded by
imadhassanCopyright:
Available Formats
Hand Hygiene and Aseptic Technique:
Hand Hygiene is the number one way of preventing the transmission of organisms and hospital-
4
acquired infections. Correct aseptic technique is integral to this process
In Australia, healthcare-associated infections (HAI) over half of which are preventable 1
are the most common complication affecting patients in hospitals.
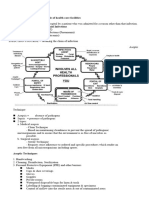
Hand Hygiene is aimed at stopping the transmission of infections. An infection requires
three elements- a pathogen, a susceptible host, and a mode of transmission (direct,
indirect, airborne, droplet)
Pathogen – any virus, microorganism, or other substance causing disease
TIP: Use detergent based wipes for cleansing of phones, stethoscopes and equipment.
The underlying principle is: All blood and body substances are potentially infectious.
Standard precautions include:
Hand hygiene – before and after every episode of patient contact
Respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette
Use of appropriate personal protective equipment to provide a barrier to blood, body fluids, non-intact skin, or mucous
membranes (gloves, goggles, aprons, masks)
Aseptic non-touch technique
Immunisation of healthcare workers
Management of sharps, blood spills, linen and waste to maintain a safe environment
Routine environmental cleaning
Hand hygiene includes:
Hand Hygiene includes:
Applying an alcohol-based handrub to the surface of the hands (including liquids, gels and foams)
OR
Washing hands with the use of water and soap or a soap solution, either non-antimicrobial or antimicrobial
Alcohol-based handrubs should be used (when hands are visibly clean) instead of
handwashing because they:
Substantially reduce bacterial count on hands
Require less time than handwashing
Are more accessible
Are self drying
Are gentler on skin and cause less skin irritation and dryness than frequent soap and water
washes, since all handrubs contain skin emollient (moisturisers)
5 moments for hand hygiene - Clean your hands:
1. Before you touch your client/patient/resident
For example before you assist a patient to move, before giving oral medications
2. Immediately before a procedure
For example prior to donning gloves before a
procedure where there is a high risk for
microorganism transmission e.g. to provide
dental care, emptying a catheter
3. Immediately after a procedure or body fluid
exposure
For example after attending a dressing in clients
home, pack up all clinical waste & clean hands
before touching anything else
4. After touching a client/patient/resident
For example after touching a client and before
touching any of your own equipment that you
have brought to them
5. After touching the client's/patient's/resident's
surroundings
For example after leaving the client's house, after
wiping down the treatment chair
You might also like
- OMNI Hypnosis Training Study GuideDocument14 pagesOMNI Hypnosis Training Study GuideJosemar Muller Lohn100% (4)
- Headache Syndromes, Oxford, 2020Document561 pagesHeadache Syndromes, Oxford, 2020luizmiranda108No ratings yet
- 1 Infection Prevention and ControlDocument57 pages1 Infection Prevention and Controlmariam100% (3)
- Hand HygieneDocument32 pagesHand HygieneRodel Agapito100% (1)
- Emergency Medicine - The Principles of Practice, 6E (2014) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument1,155 pagesEmergency Medicine - The Principles of Practice, 6E (2014) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFspadky100% (3)
- Parmed X PregnancyDocument4 pagesParmed X PregnancyRiyan WahyudoNo ratings yet
- Standard Precautions in Health CareDocument4 pagesStandard Precautions in Health CareCityhealthoffice SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Infection ControlDocument43 pagesMODULE 7 Infection ControlBitoy AlarconNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in DentistryDocument69 pagesInfection Control in DentistryShahrukh ali khanNo ratings yet
- 1st Topic Medical HandwashingDocument21 pages1st Topic Medical HandwashingDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Precautions - A Lec 6Document19 pagesLec 4 Precautions - A Lec 6mqbljbr529No ratings yet
- PRELIM NCM 103 FUNDA OF NURSING Handouts SLUDD 2023 1Document22 pagesPRELIM NCM 103 FUNDA OF NURSING Handouts SLUDD 2023 1eizyllebNo ratings yet
- Nursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl SettingDocument45 pagesNursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl Settingbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Part IDocument3 pagesInfection Control Part IFadz HadjiriNo ratings yet
- Aseptic TechniqueDocument9 pagesAseptic Techniquegabgabb1123zNo ratings yet
- Control Infection FDCDocument6 pagesControl Infection FDCDeny RakhmanNo ratings yet
- HandwashingDocument36 pagesHandwashingidelleequibalNo ratings yet
- Standard Precautions.... ALFADocument32 pagesStandard Precautions.... ALFARamadjr TzNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument14 pagesInfection ControlShiba AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument44 pagesInfection Controlkalpanagokul44No ratings yet
- Inection Control PoliciesDocument8 pagesInection Control PoliciesRubz BulquerinNo ratings yet
- Infection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresDocument25 pagesInfection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresManisha Thakur100% (2)
- Hand Hygiene and PPEDocument14 pagesHand Hygiene and PPESide GigsNo ratings yet
- NSC 221 AssignmentDocument4 pagesNSC 221 AssignmentDaniella AwurumibeNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 PDFDocument8 pagesLec 11 PDFFlorida ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06. Medical and Surgical AsepsisDocument19 pagesChapter 06. Medical and Surgical AsepsisChino Isiah CañeteNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Infection ControlDocument78 pagesWeek 1 Infection ControlKhalid Sh100% (1)
- Infection Control 2Document83 pagesInfection Control 2mrbyy619No ratings yet
- Infection Control Practices-1 (Autosaved)Document52 pagesInfection Control Practices-1 (Autosaved)mukeshkumar3142067No ratings yet
- Isolation and Hand Hygienepresentation1Document37 pagesIsolation and Hand Hygienepresentation1Nirmal Cricket UniverseNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi K3 Dalam Keperawatan: Ns. Endah Suprihatin, M.Kep., SP - MatDocument44 pagesAplikasi K3 Dalam Keperawatan: Ns. Endah Suprihatin, M.Kep., SP - MatDinda tri agustinNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument22 pagesInfection Controljwong8168100% (1)
- Area I Medical Surgical AsespsisDocument40 pagesArea I Medical Surgical AsespsisMeet JepsyNo ratings yet
- Asepsis and Infection ControlDocument120 pagesAsepsis and Infection Controlnagarjungali100% (1)
- Standard Precaution LectureDocument12 pagesStandard Precaution LecturearingkinkingNo ratings yet
- Handwashing ModuleDocument5 pagesHandwashing ModuleJerald Fernandez100% (1)
- Infection PreventionDocument64 pagesInfection PreventionAnonymous Iyf0Rjmdm3No ratings yet
- Arjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIDocument69 pagesArjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIArjumand ZargarNo ratings yet
- Hospital HygieneDocument29 pagesHospital HygieneManoj Sankaranarayana0% (1)
- Universal PrecautionDocument10 pagesUniversal PrecautionParth VasaveNo ratings yet
- Management of Infectious DiseaseDocument17 pagesManagement of Infectious DiseaseLeni CarununganNo ratings yet
- Standard Precautions (Autosaved)Document15 pagesStandard Precautions (Autosaved)Avantika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Routine PracticesDocument5 pagesRoutine PracticesGreg van BeekNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene: Infection Prevention Team May 2010Document32 pagesHand Hygiene: Infection Prevention Team May 2010kaconkkurniawanNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument16 pagesInfection ControlMohamed AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Concept of Handwashing Ncma113 LabDocument4 pagesConcept of Handwashing Ncma113 Labeverly evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control ModuleDocument16 pagesInfection Control ModuleKomite PpiNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical AsepsisDocument40 pagesMedical and Surgical AsepsisFrancr ToledanoNo ratings yet
- HH For Healthcare ProviderDocument4 pagesHH For Healthcare Providerraden samudraNo ratings yet
- Infection Control PracticesDocument9 pagesInfection Control PracticesAda Gay Olandia SerencioNo ratings yet
- Basic Clinical Skill: Hand Washing TechniquesDocument2 pagesBasic Clinical Skill: Hand Washing Techniquesdedede22898No ratings yet
- Healthcare Training OverviewDocument36 pagesHealthcare Training Overviewzaki001No ratings yet
- Infection Control Nursing StudentsDocument1 pageInfection Control Nursing StudentsAmala SebastianNo ratings yet
- Hand HygieneDocument2 pagesHand HygienevistamaniacNo ratings yet
- All Short Notes of ICDocument30 pagesAll Short Notes of ICaarti HingeNo ratings yet
- Module 8-NSTP 1-Health Program, Common Illness & Their PreventionDocument46 pagesModule 8-NSTP 1-Health Program, Common Illness & Their PreventionDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Basic Infection ControlDocument36 pagesBasic Infection ControlIlya Nur RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- ميد (2 files merged)Document70 pagesميد (2 files merged)Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- INFECTION Control and PREVENTION-1Document49 pagesINFECTION Control and PREVENTION-1Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Principles Underlying Medical and Surgical AsepsisDocument12 pagesPrinciples Underlying Medical and Surgical AsepsisKiyoteru Hiyama0% (1)
- By: Mary Angelie M. Atienza: Infection Control Nurse Bicol Regional Training and Teaching HospitalDocument70 pagesBy: Mary Angelie M. Atienza: Infection Control Nurse Bicol Regional Training and Teaching HospitalCiao AtienzaNo ratings yet
- How to Make Homemade Hand Sanitizer: Simple and Straightforward Home Recipes for a Healthy Life and FamilyFrom EverandHow to Make Homemade Hand Sanitizer: Simple and Straightforward Home Recipes for a Healthy Life and FamilyNo ratings yet
- Survival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)From EverandSurvival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)No ratings yet
- Ten Myths About AlbuminDocument35 pagesTen Myths About AlbuminFemtoson georgeNo ratings yet
- Histopathology of Common TendinopathiesDocument18 pagesHistopathology of Common TendinopathiesJulieta DiyorioNo ratings yet
- Govt. College of Nusing C.R.P. Line Indore (M.P.) : Subject-Advanced Nursing PracticeDocument17 pagesGovt. College of Nusing C.R.P. Line Indore (M.P.) : Subject-Advanced Nursing PracticeMamta YadavNo ratings yet
- Resume - Parisa BahadoriDocument2 pagesResume - Parisa Bahadorimohammadrezahajian12191No ratings yet
- Allopurinol (Drug Study)Document2 pagesAllopurinol (Drug Study)Daisy PalisocNo ratings yet
- Conscious Sedation: A Brief Overview Janette Lafroscia, Rces, Rcis, RcsDocument26 pagesConscious Sedation: A Brief Overview Janette Lafroscia, Rces, Rcis, RcsrnvisNo ratings yet
- Music For Pain Relief - Binaural Beats Instant Download PDFDocument1 pageMusic For Pain Relief - Binaural Beats Instant Download PDFIoannis ManNo ratings yet
- Prediabetes - OKE - IDI LMGNDocument48 pagesPrediabetes - OKE - IDI LMGNruthmindosiahaanNo ratings yet
- Washington - Medical Apartheid Ch4Document8 pagesWashington - Medical Apartheid Ch4Kyung Hee YounNo ratings yet
- PE Case StudyDocument5 pagesPE Case StudyMatt Joseph CabantingNo ratings yet
- The Most CommonsDocument80 pagesThe Most CommonsJmee8No ratings yet
- Activity Design COVIDDocument2 pagesActivity Design COVIDClaudine CruelNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Tracker 1Document3 pagesBlood Pressure Tracker 1Yu HasNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Secondary To DM NephropathyDocument25 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Secondary To DM Nephropathyiamine08100% (1)
- Fisiologi PenyelamanDocument17 pagesFisiologi PenyelamandararidiniNo ratings yet
- Group 1 (Science-9)Document3 pagesGroup 1 (Science-9)Joslyn Ditona DialNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Gravaboi Codes and NumbersDocument18 pagesGravaboi Codes and NumbersHenrii Arias0% (1)
- Nursing Care of Patients With Digestive & Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument29 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Digestive & Gastrointestinal DisordersjoreyneeNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Made Easy: History Taking Technique Using Life Event ChartDocument14 pagesPsychiatry Made Easy: History Taking Technique Using Life Event ChartvelanganniNo ratings yet
- Liberty University BIOL 101 Individual Assignment 3 Complete Solutions Correct Answers KeyDocument3 pagesLiberty University BIOL 101 Individual Assignment 3 Complete Solutions Correct Answers KeyLiberty0% (1)
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyKev Olaso ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠No ratings yet
- Thyroid TumorsDocument43 pagesThyroid Tumorspleasediscount pleaseNo ratings yet
- F2F School Clinic FormsDocument6 pagesF2F School Clinic FormsJellyn Cadorna100% (1)
- What Is Sunscreen? Tips For Applying Sunscreen Sun SafetyDocument2 pagesWhat Is Sunscreen? Tips For Applying Sunscreen Sun SafetyadmassuNo ratings yet
- Icu BookDocument140 pagesIcu BookRaMy “MhMd” ElaRabyNo ratings yet