Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Operation Management Formula
Operation Management Formula
Uploaded by
Bea Dela Penia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesOperations management involves managing systems and processes that create goods and services. It affects a company's ability to compete and a nation's ability to compete internationally. The three basic business functions are finance, operations, and marketing. Operations management uses models, quantitative approaches, and systems thinking to analyze trade-offs, establish priorities, and make ethical decisions that increase productivity and competitiveness.
Original Description:
Original Title
OPERATION MANAGEMENT FORMULA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOperations management involves managing systems and processes that create goods and services. It affects a company's ability to compete and a nation's ability to compete internationally. The three basic business functions are finance, operations, and marketing. Operations management uses models, quantitative approaches, and systems thinking to analyze trade-offs, establish priorities, and make ethical decisions that increase productivity and competitiveness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesOperation Management Formula
Operation Management Formula
Uploaded by
Bea Dela PeniaOperations management involves managing systems and processes that create goods and services. It affects a company's ability to compete and a nation's ability to compete internationally. The three basic business functions are finance, operations, and marketing. Operations management uses models, quantitative approaches, and systems thinking to analyze trade-offs, establish priorities, and make ethical decisions that increase productivity and competitiveness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
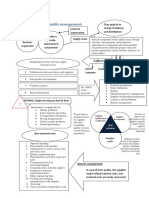
Operations Management is:
The management of systems or
processes that create goods and/or
provide services
Operations Management affects:
Companies’ ability to compete
Nation’s ability to compete
internationally
Productivity - Increasing productivity
The Three Basic Functions allows companies to maintain or
1. Finance increase their output using fewer
2. Operations workers
3. Marketing
Outsourcing - Some manufacturing work
has been outsourced to more productive
companies
Operations Management Decision
Making
Models
Quantitative approaches
Analysis of trade-offs
Systems approach
Establishing priorities
Value-added is the difference between
Ethics
the cost of inputs and the value or price
of outputs.
Models Are Beneficial
Easy to use, less expensive
Product packages are a combination of
Operations Management is The Require users to organize
Challenges of Managing Services goods and services and can make a
management of systems or processes Increase understanding of the
Service jobs are often less company more competitive.
that create goods and/or provide problem
structured than manufacturing jobs services Enable “what if” questions
Customer contact is higher Consistent tool for evaluation and
Worker skill levels are lower Operations Management affects: standardized format
Services hire many low-skill, entry- Companies’ ability to compete Power of mathematic
level workers Nation’s ability to compete internationall
Employee turnover is higher Limitations of Models
Input variability is higher Quantitative information may be
Service performance can be emphasized over qualitative
affected by worker’s personal
factors
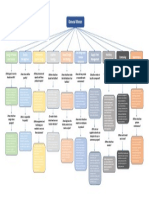
Models may be incorrectly applied Historical Evolution of Operations
and results misinterpreted Management
Non-qualified users may not
Industrial revolution (1770’s)
comprehend the rules on how to
use the model Scientific management (1911)
Use of models does not guarantee Mass production
good decisions Interchangeable parts
Division of labor
Quantitative Approaches
Linear programming Human relations movement (1920-
Queuing Techniques 60)
Inventory models Decision models (1915, 1960-70’s)
Project models
Influence of Japanese
Statistical models
manufacturers
Systems Approach - “The whole is
greater than the sum of the parts.” Trends in Business
(Suboptimization)
Major trends
Pareto Phenomenon - A few factors The Internet, e-commerce, e-
account for a high percentage of the business
occurrence of some event(s). Management technology
80/20 Rule - 80% of problems are caused
Globalization
by 20% of the activities.
Management of supply chains
Outsourcing
Agility
Ethical behavior
You might also like
- Allen Lane Case Write UpDocument2 pagesAllen Lane Case Write UpAndrew Choi100% (1)
- Accenture Value Realization For SAPDocument5 pagesAccenture Value Realization For SAPserge ziehiNo ratings yet
- Sales Management - Lecture 10 Sales Territory ManagementDocument30 pagesSales Management - Lecture 10 Sales Territory ManagementAqsa Sarfaraz100% (2)
- Cbac101 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCbac101 ReviewerJeca AranaNo ratings yet
- Cbac101 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCbac101 ReviewerJecaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Production and Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To Production and Operations Managementllpud229.karrthikhNo ratings yet
- Business & Management Mind Map - W4Document1 pageBusiness & Management Mind Map - W4Diva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Model: Analysing Business OperationsDocument1 pageDecision-Making Model: Analysing Business OperationsBb 8No ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Operations Management PDFDocument7 pages1.introduction To Operations Management PDFEmmanuel Okena67% (3)
- Newompresentation 1Document408 pagesNewompresentation 1eliasmeharu12No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Quality ManagementDocument4 pagesSupply Chain Quality ManagementkarimNo ratings yet
- A221 Poster Group9 BJMP5023Document1 pageA221 Poster Group9 BJMP5023Farah GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Yustika Adiningsih-f0319141-Spm A-Mindmap CH 4 Dan 5Document2 pagesYustika Adiningsih-f0319141-Spm A-Mindmap CH 4 Dan 5yes iNo ratings yet
- Using Operations To Create Value Nama: Muhamad Syaeful Anwar NIM: 432910Document1 pageUsing Operations To Create Value Nama: Muhamad Syaeful Anwar NIM: 432910MuhamadSyaefulAnwarNo ratings yet
- Informmation System - Hindalco MisDocument3 pagesInformmation System - Hindalco MisPurushottam WankhedeNo ratings yet
- IT and Business ProcessesDocument1 pageIT and Business ProcesseselliotttateNo ratings yet
- Mba Om NotesDocument159 pagesMba Om Notesprabu06051984No ratings yet
- CH 7 The Production Process - The Behaviour of Profit Maximising FirmDocument32 pagesCH 7 The Production Process - The Behaviour of Profit Maximising FirmBhargav D.S.No ratings yet
- Maintenance Evaluation & Benchmarking: Carlos Henrique ArrudaDocument45 pagesMaintenance Evaluation & Benchmarking: Carlos Henrique ArrudaShilpin BhadaniaNo ratings yet
- Ignition Guide PreviewDocument16 pagesIgnition Guide PreviewAlfonso VicenteNo ratings yet
- Fome Unit 3 SpectrumDocument16 pagesFome Unit 3 SpectrumAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 POM FrameworkDocument32 pages1 POM FrameworkRyan ParadinaNo ratings yet
- MGMT2006 - Management LevelsDocument6 pagesMGMT2006 - Management LevelsJamia K GriffithNo ratings yet
- El Papel de Los Activos Intangibles Es DecisivoDocument7 pagesEl Papel de Los Activos Intangibles Es DecisivosofiiNo ratings yet
- Za Deloitte Managed ServicesDocument2 pagesZa Deloitte Managed ServicesDEXCON CONSULTORESNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 Pengantar EkonomiDocument33 pagesPertemuan 4 Pengantar Ekonomirusmi.tutiNo ratings yet
- After Sales Service Management Plan SampleDocument227 pagesAfter Sales Service Management Plan SampleWamalwa KaptenNo ratings yet
- MNT 095 PEP InsertDocument84 pagesMNT 095 PEP InsertWaelNo ratings yet
- Finops Foundation PosterDocument1 pageFinops Foundation PosterCilantaro BearsNo ratings yet
- Expert Guided Post Installation 011000358700001811792008EDocument9 pagesExpert Guided Post Installation 011000358700001811792008Emuzaff_1008No ratings yet
- High PerformanceDocument11 pagesHigh PerformancemNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument30 pagesIntroductionNandini SuriNo ratings yet
- Human Resources ManagementDocument47 pagesHuman Resources Managementreda gadNo ratings yet
- O & S C M: Recap: The Scope of Operations and Supply Chain Management (OSCM)Document5 pagesO & S C M: Recap: The Scope of Operations and Supply Chain Management (OSCM)Anshul yadavNo ratings yet
- 20 Most Promising Utilities Technology Solution ProviderDocument2 pages20 Most Promising Utilities Technology Solution ProviderlololeoNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument48 pagesOperations Managementfrancine olilaNo ratings yet
- Putting The Enterprise Into The Enterprise SystemDocument11 pagesPutting The Enterprise Into The Enterprise SystemBhargav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Driving Electric Distribution ExcellenceDocument15 pagesDriving Electric Distribution Excellencekashifbutty2kNo ratings yet
- Value Realization: Maximizing Return On SAP Investments: Sapphire 2009Document20 pagesValue Realization: Maximizing Return On SAP Investments: Sapphire 2009Gaurav BhardwajNo ratings yet
- IBM Rational Enterprise Architecture Management: 25 August 2010Document33 pagesIBM Rational Enterprise Architecture Management: 25 August 2010StevensNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in MADocument1 pageContemporary Issues in MAGlydel B. MatayaNo ratings yet
- 1-49 MergedDocument49 pages1-49 Mergednesey76043No ratings yet
- Orientation To Management StudyDocument6 pagesOrientation To Management StudyDương Ngọc TrânNo ratings yet
- Om Chap 1-5Document16 pagesOm Chap 1-5cathmarquez0023No ratings yet
- Human Resources ManagementDocument41 pagesHuman Resources Managementreda gadNo ratings yet
- Operational Excellence PDFDocument3 pagesOperational Excellence PDFvuppalavhr254_189902No ratings yet
- Chap 9 and 10 EntrepDocument9 pagesChap 9 and 10 EntrepHannahnel Anasco QuidatoNo ratings yet
- Pptforpom 140306074652 Phpapp01Document36 pagesPptforpom 140306074652 Phpapp01Sonal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Computer Information in The EnterpriseCh02 PDFDocument30 pagesComputer Information in The EnterpriseCh02 PDFภาณุพงศ์ วิจิตรทองเรืองNo ratings yet
- TMForum - EtomDocument61 pagesTMForum - EtomJosé EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- VIATEC Presentation v1Document16 pagesVIATEC Presentation v1Shawn MaynardNo ratings yet
- BPMS Implementation Approach - Elab2007 - Week 7Document44 pagesBPMS Implementation Approach - Elab2007 - Week 7Rommel Risco100% (1)
- Introduction To OEE: (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)Document19 pagesIntroduction To OEE: (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)Joselito S. MalaluanNo ratings yet
- ETCIO Awards - DeckDocument16 pagesETCIO Awards - Deckkaran.shah1No ratings yet
- OM Chapter 1 Lecture Note 1Document9 pagesOM Chapter 1 Lecture Note 1Jiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- C11SL - 1 Systems Thinking and Analysis Intro 2017Document34 pagesC11SL - 1 Systems Thinking and Analysis Intro 2017Karl AbiKaramNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageMapa ConceptualManuel PerezNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Session 3 How Should My Organization (Re) Think It Business Processes?Document20 pagesInformation Systems: Session 3 How Should My Organization (Re) Think It Business Processes?hadouiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 9 Lecture Notes1er LIG Isgs 2022No ratings yet
- Recession Proofing Your ITstrategyDocument9 pagesRecession Proofing Your ITstrategyquocircaNo ratings yet
- Samcis - Ae212 - Module 12 Standard CostingDocument22 pagesSamcis - Ae212 - Module 12 Standard CostingMamaril John NathanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 EconDocument2 pagesLesson 3 EconBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 EconDocument2 pagesLesson 3 EconBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Opm CH6Document5 pagesOpm CH6Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4 (Draft)Document43 pagesChapter 1-4 (Draft)Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- CFASDocument3 pagesCFASBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument11 pagesBusiness PlanBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Uts Notes (Midterm) Lesson 2Document5 pagesUts Notes (Midterm) Lesson 2Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2 Applied Econ Part I PDFDocument108 pagesChapter 1 2 Applied Econ Part I PDFBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document13 pagesBook 1Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER5DRAFTDocument4 pagesCHAPTER5DRAFTBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics ReviewerDocument1 pageBusiness Ethics ReviewerBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Anti Smoking CampaignDocument4 pagesAnti Smoking CampaignBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Group7 (Financial Statements)Document6 pagesGroup7 (Financial Statements)Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Halverson With AdjusmentsDocument1 pageHalverson With AdjusmentsBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- FinalMarketSurvey BEADocument4 pagesFinalMarketSurvey BEABea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- GR 7Document7 pagesGR 7Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument5 pagesFinancial StatementsBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Journal EntryDocument2 pagesJournal EntryBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes EAPP 111 - 1Document221 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes EAPP 111 - 1Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument1 pageIncome StatementBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Adjusted Trial BalanceDocument1 pageAdjusted Trial BalanceBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Adjusting EntryDocument1 pageAdjusting EntryBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- ABM A Chapter1Document4 pagesABM A Chapter1Bea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- POPULAR INDUSTRIES LIMITED V EASTERN GARMENT MANUFACTURING SDN BHD, (1989) 3 MLJ 360Document14 pagesPOPULAR INDUSTRIES LIMITED V EASTERN GARMENT MANUFACTURING SDN BHD, (1989) 3 MLJ 360nurulashikin mursid0% (1)
- Fraud and Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesFraud and Risk Managementcsamkelisiwe32No ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Chapter 20Document26 pagesPrinciples of Economics Chapter 20Lu CheNo ratings yet
- Bc5 ResearchDocument4 pagesBc5 ResearchRimuruNo ratings yet
- History of Chemical Engineering - WikipediaDocument15 pagesHistory of Chemical Engineering - WikipediaEndhy Wisnu NovindraNo ratings yet
- Accenture Ripple Reisebank Video TranscriptDocument2 pagesAccenture Ripple Reisebank Video TranscriptJeffrey BahnsenNo ratings yet
- COMM2021Document2 pagesCOMM2021Lakogaharry BillclintonNo ratings yet
- Viden Io Sip Report of Aditya Birla Health Insurance Summer Internship ReportDocument22 pagesViden Io Sip Report of Aditya Birla Health Insurance Summer Internship Reportkajal malhotraNo ratings yet
- Philex Mining Corporation vs. CIRDocument3 pagesPhilex Mining Corporation vs. CIRRobNo ratings yet
- MFRS 2 SHARE BASED PAYMENTS - ALL COMBINED - Part 1 - 4Document81 pagesMFRS 2 SHARE BASED PAYMENTS - ALL COMBINED - Part 1 - 4izwanNo ratings yet
- Module - 2-Inventory ManagementDocument16 pagesModule - 2-Inventory Managementgaurav shettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report NEXA SOFTWARE - CompressDocument19 pagesProject Report NEXA SOFTWARE - CompressMr. KNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Competence, Objectivity, Independence On The Effectiveness of Internal Audit With Management Support As Moderating VariableDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Competence, Objectivity, Independence On The Effectiveness of Internal Audit With Management Support As Moderating VariableInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Financial Forecasting For Serious-Minded Entrepreneurs (And Cfos)Document43 pagesFinancial Forecasting For Serious-Minded Entrepreneurs (And Cfos)Pravin Prathip JNo ratings yet
- POM Assignment SubmissionDocument5 pagesPOM Assignment SubmissionAakriti VermaNo ratings yet
- Jaymar M Jabonillo ResumeDocument3 pagesJaymar M Jabonillo ResumeNanjiro EchizenNo ratings yet
- 24 Kimberly-Clark Phil., Inc. v. DimayugaDocument2 pages24 Kimberly-Clark Phil., Inc. v. DimayugaMikhel BeltranNo ratings yet
- Visit To A Chinese Import - Export Beauty Products Factory PDFDocument194 pagesVisit To A Chinese Import - Export Beauty Products Factory PDFpritam senseiNo ratings yet
- Rsa Securid Appliance: A Convenient and Cost-Effective Two-Factor Authentication SolutionDocument2 pagesRsa Securid Appliance: A Convenient and Cost-Effective Two-Factor Authentication SolutionAfif Al FattahNo ratings yet
- CASE ASSIGNMENT 1 - Aayush ChoudharyDocument5 pagesCASE ASSIGNMENT 1 - Aayush ChoudharyAayush ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 5 Years Anna University GE2022 Total Quality ManagemntDocument19 pages5 Years Anna University GE2022 Total Quality ManagemntManimegalaiNo ratings yet
- BSC 402 Quiz Ch. 2-3 Name: - José Antonio Céspedes PeregrinaDocument2 pagesBSC 402 Quiz Ch. 2-3 Name: - José Antonio Céspedes PeregrinaPepe Céspedes PeregrinaNo ratings yet
- Occi Mosq UfahcDocument3 pagesOcci Mosq UfahcMouctar BahNo ratings yet
- Communication in Professional Life (English)Document4 pagesCommunication in Professional Life (English)Sandesh MavliyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project Management PDFDocument173 pagesIntroduction To Project Management PDFFikri Off LineNo ratings yet
- FINAL DHSUD Branding Playbook Oct2023 1Document60 pagesFINAL DHSUD Branding Playbook Oct2023 1Yam LicNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Karimi-Lake ToursDocument25 pagesBusiness Plan Karimi-Lake ToursJoseph IbukahNo ratings yet
- Final Draft - Process ControlDocument11 pagesFinal Draft - Process Controlarif ayazNo ratings yet